Plant Description
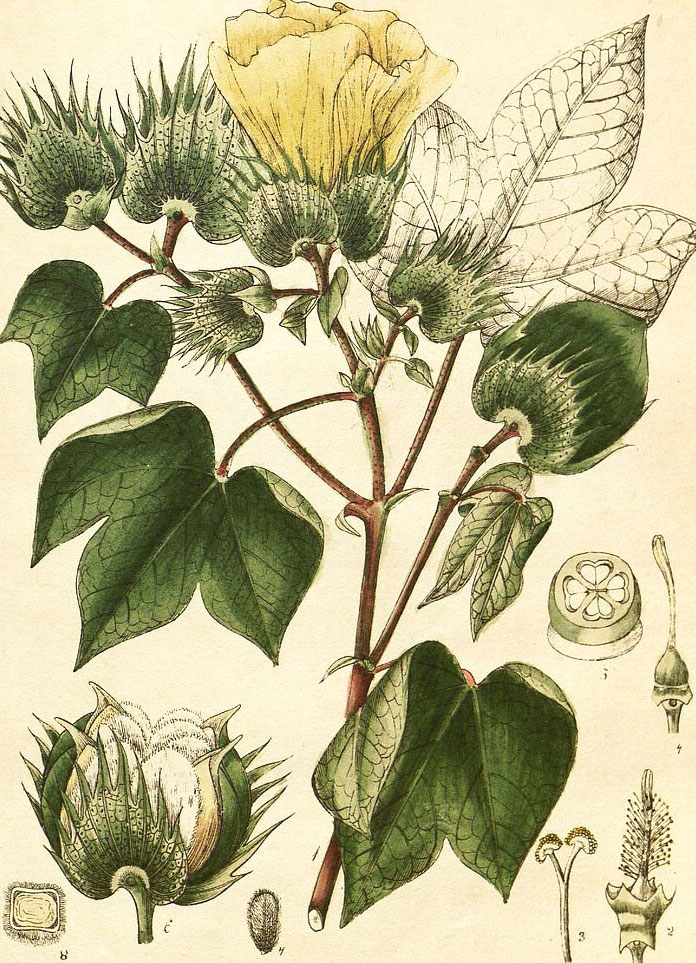
Cotton is a much-branched shrub that grows about 2-6 feet (0.61-1.8 m) high with wide with extremely variable, most parts densely covered with minute stellate hairs and patent simple hairs, nearly all parts irregularly dotted with black oil glands. The plant prefers a very sunny position in a light, fertile, well-drained soil. Plants can tolerate a range of soils, including moderate levels of salt.
Leaves
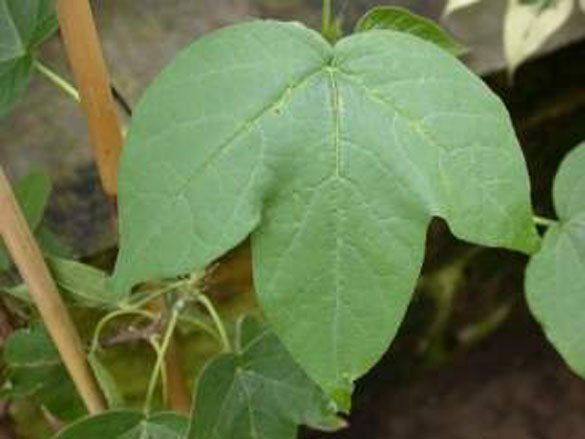
Tree cotton branches are covered with pubescence and are purple in color. Stipules are present at the leaf base and they are linear to lanceolate in shape and sometimes falcate (i.e. sickle-shaped). Leaves are attached to the stem by a 1.5 to 10 cm petiole. Blades are ovate to orbicular in shape and have five to seven lobes, making them superficially resemble a maple leaf. Lobes are linear to lanceolate, and often a tooth is present in the sinus. Glands are present along the midrib or occasionally on the adjacent nerves. Leaves are glabrescent, meaning the pubescence is lost with age, but when it is present on young leaves, it is both stellate (i.e. star-shaped) and simple.
