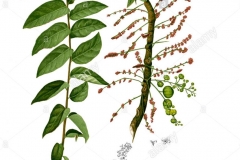
Genus name comes from the Greek words phyllon meaning leaf, and anthos meaning flower, as in some species the flowers are produced on the edges of a leaf-like branch. The specific epithet acidus means acidic, in reference to the sharp acidity of the fruits. The common name gooseberry refers to the acidity of the fruits, which is similar to European gooseberry (Ribes uva-crispa). Tree is not only cultivated for its ornamental value, but also for food and medicinal purposes. Although it produces fruit throughout the year, it is mostly collected in January except in South India.
Different parts of the plant are used for food. In Bangladesh and Indonesia, the cooked leaves are eaten. Fruit is eaten fresh, and is occasionally used as flavoring for other dishes in Indonesia. It is candied in sugar or pickled in salt, used in chutney, relish or preserves. In Philippines, it is used to make vinegar as well as eaten raw, soaked in salt or vinegar-salt solution and sold along the roadside. Similarly different parts of the plants are used medicinally. Peppered leaves are used to make a poultice to treat sciatica, lumbago and rheumatism, while the seeds are used as a cathartic and the root, if prepared with care, as a purgative. The syrup is used to medicate the stomach, and in India the fruit is eaten as a blood-enhancer for the liver.
Star Gooseberry Facts
| Star gooseberry Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Star gooseberry |
| Scientific Name: | Phyllanthus acidus |
| Origin | Coastal region of north-eastern Brazil, and has been frequently wrongly ascribed to Madagascar, India or Polynesia |
| Colors | Whitish green and hard when young turning to pale gold as they mature |
| Shapes | Drupaceous, oblate fruit, 1.5–2.5 cm diameter, shallowly 6- or 8-lobed borne on 2–4 mm long pedicels |
| Taste | Sour and tart |
| Health benefits | Constipation, Healthy Skin, Good for Digestion, Cure Cancer, Treat Asthma and Healthy Bones, rheumatism, headache and bronchial catarrh |
| Name | Star gooseberry |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Phyllanthus acidus |
| Native | Coastal region of north-eastern Brazil, and has been frequently wrongly ascribed to Madagascar, India or Polynesia. It is now naturalized and cultivated pan-tropically in India, Thailand, Myanmar, Indonesia, South Vietnam, Laos, Peninsular Malaysia, Polynesia and all the larger islands of the West Indies |
| Common Names | Indian-gooseberry, Malay-gooseberry, Otaheite-gooseberry, Gooseberry-tree, Tahitian-gooseberry, Star-gooseberry, Tahitian gooseberry tree, Gooseberry, Otaheite Gooseberry-tree, Otaheite gooseberry, Cela usiri, Cerejeira-do-Taiti, Grosellero, Jumbilin, Sour gooseberry, Ceremmè, Cermen, Goose Berry, Country gooseberry, West India gooseberry, Starberry, arbari |
| Name in Other Languages | Arabic: Milh himdiun (أملج حمضي) Assamese: Holphali, Pora Amlokhi / Pom lokhi / Holpholi, Pom-lokhi, Pora-amlokhi, Leyoir, Pomlokhi Bengali: Hari-phal (হরি ফল), Noyal, harphal, orboroi, noyar, Loboni, Hariful, Arabara’i (অরবরই) Brazil : Groselha Bulgarian: Kisel filantus (кисел филантус) Burmese: Thinbozihpyoo, Mak-Hkam sang paw Cambodia: Kântûët, kântouot srôk Central Khmer: Kantuot (កន្ទួត) Chamorro: Iba Chinese: E Mei Shu, Yuènán yè xià zhū (越南葉下珠), Xī yìndù cù lì (西印度醋栗) Costa Rica : Grosella Cuba : Cerezo Occidental, Grosella Divehi: Gōnbili (ގޯނބިލި) Dutch: Kleine Birambi, Ronde