Because of its pretty leaves and fragrant flowers, Toona ciliata is often used as a decorative tree in parks and gardens. The plant comes from tropical parts of eastern and southeast Asia, tropical Central and South America, and tropical Australia. It is grown a lot in tropical Africa, especially in East and Southern Africa. It is also grown in small amounts in West Africa, Madagascar, and Mauritius. As early as the beginning of the 20th century, this tree was known to live in Zambia and Zimbabwe.
Toona is a type of plant that is also called “toon” or “tun” in India. It belongs to the genus ciliata, which means that its flower stalks and leaves are hairy. Even though this trait can be different in different places, with some groups having no hairs at all, it is still a unique trait of the plant. Also, Toona is sometimes called “cedrela” because its wood smells like cedar and is highly valued for its quality. Its wood comes from both wild and farmed sources.
In addition to being useful, Toona is often grown as an ornamental plant because of its beautiful flowers. In north India, it is often placed as an avenue tree. Unfortunately, too much logging on Toona for its valuable wood has made it scarce, especially in places where too much logging has happened. Even though there have been worries about the species going extinct, this has only been reported in a few places, like China, Sabah, and India. Still, it’s important to know that the plant is currently on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species as a “Least Concern” species.
Toon Tree Facts
| Toon tree Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Toon tree |
| Scientific Name: | Toona ciliata |
| Origin | Tropical Asia, tropical parts of Central America and South America and tropical Australia |
| Colors | Initially green that turn brown with age |
| Shapes | Dry, oblong capsules with five valves and thin walls, typically 20–30 mm long and 8–12 mm wide |
| Taste | Strong, bitter taste |
| Health benefits | Anti-inflammatory properties, Antioxidant properties, Immune system, support Digestive health, Respiratory health |
| Name | Toon tree |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Toona ciliata |
| Native | Tropical Asia, tropical parts of Central America and South America and tropical Australia. It is extensively planted in tropical Africa, particularly in East and southern Africa, but also locally in West Africa, Madagascar and Mauritius. It was recorded from Zambia and Zimbabwe as early as the beginning of the 20th century |
| Common Names | Indian Mahogany, Toon, Tuna, Red cedar, Surian, Australian Red Cedar, Burma Cedar, Lud, Toona Tree, Indian cedar, moulmein cedar, Australian-cedar, Toon tree, Chinese mahogany, Cedrela, Moulmein cedar, red toon, Queensland red cedar, Sandal neem |
| Name in Other Languages | Afrikaans: Toonboom Arabic: Sidrilaa tuna (سيدريلا تونا) Assamese: Poma Jatipoma, Lal-poma, Poma, Pama (পমা) Bengali: Tun, Tuni Brazil: Cedro-australiano Burmese: Sait k toe (သစ်ကတိုး), taung-tama, taw thamgo, thit kador China: Chinese mahogany, Hong shan mu, Yun nan shan mu, Hong Chun (红椿), Máohóngchūn (毛红椿), Zǐ chūn (紫椿), Zhǒng bǐng jú (肿柄菊), Chì zuó (赤昨), Hóng liàn zi (红楝子) English: Australian red-cedar, Australian redcedar, Australian-cedar, Red-cedar, Toon, Toontree, Red Cedar, Chinese mahogany, Cedrela, Burma cedar, Indian cedar, Indian mahogany, Moulmein cedar, red toon, toona, Queensland red cedar, Indian maghogany, Sandal neem French: Cèdre rouge, cèdre rouge d’Australie, acajou indien Hindi: Toon (तून), toona, tun, Tunna (तुन्न), Nandik (नन्दिक), Nandi (नन्दी) Indonesia/Java: Suren kapar, suren mal, Mahoni merah, Toon Indonesia/Moluccas: Kukoru Indonesia/Sulawesi: Malapoga Japanese: Beni-kujira-nara, Hime-kujira-nara Kannada: Gandhagarige (ಗಂಧಗರಿಗೆ), Gandhagarage (ಗಂಧಗರಗೆ), Noge (ನೊಗೆ), Noga (ನೊಗ), Nanduri (ನಂದುರಿ), Nandi (ನಂದಿ), Belandi (ಬೆಳಂದಿ), kempu gandha gari (ಕೆಂಪುಗಂಧಗರಿ), Toona mara (ಟೂನಮರ), Belamdi (ಬೆಳಮ್ದಿ) Kashmiri: Tuni (तूनी), Drab (द्रब्), Drawi (द्रावी) Laos: Mai-yom-horm Lithuanian: Raudonasis indenis Malay: Mahang, Merawan Siput Jantan, Limpaga Malaysia/Sabah: Ranggoh, surian limpaga Malayalam: Vempu, Chandana Vembu (ചന്ദനവേമ്പ്), Mathagiri,Thunee maram, Chuvanna Akilu (ചുവന്ന അകില്), Akil, Arana, Aranamaram, Aroma, Chandanaveppu, Chuvannaakil, Devadaram, Ekana, Ikana, Madhageri Vembu, Mathagirivembu, Padukaranna, Patukarana, Thunnam, Vedivembu, Vembu, chandana vembu (ചന്ദന വേമ്പ്) Candana Veemp, Cuvanna Akil (ചുവന്ന അകില്), Patukarana (പടുകരണ) Madagiriveemp (മദഗിരിവേമ്പ്) Manipuri: Tairen, Tairel Marathi: Kunant, Tunna (तुन्न), Nandurki (नांदुरकी) Mizo: Tei-pui Myanmar: Mai yom horm, moulmein cedar, taung tama, taw thamgo, thit kador Nepali: Toon, Toona, Tuni (टुनी) Oriya: Mahalimbo, Teipui Pali: Kacchaka (कच्छक) Persian: ماهون هندی Philippines: Danupra Portuguese: Cedro-australiano, Cedro-vermelho-da-austrália Puerto Rico: Tun Samoan: Tuna Sanskrit: Nandikah (नन्दिकः) , Tunna (तुन्न) , Kacchapah (कच्छपः), Tunnak (तुन्नकः), Kuberak (कुबेरकः), Nandi (नन्दी) Swedish: Toon Tamil: Tun Maram (துந் மரம்), Santhana Vembu, Thera Tharam, Tunumaram, Ayil (ஆயில்), Tuna-maram (தூணாமரம்), Matakari-vempu (மதகரிவேம்பு), Malaya-p-pu-t-tunna-maram (மலயப்பூத்துன்னமரம்) Telugu: Nandi vr̥kṣamu (నందివృక్షము), Nandichettu, Nandivrikshamu (నందివృక్షము) Thailand: Yom hom, Makhamthet Tongan: Sita kula Urdu: Tunna, Tun, Nandik, Nandi Vietnamese: Lim xanh, Lim gai, Hồng xuân |
| Plant Growth Habit | Large, fast-growing, light-demanding, early successional, deciduous tree |
| Growing Climates | Shade or open habitats, moist localities, in sheltered ravines, valleys, ravines, woods, thickets, swamp forests, hillsides, mountaintops, slopes, near rivers and streams, forest gaps, plantations, roadsides and riparian zones (banks of watercourses) |
| Soil | Grows well on well drained and slightly alkaline soils, but does not do well on compact clay or poor sands. In Zambia it has been successfully established on light loams and deeper soils near streams |
| Plant Size | 20 m – 30 m (70 ft -100 ft) high and 1.8 m – 3 m (6 ft -10 ft) in girth |
| Root | Shallow but large. Instead of growing deep into the dirt, the roots spread out horizontally. |
| Stem | Stem is straight and cylinder-shaped |
| Bark | Smooth and grayish brown, with many vertical cracks. It is thin and papery |
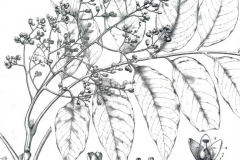
| Leaf | Pinnately compound, usually with 9–17 leaflets. Each leaflet is lanceolate and 45–160 mm long, with the whole leaf being around 300–600 mm long. The leaflets are hairless or sparsely hairy |
| Flower | Borne in large, pendent, densely-branched panicles. There are separate male and female flowers, although vestiges of the non-functional sex are usually present. Flowers are pentamerous and sweetly scented, with 1-mm-long sepals surmounted by white petals, each 5–6 mm long, with ciliate margins |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Dry, oblong capsules with five valves and thin walls, typically 20–30 × 8–12 mm. There are around 5 seeds per loculus, each 10–20 × 3–5 mm, light brown and membraneously winged at one or both ends |
| Fruit Color | Initially green that turn brown with age |
| Seed | Seeds are small and winged |
| Flavor/Aroma | Leaves: slightly citrusy scent Flowers: strong, sweet fragrance Wood: pleasant, woody aroma Bark: strong, earthy smell |
| Taste | Young leaves and shoots: slightly bitter, onion-like flavor Bark: strong, bitter taste Seeds: nutty flavor |
| Plant Parts Used | Bark, flowers, leaves, Seeds, root, fruit, oil |