Flower
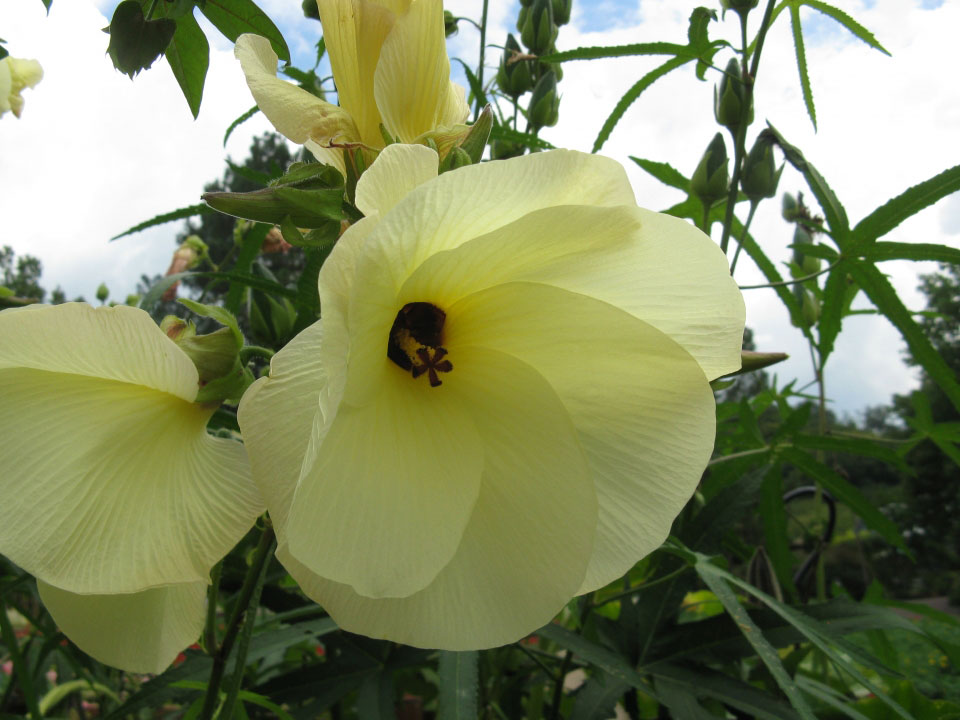
Flowers are set on short pedicels (i.e. flower stalks). An epicalyx is present, which is a series of subtending bracts that look like sepals. Its large, ovate segments are dentate (i.e. toothed along the margins), though occasionally only very slightly so. They are cordate (i.e. heart-shaped) at the base and acute at the apex. True calyx is small, measuring only about 5 millimeters (0.20 in) long. Its shape is cupular, and five subtle dentations are present. The corolla is a pale yellow on color, sometimes with a purple center, and occasionally entirely purple. It measures 3 to 4 centimeters (1.2 to 1.6 in) long. The staminal tube bears the anthers and is 1.5 to 2 cm in length.