Birambi, Grosella El Salvador : Ciruela Corteña, Guinda, Pimienta English: Country gooseberry, Indian gooseberry, Malay gooseberry, Otaheite gooseberry, Star gooseberry, Tahitian gooseberry, West India gooseberry, Wild plum, Tahitian gooseberry tree, Gooseberry-tree, Goose Berry Filipino: Karmay, bangkiling, iba Finnish: Karvaslaipikka French : Groseillier des Antilles, Surette, Cerisier de Tahiti, Cherimbillier, Pomme surelle, Surelle, Surette, phyllanthe sour, Grosella, Cerisier De Tahiti, Surette De La Martinique, Groseillier Des Antilles, cherimelier, girembellier German: Sternstachelbeerbaum Ghana : Dunyan Greek: Tahitian Frankostáfylo (Φραγκοστάφυλο) Guatemala : Grosella Guinea–Bissau: Azedinha Gujarati: Amala (આમળા), Ghati aavla Hindi: Chalmeri, Chillimilli (चिल्लीमिल्ली), Chota aonla (छोटा आंवला ), Harparauri, Harphanevadi, Harpharauri (हरफरौरी), Harpharevadi, Harpharewri (हरफारेवड़ी ), Nari, lavali, Harparauri, Harphanevadi Indonesia: Ceremoi, ceremai, cereme, cerme, caramele , Carameng, Karsinta, Kemlaka, Kemloko Jamaica: Cheramina, Jimbling, Short Jimbelin Javanese: Cerme Kampuchea : Kântûet, Kântouot Srôk, Sloek Morom Kannada: Kirunelli (ಕಿರುನೆಲ್ಲಿ ), Raayaranelli (ರಾಯರನೆಲ್ಲಿ), Karinelli Khmer: Kântouot srôk Konkani: Rajamvali Laotian: Mak-nhom, Nhom ban, nhôm baanz Madurese: Careme Malay: Balangka, Carameng, Ceremai, Ceremoi, Cerme, Cermen, Chermai, Karsinta, Kemlaka, Kemloko, Malaka , Pokok Cermai Malayalam: Arinellikka, Rāyaranelli (ചതുരനെല്ലിക്ക) Caturanellikka, puḷinelli (പുളിനെല്ലി) Malaysia: Chermai, chermala, kemangur, Cermai, Ceremai, Cermela, Camincamin Manipuri: Gihori (গিহোৰী) Marathi: Harapararevadi (हरपररेवडी), Harparrevdi, Rayamvala (रायआंवळा), Roi-avala, Harpharori (हरफ़रौरी) Mexico : Manzana Estrella Mizo: Kawlsunhlu Nepali: Harii phala, Kaathe amalaa, Paate amalaa, kaansee amala (काँसी अमला) Nicaragua : Grosella Others: Catataram, Chillimilli, Indian Gooseberry, Wild Plum, Chota Aonla, Puttattiri, Malay Gooseberry, Raayaranelli, Harapararevadi, Otaheite Gooseberry, Rayamvala,Hari-phal, Pandu, Skandhaphala, Star Gooseberry, Aranelli, Veku-pattiri, Tahitian Gooseberry, Usiri, Caturanellikka, Ratsa-yusirika, West India Gooseberry, Tavittu-p-palam, Tanuttuvacai, Kirunelli, Haripaveri, Pora amlokhi Persian: انگور تاهیتی Philippines: Layoan, Bangkiling, Poras, Kagindi, Bagbagútut Karmay, Karmai, Karamai, Bagbagutut, Iba, Bangkiling, Karmai Polish: Liściokwiat kwaśny Portuguese: Groselha, Cerejeira-do-Taiti Puerto Rico: Cereza Amarilla, Cerezo De La Tierra, Cerezo Comun Russian: Antil’skiy kryzhovnik (Антильский крыжовник) Samoan: Vine Sanskrit: Ghana, Haripaveri (हरिपवेरी ), Komalavalkala, Lavali, Laveni, Pandu (पाण्डु), Skandhaphala (स्कन्धफल), Skandhaphara Senegal : Azedina Spanish: Cereza amarilla, Cerezo agrio, Cerezo comun, Cerezo de la tierra, Cerezo occidental, Ciruela corteña, Guinda, Grosella, Manzana estrella, Pimienta , Grosellero Sri Lanka: Rata Nelli, Nelli Bilin Sudanese: Careme, Cerme, Cereme Swedish: Tahitikrusbär Tagalog: Iba, Bangkiling, Karmay Tahitian: Mue, Surette Tamil: Aranelli, Arunelli (அருநெல்லி), Catataram (சடாதரம்), Puttattiri (புத்தாத்திரி), Tanuttuvacai (தனுத்துவசை), Tavittuppalam (தவிட்டுப்பழம்), Vekupattiri (வெகுபத்திரி), arainellikai Telugu: Ratsa-yusirika (రాచయుసిరిక), Usiri (ఉసిరి), Rāca usiri (రాచ ఉసిరి) Thai: Ma yom (มะยม) Urdu: هرپهروري Harpharauri Venezuela : Cerezo Agrio Vietnamese: Chùm ruột, Tầm ruột Wolof: Seriis |