| Propagation | By seeds or vegetatively through stem cuttings |
| Lifespan | 20-30 years and can live for up to 100 years or more in optimal conditions |
| Health benefits |
|
| Precautions |
|
Plant Description
Toona ciliata is a flexible deciduous tree that grows quickly and can reach heights of 20 m to 30 m (70 ft. to 100 ft.), with a girth of 1.8 m to 3 m (6 ft. to 10 ft.) and a wide-spreading crown. Some people have been said to grow to be as tall as 35.7 m in Hawaii and 54.5 m in New South Wales. Most of the time, the bark is dark grey or reddish brown. It starts out smooth but gets rougher as it ages. There are small cracks on the bark that turn into woody scales.
The plant can grow in a variety of places, from the shade to the open. It can be found in moist places like ravines, valleys, woods, and swamp forests, as well as on hillsides, mountaintops, slopes, and near rivers and streams. It does best in slightly acidic, well-drained soils, but not in hard clay or poor sands. In Zambia, it has grown well on light loams and in deeper soils near streams. Overall, Toona ciliata is a hardy tree that can adapt to different settings and is useful in many ways. This makes it an important species to protect and take care of for the sake of future generations.
Root
The roots of a tree are very important to its life. Not only do they hold the tree in place, but they also help the tree get water and nutrients from its surroundings. In the case of Toona ciliata, the root system is shallow but large. Instead of growing deep into the dirt, the roots spread out horizontally.
This shallow root system makes the tree vulnerable to damage from the wind, especially during storms like hurricanes or cyclones. However, it also lets the tree respond quickly to changes in its surroundings, like changes in soil moisture or the amount of nutrients available. Overall, the tree’s root system is an important part of its biology that helps it adapt to different situations and grow well in them.
Stem
The Toona ciliata tree’s stem is an important part of its life because it gives the tree support and moves water and nutrients between the roots and leaves. Usually, the stem is straight and cylinder-shaped, and the bark is smooth and grayish brown, with many vertical cracks. The bark is thin and papery, so it is easy to pull off in strips or flakes.
The stem’s importance is also shown by its high value in the lumber industry, where the wood is highly valued for its smooth texture, attractive color, and natural resistance to rot, decay, and termite attack. Because of this, it is often used to make high-quality lumber for a wide range of uses. Also, in some places, like Southeast Asia, the stem has a very important traditional meaning. In some countries, it is used to make musical instruments, furniture, and other things for decoration, which shows how useful and versatile it is.
Leaves
Toona ciliata is known for its pinnate leaves, which grow in pairs along the stem and end in a single leaflet. Most of the time, the leaves are 30 to 60 cm long and have 9 to 25 leaflets that can be anywhere from 6 to 18 cm long and 2 to 5 cm wide. Most of the time, the leaflets are oblong or lance-shaped, with a pointed tip and a serrated edge. The bottom of the leaflets may be a little hairy.
The leaves are an important part of the tree’s life because they help the tree turn sunshine into energy through a process called photosynthesis. In traditional medicine, the leaves of Toona ciliata are used for their calming and astringent effects, in addition to their important role. Also, many herbivorous animals, like koalas, possums, and wallabies, eat the leaves because they are a good source of food. Overall, the Toona ciliata tree’s leaves are a big part of its ecosystem and add to its value as a plant species.
