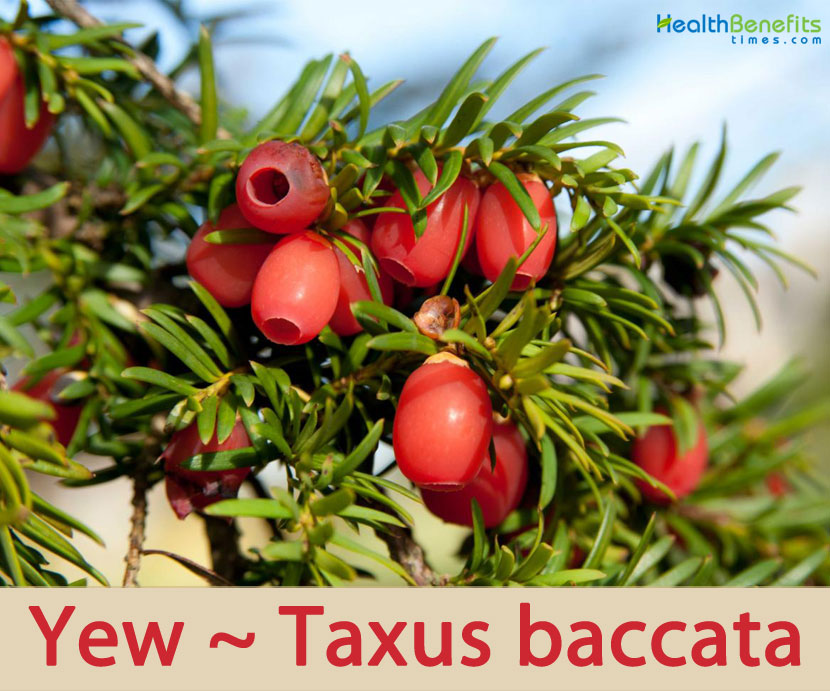
Genus name is an old Latin name for yews. Specific epithet means fruit-bearing in reference to the showy red arils. No tree is more associated with the history and legends of Great Britain than the Yew. Before Christianity was introduced it was a sacred tree favored by the Druids, who built their temples near these trees – a custom followed by the early Christians. The association of the tree with places of worship still prevails.
Yew or Common Yew Facts
| Yew Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Yew |
| Scientific Name: | Taxus baccata |
| Origin | Western, central and southern Europe (including the British Isles), northwest Africa, northern Iran and southwest Asia |
| Colors | Initially green turning to red as they mature |
| Shapes | Ornamentally-attractive, berry-like fruits, each having a single seed 4–7 mm (3⁄16–1⁄4 in) long, |
| Flesh colors | Red |
| Taste | Very sweet and a bit like a lychee |
| Health benefits | Beneficial for epilepsy, asthma, indigestion, bronchitis, hiccup, rheumatism, cystitis, eruptions, headaches, heart and kidney problems, dimness of vision, gout, breast cancer and ovarian cancer |
| Name | Yew or Common Yew |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Taxus baccata |
| Native | Western, central and southern Europe (including the British Isles), northwest Africa, northern Iran and southwest Asia |
| Common Names | Common yew, English yew, European yew, Yew, Irish Yew |
