Genus name comes from the classical Latin name for garlic. Specific epithet comes from the Greek word ampelos meaning vine and parson meaning leek for a leek found growing in vineyards. Few of the popular common names of the plant are Elephant Garlic, Giant garlic, Great-headed garlic, garlic, Levant, Russian garlic, Wild leek, Yorktown onion, Broadleaf wild leek, garden leek, Puerro Silvestre. Allium ampeloprasum has been distinguished into four cultivated vegetables, namely leek, elephant garlic, kurrat and Persian leek. With a flavor best described as like green onions with a strong garlic smell, wild leeks are used in many springtime recipes like soup and egg dishes, or pickled and used in salads. They can also substitute for onion or garlic in any dish.
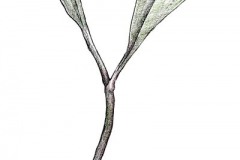
Leaves
Leaves are alternate distichous, simple and sheathing; sheath closed, cylindric to low–ridged, to 600 mm long increasing from the lowest to uppermost leaf, to mid-plant and hiding peduncle (scape), with membranous, ligule like extension 2—3 mm above base of blade, persistent; blade long–tapered lanceolate–linear, 300—500 × < 15—36 mm, papillate–ciliate on margins, long–acuminate at tip, parallel–veined with midrib raised to keeled on lower surface.
Inflorescence
Inflorescence is umbel–like, spheroid, in range 70—80 mm, 300—500–flowered, with old flowers and younger flowers mixed, flowers opening over several weeks for each inflorescence, bracteate, glabrous; bracts subtending umbel 2, covering flower buds when first formed, the lower bract encircling axis, to 100 mm long, triangular to below midpoint and with an abruptly tapered and linear upper portion, leaf like, separated from upper bract by internode of several mm, upper bract narrower and shorter, to 65 mm long and only half–encircling axis, often abscising after flowering; bractlet subtending pedicel present, membranous, long–acuminate triangular, to 6 mm long, aging scarious and wedged between pedicel bases; pedicels radiating from spheroidal center of inflorescence, at anthesis < 35—45 mm long, 0.5—0.7 mm diameter at midpoint, pink aging whitish, glabrous.
Flower
Flower is bisexual, radial, 3 mm across, ovoid (urn–shaped); tepals 6 in 2 whorls, dimorphic, free, white at base to pink or pinkish above midpoint and having green mid stripe from above base to tip; outer tepals ovate and cupped, ca. 5 × 2 mm, ± keeled, conspicuously papillate on surface, keel, and margins; inner tepals appressed to ovary, oblong–elliptic, ca. 5 × 1.5—1.7, faintly pink above midpoint, flatter and narrower > outer tepals, mid vein raised to midpoint, with some papillae only on margins; stamens 6 in 2 whorls, dimorphic, whorl opposite outer tepals ± free, other whorl fused to bases of inner tepals, ca. 6 mm long at maturity. Filaments is membranous, glabrous, of free stamens ovate to midpoint and threadlike above midpoint, of stamens opposite inner tepals 3–lobed to midpoint, central lobe somewhat cylindric gradually tapered to tip, lateral lobes (teeth) flattened and triangular in lower portion and threadlike above, sub equal with filament of fertile stamen; anthers dorsi fixed–versatile, dithecal, ± 1 mm long, pale yellow, arrow–shaped at base, longitudinally dehiscent; pollen pale yellow; nectary beneath ovary not producing nectar; pistil 1, ca. 6 mm long; ovary superior, low 6–lobed, ovoid but when pollen released elongating to 0.7 mm below an interrupted ledge, ca. 2.5 × 2.2—2.3 mm, green with whitish furrows, lobes without crest but papillate at top, 3–chambered, each chamber filled with 2 ovules attached to center; style arising from pit at top of ovary, when pollen released 4—4.5 mm long, pinkish to white, tapered to tip; stigma capitate, exerted at same level as anthers, not lobed.
Fruit
Fruit is capsule, loculicidal, typically sterile with 6 aborted ovules, sterile fruit ± dehiscent, ± pyramidal and 3–sided, 3—3.5 mm long; hidden by persistent, papery tepals. Capsules are up to 6-seeded. Seeds are 2–3 mm long and 2 mm wide and black colored.