Flower
The small, creamy-white flowers of the Toona ciliata grow in big, impressive clusters that can be up to 40 cm long. There are many individual flowers in each clump. Each flower has five petals and ten stamens. Depending on the climate and growing factors, most plants flower in late spring or early summer.
The male and female trees of this species are different from each other. The flowers on male trees are longer and hang down more than those on female trees, making them more obvious. The female flowers, on the other hand, are smaller and less noticeable, but they turn into fruit that holds the tree’s seeds.
The flowers are a very important part of the tree’s life cycle. Male flowers make pollen that is taken to female flowers by insects or the wind, where it is used to make babies. This process helps the species stay alive and adds to its value as a plant species as a whole. So, the tree’s flowers are an important part of its ecosystem and a key part of its life cycle.
Fruits
The female flowers of the tree Toona ciliata turn into woody pods that are the tree’s fruits. These shells are usually between 5 and 8 cm long and hold many seeds. Each seed has a papery wing around it that helps the wind spread it. The seeds that will grow into the next generation of trees are inside the fruit, so it is a very important part of the tree’s life cycle. Once the fruit is ripe and dry, it splits open to let the seeds out. The seeds are then carried by the wind to places where they can grow into new trees.
Fruits are not only important for breeding, but they also have some value in the market. In traditional medicine, the pills are sometimes used because they can reduce fever and pain. Humans don’t usually eat the fruit, though, because it is woody and not very tasty. Overall, the fruit of the Toona ciliata tree is an important part of the tree’s life cycle and adds to the biological value of the species as a whole.
Seeds
Toona ciliata seeds are small and oval-shaped. They are wrapped in a papery wing that helps the wind carry them to places where they can grow into new trees. Each seed is about 5 to 6 mm long and dark brown or black in color.
The seeds are very important to the tree’s ability to reproduce, since they are what make the next generation of trees. When the fruit is ripe and dry, it splits open to let the seeds out. The seeds can then be taken by the wind over long distances to places where they will grow into new trees.
In addition to being used to make more plants, the seeds can also be sold. The seeds are an important part of the timber business because they are used to grow new trees that can be farmed and harvested in a sustainable way. This makes sure that the species’ expensive wood can continue to be used in a way that is good for the environment and good for business. Overall, the seeds of the Toona ciliata tree are an important part of its life and add to its value as a species of plant.
History
Toona ciliata is a type of tree that is native to tropical and subtropical areas of Asia and Australasia. It has been grown and used by people for thousands of years for its valuable wood, which is highly valued for its smooth texture, beautiful color, and natural resistance to rot, decay, and termite attack.
The Toona ciliata has been used since ancient times, which shows that it has a long and rich past. For example, the ancient Egyptians thought the wood of the Toona ciliata tree was very valuable and used it to make furniture, decorations, and even coffins for the dead. In the same way, the tree has been grown in China for hundreds of years to make high-quality furniture, singing instruments, and other items used for decoration.
Today, the Toona ciliata is still an important source of wood for the world market. Large-scale plantations have been set up in many countries, including Australia, India, Indonesia, and Papua New Guinea. The tree’s wood is still highly prized because it is strong and long-lasting. It is used to make a wide range of things, such as furniture, flooring, paneling, and veneers.
But the plant has been facing a lot of problems in recent years, such as being overharvested and having its environment destroyed. To deal with these problems and make sure the Toona ciliata will be around for a long time, people are working to set up sustainable forestry practices and protect natural areas. By doing this, we can keep using the tree’s valuable wood and also make sure it stays around for future generations.
Varieties/Types
Listed here are some of the varieties of Toona ciliata
- Australian Red Cedar: This type of Toon tree is the most popular and comes from eastern Australia. It can grow up to 40 meters high, and its wood is very valuable.
- Indian Red Cedar: This type of Toon tree is native to India and can grow up to 45 meters tall. Its wood is also very valuable because it lasts long and doesn’t get eaten by bugs.
- Chinese Mahogany: This type of Toon tree comes from China and can grow up to 30 meters tall. It is also used for the wood it produces, which is often used to make furniture and decorate rooms.
