Genus name comes from the Greek words ornis meaning a bird and gala meaning milk for the white flowers. Specific epithet refers to the flowers being in an umbel. The common name of the plant, ‘Star of Bethlehem’, is based on its star-shaped flowers and referred to the Star of Bethlehem that appeared in the biblical account of Jesus birth. It is recorded that the Swedes have eaten this bulb in times of shortage. Round the main small bulb there are usually a number of bulbules about the size of sago grains, but only the parent bulb is enclosed in a yellowish outer skin. Some states regard them as noxious weeds & wetlands invaders. We have patches of them in our gardens that we never planted, but which we’ve made no attempt to eradicate, as they’re really quite lovely. This species is listed as a Class C Noxious Weed in the State of Alabama.
Plant description
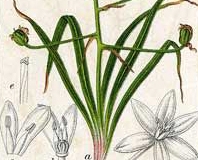
Star of Bethlehem plant is a short, herbaceous, perennial bulbous flowering plant that grows about 0.2 to 0.3 m tall. The plant is found growing in roadsides, open forests, cemetery prairies, grassy meadows, sunny or semi-shaded banks of rivers and streams and drainage ditches, and miscellaneous waste areas. The plant thrives in moderately fertile, moist and well-drained soil. The plant has white bulb which is 15–25 millimeters (0.6–1.0 in) long and 18–32 mm (0.7–1.3 in) in diameter with fibrous roots at the base and increase to form large clumps. Each bulb can produce up to 7 secondary bulbs. The coat of the bulb is membranous. Flowering stem is leafless, cylindrical, erect and 100-300 mm tall.
Leaves
Plant has 6–10 leaves that are narrow and linear, measuring 10-30 cm (4-12 in.) long and 2-5 mm (0.1-0.2 in.) wide. The leaves form a tuft from which a scape emerges. It has a waxy surface and is dark green in color with a white mid-rib. They are hollow and tend to arch over as they grow longer.
Flower
The white, star-shaped flowers are borne on a scape that can grow up to 30 cm (1 ft.) in height, but is usually shorter. The umbel-like raceme consists of 3-10 flowers. Each flower has 6 petals and measures 1.5-2 cm (0.5-0.75 in.) in diameter. The outside of the flower is green with white margins. The flowers appear on the plant from April to May. The blooming period occurs during the late spring and lasts about 2 weeks. There is a pleasant floral scent. The flowers open during the morning and usually close by noon.
Fruit
Each fertile flower is replaced by a 3-celled seed capsule that is sub-globose in shape about 8–18 mm long. Each locule contains many black seeds. Seeds are black, oval to spherical, 2 mm diameter. Surface is rough and hairless.
- Plant’s extract is used as sedative, for the treatment of nervous breakdown, suicidal behavior in people with depression or sadness and intestinal disorders (gases).
- Homeopathic remedy is made from the bulbs.
- It is useful in the treatment of certain forms of cancer.
- It is also one of the five ingredients in the Rescue remedy.
- It is applied externally to the skin against ulcers and blisters.
- In folk medicine it is used to improve cardiac function and treat pulmonary edema and fluid retention, especially against leg swelling.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DaEnAoAecC4
Precautions
- Skin contact with the bulb can cause dermatitis in sensitive people.
- The bulb consists of alkaloids and is poisonous.
- Bulb is poisonous to grazing animals.
- Plant is known to be poisonous causing nausea, vomiting, stomach and intestinal irritation, burning, dilated pupils, tremors, seizures, shortness of breath, swelling of the lips, tongue and throat, abnormal heart rate, cardiac arrest, and death.
- The whole plant is poisonous and its consumption may cause skin irritation, nausea, salivation, vomiting, diarrhea, dyspnea (shortness of breath), and pain, swelling of lips, tongue and throat.
Common star of Bethlehem plant Management
Identification and awareness of Star of Bethlehem, together with good farm hygiene, are important for handling the weed due to the limited control options available.
As spread is mostly by means of machinery, farm hygiene is imperative to prevent the spread of Star of Bethlehem. Thoroughly wash machinery when moving from areas of known infestations and avoid the areas altogether where possible, e.g. sow around infestations.
Physical removal of bulbs is the most effective form of eradication however it is only practical for small infestations. Once the infested area becomes too large for physical removal, control is very difficult. Star of Bethlehem is near impossible to control in winter crops and pastures and severe infestations are likely to need a complete crop or pasture renovation.
There are no herbicides listed for the control of Star of Bethlehem in dry land cropping systems in New South Wales. Some are registered for use in Sugar Cane in New South Wales and some are registered in Queensland for other situations however the efficacy is variable.