| Name in Other Languages | Afrikaans: Taxus Albanian: Bërshen, Tis Amharic: Eewo (አዎ) Arabic: Khashab altuqsus (خشب الطقسوس), dakhs, taqsus tuti (طقسوس توتي) Armenian: keni (կենի), keni hataptghayin (կենի հատապտղային) Azerbaijani: Yew, Giləmeyvəli qaraçöhrə Basque: Hagin, hagina, Hagin arrunt Belarusian: Tsis (ціс), cis jeŭrapiejski (ціс еўрапейскі) Bengali: L’u kāṣṭha (ইউ কাষ্ঠ) Bosnian: Tisa, Tisa (biljka) Breton: Ivin (gwez) Bulgarian: Tys (тис), obiknoven tis (обикновен тис) Catalan: Teix, teixero Cebuano: Yew Chichewa: Yew Chinese: Hóngdòu shān (红豆杉), ou zhou hong dou shan (欧洲红豆杉) Cornish: Ewin Corsican: Tassu Croatian: Tisa, šumska tisa Czech: Tis, Tis cervený Danish: Taks, Almindelig taks, Barlind, Norsk ibenholt Dutch: Taxusboom, Gewone taxus, Taxus English: Common yew, English yew, European yew, Yew, Irish Yew Esperanto: Taksuso, Eŭropa taksuso Estonian: Jugapuu, harilik jugapuu, Filipino: Yew Finnish: Marjakuusi, Euroopanmarjakuusi French: Yew, if, If commun, if d’Europe, if à baies, ifreteau Frisian: Taks Galician: Teixo, teixeiro Georgian: Utkhovari (უთხოვარი) German: Eibe, Beereneibe, Europäische Eibe, Gemeine Eibe, Gewöhnliche Eibe, Ifenbaum Greek: Pournári (πουρνάρι), Ímero élato (Ήμερο έλατο), ítamos (ίταμος), ragofóros (ραγοφόρος), Déndro tou thanátou (Δένδρο του θανάτου), Mavroélato (Μαυροέλατο), Táxos ragofóros (Τάξος ραγοφόρος) Gujarati: Yū (યૂ) Haitian Creole: If Hausa: Yew Hawaiian: ʻē Hebrew: טקסוס, טקסוס מעונב Hindi: Yū (यू) Hmong: Yew Hungarian: Tiszafa, Európai tiszafa, közönséges tiszafa Icelandic: Yew, Ýviður Igbo: Yew Indonesian: Yew Ingush: Baza (База) Irish: Iúir Italian: Tasso, Albero della