- Indonesian Cedar: This kind of Toon tree grows in Indonesia and is often used to build things and make furniture.
- Pacific Red Cedar: This type of Toon tree grows naturally in the Pacific Islands, where it is often carved and used to make canoes.
Health benefits of Toon Tree
Toon tree might be good for your health in many ways, especially when it comes to reducing inflammation, protecting against free radicals, helping your immune system, keeping your digestive system healthy, and keeping your lungs healthy. Here’s some information about the health benefits of the Toon tree
1. Anti-inflammatory properties
In the bark and leaves of the Toon tree, there are chemicals that help reduce inflammation. These chemicals might be able to lower inflammation all over the body, which could help treat conditions like arthritis. The fact that these chemicals were found shows that the Toon tree could be used not only as a source of valuable wood but also as a medicine. More study is needed to fully understand how these compounds work to reduce inflammation and how they might be used in medicine.
2. Antioxidant properties
Toon tree is a good source of antioxidants, which are chemicals that help protect the body from damage caused by free radicals. Antioxidants have been shown to be very important in lowering the chance of chronic diseases like heart disease and cancer.
The fact that antioxidants are found in Toon tree shows that this plant has the ability to not only provide valuable wood but also provide important health benefits. More study is needed to fully understand how big these benefits are and how they can be used in medicine and other fields.
3. Immune system support
Compounds found in the Toon tree tree may help the immune system, which is the body’s natural defense against illness and infection. These chemicals might help the immune system work better and could help avoid and treat infections.
The fact that the Toon tree has these chemicals that help the immune system adds to the growing list of possible health benefits of this tree. More study needs to be done to fully understand how these benefits can be used in medicine and other fields.
4. Digestive health
In some countries, the Toon tree tree has been used as a natural treatment for digestive problems like gas, diarrhea, and constipation. This is probably because the plant contains chemicals that help the digestive system work better and lower inflammation in the digestive tract.
When these gut health benefits of the Toon tree were found, it showed that this plant could be used not only for its valuable wood, but also as a medicine. But more study is needed to fully understand how big these benefits are and how they can be used in medicine and other places.
5. Respiratory health
In some countries, the Toon tree has been used for years as a natural way to treat coughs, colds, and other problems with the lungs. It is thought that this is because the plant contains compounds that have been shown to reduce inflammation in the respiratory system and may help treat respiratory infections.
The fact that the Toon tree might help with lung health shows how versatile it could be as a source of medicine. But more study is needed to fully understand how big these benefits are and how they can be used in medicine and other places.
Traditional uses and benefits of Toon tree
- The bark is used to treat fever and malaria, and the leaves are used as a medicine and to get rid of worms.
- Bark is used to treat a wide range of health problems, such as fever, headaches, and stomach problems.
- The leaves are used to treat asthma, pneumonia, and coughs, among other lung problems.
- Seeds are used to treat ringworm and other fungal diseases of the skin.
- Roots can help with fever, diarrhea, and other stomach problems.
- In traditional medicine, fruit is used to treat stomach problems like constipation and gas.
- The bark is used to treat wounds and long-lasting diarrhea in babies.
- In Zimbabwe, a leaf decoction is used to treat diseases of the genital area.
- Boils can be treated with gum made from the bark.
Culinary Uses
Here are some culinary uses of the Toon tree
- Leaves: Young Toona tree leaves are used as a vegetable in many different dishes. They taste a little bit like onions and are good both raw and cooked. They are often added to soups, salads, and stir-fries.
- Shoots: Tender Toona tree shoots can also be used as vegetables, especially in Chinese food. They are often pickled or put in soups and stir-fries.
- Flowers: The flowers of the Toona tree can be eaten. They taste sweet and light. You can eat them raw or use them as a salad topping.
- Seeds: Some dishes use the seeds of the Toona tree as a spice or dressing. They taste like nuts and can be ground into a powder or used whole in recipes like stews and curries.
- Bark: In some countries, the bark of the Toona tree has been used to add flavor to traditional dishes. It tastes strong and bitter, so only small amounts are usually used.