Fruit
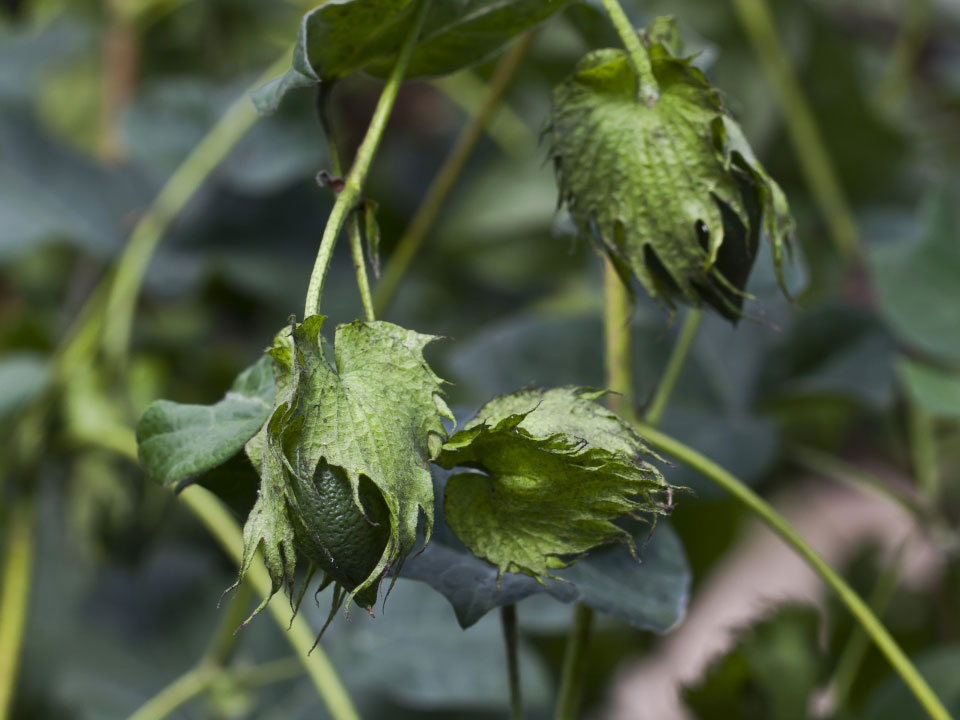
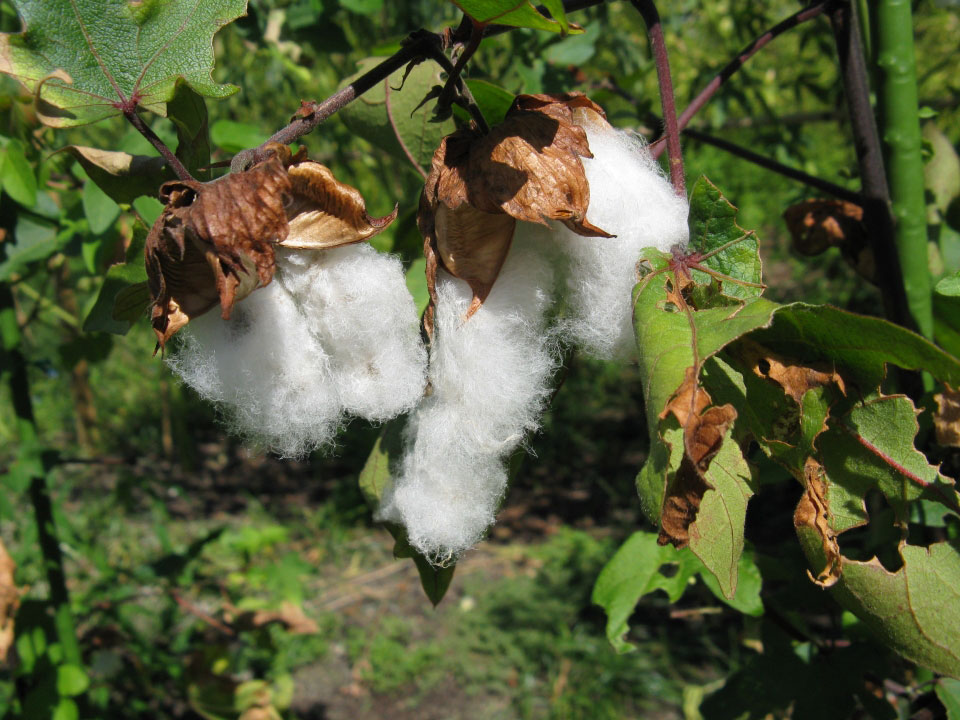
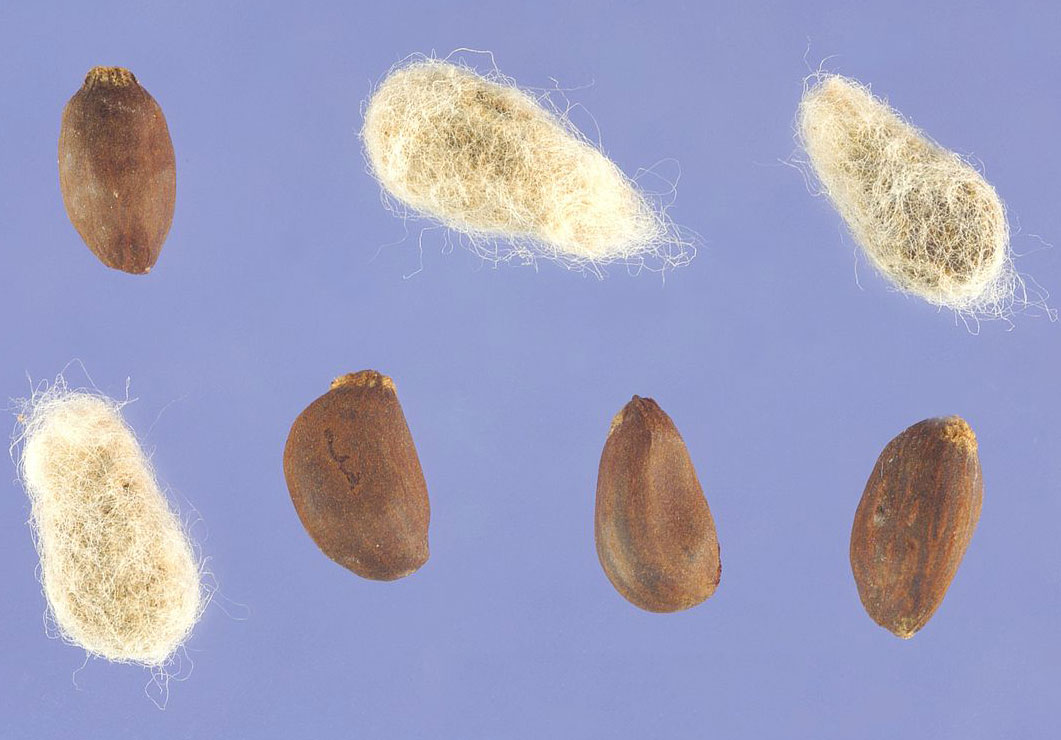
The fruit is a three- or four-celled capsule measuring 1.5 to 2.5 centimeters (0.59 to 0.98 in) across. It is ovoid or oblong in shape and glabrous (i.e. hairless). The surface is pitted and a beak is present at the terminal end. Fruits are initially green in color and turns to brown as they mature. The seeds within are globular and are covered in long white cotton.
Health benefits of Tree Cotton
Tree Cotton leaves consist of mucus, tannins, flavonoids, essential oil, and other substances. Listed here are some interesting health benefits of cotton herbs:
1. Treats respiratory diseases
Cotton leaves have been used as a traditional herbal medicine for respiratory diseases such as asthma, bronchitis, coughing, throat infections, and emphysema. It is a widespread herbal medicine for respiratory diseases because it has healing features that may help mucosa of the upper respiratory tract. One of those healing attributes is the mucus substances that protect or recover the tissue from inflammation.
Tea made from the cotton leaves may be used as a medicine for a cough and similar illness. Be aware that you should allow the leaves to be soaked for a few hours in slightly warm water before use. To keep the medical attributes from fading away, do not boil the leaves.
2. Treats skin problems
This medicinal herb can be used as an alternative treatment for your skin problems like wounds, boils, skin rashes, insect bites, pimples, eczema, acne, and swelling. It is due to the astringent, anti-bacterial, and anti-inflammatory attributes of the leaves. It seems like an effective remedy for inflammation.
3. Treat wounds or inflamed mucus membrane in the respiratory organs
Mucus substances contained in, cotton leaves can heal wounds or treat inflammation of mucosa in the upper respiratory organs such as mouth and throat, and also in the stomach and intestines.
4. Beneficial for breastfeeding mothers
If consumed as tea, it has been said that cotton leaves may help in producing breast milk.