A small amount of research (mostly in America) has been carried out to evaluate herbicides for the control of Star of Bethlehem. The results indicate that Gramoxone® is the only herbicide to provide effective control the season following herbicide application.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=42754#null
https://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/go/495/
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Ornithogalum+umbellatum
http://www.missouribotanicalgarden.org/PlantFinder/PlantFinderDetails.aspx?kempercode=f298
http://www.floracatalana.net/ornithogalum-umbellatum-l-
https://botanical.com/botanical/mgmh/s/starbe89.html
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=ORUM
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-283298
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/OTGUM
https://nutrawiki.org/ornithogalum-umbellatum/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ornithogalum_umbellatum
http://www.docs.dcnr.pa.gov/cs/groups/public/documents/document/dcnr_010226.pdf
Comments
| Star of Bethlehem plant Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Star of Bethlehem plant |
| Scientific Name: | Ornithogalum umbellatum |
| Origin | North-western Africa, Europe and western Asia |
| Shapes | Capsules are sub globose in shape about 8–18 mm and 3-sided |
| Health benefits | Beneficial for nervous breakdown, depression, intestinal disorders, ulcers, blisters, pulmonary edema, fluid retention and certain forms of cancer |
| Name | Star of Bethlehem plant |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Ornithogalum umbellatum |
| Native | North-western Africa (i.e. Algeria and Morocco), Europe (i.e. Austria, Belgium, Hungary, the Netherlands, Switzerland, Ukraine, Albania, Bulgaria, Greece, Italy, Romania, Yugoslavia, France, Portugal and Spain) and western Asia (i.e. Cyprus and Turkey) |
| Common Names | Bird’s milk, chincherinchee, common star of Bethlehem, dove’s dung, nap at noon, nap-at-noon, pigeon dung, sleepy Dick, sleepy-Dick, sleepydick, snowdrop, snowdrops, star flower, star of Bethlehem, starflower, star-of-Bethlehem, summer snowflake, summer snow flake, ten o’clock lady |
| Name in Other Languages | Albanian: Lulë dalldyshe, minikelä ombrelore, munikël Arabic: Sâsal, Zîtah, صاصل خيمي Basque: Oiloesne Bulgarian: Sennikov garvanski luk (сенников гарвански лук), chadŭrest garvanski luk (чадърест гарвански лук) Catalan: All de bruixa, Estrelleta de monja, Llet d’ocell, Llet de gallina, Llet de pardal, Ornitògal Chinese: San hua hu yan wan nian qing Croatian: Stitasto ptičje mlijeko Czech: Snědek chocholičnatý, snědek rozkladitý Danish: Kost-fuglemælk Dutch: Gewone vogelmelk, Ster van bethlehem English: Common star of Bethlehem, Sleepy-dick, Sleepydick, Star of Bethlehem, Garden star-of-Bethlehem, Nap-at-noon, Pyrenees star-of-Bethlehem, Summer snowflake, Gewone vogelmelk, Morgonstjrna, eleven o’clock lady, grass lily, dove’s dung, Jack-go-to-bed-at-noon, ten o’clock lady Estonian: Sarik-linnupiim Finnish: Sarjatähdikki, Beetlehemintähti French: Dame de onze heures, Ornithogale en ombelle, Dame donze heures, Dame de 11 heures, Ornithogale à ombelle, belle d’onze heures, étoile blanche German: Dolden-Milchstern, Doldiger milchstern, Vogelmilch, Stern von Bethlehem, Gewöhnlicher Dolden-Milchstern, Stern von Bethlehem, schmalblättriger Milchstern Greek: Ornithógalo (ορνιθόγαλο) Hebrew: Netz-chalav mefussak, נֵץ-חָלָב מְפֻשָּׂק, ernyős madártej Hungarian: Ernyős sárma Italian: Bella di undici ore, Dama d’ undici ore, Fior d’ undici ore, Latte d’uccello, Latte di gallina, cipollone bianco, latte di gallina comune Japanese: Orunitogarumu unberatumu, Ooamana (ōamana) オオアマナ(大甘菜), ôamana (オオアマナ) Norwegian: Fuglestjerne Occitan: Bèla de jorn, Crotz de malta, Penitent blanc, Penitènt-blanc Persian: ارنیتگالوم آمبلاتوم Polish: Śniedek baldaszkowaty Portuguese: Estrela-de-Belém, leite-de-galinha Romanian: Balusca Russian: Ptitsemlechnik zontichnyi (птицемлечник зонтичный) Serbian: štitasti vranji luk (штитасти вранји лук) Slovak: Bledavka chocholíkatá, bledavka okolíkatá Slovene: Kobulasto ptičje mleko Sorbian: Łučny hwěžkan Spanish: Leche de gallina, Estrella de Belén, Leche de ave, Leche de pájaro, ajo de lobo, culebrilla ajera Swedish: Morgonstjärnor, Morgonstjärna, Stjärnlök, Sarjatähdikki, spärrmorgonstjärna Turkish: Sasal, Sunbala Mariam Ukrainian: Рястка зонтична |
| Plant Growth Habit | Short, herbaceous, perennial bulbous flowering plant |
| Growing Climates | Roadsides, open forests, cemetery prairies, grassy meadows, sunny or semi-shaded banks of rivers and streams and drainage ditches, and miscellaneous waste areas |
| Soil | Thrives in moderately fertile, moist and well-drained soil |
| Plant Size | 0.2 to 0.3 m tall |
| Bulb | White and 15–25 millimeters (0.6–1.0 in) long and 18–32 mm (0.7–1.3 in) in diameter with fibrous roots at the base and increase to form large clumps. Each bulb can produce up to 7 auxiliary bulbs |
| Flower Stem | Leafless, cylindrical, erect, 100-300 mm tall |
| Leaf | 6–10 leaves are narrow and linear, measuring 10-30 cm (4-12 in.) long and 2-5 mm (0.1-0.2 in.) wide. The leaves form a tuft from which a scape emerges. |
| Flowering season | April to May |
| Flower | Each flower has 6 petals and measures 1.5-2 cm (0.5-0.75 in.) in diameter. The outside of the flower is green with white margins. |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Capsules are sub globose in shape about 8–18 mm and 3-sided. Each locule contains many black seeds |
| Seed | Black, oval to spherical, 2 mm diameter. Surface rough and hairless |
| Propagation | Seeds, bulbils and bulbs |
| Plant Parts Used | Flowers, leaves |
| Season | June to July |
| Culinary Uses |
|