| White Mustard Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | White Mustard |
| Scientific Name: | Sinapis alba |
| Origin | Mediterranean region |
| Colors | Green when young turning to light brown as they mature |
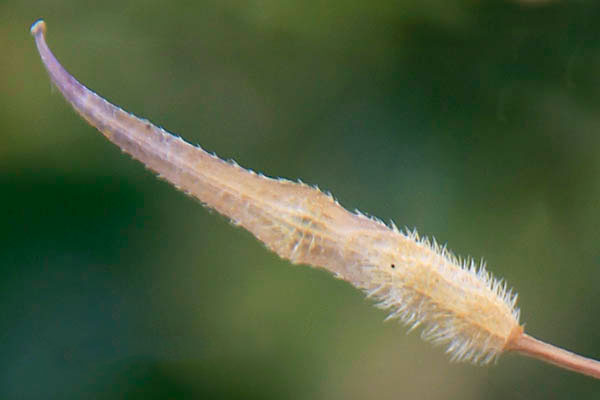
| Shapes | Many-seeded, densely stiff-haired, 3-veined, 2-4 cm long siliqua terminated by a flat, slightly curved, seedless beak |
| Taste | Astringent, Acrid |
| Health benefits | Accelerates the digestive process, Improves body immunity, Relieves muscle spasms, Reduces breath odor, Cures respiratory disorders, Cures body aches, Heart Health, Fights cancer, Aids in metabolism, Overcome Rheumatoid Arthritis, Promotes hair growth, Strengthens bones and teeth, Soothes Cold and Cough, Prevent Anemia |
| Name | White Mustard |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Sinapis alba |
| Native | Probably originates from the Mediterranean region, but various cultivars are grown in Northern, Central, Eastern Europe, North Africa, the Middle East and Central Asia, it can be found worldwide. It has been found as far north as Greenland, and naturalized throughout Great Britain and Ireland |
| Common Names | White Mustard, kedlock, white mustard, yellow mustard, yellow or white mustard, Wild mustard, Salade mustard, charlock, rough mustard |
| Name in Other Languages | Afrikaans: Wit mosterd Albanian: Sinap, sinapi i bardhë Amharic: Netch Senafich (ነጭ ሰናፍጭ), spad (ܣܦܕ) Arabic: Bahammou, kbr(kabar), khardal (khardl) (كبر(كَبَر)، خردل (خَردل), khardal ‘abyad (خردل أبيض), khardal asfur (خردل اصفر), خَرْدَل أَبْيَض, Khardal abyad, Khardal asfur Azeri: Xardal ağı (Хардал ағы) Azerbaijani: Ağ xardal Basque: Ziapia Belarusian: Harčyca (Гарчыца), Bielaja harčyca (Белая