History
The plant is known since antiquity. Although Theophrastus (third century BC) does not include a clear description of the species when he treats the cultivated leek, onion, and garlic, it is likely that he referred to A. ampeloprasum when he mentioned other wild similar species. Nevertheless, Dioscorides (first century AD) clearly stated the medicinal properties of the wild leek, a plant known as ampeloprason by the Greeks. He said that it is worse for the stomach than leeks but warmer and more diuretic, expelling the menstrual blood, and also being good for those bitten by poisonous beasts. Andres Laguna, the Spanish translator of Dioscorides, explained in his own comments that this wild species typically grows inside the vineyards, hence called ampeloprason (vineyard leek). According to the Spanish botanist Bernardo Cienfuegos (1627), this species was consumed in the seventeenth century in Spain and was described as a plant, with intermediate characteristics between garlic and leek.
Health benefits of Wild Leek
Iron found in wild leeks helps boost oxygen distribution in the body, increases energy levels, and supports healthy immune function. Iron is particularly important for premenopausal women, who experience iron loss during their menstrual cycles. There are various potential wild leeks health benefits to consider. Here are a few you should keep in mind:
1. Heart Health
As Native Americans have believed for centuries, Wild Leek could benefit the heart and circulatory system. Folate in wild leeks helps regulate the homocysteine levels of the body. In high amounts, protein homocysteine can contribute to heart diseases, especially atherosclerosis. Research also shows that the kaempferol in wild leeks may reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Kaempferol protects the blood vessels against damage, while also supporting the liver with elimination of cholesterol. Wild leeks may also reduce low density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and total cholesterol, which is very important for preventing heart disease and atherosclerosis.
2. Treat and Prevent Cancer
One of the most well-known health benefits of wild leeks is this vegetable’s potential to fight or prevent cancer due to its high antioxidant content.
Research suggests that the flavonoid antioxidant kaempferol found in wild leeks is involved in apoptosis (cell death) in various cancer types. Research published in the Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry in 2000 recommended that selenium-rich wild leek have potential for cancer reduction in humans.
3. Support brain function and development
Wild leeks consist of choline, which is a used as a chemical messenger in the brain (neurotransmitter). Sufficient amounts of choline in the diet have been shown to support proper cognitive function and facilitate learning in adults and children.
4. Prevent high blood pressure and stroke
Wild leeks consist of folate, which is an essential B vitamin that keeps our bodies levels of homocysteine in check. Homocysteine is a protein found in the blood that contributes to atherosclerosis when it is in high amounts.
Traditional uses and benefits of Wild Leek
- It has a very long folk history of use in a wide range of ailments, particularly ailments such as ringworm, Candida and vaginitis where it’s fungicidal, antiseptic, tonic and parasitical properties have proved of benefit.
- It is also said to have anticancer activity.
- Daily use of garlic in the diet has been shown to have a very beneficial effect on the body, especially the blood system and the heart.
- Bulb is said to be anthelmintic, anti-asthmatic, anti-cholesterolemic, antiseptic, antispasmodic, cholagogue, diaphoretic, diuretic, expectorant, febrifuge, stimulant, stomachic, tonic, and vasodilator.
- Crushed bulb may be applied as a poultice to ease the pain of bites, stings etc.
- Its consumption has been also popularly considered healthy for its digestive properties or for lowering fat content
Culinary Uses
- Bulb can be consumed raw or cooked.
- Small bulbs can vary considerably in size from 2 – 6 cm, they have a fairly strong leek to garlic flavor and are nice as a flavoring in cooked foods.
- Bulbs of selected cultivars are very large with a mild garlic flavor.
- Flowers have similar flavor to the leaves but they have a somewhat dry texture and are best used as a flavoring in cooked foods.
- Bulbils have a mild garlic flavor and make a nice flavoring in salads and cooked foods.
- Bulb and the pseudo stem formed by the overlapping basal leaves are traditionally gathered before blooming and consumed both as a vegetable and as a condiment in the Mediterranean region.
- As a vegetable, it is consumed raw, directly from the field or used in salads, and much more frequently cooked.