| Plant Growth Habit | Small, monoecious, deciduous, glabrous tree or shrub |
| Growing Climates | Gardens, open disturbed areas, quarries and in home gardens |
| Soil | Gardens, open disturbed areas, quarries and in home gardens |
| Plant Size | 2 to 9 m in height |
| Bark | Bark rough, grey, with prominent lenticels; cataphylls not persistent, blackish-brown, their stipules triangular-ovate |
| Leaf | Compound, alternate leaves that are ovate or lanceolate in form, 14-25 inches long, with short petioles and pointed ends. Leaflets are 2-3.5 inches long and 1-1.5 inches wide, arranged alternately along the rachis |
| Flowering season | April-May |
| Flower | Flowers are small and pinkish and appear in clusters in 5 to 12.5 cm long panicles at leafless parts of the main branches, at the upper part of the tree |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Drupaceous, oblate fruit, 1.5–2.5 cm diameter, shallowly 6- or 8-lobed, borne on 2–4 mm long pedicels |
| Fruit Color | Whitish green and hard when young turning to pale gold as they mature |
| Flesh | Firm, thin, sour |
| Seed | 6–8 smooth, globose, 5–8 mm diameter seeds |
| Propagation | By seed but may also be multiplied by budding, greenwood cuttings, or air-layers |
| Taste | Sour and tart |
| Plant Parts Used | Fruits, leaves, roots |
| Season | June-August |
| Health Benefits |
|
Plant Description
Star Gooseberry is a small, monoecious, deciduous, glabrous tree or shrub that normally grows about 2 to 9 m (6½ to 30 ft.) tall. The tree’s dense and bushy crown is composed of thickish, tough main branches, at the ends of which are clusters of deciduous, greenish, 15-to-30-cm long branchlets. The plant is found growing in gardens, open disturbed areas, quarries and in home gardens. Plant grows on a wide range of soils but prefers rather moist sites.
Leaves
The branchlets bear compound, alternate leaves that are ovate or lanceolate in form, 14-25 inches long, with short petioles and pointed ends. Leaflets are 2-3.5 inches long and 1-1.5 inches wide, arranged alternately along the rachis, ovate or obliquely ovate, acute or somewhat acuminate, base rounded or somewhat wedge-shaped. They are green and smooth on the upper side and blue-green on the underside. In general, the Otaheite gooseberry tree very much looks like the bilimbi tree. Both the leaves and branchlets are deciduous.
Flower
The flowers can be male, female or hermaphrodite. They are small and pinkish and appear in clusters in 5-to-12.5-cm long panicles. Flowers are formed at leafless parts of the main branches, at the upper part of the tree. Flowers are small, axillary in fascicles, with 2–6 staminate flowers in proximal axils. Pistillate flowers are cauliflorous on old branchlets, rarely in distal axils. Staminate flowers are 4-merous with free filaments and anthers that dehisce vertically. Pistillate flowers are 4-merous, borne on a stout pedicel, with deeply lobed or split disk, connate, deeply bi fi d styles, staminodes and a superior, glabrous, 6–8 lobed ovary. Flowering normally takes place in between April and May.
Fruit
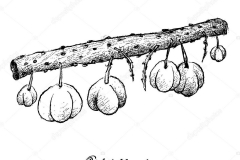
Fertile flowers are followed by drupaceous, oblate fruit, 1.5–2.5 cm diameter, shallowly 6- or 8-lobed, greenish–yellow to pale yellow, waxy and glossy and borne on 2–4 mm long pedicels. The flesh is firm, thin, sour enclosing a hard, bony, grooved stone containing 6–8 smooth, globose, 5–8 mm diameter seeds. Fruits develop in dense clusters along the old branchlets.