гарчыца), Belaja harčyca Bengali: Sādā saraṣē (সাদা সরষে), Sada sores Breton: Sezv-gwenn Bulgarian: Byal sinap (Бял синап) Catalan: Mostassa blanca, mostalla, mostassa, senabre Chuvash: Shură părăç (Шурă пăрăç) Croatian: Bijela gorušica Chinese: Bai Jie Zi, Bai Jie (白芥), bái gài, Bái jiècài (白芥菜), Bái jièzǐ (白芥子), Baahk gaai choi, Baahk gaai ji Croatian: Bijela gorušica Czech: Hoř, hořčice bílá, hořčice setá Danish: Gul sennep, Hjortetaktræ, Kongekommen, Sommer-hvidblomme, Hvid Sennep Divehi: Rīndū revi (ރީނދޫ ރެވި),Hudhu revi (ހުދުރެވި) Dutch: Witte mosterd, gele mosterd English: White Mustard, Yellow mustard, Wild mustard, Salade mustard, charlock, rough mustard Esperanto: Sinapo, Blanka sinapo Estonian: Valge sinep Farsi: خردل سفید, Khardel sefid Finnish: Keltasinappi French: Moutarde blanche, Moutarde rude, moutarde anglaise, moutarde cultivée, hurlu Gaelic: Sgeallan geal Galician: Mostaza branca German: Echter Weißer Senf, Hederich, Weisser Senf, Weißer Senf, Zerschlitzter Weißer Senf Greek: Imero sinápi (ήμερο σινάπι), sínapis lefkí (σίναπις λευκή), Moustárda (Μουστάρδα), Sinápi ágrio (Σινάπι άγριο), Sinápi áspro (Σινάπι άσπρο), Moustarda, Sinapi agrio, Sinapi aspro Gujarati: Saphed rai (સફેદ રાઇ) Hebrew: Chardal lavan, khrdl lbn (חַרְדָּל לָבָן), Hardal lavan Hindi: Sarson, pudeena (पुदीना), Saphed rai, (सफेद राई), Pili rai (पीली राई) Hungarian: Zöld mustármag, Angol mustár, Fehér mustár, Kerti mustár, Sárga mustár Icelandic: Hvítnur mustarður, Sinnepsfræ Indonesian: Sesawi putih, Biji sesawi putih Irish: Sceallagach Italian: Senape Bianca, ruchettone Japanese: シロガラシ, kikugarashi, shirogarashi, キクガラシ, 白芥子, しろがらし, Kannada: Mayirmanikkam,Beeli sasive Korean: baeggaeja (백개자), baeggyeoja (백겨자), meoseutadeu (머스타드), Paekkaeji, Meosutadu, Mosutadu