The plant is gathered from the wild for local use as a food and a medicine. It is occasionally grown as a salad crop and also sometimes as an ornamental (the cultivar ‘Variegata’ with variegated leaves is used ornamentally). Research has also shown that, with its winter hardiness and high seed yields, it has the potential to become a new oil seed crop.
Plant Description
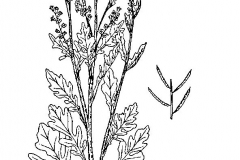
Yellow Rocket cress is a tap rooted biennial forb, or occasionally annual or short-lived perennial plant that grows about 30–60 cm (12–24 in) high, with a maximum of 1 m (3 ft. 3 in).The plant is found growing in damp ground and lowland areas including riverbanks, meadows, shingle and ditches, to more disturbed habitats such as roadside verges, arable land, wasteland and docklands, fresh or moist places, in arable land, or on the slopes, pastures, amongst crops and fields, gardens, vacant lots, construction sites, fallow fields, hay fields, ditch banks, rocky outcrops, stony slopes. The plant prefers siliceous, calcareous, sandy, alluvial and clay soils, avoiding highly acidic sites. Root crown diameter ranges from less than 0.1 cm to 5 cm. Tap roots often exceed 50 cm in depth. An extensive, much branched, fibrous secondary root system develops. Stem is erect, branched, and hairless, ridged or angled, about 0.4 to 80 cm tall, purplish or green with purple streaks or stripes. Multiple stems arise from the base, forming a clump.
Leaves
Leaves become progressively smaller as they ascend the stem. Near the base of the plant they are deeply lobed with a large rounded lobe at the tip and 1 to 4 pairs of small rounded lobes on the stalk. Basal leaves are up to 6 inches long and 2½ inches wide. The edges are often somewhat wavy. Stem leaves typically have a pair of lobes (auricles) at the base of the stalk that clasp the stem.
At the top of the plant leaves are rather smaller and somewhat variable, may be unlobed, wedge shaped to oval or shallowly lobed with little or no stalk. The upper surface of all leaves is dark green and glossy. Attachment is alternate.
Flower
Yellow rocket flowers are yellow and often appear in a cluster. Each flower measures 1 to 1.5 cm across. The flower has four petals generally appearing in the formation of a cross. The flower has six stamens, two are short and four are long. Clusters elongate as the plant matures, with flowers blooming at the tip and fruit forming along the stem below. During the second year of growth flowers can occur at any time once matured.
Fruit
Fertile flowers are followed by narrow silique fruit, glabrous, erect to spreading, 1.5-3.0 cm long, slightly compressed and beaked. Beak is about 3 mm long. Nearly 18-24 seeds are produced per fruit. Seeds are 1.0-1.5 mm long, circular in outline, oblong in cross-section and somewhat flattened.
The plant flowers from April through July and bears fruit from July to September, starting during second year of vegetation. After fruiting, the above-ground parts of the plant die off, and every spring a new flowering and fructiferous stem develops from root collar. B. vulgaris propagates by seeds and rootstocks. Maximum productivity is up to 10000 seeds.
Barbarea vulgaris was introduced to North America about 1800 although specimens’ were still rare to absent in Ontario as late as 1878. It was not listed as one of the 149 common weeds in Canada in 1930 and was relatively rare, being restricted to low, wet ground (Montgomery 1955).
By 1948 it was common throughout Ontario and Quebec and had been found as far north as Moosonee. It was known to be spreading and was a common impurity in clover, grass and alfalfa seeds. It had been added to the list of secondary noxious weeds. At that time it was felt that draining of the field, followed by ploughing and fall or spring cultivation, or by grazing by sheep, would eradicate the weed.
From the 1950s up to the present, it has increased in numbers in the central region of the continent. By 1976 the species was considered to be one of the 117 most common weeds in Canada. It is also one of the three most important broadleaved perennial weeds in Wisconsin forage crops but its numbers have not increased significantly recently.
Few Traditional uses and benefits of using Yellow Rocket cress
- The leaves are vulnerary and have been used as a poultice for treating wounds.
- A tea made from the leaves is appetizer, antiscorbutic and diuretic.
Culinary Uses
- Young leaves are consumed raw or cooked like spinach.
- Young leaves are chopped up finely and added to salads.
- Older leaves can be used as a potherb but they are rather strong and are best cooked in one or two changes of water.
- Young flowering stems are harvested before the flowers open and cooked like broccoli.
- Basal leaves are edible early spring; they can be chopped up and added to salads like rucola, which has a similar tang.
- You can dry the leaves to make tea.