- Edible part is usually boiled and then consumed in different ways, such as seasoned with olive oil and vinegar, fried in the pan, sometimes with scrambled eggs or in omelets.
- Occasionally, they are preserved in vinegar or in oil, after being boiled for some minutes in water and vinegar.
- As a condiment, it has been used as a garlic substitute being included in different recipes, such as soups, sauces, chicken broth, potato stews, or as a seasoning for olives.
- The Cherokee boiled or fried the young plants.
- The Iroquois consumed them seasoned with salt and pepper.
- In Appalachia, they are commonly consumed by frying them in butter or animal fat, though they are also consumed raw in salads.
- They are often consumed with potatoes or scrambled eggs, and used in soups and other savory dishes (Davis & Greenfield).
Pickled wild leeks
Ingredients
- 225 g (1/2 pound) cleaned wild leeks (ramps)
- 1 tsp black mustard seed
- 4 tsp coriander seed
- 3 tsp fennel seed
- 1 L apple cider vinegar
- 500 ml water
- 2/3 cup honey
Directions
- In a medium saucepan, roast the spices on medium heat until they are fragrant. Add this to the vinegar and water and bring to a boil.
- Place the wild leeks into a clean container or glass Mason jar and pour pickling liquid over them. Cover with a lid and allow them to cool at room temperature.
- Refrigerate for one week and then use them with everything and anything! Makes 225 g of pickles.
Wild Leek and Cashew Pesto
Ingredients
- 1 bunch or about 6-8 wild leeks
- 1/2 cup of fresh basil leaves
- 1/2 cup of fresh dill
- 2 garlic cloves
- 1 cup of cashews, soaked overnight, or for 4 hours or more
- 1 tbsp of dried oregano
- 1/4 cup of nutritional yeast
- 1/2 cup of filtered water
- Juice of 2 lemons
- 1/4 cup of extra virgin olive oil
- 1 tbsp of coarse sea salt
Directions
- In a food processor or high-speed blender, combine all ingredients until the pesto is smooth and creamy. Use as a pasta sauce in your favorite pasta, or as a creamy salad dressing.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=42708#null
https://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/go/55019/
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=2217
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Allium+ampeloprasum
http://www.missouribotanicalgarden.org/PlantFinder/PlantFinderDetails.aspx?taxonid=281717
http://www.floracatalana.net/allium-ampeloprasum-l-
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=ALAM
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-294972
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Allium_ampeloprasum
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/4237
http://w3.biosci.utexas.edu/prc/K12/pages/Allium%20ampeloprasum.html
Comments
| Wild Leek Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Wild Leek |
| Scientific Name: | Allium ampeloprasum |
| Origin | Mediterranean region (S. Europe, Northern Africa to W. Asia) |
| Shapes | Depressed globose to ovoid capsule 2–4 mm in diameter |
| Taste | Cross between onions and garlic with an extra bit of sweetness |
| Major nutrients | Vitamin B9 (36.25%) Carbohydrate (12.77%) Copper (12.22%) Total dietary Fiber (11.13%) Potassium (9.68%) |
| Health benefits | Beneficial for Heart Health, Treat and Prevent Cancer, Support brain function and development, Prevent high blood pressure and stroke |
| Name | Wild Leek |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Allium ampeloprasum |
| Native | Mediterranean region (S. Europe, Northern Africa to W. Asia), though it has been introduced in other regions of the world, such as North and South America and Australia and cultivated in different parts of Asia including India |