5. Cure for Rat bite
Drinking 50 grams Juice of cotton tree leaves mixed with 100 grams of rice socked water cures poison spread by rat bite.
6. For Scorpion Bite
Finely Grind together cotton tree leaves and mustard seeds. Apply this mix immediately on the area bitten by scorpion. This cures soon.
7. For Joint Pains
Boil the crushed baby cotton leaves in castor oil or with cow ghee. Apply this on joints and bandage it. This gradually removes joint pains.
8. For Swollen Legs
Crush cotton leaves and extract its juice. Apply this on the swollen area of the leg to cure.
9. For Eye Pains
Boil cotton leaves in butter milk. Apply these leaves on the eyes and bandage them to get relief from eye pains.
10. For removing Bacteria in Teeth
Deep Fry some cotton seeds in a vessel till they turn black. This can be used to massage the teeth to get rid of bacteria and give healthy teeth.
11. For Mumps
Crush cotton tree leaves and extract juice from them. Apply this on mumps to cure.
12. For curing Puss in the Ears
Make juice from cotton “boll” and filter it. Add some guggilam and honey to the juice. Put 2 to 3 drops to remove puss from the ear.
13. For Blood and Sticky Motions
Crush cotton leaves and obtain 30 grams of juice. Add 30 grams of candy sugar powder to this. Drink this twice a day to cure.
14. Alternative medicine for various diseases
Beside respiratory and skin problems, cotton leaves may also be used as an alternative herbal medicine for other diseases such as gallstones, kidney stones, kidney inflammation, headache, constipation, gastritis, toothaches and insomnia.
Traditional uses and benefits of Tree Cotton
- Juice of the root is used in the treatment of fevers.
- Root bark is used as an Abortifacient.
- Root decoction is used to prevent Abortion.
- Powdered root bark is used to treat Lymphatic swellings.
- Fresh leaves of tree cotton are used to treat Ulcers.
- Macerated leaf is taken against Vomiting.
- It is used for wound dressing and curbing infection.
- It is applied on forehead to relieve headache.
- It cures digestive disorders.
- It encourages proper Bile secretion in the Liver.
- It helps in uterine contraction.
- It helps in Breast enlargement.
- It supports healthy immune system.
- Chewing the root bark of the cotton plant is thought to stimulate the sex organs and it has a reputation for being an aphrodisiac.
- Seeds and leaves are used in South East Asia and the subcontinent to treat a variety of health problems, and are used both internally and externally for skin problems and injuries.
- Powdered cotton seeds mixed with milk are given to those with headaches.
- An infusion of the seeds and leaves is said to be useful for cases of dysentery.
- Cotton seeds or the expressed juice from the leaves are used to treat skin problems.
- Leaves can be made into a poultice for sprains or painful areas of the limbs.
- Seeds are ground and made into a paste with water and ginger for burns.
- An infusion, a mixture of the seeds and leaves and perhaps also mustard seeds is used for snake bites and scorpion stings.
Ayurvedic Health benefits of Tree Cotton
- Diarrhea: Make a decoction with dried leaves of Tree Cotton. Have 2 tsp. of it thrice a day.
- Maturant: Apply leaf paste of Tree Cotton on the Ulcer. Use it for 1 week.
- Leucorrhoea: Add 35 ml leaf juice of Tree Cotton in a 300 ml of Milk. Drink it once a day.
- Ear Discharge: Crush fruit of Tree Cotton to obtain juice. Use it as an Ear drop.
- Galactagogue: Grind roots of Tree Cotton using warm water. Have quarter tsp. of it once a day.
- Emacitation: Powder the dried seeds of Tree Cotton. Take half tsp. of it with 1 glass warm Milk.
- Epilepsy: Take the leaves of Jequirity. Grind them with the roots of Tree Cotton. Apply this paste on the whole body.
- Menstrual Pain: Collect juice from equal quantities of cotton flower petals, cotton leaves, bamboo leaves and boil them along with water to make syrup. Consuming 1 small cup of this juice thrice a day during menstruation, will remove pains.