Lao: Mad satad (ມັດສະຕາດ), Som sian (ສົ້ມສ້ຽນ) Latin: Sinape, Sinapis Latvian: Balt, baltā sinepe Lithuanian: Baltoji garsty, Baltoji garstyčia, garstyčios Macedonian: Bel sinap (Бел синап) Maithili: Sarso (सरैसो) Malay: Sesawi putih Malayalam: Vellakatuk (വെള്ള കടുക്) Maltese: Mustarda Manx: Brashlagh rangagh Mongolian: Tsagaan gich (Цагаан гич) Nepali: सऱ्सों (Sarso) Netherlands: Witte mosterd Newari: Ika (ईका) Norwegian: Villgulrot, kvitsennep, Hvitsennep Northern Sami: Vilgessennet Norwegian: Hvitsennep, Kvitsennep Occitan: Airúgas Oriya: ଧଳା ସୋରିଷ, Dhala sorissa Ossetian: Baeltaerna (Бӕлтӕрна) Persian: خردل سفید Philippines: Mustasa Polish: Gorczyca jasna, Gorczyca biała, Gorczyca żółta Portuguese: Mostarda, Mostarda-branca Punjabi: Chitti rai (ਚਿੱਟੀ ਰਾਈ) Quechua: Yuraq mustasa Romanian: Muştar alb Russian: Gorchitsa belaya (Горчица белая), gorchitsa angliyskaya (горчица английская) Sanskrit: Shvetasarshapa, siddhartha Serbian: Bela gorušica (бела горушица), Bela slačica (Бела слачица), Gorčica bela (Горчица бела) Sinhala: Ela aba (එල අබ) Slovak: Horčica biela Slovene: Bela gorjušica, bela gorčica Spanish: Mostaza blanca, jaramago, jenabe, Mostaza silvestre Swedish: Miniatyrpåsklilja, Rönnsumak, Slöjsilja, Grön snödroppe, Keltasinappi, Sommarsnöklocka, Vitsenap Tamil: Veḷḷaik kaṭuku (வெள்ளைக் கடுகு), mayirmanikkam, venkadugu, venkatuku Telugu: Avalu Tigrinya: Senafech tseda (ሰናፍጭ ጻዕዳ) Turkish: Beyaz hardal, mamanık, Beyaz hardal tohum, Deve tüyü hardalı tohumları Turkmen: Ak gorçitsa (Ак горчица) Ukrainian: Hirchitsya bila (Гірчиця біла), hirchytsya rozsichena (гірчиця розсічена) Uzbek: Oq gorchitsa (Оқ горчица), Oq xantal (Оқ хантал) Vietnamese: Bạch giới tử Welsh: Cedu Gwyn, Cedw Gwyn, Mwstard Gwyn, Mwstart wen Yiddish: Vayser zeneft (װײַסער זענעפֿט), Vayse gortshitse (װײַסער גאָרטשיצע), װײַסער מושטאַרדע (Vayse mustarde) |