The tree usually flowers and produces fruit twice a year. Fruits appear simultaneously with the flowers. So, the tree usually has fruits hanging from it, at any time of the year. The fruit is used chiefly for pickling and for the preparation of preserves. It makes an excellent jam. Star Gooseberry is native of Malay Islands and Madagascar and frequently grown in India for its acid fruit.
Health benefits of Star Gooseberry
Listed below are some of the popular health benefits of using star gooseberry
1. Treat Constipation
Star gooseberry is considered beneficial in treating constipation. Because it consists of lots of Vitamin C, Star gooseberry fruit has the benefit of digestion and overcome constipation. Just like other vitamin C fruit, this fruit is suitable for intestinal cleansing as well.
2. Healthy Skin
Vitamin C contained in fruit provides benefits to our skin. The skin will be bright, clean, and soft. Vitamin C plays an important role in skin health affairs. Therefore try Star gooseberry consumption in any form because vitamin C is high.
3. Good for Digestion
Star gooseberry fruit becomes the fruit that can help slimming body. Star gooseberry has a sour taste and can also make the stomach become slimmer when consumed frequently. This is because the digestion is supported and the appetite is reduced somewhat due to the taste of acid on the tongue. Keep in mind this drug works very strongly, therefore consume it efficiently only occasionally.
4. Cure Cancer
You can use young Star gooseberry leaves as much as 1/4 handheld mixed with leaf 1/3 handheld leaf, ladle upas 1/2 finger, Chinese gadung 1/2 finger, sugar enau 3 fingers, washed and cut into pieces. Boil all ingredients using 3 cups water until the remaining 3/4 parts only. Chill and strain and drink three times a day.
5. Treating Asthma
To cure your asthma you can take about 6 seeds of Star gooseberry, mixed with red onion 2 grains, kara root 1/4 handheld and 8 grains of litchi. All materials are washed and then ground. Boil all ingredients and let it boil from 2 cups water until remaining 1 1/2 cups. Then drink boiled water Star gooseberry leaves earlier.
6. Healthy Bones
Star gooseberry fruit can nourish the bones. Calcium and iron contained in this fruit can help nourish the bones to keep strong and not porous. Bones will be stronger.
Traditional uses and benefits of Star Gooseberry
- Acidic fruits are considered to have medicinal properties and are consumed as blood-enhancer for liver.
- Syrup is also used in the treatment of stomach ailments.
- Peppered leaves are used to make a poultice for treatment of rheumatism.
- Latex is recognized with emetic and purgative activity.
- Bark is heated with coconut oil and spread on eruptions on feet and hands I Indonesia.
- An infusion of the root is taken to alleviate asthma in Java.
- Roots are used in the treatment of psoriasis of the feet in Bornea.
- Although the roots are weakly poisonous, they used to be boiled and the vapor inhaled to relieve cough and headache in Malaysia.
- Leaf decoctions are applied to urticaria, and a decoction of the bark is used to treat bronchial catarrh in Philippines.
- Fruits are taken as a liver tonic to enrich the blood in India.
- Juice of the root bark is reported to have been used in criminal poisonings.
- It is used in the treatment of psoriasis, sciatica, rheumatism, constipation, renal calculus, diabetes, asthma, gonorrhea, amnesia and piles.
- The syrup is prescribed as a stomachic; and the seeds are cathartic.
- Leaves, with added pepper, are poultice on sciatica, lumbago or rheumatism.
- Decoction of the leaves is given as a sudorific.
- Because of the mucilaginous nature of the leaves, they are taken as a demulcent in cases of gonorrhea.
- Root is severely purgative and regarded as toxic in Malaya but is boiled and the steam inhaled to relieve coughs and headache.
- Root infusion is taken in very small doses to alleviate asthma.
- Externally, the root is used to treat psoriasis of the soles of feet.
- Juice of the root bark, which consists of saponin, gallic acid, tannin and a crystalline substance which may be lupeol, has been used in criminal poisoning.
- Bark yields a decoction, which is used in bronchial catarrh.
- Root is drastically purgative and regarded as toxic in Malaya but is boiled and the steam inhaled to relieve coughs and headache.