- Curing Hysteria and Fear: Extract 10 ml of cotton flowers juice and mix 2 gm. of Saffron along with 1 tablespoon of honey. Consuming this quantity everyday will cure all mind related fears, weaknesses and phobias.
- Burn Skin Mark Removal and Healing: Grind and make a thick paste from cotton flowers. Apply it as a cream on first degree burns to heal the wounds. This helps in quick recovery of skin’s original color by removing burn marks too
Other Facts
- Floss contained in the seedpods is used for making cloth and for the wicks of oil lamps.
- Cotton fibers have a wide range of used including making clothes; rubber-tyre fabrics; stuffing material for pillows, cushions etc.; surgical dressings; making twine and ropes; carpets etc.
- The 1000-seed weight of Gossypium arboreum is 46–91 g.
Precautions
- Large doses of cotton leaves may have laxative effects and cause diarrhea.
- It is suggested that pregnant women should avoid consuming this herb as a safety measure.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=506098#null
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=17897
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Gossypium+arboreum
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=GOAR2
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-2830992
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gossypium_arboreum
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/GOSAR
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/229856
http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Gossypium+arboreum
http://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Cotton.html
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/25793
Comments
| Tree Cotton Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Tree Cotton |
| Scientific Name: | Gossypium arboreum |
| Origin | India, Pakistan and other tropical and subtropical regions of the Old World |
| Colors | Initially green in color and turns to brown as they mature |
| Shapes | Three- or four-celled ovoid or oblong shaped capsule measuring 1.5 to 2.5 centimeters (0.59 to 0.98 in) across |
| Taste | Astringent, bitter, sweet, acrid |
| Health benefits | Treats respiratory diseases, For Mumps, For Blood and Sticky Motions, Cure for Rat bite, For Eye Pains, For curing Puss in the Ears, For removing Bacteria in Teeth, Treats skin problems, For Scorpion Bite, For Joint Pains, Treat wounds or inflamed mucus membrane, For Swollen Legs, Beneficial for breastfeeding mothers, |
| Name | Tree Cotton |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Gossypium arboreum |
| Native | India, Pakistan and other tropical and subtropical regions of the Old World |
| Common Names | Bluntleaf cotton, Tree cotton, Ceylon cotton, Ceylon tree cotton, Cotton tree, Indian cotton tree, Red-flowered cotton tree, Tree cotton, Asiatic cotton |
| Name in Other Languages | Afrikaans: Katoen Albanian: Pambuk Arabic: Qatan alhind (قطن الهند) shakharat qatan alhind (شخرة قطن الهند), qatn (قطن) Armenian: Bambak (բամբակ) Azerbaijani: Pambıq Basque: Kotoia Belarusian: Bavoŭna (бавоўна) Bengali: Kārpāsa (কার্পাস) Bosnian: Pamuk Bulgarian: Pamuk (памук) Catalan: Cotó Cebuano: Gapas Chichewa: Thonje Chinese: Dun ye shu mian, Ji jiao mian, Shu mian (树棉), Zhong mian Croatian: Pamuk Czech: Bavlna Danish: Bomuldstræ, bomuld Dutch: Katoenboom, katoen English: Bluntleaf cotton, Tree cotton, Ceylon cotton, Ceylon tree cotton, Cotton tree, Indian cotton tree, Red-flowered cotton tree, Tree cotton, Asiatic