| Plant Growth Habit | Quick-growing, erect, sparsely-hairy, annual herbaceous plant |
| Growing Climates | Arable and waste land, especially on calcareous soils, waste ground near fields, roadsides, disturbed areas, grain fields, cultivated areas, gardens and orchards |
| Soil | Requires high nutrient soils with a high level of nitrogen, but it may be grown on a wide range of soils from light to heavy, growing best on relatively heavy sandy loamy soils. It is not suited to very wet soil |
| Plant Size | About 30 – 100 cm tall |
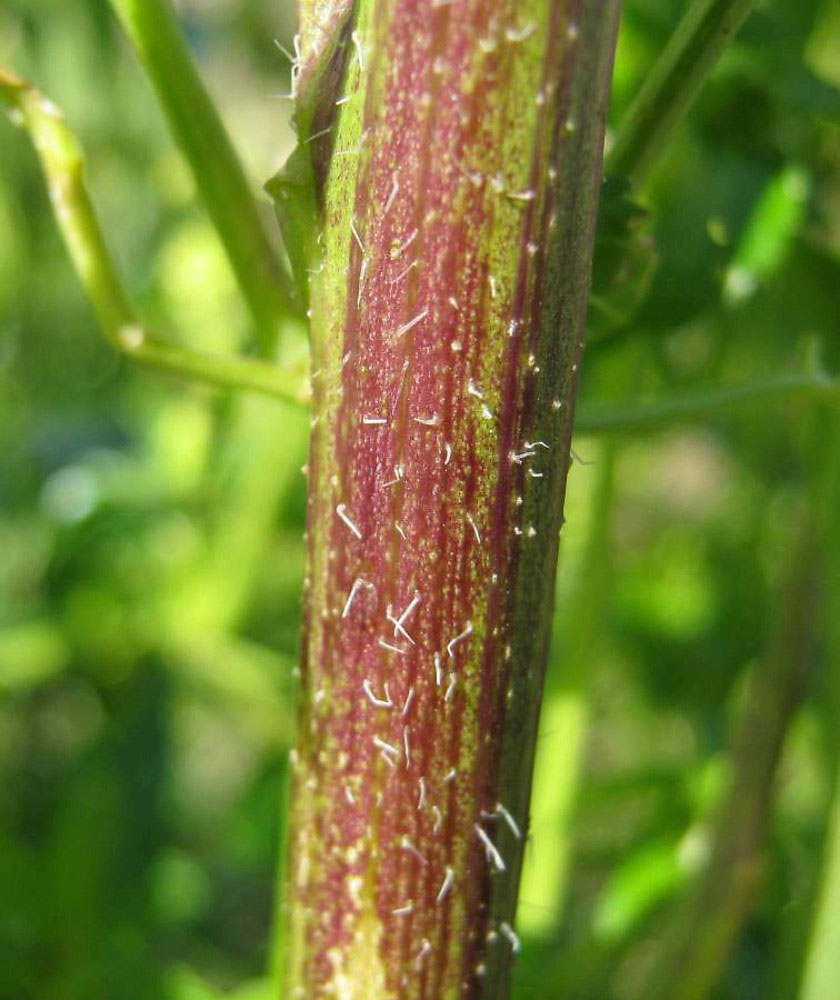
| Stem | Ribbed, branched, bristly, with hairs pointing downward, usually only branching in upper part |
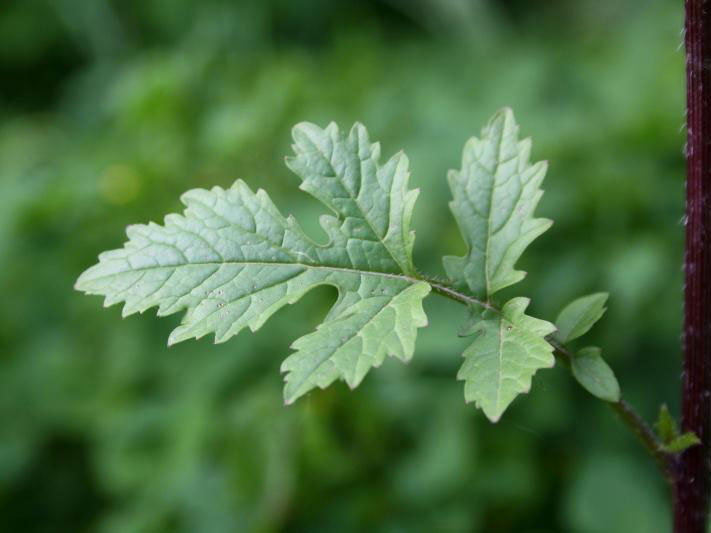
| Leaf | Pale green leaves of this plant are smooth, haphazardly dentate (having toothed margins), lyrately pinnate, rugged and have an uneven surface. Blade are elliptical, ovate or obovate in outline, up to 15 cm long, divided deeply or even to the midrib into 1-3 pairs of lobes with irregularly crenate or dentate margins. Uppermost stem leaves clearly lobed. Petiole is longest in largest leaves |
| Flowering season | June to August |
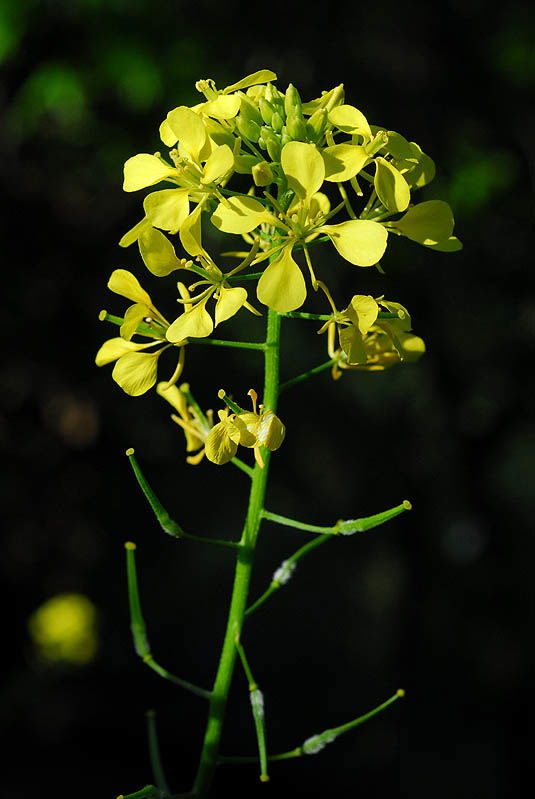
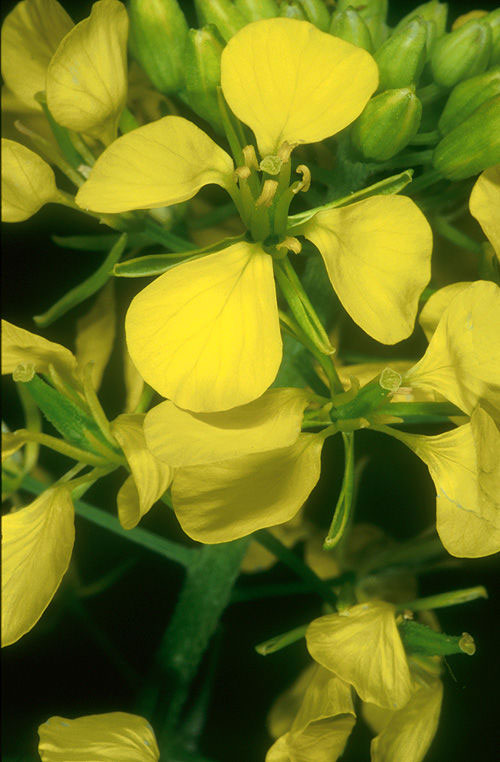
| Flower | Bisexual about 1.5 long and 4-merous. Pedicel is 5-7 mm long. Sepals are 4, narrowly elliptical and 4-5 mm long. Petals four, obovate, 10 mm long and 4 mm wide narrowly clawed at base and are bright yellow |
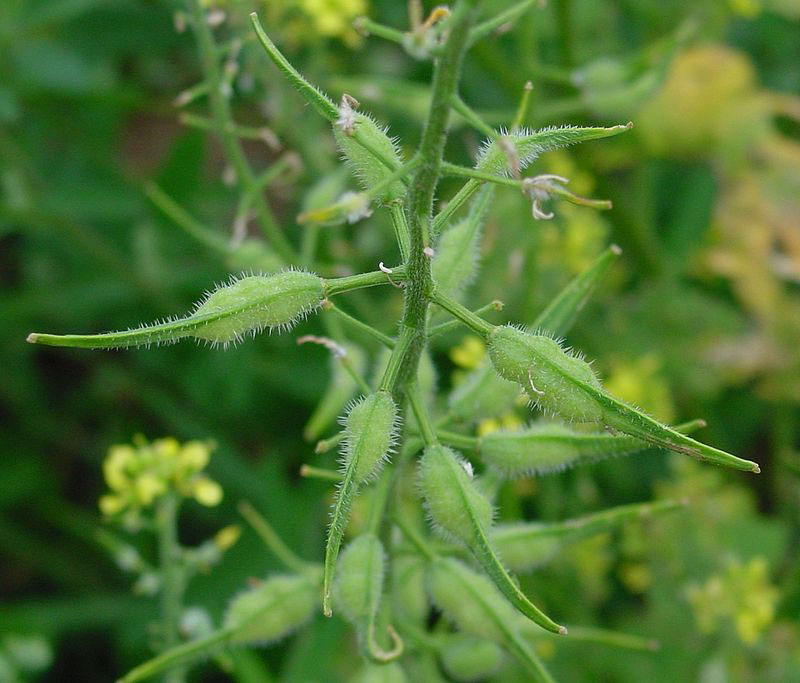
| Fruit Shape & Size | Many-seeded, densely stiff-haired, 3-veined, 2-4 cm long siliqua terminated by a flat, slightly curved, seedless beak |