morte, Libo, Nasso, tasso comune Japanese: Ichī (イチイ), Yōroppaichii (ヨーロッパイチイ) Javanese: Yew Kabyle: Teyfuzzel Kannada: Yū (ಯೂ) Kashubian: Zwëczajny cës Kazakh: YU (Ю) Khmer: Yew Kinyarwanda: Yew Korean: Yeu (예우) Kurdish (Kurmanji): Yew Kyrgyz: Yew Lao: Yew Latin: Taxi torquentur Latvian: Ive, Parasta ive Lithuanian: Kukmedis, europinis kukmedis Luxembourgish: Yew, Franséische Pällem Macedonian: Tys (Тис), obychna tysa (обична тиса) Malagasy: Yew Malay: Yew Malayalam: Oru (ഒരു) lley, ṭāksas bakkāṭṭa (ടാക്സസ് ബക്കാട്ട) Maltese: Yew Manx: Euar Maori: Yew Marathi: Garda hiravyā raṅgācī pānē asalēlā ēka sadāparṇī vr̥kṣa (गर्द हिरव्या रंगाची पाने असलेला एक सदापर्णी वृक्ष) Mongolian: Yuyeü (Юеү) Myanmar (Burmese): Yew Nepali: Yew, barmesalla (बर्मेसल्ला) Norwegian: Barlind, Norsk ibenholt Odia: Ham̐ (ହଁ) Ossetic: Zaz (Заз) Pashto: یوځل Persian: سرخدار, سرخدار Polish: Cis, Cis pospolity Portuguese: Teixo Punjabi: ਯੂ Pushto: اروپايي ټاکسوس Romanian: Tisă Romansh: Taisch Russian: Tis (тис), tis yagodnyi (Тис ягодный), tiss âgodnyj, tiss evropejskij, nehnoy derevo (негной дерево), (тис европейский) Samoan:: Ioe Scots Gaelic: Iubhair, Iogh, Iubhar, Iubharan Serbian: Tis (тис), Cis, Sis, evropska tysa (европска тиса), tysa (тиса) Sesotho : Japanese yew Shambala: Tisa Shona: Yew Sindhi: يار Sinhala: Yū (යූ) Slovak: Tis, Tis obycajný Slovenian: Tisa Somali: Yew Spanish: Tejo, taxo, tejo común, tejón, Navadna tisa Sundanese: Yeuh Swahili: Yew Swedish: Idegran, Euroopanmarjakuusi, Idgran Tajik: Yew Tamil: யூ Tatar: Jə (йә) Telugu: Yū (యూ) Thai: T̂n yū (ต้นยู) Turkish: Porsukağacı, Porsuk, yaygın porsuk Turkmen: Yew Ukrainian: Tys (тис), tys yahidnyy (тис ягідний) Upper Sorbian: Wšědny ćis Urdu: یو, یورپی سرخدار Uyghur: Yew Uzbek: Tis Vietnamese: Thủy tùng, thanh tùng châu Âu Welsh: Ywen, Pren Yw, Yw, Xhosa: Yew Yiddish: Yw (יו) Yoruba: Yew Zulu: Yew |
| Plant Growth Habit | Long-lived, medium sized, evergreen, conifer tree |
| Growing Climates | Hedgerows, woodland, churchyards, parks and shady field edges and can also be grown and used as hedging |
| Soil | Can grow on almost all soil types with adequate drainage, typically on humus and base-rich soils, but also on dry rendzina and sandy soils with adequate moisture. The yew is intolerant of prolonged frost and cold although its tolerance varies by region and season. They are moderately drought tolerant and can cope with temporary flooding but are susceptible to long term poor drainage |
| Plant Size | 10–20 m (35–65 ft.) (exceptionally up to 28 m or 92 ft) tall, with a trunk up to 2 m (6 ft. 7 in) (exceptionally 4 m or 13 ft. 1 in) in diameter |
| Root | Root systems are shallow with extensive horizontal roots |
| Twigs | Light green in color, turning brown after several years; buds green with scales keeled |
| Bark | Bark is dark, thin, usually red-purple, and scaly coming off in small flakes aligned with the stem |
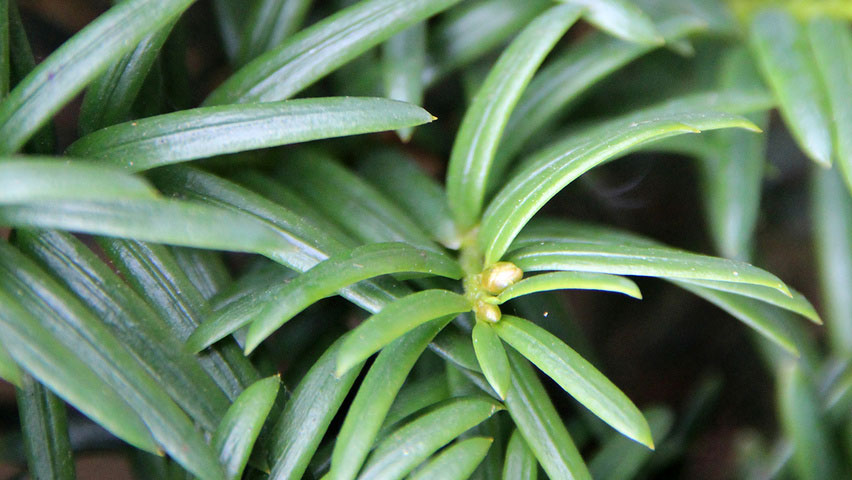
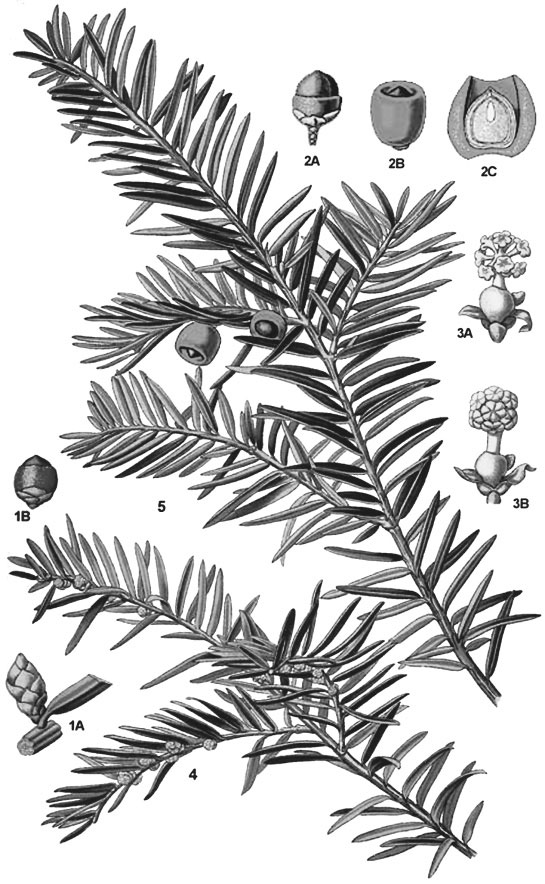
| Leaf | Leaves are flat, dark green, 1–4 centimeters (1⁄2–1+1⁄2 in) long and 2–3 mm (3⁄32–1⁄8 in) broad, arranged spirally on the stem, but with the leaf bases twisted to align the leaves in two flat rows |