- In Borneo, leaves are used, with pepper, for poulticing for lumbago, or sciatica, and the root is used externally to treat psoriasis of the soles of feet.
- Extract from the root to cure skin diseases especially relief from itching in Thailand.
- Leaves are used as one of the ingredients in Thai medicine to control fever.
Culinary Uses
- Mature fruits are acidic, eaten fresh or as pickles.
- Fruit flesh is added to many dishes in Indonesia as a flavoring.
- Fruit juice is used to make cold drinks in Philippines.
- Ripe and unripe fruits are served as a relish, syrup or sweet preserve in Malaysia.
- Fruits are also combined with other fruits in making chutney or jam, because of their setting properties.
- Young leaves are cooked as a vegetable in Indonesia, Thailand and India.
- Fruit juice added with sugar is used as cold drinks.
- Fruits are also made used to prepare chutney, rely or preserves along with other fruits.
- Flesh must be sliced from the stone, or the fruits must be cooked and then pressed through a sieve to separate the stones.
- Sliced raw flesh can be covered with sugar and let stand in the refrigerator for a day.
- Bahamian cooks soak the whole fruits in salty water overnight to reduce the acidity, then rinse, boil once or twice, discarding the water, then boil with equal amount of sugar until thick, and put up in sterilized jars without removing seeds.
- Ripe or unripe Otaheite gooseberry is cooked and served as a relish, or made into a thick syrup or sweet preserve in Malaya.
- Fruits are candied, or pickled in salt.
- They are used to make vinegar in Philippines.
- Fruits are excellent for processing into pickles and sweetened dried fruits.
- In Indonesia, the sour fruits are used as a condiment in cooking to flavor dishes and served as a substitute for Assam and used as an ingredient in sambal and sayur or used in rojak mixture.
Star gooseberry Pickle
Ingredients
- 2 cups star gooseberries
- 1/2 cup water
- 3 tbsp. gingerly oil
- 3 tsp. red chili powder
- 1 tsp. turmeric powder
- 2 tsp. fenugreek powder
- 1/2 tsp. asafetida
- 1 tbsp. chopped garlics
- 1 tbsp. chopped ginger
- 1 tsp. mustard
- 4 red chilies – cut into pieces
- 4 green chilies – chopped
- 1 bunch curry leaves
- Salt as required
Directions
- Wash and clean the star gooseberries, and drain the water.
- Keep the star gooseberries in a vessel, add salt and 1/2 cup water, and boil it for 15 minutes in medium flame.
- Remove from stove and drain the water, preferably through a strainer.
- Keep a pan on stove and add 1 tbsp. of gingerly oil, and sauté the gooseberries for about 5-7 minutes, then keep aside.
- Keep another pan on stove; add the remaining 2 tbsp. oil.
- Add the mustard seeds. After they splutter add ginger, garlics, green chilies, red chilies, curry leaves etc.
- When they mix well, add fenugreek powder, turmeric powder, chili powder, and asafetida. Mix well.
- Add the star gooseberries and mix well for about 5 minutes.
- Now your pickle is ready.
Other Facts
- Wood is light-brown, fi ne-grained, attractive, fairly hard, strong, tough, and durable if seasoned and used for utensils and other small objects.
- Bark has limited use in India as a tanning agent.
- Wood is used for fuel.
- Fruits mature in 90-100 days.
- It is used for utensils and other small objects.
Precautions
- Juice of the root bark is weakly poisonous.
- It has been used in criminal poisoning.
- It was reported to produce headaches, sleepiness, and deaths accompanied by severe abdominal pains.
- Root paste is applied externally to prevent itching and to treat general skin ailments.
- Boil the leaves and use this water for a bath to take care of measles and chicken pox.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=28366#null
http://www.hear.org/pier/species/phyllanthus_acidus.htm
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-153279
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/266545
https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Phyllanthus_acidus_(PROSEA)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phyllanthus_acidus
http://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Star%20Gooseberry.html
https://hort.purdue.edu/newcrop/morton/otaheite_gooseberry.html
http://apps.worldagroforestry.org/treedb/AFTPDFS/Phyllanthus_acidus.PDF
https://plants.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=PHAC3
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/PYLAC
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/46048