| Fruit Color | Green when young turning to light brown as they mature |
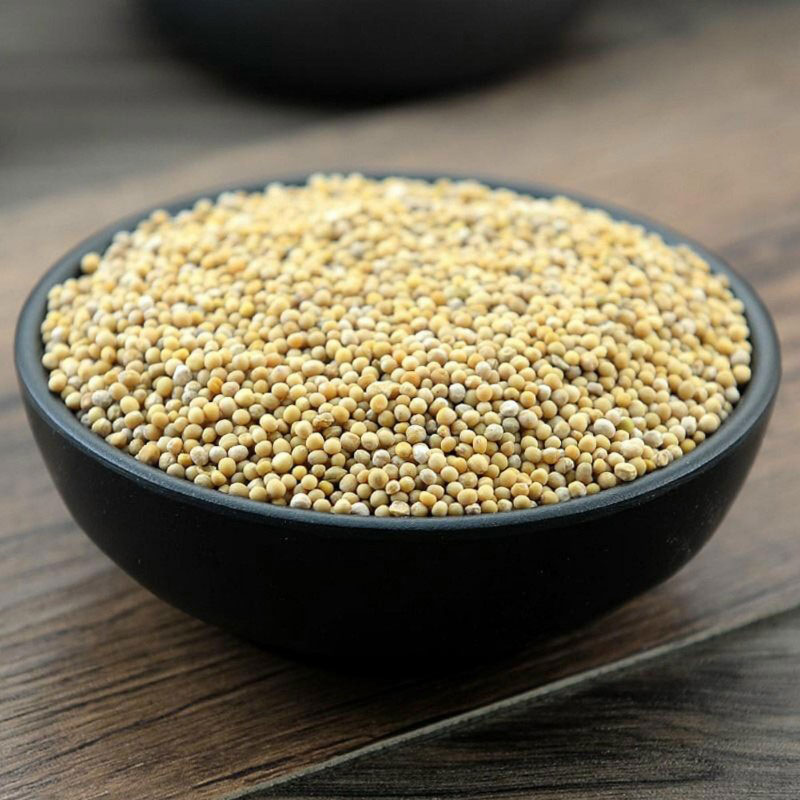
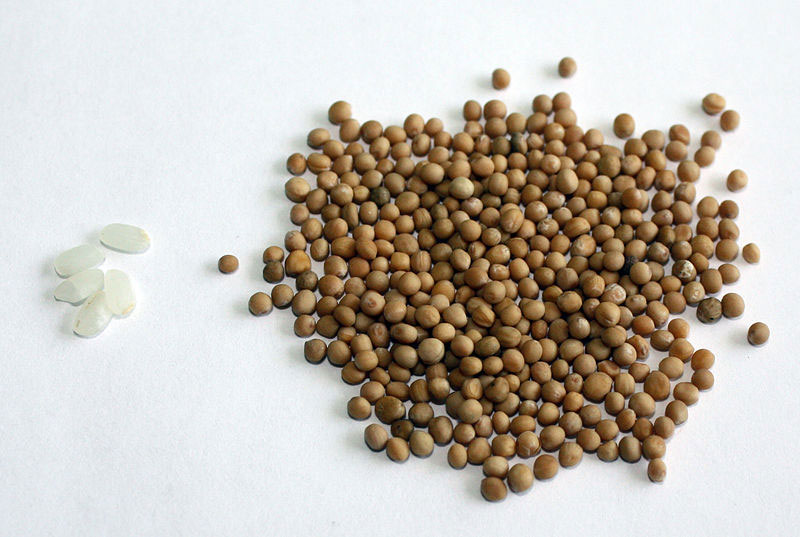
| Seed | Hard, spherical, usually around 1 to 1.5 millimeters in diameter, with a color ranging from beige or yellow to light brown |
| Texture | Both tender and succulent when young, but later becomes more fibrous with maturity |
| Propagation | By Seed |
| Taste | Astringent, Acrid |
| Plant Parts Used | Leaves, Flowers, Seeds |
| Season | July to September |
| Health Benefits |
|
Plant Description
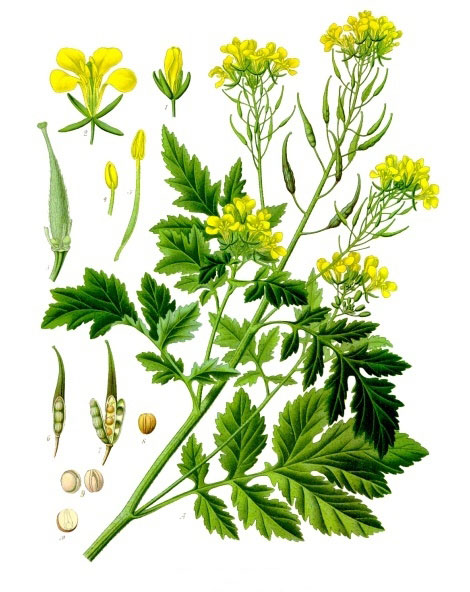
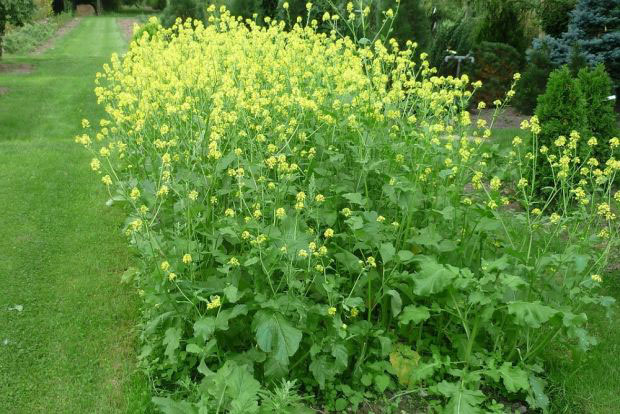
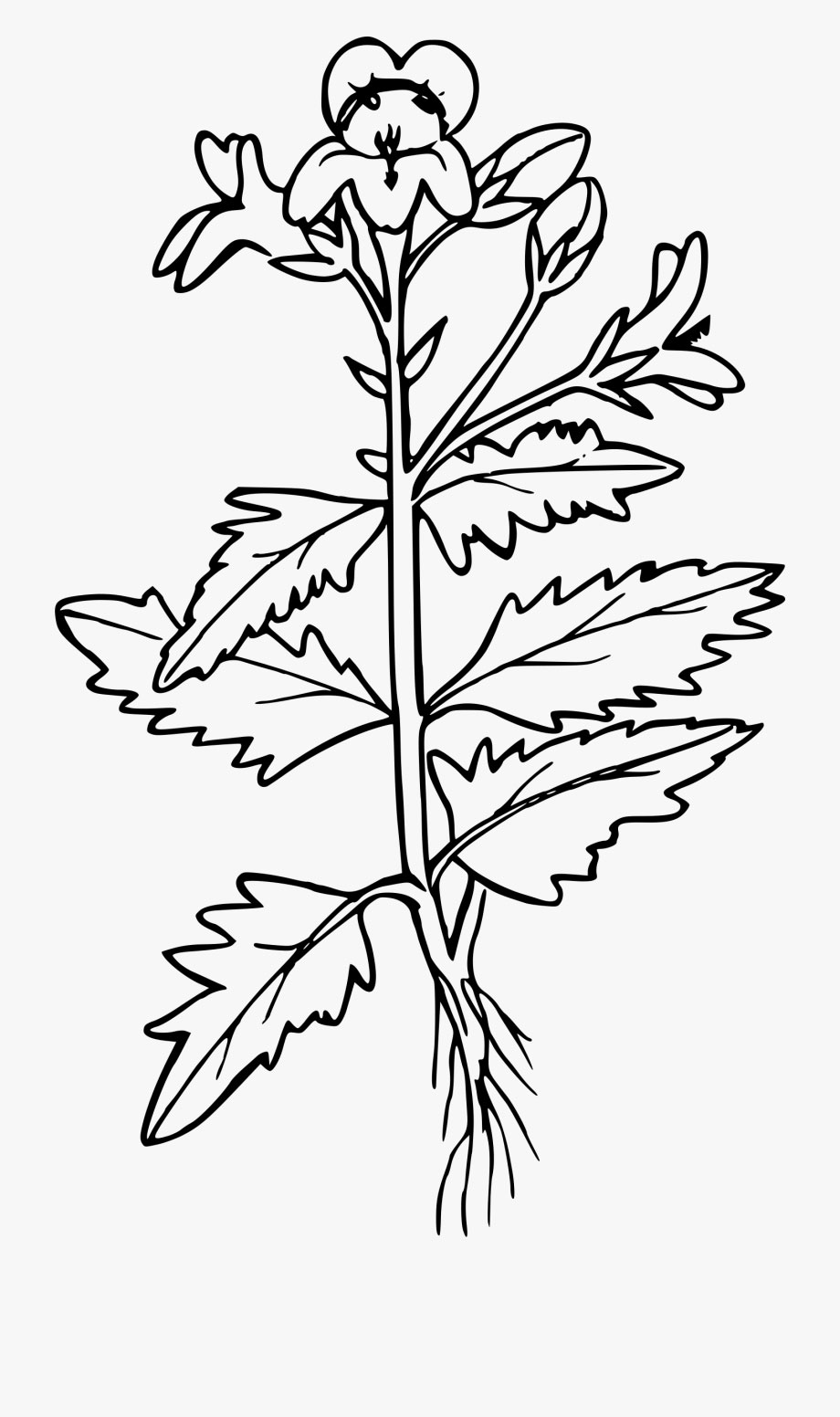
White mustard is a quick-growing, erect, sparsely-hairy, annual herbaceous plant that normally grows about 30 – 100 cm tall. The plant is found growing in arable and waste land, especially on calcareous soils, waste ground near fields, roadsides, disturbed areas, grain fields, cultivated areas, gardens and orchards. The plant requires high nutrient soils with a high level of nitrogen, but it may be grown on a wide range of soils from light to heavy, growing best on relatively heavy sandy loamy soils. It is not suited to very wet soil. Stems are ribbed, branched, bristly, with hairs pointing downward, usually only branching in upper part.
Leaves
The pale green leaves of this plant are smooth, haphazardly dentate (having toothed margins), lyrately pinnate, rugged and have an uneven surface. Blade are elliptical, ovate or obovate in outline, up to 15 cm long, divided deeply or even to the midrib into 1-3 pairs of lobes with irregularly crenate or dentate margins. Uppermost stem leaves clearly lobed. Petiole is longest in largest leaves.