| Flowering season | March to April |
| Flower | Yew is mainly dioecious; although examples of monoecious trees exist this is rare and usually consists of separate sexed branches. Male flowers are small green globules along the underside of last year’s shoots, whilst the female flowers are minute green flowers borne in the leaf axils of the previous year’s growth |
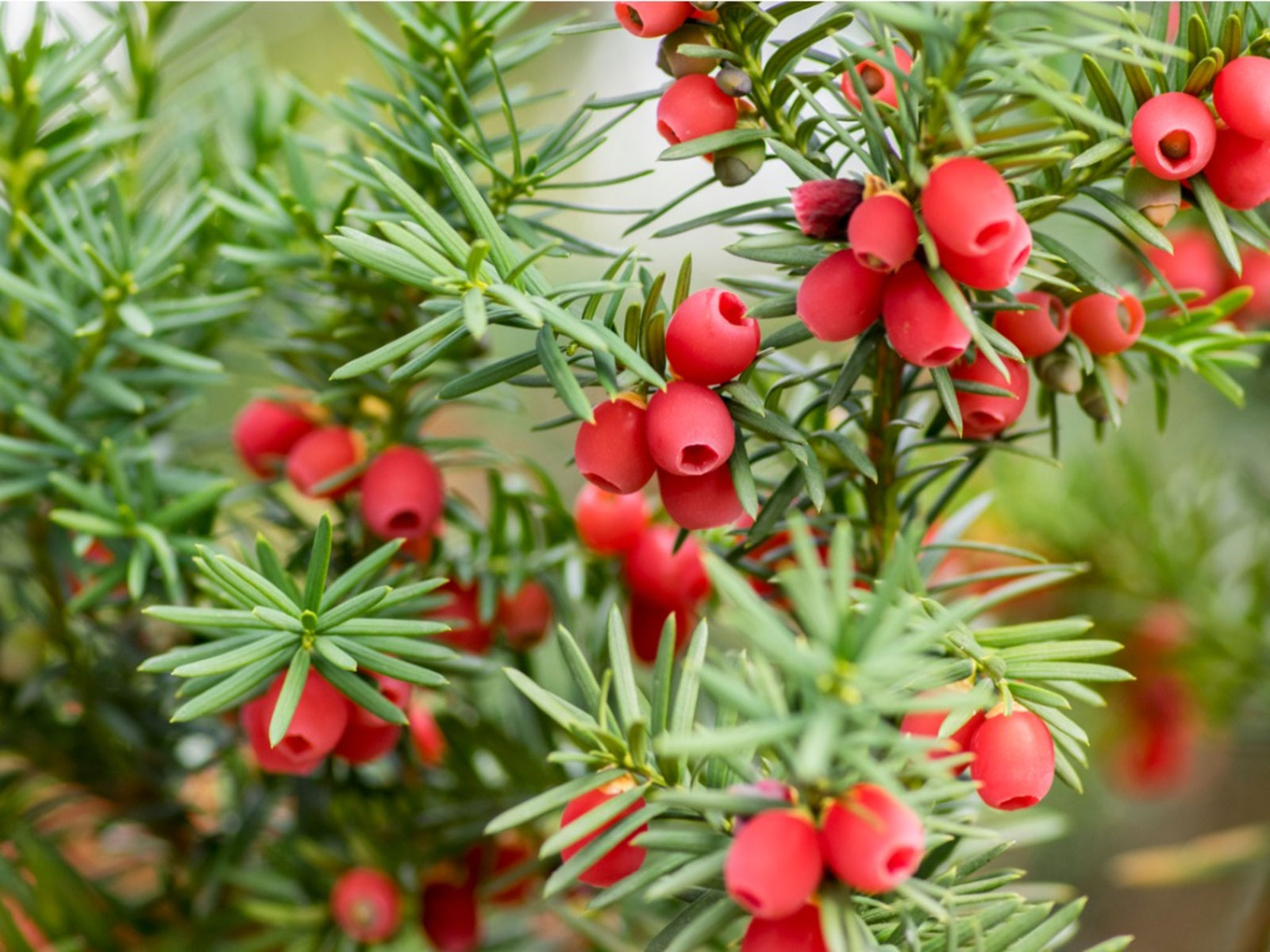
| Fruit Shape & Size | Ornamentally-attractive, berry-like fruits, each having a single seed 4–7 mm (3⁄16–1⁄4 in) long |
| Fruit Color | Initially green turning to red as they mature |
| Flesh Color | Red |
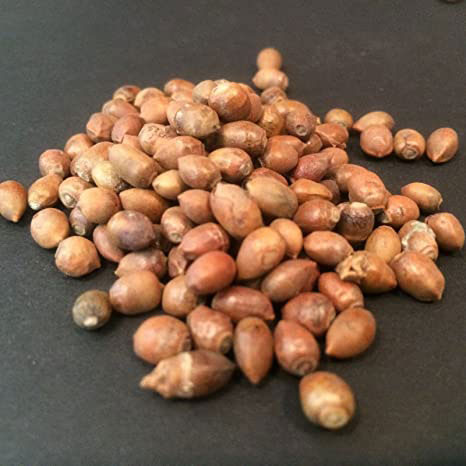
| Seed | Single seed 4–7 mm (3⁄16–1⁄4 in) long |
| Propagation | By cuttings and from seed |
| Lifespan | 400 to 600 years of age |
| Taste | Very sweet and a bit like a lychee |
| Plant Parts Used | Berries, leaves |
| Season | September to November |
| Culinary Uses |
|
Plant Description
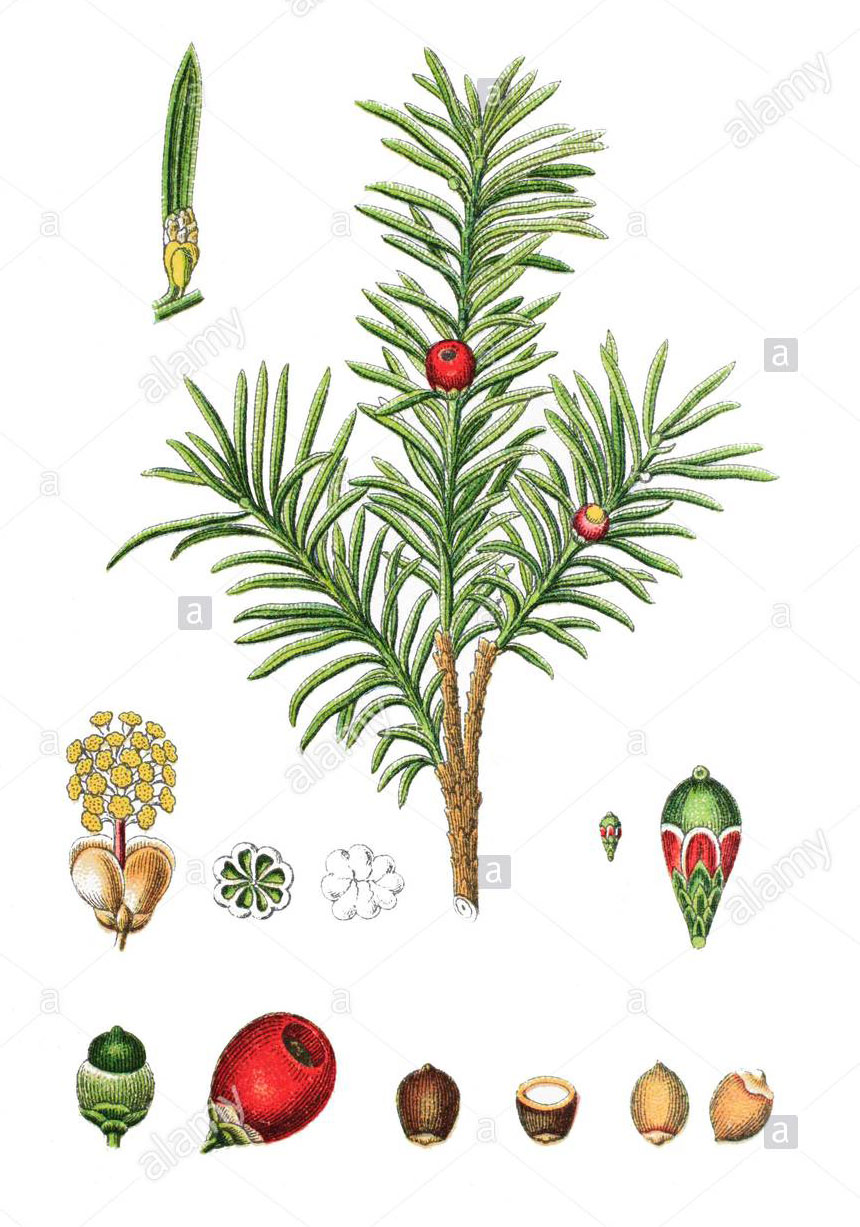
Yew Or Common Yew is a long-lived, medium sized, evergreen, conifer tree that normally grows about 10–20 m (35–65 ft.) tall (exceptionally up to 28 m or 92 ft.), with a trunk up to 2 m (6 ft. 7 in) (exceptionally 4 m or 13 ft. 1 in) in diameter. The plant is found growing in hedgerows, woodland, churchyards, parks and shady field edges and can also be grown and used as hedging. The plant can grow on almost all soil types with sufficient drainage, typically on humus and base-rich soils, but also on dry rendzina and sandy soils with adequate