Different uses
Here’s a list of some traditional uses of Toon tree
Timber
Wood is highly valued because it doesn’t rot, decay, or get eaten by termites. It also has a nice feel and color. It has been used to make furniture, floors, walls, and decorations for hundreds of years.
Medicine
In traditional medicine, the toon tree has been used to treat fever, coughs, and stomach problems, among other things.
Food
Some cultures eat both cooked and raw leaves and shoots as vegetables. They taste a little bit bitter and can be eaten raw or cooked.
Ornamental purposes
Some societies have used the toon tree as a decoration, especially in Southeast Asia, where its beautiful leaves and fragrant flowers make it a prized plant.
Religious and cultural practices
Some countries have used the toon tree for religious and cultural things, like making incense or carving statues and other things to decorate with.
Timber industry
The toon tree is an important species in the global wood business. High-quality lumber is grown on large plantations of toon trees in many countries.
Essential oil
Steam distilling leaves makes an essential oil that is used in massage and to add a scent to soaps and other personal care items.
Insecticide
Scientists have found that extracts from the Toon tree kill insects and can be used as a natural alternative to chemical poisons.
Biofuel
Wood has been looked at as a possible source of energy because it has a lot of cellulose and grows quickly.
Soil improvement
Leaves are full of nutrients and can be used as a natural fertilizer or to improve the structure of the soil.
Agroforestry
Toon tree can be a part of agroforestry systems because it can provide shade, improve soil fertility, and be used to make wood and other goods.
Traditional crafts
Wood can be carved and shaped into bowls, boxes, and figures, among other things.
Other Uses
- Wood is often used for furniture, floors, walls, and musical instruments.
- It is highly prized for its smooth, even texture, attractive color, and resistance to rot, decay, and termite attack.
- Wood is used to make furniture, floors, walls, musical instruments, and things that go outside, like cladding, decking, and fences.
- The toon tree grows quickly and can be fully grown in as little as 15 years.
- It is often placed as an ornamental tree in parks and gardens because its leaves and flowers smell nice.
- It is an important species in agroforestry systems because it can provide shade, make the land more fertile, and be used to make wood and other things.
- The leaves and young shoots of the Toon tree are used as vegetables in many dishes, especially in Asia.
- It has been used in traditional medicine, religious and cultural practices, and as a source of food and wood products.
- The flowers have a strong, sweet scent that is often used in perfumes and cosmetics.
- The wood of the Toon tree has a pleasant, woodsy smell that is prized for making furniture and other wood products.
- The bark of the tree has a strong, earthy smell that is often used in traditional medicine and as a natural bug repellent.
- Wood is useful as firewood, charcoal, logs, windbreaks, furniture, and as a place to grow shitake mushrooms.
- In India, leaves are often used to feed animals and as mulch.
- Some products of bark can keep insects away.
- The bark is used to tan leather and make string.
- It is often grown as a street tree in India and as a decorative and path tree in many tropical parts of Africa and Asia.
- It is used to make pencils in Thailand.
- Wood is also used to make carvings, tea chests, oil barrels, and musical instruments.
- In South-East Asia, the wood is considered valuable and is used to build houses and ships, make joinery, high-quality furniture, musical instruments, tea chests, carvings, toys and novelties, plywood, veneer, and pencils.
- Flowers make a yellow or red dye that has been used to color silk in warm Asia.
- Bark of trees can be used to tan leather and has traditionally been used to make twine and string bags.
- Honey bees get sap from flowering trees.
- Fruit can be used to make oil that smells good.
References:
https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/10.1079/cabicompendium.54175
https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Toona_ciliata_(PROTA)
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=29029#null
http://www.hear.org/pier/species/toona_ciliata.htm
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/TOOCI
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-2515118
http://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Toon%20Tree.html
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/31866
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Toona_ciliata
https://www.efloraofgandhinagar.in/tree/toona-ciliata
https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Toona_ciliata_(PROSEA)
https://www.fs.usda.gov/nsl/Wpsm/Toona.pdf
https://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Toona+ciliata
http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=2&taxon_id=220013595
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Toona+ciliata
https://apps.worldagroforestry.org/treedb/AFTPDFS/Toona_ciliata.PDF
https://plants.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=TOCI