Flowers
Flowers are yellow, bisexual about 1.5 long and 4-merous. Pedicel is 5-7 mm long. Sepals are 4, narrowly elliptical and 4-5 mm long. Petals four, obovate, 10 mm long and 4 mm wide narrowly clawed at base and are bright yellow. Stamens are 6, of which outer whorl of 2 shorter, inner whorls of 4 longer ones. Pistil is slightly shorter than longest stamens, ovary elongated, sessile and style ending in a semi-globose stigma. Gynoecium is fused in a single carpel. Flowering normally takes place in between June to August.
Fruits
Fertile yellow flowers of the plant are followed by hairy seed pods or siliques, each pod containing roughly a half dozen seeds. They are also short compared to the compressed, nerved, sword shaped (ensiform) beak. Seeds are hard, spherical, usually around 1 to 1.5 millimeters in diameter, with a color ranging from beige or yellow to light brown. These seeds are harvested just prior to the pods becoming ripe and bursting.
They can be used whole for pickling or toasted for use in dishes. When ground and mixed with other ingredients, a paste or more standard condiment can be produced. Seed consists of sinalbin, which is a thioglycoside responsible for their pungent taste. White mustard has fewer volatile oils and the flavor is considered to be milder than that produced by black mustard seeds.
Health benefits of White Mustard
Using White mustard in the food not only gives you taste, but also provide many health benefits. White mustard consists of carbohydrate, dietary fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, iron and calcium as well as many nutrients that help the body fight bacteria and germs. Apart from this, there is also phosphorus and zinc which helps to destroy the body’s toxic substances. Other nutrients found in White mustard protect the body from infections and various diseases. Let’s know about the health benefits of White mustard.
1. Accelerates the digestive process
White mustard helps to improve the digestive system of the body. By consuming it, the production of saliva can increase up to 8 times. It actually helps to increase the metabolism and digestion process of food. Additionally, White mustard consists of anti-fungal and antiseptic substances that help in strengthening the body’s immune system.
2. Improves body immunity
As we all know that infection due to viruses and bacteria can harm our body. White mustard consists of nutrients such as manganese, iron, magnesium, and selenium. These nutrients help to balance blood pressure and help to increase immunity.
3. Relieves muscle spasms
White mustard can be used for quick relief from any kind of muscle cramps, whether it is a back or shoulder. It encourages the nerves. White mustard is also a good source of potassium and calcium, which is an essential nutrient to maintain strong bones, joints and muscles.
4. Reduces breath odor
White mustard is a natural substance that helps to reduce breath odor. Aroma in it removes odor and also helps to relax the breath. Put a tsp. of white mustard oil in your mouth and swish it for about a minute. Rinse your mouth thoroughly with water.
5. Cures respiratory disorders
It is a wonderful decongestant that helps in clearing the mucus in the air passage. Inhaling the steam of heated mustard seeds or gargling with mustard tea, helps in expelling mucus out of the throat and lungs.
6. Cures body aches
Mustard oil made from White mustard seeds helps to get quick relief from any kind of pain, including arthritis pain. Massage the painful area with mustard oil for 10-15 minutes. Do this 2 or 3 times daily for instant results.
7. Heart Health
Both the White mustard greens and oil can be used to improve your heart health. Being rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, mustard oil can help balance your cholesterol levels. It reduces the low-density lipoprotein (LDL or “bad” cholesterol) level and increases the high-density lipoprotein (HDL or “good” cholesterol) level in the body, thus decreasing your risk of cardiovascular diseases
8. Fights cancer
White mustard consists of an abundance of phytochemicals called glucosinolates that have been scientifically 10.proven to fight against various types of cancer like bladder, cervical, and colon cancer.
9. Aids in metabolism
White mustard is considered an excellent source of magnesium, which plays an important role in metabolic processes and is in charge of the synthesis of protein. Phosphorous content of White mustard contributes to the metabolism of carbohydrates, protein, and fats in the body.
10. Overcome Rheumatoid Arthritis
A white mustard seed consists of selenium and magnesium. It is supposed that both nutrients can overcome rheumatoid arthritis disease and prevent asthma. They have anti-inflammatory properties that can be used to do those, so we should consume this if we have rheumatoid arthritis or asthma disease.
11. Promotes hair growth
White mustard is loaded with beta-carotene, protein, iron and calcium which help in promoting hair growth and keep your hair healthy. Massaging your scalp regularly with yellow mustard oil, helps in promoting stronger and faster hair growth by increasing blood circulation in the scalp.
12. Strengthens bones and teeth
Calcium, phosphorus, manganese, and magnesium contained in White mustard are very good for bone and teeth. It help to accelerate the growth of bone and teeth, so we should consume White mustard appropriately because bones and teeth are the important parts to move other parts or body systems. Additionally, it can prevent some bone problems, such as osteoporosis and fracture.
13. Soothes Cold and Cough
Mustard oil is an excellent remedy for a cold or cough. Being naturally warm, it acts as a natural decongestant. With its high manganese and iron content, consuming mustard greens and sauce can help strengthen your immune system and prepare you for the cold and flu season.
14. Prevent Anemia
Zinc found abundantly in White mustard helps to prevent anemia. As we already know that zinc substance is very beneficial for blood in the body because it produces hemoglobin and red blood cells. It is the main cause of anemia disease, so we should consume this if we need more red blood cells.
Traditional uses and benefits of White Mustard
- Seed is antibacterial, antifungal, appetizer, carminative, diaphoretic, digestive, diuretic, emetic, expectorant, rubefacient and stimulant.
- Seed has a cathartic action due to hydrolytic liberation of hydrogen sulphide.
- It is used in the treatment of coughs with profuse phlegm and tuberculosis, pleurisy in China.
- Seed is seldom used internally as a medicine in the west.
- Externally it is usually made into mustard plasters (using the ground seed), poultices or added to the bath water.
- It is used in the treatment of respiratory infections, arthritic joints, chilblains and skin eruptions etc.
- Seed has an inhibitory action on the growth of fungus.