moisture. The yew is intolerant of prolonged frost and cold although its tolerance varies by region and season. They are moderately drought tolerant and can cope with temporary flooding but are susceptible to long term poor drainage. Root systems are shallow with extensive horizontal roots. Twigs are light green in color, turning brown after several years. Buds are green with scales keeled. Bark is dark, thin, usually red-purple, and scaly coming off in small flakes aligned with the stem.
Leaves
The leaves are flat, dark green, 1–4 centimeters (1⁄2–1+1⁄2 in) long and 2–3 mm (3⁄32–1⁄8 in) broad, arranged spirally on the stem, but with the leaf bases twisted to align the leaves in two flat rows either side of the stem, except on erect leading shoots where the spiral arrangement is more obvious. Leaves are dark green and shiny above, yellow or pale green below with 8-10 stomatal rows. The leaves are poisonous. Leaves are green all through the year but turn dull in the autumn color.
| Leaf arrangement | Alternate |
| Leaf type | Simple |
| Leaf margin | Entire |
| Leaf shape | Linear |
| Leaf venation | Parallel, none, or difficult to see |
| Leaf type and persistence | Evergreen, needled evergreen |
| Leaf blade length | Less than 2 inches |
| Leaf color | Green |
| Fall color | No color change |
| Fall characteristic | Not showy |
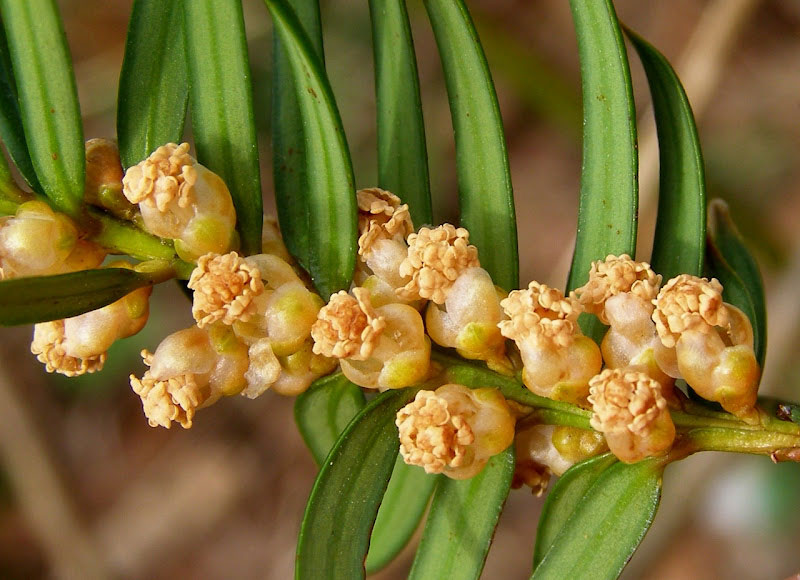
Flower
Flower of yew is dioecious, meaning that male and female flowers grow on separate trees. Flowers are visible in March and April from the leaf axils of the preceding summer’s twigs.