cotton Esperanto: Kotono Estonian: Puuvill Filipino: Bulak Finnish: Puuvilla French: Coton, Cotonnier arborescent, Cotonnier de l’Inde, Cotonnier en arbre, Cotonnier rouge, coton arborescent, cotonnier en arbre Galician: Algodón Georgian: Bamba (ბამბა) German: Baumwolle, Baumformige Baumwolle, Indische Baumwolle, Wollpflanze, asiatische Baumwolle Greek: Vamvaki dendrodes (Βαμβάκι δενδρώδες) Gujarati: Kapāsa (કપાસ) Haitian Creole: Koton Hausa: Auduga Hebrew: כותנה Hindi: Diyokapaas, Kapaas (कपास), Kapaas kaa per (कपास का पेड़), Kaarpaas (कार्पास) Hmong: Paj rwb Hungarian: Pamut Icelandic: Bómull Igbo: Owu Indonesian: Kapas Irish: Cadás Italian: Albero del cotone, Cotone a fibra corta, Cotone arborescente, Cotone arbusto, Cotone delle Indie, Cotone di pietra, Cotone indiano Japanese: Wata (ワタ), kotton (コットン) Javanese: Katun Kannada: Bangaali hathhi, Hatti (ಹತ್ತಿ) Kazakh: Maqta (мақта) Khmer: Kabbas (កប្បាស) Korean: Moghwa, myeon (면) Lao: Fai (ຝ້າຍ) Latin: Bombacio Latvian: Kokvilna Lithuanian: Medvilnė Macedonian: Pamuk (памук) Malagasy: Landihazo Malay: Kapas Malayalam: Cemparutti, Karuparutti , Kaattuparutti, parutti (പരുത്തി), Kaattupparutti Maltese: Qoton Maori: Miro Marathi: Kāpūsa (कापूस) Mongolian: Khövön (хөвөн) Myanmar (Burmese): War (ဝါ) Nepali: Kapaas (कपास), Ruuk kapaas Norwegian: Bomull Persian: پنبه Polish: Bawełna Portuguese: Algodoeiro-arbóreo, Algodoeiro gigante, algodão Romanian: Bumbac Russian: Khlopchatnik drevovidnyj (Хлопчатник древовидный), khlopok (хлопок) Sanskrit: Raksatika Serbian: Pamuk (памук) Sesotho: k’hothone Sinhala: Kapu (කපු) Slovak: Bavlna Slovenian: Bombaž Somali: Suuf Spanish: Algodonero arbóreo, Algodón asiático, Arbol del algodón Swahili: Pamba Swedish: Trädbomull, bomull Tajik: Paxta (пахта) Tamil: Cemparutti, Kaattupparutti (காட்டுப்பருத்தி), Parutthi (பருத்தி), Semparutti Telegu: Karpasamu, Paminda pratti, Patti (పత్తి) Thai: F̄̂āy theṣ̄ (ฝ้าย เทศ) Faai daeng Turkish: Hind pambuk fidanı, Pambuk ağaçı, pamuk Ukrainian: Bavovna (бавовна) Urdu: کپاس Uzbek: Paxta Vietnamese: Bông Welsh: Cotwm Yiddish: Vate (וואַטע) Yoruba: Owu Zulu: Ukotini |
| Plant Growth Habit | Much-branched shrub |
| Soil | Prefers a very sunny position in a light, fertile, well-drained soil. Plants can tolerate a range of soils, including moderate levels of salt |
| Plant Size | 2 feet (0.61 m) to 6 feet (1.8 m) high with wide |
| Leaf | Leaves are attached to the stem by a 1.5 to 10 cm petiole. The blades are ovate to orbicular in shape and have five to seven lobes, making them superficially resemble a maple leaf. The lobes are linear to lanceolate, and often a tooth is present in the sinus. Glands are present along the midrib or occasionally on the adjacent nerves. |
| Flower | True calyx is small, measuring only about 5 millimeters (0.20 in) long. Its shape is cupular, and five subtle dentations are present. The corolla is a pale yellow on color, sometimes with a purple center, and occasionally entirely purple. |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Three- or four-celled ovoid or oblong shaped capsule measuring 1.5 to 2.5 centimeters (0.59 to 0.98 in) across |
| Fruit Color | Initially green in color and turns to brown as they mature |
| Seed | Globular seeds that are covered in long white cotton |
| Propagation | By seed. It is also possible to propagate cotton vegetative by cuttings, budding or grafting |
| Taste | Astringent, bitter, sweet, acrid |
| Plant Parts Used | Leaves, root |
| Culinary Uses |
|
| Health Benefits |
|