References:
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-2669712
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=22741#null
https://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/go/99760/
http://www.hear.org/pier/species/barbarea_vulgaris.htm
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=6491
https://pfaf.org/User/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Barbarea+vulgaris
http://www.floracatalana.net/barbarea-vulgaris-r-br-in-aiton
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=BAVU
https://www.invasiveplantatlas.org/subject.html?sub=5175
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barbarea_vulgaris
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/BARVU
http://www.agroatlas.ru/en/content/weeds/Barbarea_vulgaris/index.html
Comments
| Yellow Rocket cress Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Yellow Rocket cress |
| Scientific Name: | Barbarea vulgaris |
| Origin | Eurasia and North Africa |
| Colors | Green when young turning to brown as they matures |
| Shapes | Narrow silique, glabrous, erect to spreading, 1.5-3.0 cm long, slightly compressed and beaked |
| Taste | Hot and cress like with a peppery, slightly bitter taste |
| Health benefits | Beneficial for treating wounds and works as appetizer, anti-scorbutic and diuretic |
| Name | Yellow Rocket cress |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Barbarea vulgaris |
| Native | Eurasia and North Africa |
| Common Names | Rocket cress, Winter cress, Yellow rocket, Bittercress, Cressy-greens, Garden yellow rocket, Herb-Barbaras, Upland cress, Bitter wintercress, Common wintercress, Cress, herb Barbara, winter rocket, wound rocket, yellow rocketcress |
| Name in Other Languages | Albanian: Barbare, barbarea e zakonshme Arabic: Kuth’ shayie (كثء شائع) Bashkir: Тиле шалҡан Bulgarian: Obiknovena zlina (обикновена злина) Catalan: Barbàrea, herba bàrbara, herba de los feridos, herba de Santa Bàrbara Chinese: Ou zhōu shān gài (欧洲山芥) Croatian: Barica, obična repnica Czech: Barborka obecná Danish: Almindelig vinterkarse, Udspærret Vinterkarse Dutch: Barbarakruid, Gewoon Barbarakruid English: Rocket cress, Winter cress, Yellow rocket, Bittercress, Cressy-greens, Garden yellow rocket, Herb-Barbaras, Upland cress, Bitter wintercress, Common wintercress, Cress, herb Barbara, winter rocket, wound rocket, yellow rocketcress Esperanto: Barbara-herbo Estonian: Kaarkollakas, läänekollakas Finnish: Peltokanankaali, Kanankaali French: Barbarée, Barbarée commune, Barbarée vulgaire, Girarde jaune, Herbe aux charpentiers, Herbe de Sainte-Barbe, Cresson d’hiver, Cresson de terre, barbarée arquée, barbarée officinale Gaelic: Treabhach German: Barbarakraut, Echtes Barbarakraut, Echte Winterkresse, Gewöhnliches Barbarakraut, Winterkresse, echtes Barbenkresse, gemeine Winterkresse, gewöhnliche Winterkresse Greek: Varvaréa makrófyllos (βαρβαρέα μακρόφυλλος), varvaréa toxoeidís (βαρβαρέα τοξοειδής) Hungarian: Közönséges borbálafű Icelandic: Garðableikja Italian: Erba disanta Barbara, barbarea commune, erba di Santa Barbara, erba di Santa Barbara comune Japanese: Haruzakiyamagarashi (ハルザキヤマガラシ), seiyoyamagarashi (セイヨヤマガラシ), yamagarashi (ヤマガラシ) Latvian: Lokaugļu zvērene, parastā zverēne Lithuanian: Lenktavaisė barborytė, Paprastoji barborytė Norwegian: Vinterkarse Occitan: Erbo de santo barbo, Grascap Polish: Gorczycznik Pospolity Portuguese: Erva-de-Santa-Bárbara, agrião-da-terra, erva-de-são-julião, erva-dos-carpinteiros, agrião-de-inverno, erva-carpinteira, erva-de-santa-bárbara Romanian: Bărbişoară, krușețiă obișnută, krușețiă țаrpănă Russian: Surepitsa obyknovennaya (Сурепица обыкновенная), Surepka obyknovennaya (Сурепка обыкновенная) Serbian: Dičak (дичак) Slovak: Barborka obyčajná Slovene: Navadna barbica Spanish: Hierba de Santa Bárbara, hierba de los carpinteros, yerba de Santa Bárbara, yerba de los carpinteros, barbarea, berro de invierno Swedish: Bangyllen, Sommargyllen, Vanlig sommargyllen, Vanlig vinterkrasse, Peltokanankaali Turkish: Nicar out Ukrainian: Campe barbarea, Suripytsya zvychayna (Суріпиця звичайна) Welsh: Berwr y gaeaf |
| Plant Growth Habit | Tap rooted biennial forb, or occasionally annual or short-lived perennial |
| Growing Climates | Found growing in damp ground and lowland areas including riverbanks, meadows, shingle and ditches, to more disturbed habitats such as roadside verges, arable land, wasteland and docklands, fresh or moist places, in arable land, or on the slopes, pastures, amongst crops and fields, gardens, vacant lots, construction sites, fallow fields, hay fields, ditch banks, rocky outcrops, stony slopes |
| Soil | Siliceous, calcareous, sandy, alluvial and clay soils, avoiding highly acidic sites |
| Plant Size | 30–60 cm (12–24 in) high, with a maximum of 1 m (3 ft. 3 in) |
| Root | Root crown diameter ranges from less than 0.1 cm to 5 cm. The tap roots often exceed 50 cm in depth. An extensive, much branched, fibrous secondary root system develops |
| Stem | Erect, about 0.4 to 80 cm tall, sometimes branching, glabrous, herbaceous, ridged |
| Leaf | Basal leaves are stalked and lyre-pinnatifid, that is with a large terminal lobe and smaller lower lobes. The cauline leaves are smaller, ovate, toothed, or lobed |
| Flowering season | April through July |
| Flower | Borne in spring in dense terminal clusters above the foliage. They are 7–9 mm (0.28–0.35 in) long, with four bright yellow petals |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Narrow silique, glabrous, erect to spreading, 1.5-3.0 cm long, slightly compressed, beaked |
| Fruit Color | Green when young turning to brown as they matures |
| Seed | 1.0-1.5 mm long, circular in outline, oblong in cross-section, somewhat flattened |
| Propagation | By seeds |
| Taste | Hot and cress like with a peppery, slightly bitter taste |
| Season | July to September |
| Other Facts |
|
| Precautions |
|