Male Flowers
They are not true flowers but clusters of stamen. The male flowers appear in February/March and start as Brussels sprout like growths that turn into pale yellow sacs of small spheres before opening to drop its anthers and release lots of pollen.
Female Flowers
The female flower is a single ovule covered in scale like bracts that when pollinated will develop over the summer into a seed surrounded in bright red sometimes yellow flesh.
| Flower color | Green, yellow |
| Flower characteristics | Not showy |
Fruit
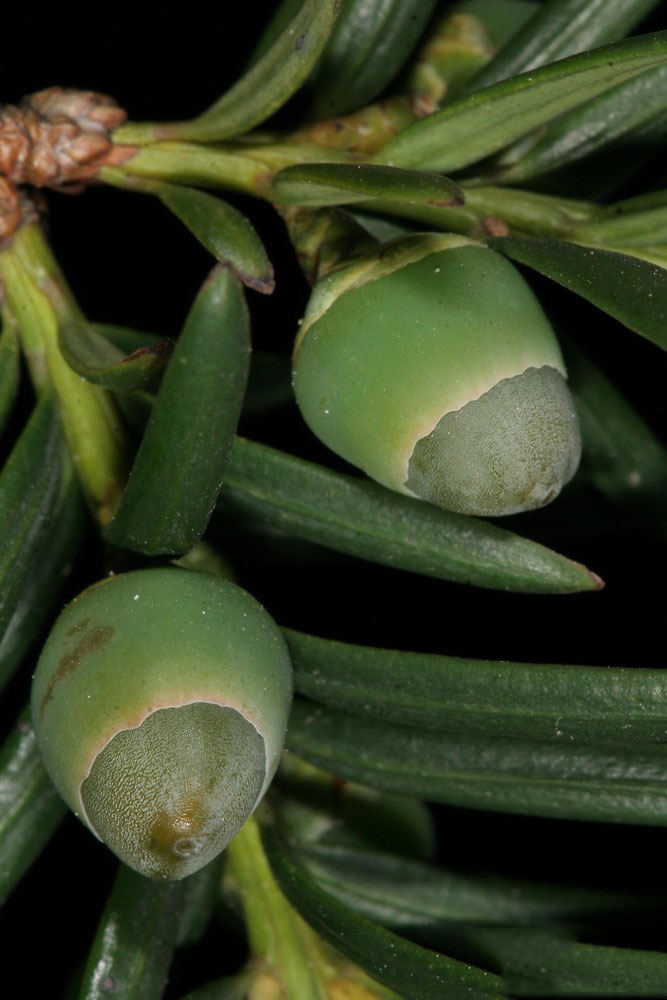
Although classified as a conifer, female yews do not produce cones, but instead produce red, ornamentally-attractive, berry-like fruits, each having a single seed 4–7 mm (3⁄16–1⁄4 in) long, almost completely surrounded by a fleshy red aril. The aril is 8–15 mm (5⁄16–9⁄16 in) long and wide and opens at the end. The arils mature 6 to 9 months after pollination, and with the seed contained, are eaten by thrushes, waxwings and other birds, which disperse the hard seeds undamaged in their droppings. Maturation of the arils is spread over 2 to 3 months, increasing the chances of successful seed dispersal. The seeds themselves are poisonous and bitter, but are opened and eaten by some bird species including hawfinches, greenfinches and great tits.[14] The aril is not poisonous, it is gelatinous and very sweet tasting. The male cones are globose, 3–6 mm (1⁄8–1⁄4 in) in diameter, and shed their pollen in early spring. All parts of this plant are poisonous if ingested. Taxine, the toxic chemical, is found in the leaves, bark, and hard part of the seed.
| Fruit shape | Round |
| Fruit length | Less than .5 inch |
| Fruit covering | Fleshy |
| Fruit color | Red |
| Fruit characteristics | Attracts birds; showy; fruit/leaves not a litter problem |
Traditional uses and benefits of Yew
- Leaf and fruit are used as an anti-spasmotic, sedative, and emmenagogue in India.