| Common Names | Elephant Garlic, Giant garlic, Great-headed garlic, garlic, Levant, Russian garlic, Wild leek, Yorktown onion, Broadleaf wild leek, garden leek, Puerro silvestre |
| Name in Other Languages | Arabic: Kurat ( كرات), bsl aleafriat (بصل العفريت), Bassal Africans Armenian: Aygepras (Այգեպրաս), Dziaskhtor (Ձիասխտոր) Catalan: Porradell, Porro de bosc Chinese: Dàtóu suàn ( 大头蒜) Give Tou suan Croatian: Divlji Lu, Divj vinogradski pure Lucac, Lučec, Lu puricius, puricius, Vinogradski Luk, Vinogradski porjak, Poriluk Czech: Pór zahradní Dutch Grootkoppige knoflook, Olifantsknoflook, wild look, Prei English: Elephant Garlic, Giant garlic, Great-headed garlic, garlic, Levant, Russian garlic, Wild leek, Yorktown onion, Broadleaf wild leek, garden leek, Puerro silvestre Estonian: Hobulauk, Porrulauk, porro, porru Finnish: Kesapurjo French: All d’Orient, all faux Poireau, carambola, Faux poireau, Poireau d’ete, Poireau du Levant, Poireau sauvage, Ail faux poireau Galician: Allo porro, porro German: Ackerknoblauch, Breitblättrige Wilder Lauch, Pferdeknoblauch, Sommerlauch, Ackerlauch Greek: Práso (Πράσο) Hindu: Ailiyama ēmapōlōprāsama (ऐलियम एमपोलोप्रासम) Hebrew: שום גבוה , שׁוּם גָּבוֹהַּ Hungarian: Francia v. nyári hagyma Italian: Porraccio, porro selvatico, porandello Japanese: Ariumu• anperopurasumu (アリウム·アンペロプラスム), Rīki (リーキ) Macedonian: Праз Netherlands: Wilde Look Occitan: Porri fèr Polish: Czosnek Dzik, For Dzik Portuguese: alho-porro, alho-porro-bravo, alho-poró, porro Russians: Jl uk vinogradnyy (Jl ук виноградный), Lu vinogradnyi (Lu vinogradnyj) Serbian: Divlji Lu , Lu, Lukomača whether ljutika, Veljo ljutika, Vinogradski Luk Slovenian: Pasji Luk, Poletne Luk Spanish: chilotes Ajo, Ajo Elefante, Ajoporro, Puerto wild Puerto field, Puerro agreste, Puerro de viña, Puerro silvestre Swedish: Vild purjolök, Purjolöek, Kajpar Tamil: Iraakuuccittam (இராகூச்சிட்டம்) Thai: Kra Thiam thon Hua Yai (กระเทียม โทน หัว ใหญ่ ) Turkish Karaköremen, Kaya sarımsağı, kecit körmeni, Pirasa Welsh: Cennin gwyllt, cenhinen wyllt |
| Plant Growth Habit | Robust herbaceous, Perennial and bulbous plant |
| Growing Climates | Sandy and rocky places near the coast, as well as in disturbed areas such as old fields and hedge banks, sheltered cliff-slopes, alongside paths, in drainage ditches, clearings, thickets, meadows, rocky outcrops, dunes, and also roadsides and path verges, gardens, and waste ground |
| Soil | Grows in almost all types of soils with preference for well drained and rich in organic matter ones |
| Plant Size | More than 1 m tall when in bloom |
| Stem | Thick cylindric, to 8 mm diameter at top of bulb, white where covered by leaf sheaths, green above the uppermost leaf sheath; solid |
| In Leaf | October to August |
| Leaf | Flat, broad, long, and dark green and wrap around tightly like a rolled newspaper that also have a deep purple or burgundy tints on their lower stems |
| Flowering season | July to August |
| Flower | Inflorescence is a characteristic umbel, almost spherical, about 8 cm in diameter, with numerous tiny white to purple flowers |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Depressed globose to ovoid capsule 2–4 mm in diameter, up to 6-seeded |
| Seed | 2–3 mm long and 2 mm wide and black colored. |
| Taste | Cross between onions and garlic with an extra bit of sweetness |
| Season | August |
| Health Benefits |
|
| Major nutritions | Vitamin B9 (Folate) (145 µg) (36.25%) Carbohydrate (16.6 g) (12.77%) Copper, Cu 0.11 mg (12.22%) Total dietary Fiber (4.23 g) (11.13%) Potassium, K (455 mg) (9.68%) Calcium, Ca (75.6 mg) (7.56%) Zinc, Zn (0.752 mg) (6.84%) Iron, Fe (0.54 mg) (6.75%) Manganese, Mn (0.11 mg) (4.78%) Magnesium, Mg (17.1 mg) (4.07%) |
| Other Facts |
|