- Green leaves of white mustard possess carminative (a medicine that helps to expel gas formed in the stomach) properties.
- It inhibits the growth of Cancer cells.
- The mustard seeds are effective in curing inflammation and lesions associated with Psoriasis.
- The seeds are good for curing Cold and Sinus problem. It provides relief in Respiratory Disorders.
- Poultice made from mustard seeds helps in curing spasms and pains.
- It is applied as plaster and provides relief in paralysis of limb, rheumatism and muscular aches.
- It fights the effect of poison on the Body.
- The oil is good for skin, hair and cardiovascular health.
- Seed oil is taken both internally and applied externally to treat tumors.
- Tea prepared from the seed is used to cure sore throat and to relieve bronchitis and rheumatism.
- Seed or its oil is taken both internally or externally, for cancers, growths of the abdomen, spleen, stomach, throat, uterus or wrist indurations.
- Seeds are used in poultices for acute local pain, pneumonia, bronchitis, and other diseases of the respiratory organs.
- Volatile oil is a powerful irritant, rubefacient, and vesicant, used for rheumatic pains and colic.
- Seeds are ground and mixed with vinegar are recommended for rheumatism, yet used internally for digestive disorders.
- Mustard seed tea has been recommended as a gargle for sore throat, and it is said to relieve bronchitis and rheumatism.
- Herbalists in China used the white mustard leaves to treat coughs accompanied by copious phlegm, pleurisy as well as tuberculosis.
- Seeds of this plant are used to prepare a mustard plaster by adding water to the ground seeds, poultices or even added to one’s bath water.
- Mustard seeds are also used for treating arthritic joints, skin eruptions, respiratory infections and chilblains.
- When added with water in a proportion of 1:3, white mustard seeds have the aptitude to inhibit fungal growth.
- White mustard seeds are widely used as plasters, poultices and other substance while treating bronchitis, pleurisy, and pneumonia as well as also in the form of a counter-irritant for alleviating deep-entrenched pains.
- Seeds as well as the oil extracted from them are used internally as well as externally in folk medicine for treating cancers, abnormal growths in the stomach, abdomen, spleen, uterus, and throat or wrist indurations.
- Seeds are also used in poultices to ease severe local pains, bronchitis, pneumonia as well as other ailments related to the respiratory tract.
- Oil is used to cure colic and rheumatic pains.
- Gargling with a tea prepared with white mustard seeds for treating sore throats.
Ayurvedic Health benefits of White Mustard
- Rheumatism: Add One tablespoon Mustard powder in Four tablespoons of Flour. Make a paste. Apply on the affected area as a plaster for 15-20 Minutes. (Note: Do not keep it for too long.)
- Liver Diseases: Add half cup White Mustard powder in One liter of water. Soak your foot in this water for half an hour.
- Sinusitis: Take half teaspoon White Mustard Seeds. Boil in one cup water till it remains half. Strain. Cool. Use it as ear drop.
- Painful Intercourse: Apply White Mustard oil on your private parts to remove the dryness that may cause pain. Drink plenty of water. Try various lubricants.
- Sneezing: The aim is to inhale droplets of White Mustard oil through the nose. You may dip your little finger in a few drops of White Mustard Oil. Put it in one nostril. Inhale deeply. Repeat with the other nostril. Alternatively put the oil in a nasal spray bottle and spray into your nose and inhale deeply. Repeat once a day for 15 days. Do this exercise once a year just before the onset of winter.
- Acid Reflux: Have half teaspoon of White Mustard with half glass of water.
- Asthma: Massage with a few drops of Mustard Oil on the chest during the asthma attack. It prevents the risk of getting the Asthmatic Attack.
- Menstrual Disorders: Take 3 liters of warm water in a small tub. Add 6 tablespoon of Mustard Seed powder in it. Soak your legs in it for 30 minutes.
- Menometrorrhagia: Grind 1 teaspoon of Mustard seeds to make a fine powder. Mix the powder in one glass of milk. Drink it twice daily.
- Head Lice: Prepare a paste of the roots of Syrina Rue with Mustard oil. Apply for 30-45 minutes. Wash with lukewarm water.
- Lower Back Pain: Prepare a paste of Coriander leaves, Coriander seeds and Mustard Seed Extract. Apply it on back for 15 minutes.
- Lower Back Pain: Grind Garlic, Onion, Ginger and Turmeric. Mix it in Mustard Oil. Heat it. Use it for Back massage. It is considered the best remedy for Backache.
- Arthritis: Take out the juice of Fresh Black Nightshade. Add equal amount of Sesame oil, Ginger powder and two tablespoons Mustard oil. Mix and Boil them. Apply on the affected part twice a day.
- Rheumatism: Mix equal quantity of Fresh Black Nightshade juice, Sesame oil, Ginger powder and two tablespoons of Mustard oil. Boil. Strain. Apply lukewarm on the affected part twice a day.
- Body ache: Take 8 peeled cloves of Garlic and one teaspoon Caraway. Pour them in 60 ml Mustard oil and heat till they turn black. Apply lukewarm on body at night.
- Toothache: Take One tablespoon of each roasted Alum, Mustard oil, Rock Salt, Sal Ammoniac, Black Salt and one teaspoon Blue Vitriol. Powder them and Strain through cotton cloth. Use it as tooth powder once a day.
- Epilepsy: Make a paste of Drumstick Bark and White Mustard with mixing some Cow Urine. Apply the mixture on the body.
- Elephantiasis: Take 10 grams each of Dried Ginger Powder, White Mustard and Giant Hogweed. Add Cow’s Urine and make a paste. Apply the paste on the feet to get relief.
- Age Spots: Mix Yellow Mustard paste with Milk. Apply it on the Freckles at night. Wash in the morning.
- Baldness: Heat 25 gram Henna leaves in 100 gram of White Mustard oil until leaves turn to black. Cool and strain. Apply lukewarm on scalp twice a week. It is a very effective remedy for hair fall.