- Leaf is also used as an aphrodisiac and is used to treat epilepsy, asthma, indigestion, and bronchitis.
- It is also used as expectorant, pectoral, sedative, stomachic, tonic; abortifacient, antifertility, contraceptive; for headache, bilious, calculus, for cancer, carminative, cyanogenetic, epilepsy, lithontriptic, medicine Tacholm; giddiness, nerves, spasm; poison, vermifuge, insecticide.
- Yew tree is a highly toxic plant that has occasionally been used medicinally, mainly in the treatment of chest complaints.
- All parts of the plant, except the fleshy fruit, are antispasmodic, cardio tonic, and diaphoretic, emmenagogue, expectorant, narcotic and purgative.
- Leaves have been used internally in the treatment of asthma, bronchitis, hiccup, indigestion, rheumatism and epilepsy.
- Externally, the leaves have been used in a steam bath as a treatment for rheumatism.
- A homeopathic remedy is made from the young shoots and the berries.
- It is used in the treatment of many diseases including cystitis, eruptions, headaches, heart and kidney problems etc.
- In homoeopathy a tincture of the young shoots and also of the berries is used in a variety of diseases: cystitis, eruptions, headache and neuralgia, affections of the heart and kidneys, dimness of vision, and gout.
- The oil derived from Yew bushes is best for treating breast cancer and ovarian cancer.
- Leaves are used in the treatment of asthma, bronchitism hiccough, epilepsy and indigestion.
Other Facts
- The plant is very tolerant of trimming; this plant makes an excellent hedge.
- Plants are often used in topiary and even when fairly old, the trees can be cut back into old wood and will resprout.
- One report says that trees up to 1000 years old respond well to trimming.
- Decoction of the leaves is used as an insecticide.
- Wood is heavy, hard, durable, and elastic, takes a good polish but requires long seasoning.
- It is also used for bows, tool handles etc.
- It makes good firewood.
- The wood was formerly much valued in archery for the making of long bows.
- It has been suggested that the sacred tree at the Temple at Uppsala was an ancient yew tree.
- The male plant part is allergic and female part is Anti-allergic.
- Yew trees were often linked with immortality, as well as doom and death.
- The inner bark produces a red dye, often used in religious ceremonies by Brahmins of Nepal.
- Wood is burnt as incense in Nepal and parts of Tibet.
Precautions
- All parts of the plant, except the flesh of the fruit, are highly poisonous, having a paralyzing effect on the heart.
- Poisoning symptoms are dry mouth, vomiting, vertigo, abdominal pain, dyspnoea, arrhythmias, hypotension & unconsciousness.
- Ingestion of 50-100 g of needles can cause death.
- Ingestion of the seeds can cause trembling and difficult breathing.
- The poison is highly toxic and may even cause death after 1-3 hours of ingestion.
- The plant pollen may cause headache, lethargy, aching joints, itching and skin rashes.
- It can also cause asthma.
- It may cause abdominal pain, dyspepsia.
- Not recommended for Pregnant and Breast feeding women.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=194883#null
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxon/taxonomydetail?id=80070
https://pfaf.org/User/plant.aspx?LatinName=Taxus+baccata
https://www.missouribotanicalgarden.org/PlantFinder/PlantFinderDetails.aspx?taxonid=287305
https://www.botanical.com/botanical/mgmh/y/yew—08.html
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/ST624
http://dendro.cnre.vt.edu/dendrology/syllabus/factsheet.cfm?ID=115
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Taxus_baccata
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl/record/kew-2434158
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/TAXBA
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/52812
http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Taxus+wallichiana
https://plants.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=TABA80