- Asthma: Heat a little Camphor with some White Mustard Oil. Massage gently on the chest and upper back 2-3 times a day.
- Flatulence: Soak White Mustard seeds in a cup of water for 2 hours. Grind them with Turmeric powder to make paste. Store. Take quarter tsp. with lukewarm water.
- Asthma: Put some Camphor powder in warm White Mustard Oil. Massage it on the back of patient. It aids breathing in case of a sudden attack.
- Arthritis: Heat One cup of Mustard Oil and add 1-2 tablespoons of Camphor. Remove from heat when Camphor dissolved completely. Massage the affected parts with this lukewarm oil.
- Corns: Make a paste by mixing 2 tablespoons each of Licorice powder and White Mustard Oil. Apply it on the affected area at night before going to bed. Repeat daily for a month.
- Hiccups: Mix Half tablespoon White Mustard powder with an equal quantity of Clarified Butter. Consume it once a day.
- Cold Extremities: Put 5 to 7 Black Peppers, a few chopped pieces of Garlic and add few White Mustard seeds in a cloth bag. Hang this cloth bag around your neck.
- Diabetes: Make a fine powder of 1 cup of Black Cumin, 1 cup of Mustard seeds, 2/3 cup of rind Pomegranate and ½ cup of Shahtara and collect in a vessel. Take 1 tsp. of powder with 12 drops of Black Cumin seeds oil and consume it with water on an empty stomach.
- Joint Pain: Make a paste by mixing Turmeric powder in few drops of White Mustard Oil. Apply a layer of this paste daily on the affected area to reduce the pain and inflammation.
- Joint Pain: Mix Aloe Vera gel in a half teaspoon of White Mustard Oil. Apply this mixture on aching joints to get relief from pain in joints.
Menstrual Disorders: (Horse Gram soup): Take 2 cups Horse Gram, 3 teaspoon Tamarind paste, 1 tablespoon Black Pepper, 1 tablespoon Cumin Seeds, 1 teaspoon Mustard Seeds 2-3 Curry leaves, Coriander leaves, Salt to taste and 2 tablespoon Oil
Preparation
Soak the Horse Gram seeds overnight. The next morning, strain the water and pressure cook Horse Gram seeds till they get soft. Mash half of the cooked Horse Gram. Roast Mustard, Cumin and Black Pepper seeds and grind them to make a fine powder. Heat the oil in a pan and add Curry leaves, Tamarind paste, strained Horse Gram water, roasted powder, mashed Horse Gram and Salt. Cook for 5 minutes. Make sure the gravy is not too thick. You can also add water if needed. Add the remaining Horse Gram to the mixture and cook for 3 minutes. Add finely chopped coriander leaves.
Culinary Uses
- Leaves can be consumed raw or cooked.
- Young leaves are used as a flavoring in mixed salads, whilst older leaves are used as a potherb.
- Seed can be sprouted and eaten raw.
- It is often used in salads.
- Seed can be ground into a powder and used as a food flavoring, it is the ‘white mustard’ of commerce.
- Seeds can be used whole for pickling or toasted for use in dishes.
- Mustard paste is a common condiment for boiled or broiled meat in Central and Northern Europe (and in the US); it also is often used for sauces.
- Oil is also used in Sweden in the manufacture of mayonnaise.
- Seedling is used as a salad plant, eaten raw in salads and sandwiches.
- Leaves are used as potherbs.
- You can use the seeds as tempering in your curries to add a final touch to your preparations.
- Season your rice with crackled yellow mustard seeds.
- Stir-fry yellow mustard greens in clarified butter and sprinkle it with a pinch of salt and black pepper.
- Prepare a sweet dip by combining mustard, honey, and seasonings of your choice.
- Whole white mustard seeds are used for making pickles and they may also be boiled together with some vegetables like cabbage and sauerkraut.
Other Facts
- Seed consists up to 35% of semi-drying oil and is used as a lubricant and for lighting etc.
- Plant can be grown as a green manure crop.
- It is very fast growing, producing a good bulk in just a few weeks from seed, but it is shallow rooted so does not do so well in dry periods.
- It is also susceptible to all the diseases of the cabbage family such as club-root so is best avoided if this is likely to be a problem.
- Dried seed do not have any fragrance, but exhibit a pungent taste after some time of chewing.
- In the US mustard is second in demand only to pepper among spices.
- Whole seeds are used for pickles and may be boiled with such vegetables as cabbage and sauerkraut.
- Do not confuse mustard oil with mustard essential oil.
- Oil is also used in the form of a fuel for lamps and a lubricant.
Precautions
- Seed consist of substances that irritate the skin and mucous membranes
- Plant is possibly poisonous once the seedpods have formed.
- Retention of seeds possibly in intestines if taken internally.
- It can cause blisters or ulcers.
- Avoid use during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- If you are suffering from chronic cough, stop consuming it.
- Avoid excessive dosage, as it may cause diarrhea.
- If applied topically on the skin, it may cause skin diseases, blisters and allergy. As the herb is very potent.
- Avoid mustard seeds if you are allergic to it.
- Avoid excess consumption of white mustard sauce if you suffer from heart disease.
- Excessive intake of mustard sauce can cause digestive problems.
- Avoid mustard if you have been diagnosed with kidney or gallbladder conditions. Mustard seeds are rich in oxalates, which block the absorption of calcium.
- Being warm, mustard may increase your body temperature, which is a reason to consume it in moderation.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=23309#null
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxon/taxonomydetail?id=33963
https://pfaf.org/user/plant.aspx?LatinName=Sinapis+alba
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/SINAL
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-2476404
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/White_mustard
https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Sinapis_alba_(PROSEA)
https://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/White%20Mustard.html
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/50066
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=SIAL5
https://hort.purdue.edu/newcrop/duke_energy/Sinapis_alba.html
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/245759