Few of the popular common names of the plant are Spotted bur-clover, Spotted medic, Spotted medick, Spotted-leaf medic, Burclover, Spotted Bur Medick, Spotted Burclover, Southern burr clover, Spotted burrclover, Spotted burr-clover, Calvary Clover and Cogweed. The genus name Medicago is derived from the Greek word medice which is the name of Alfalfa. Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) was believed to have been brought to Greece from a city called Medea in the North-African country of Algeria. The species epithet arabica means “Arabian, of Arabia” referring to the plants origin. The common name spotted medick describes the plant’s physical appearance.
Spotted Medick Facts
| Spotted medick Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Spotted medick |
| Scientific Name: | Medicago arabica |
| Origin | Mediterranean region and introduced in North and South America and Australia |
| Colors | Green when young turning to brown as they mature |
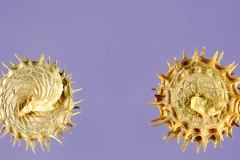
| Shapes | Barrel-shaped pod with 3 to 5 spirals, round, 4-8 mm in diameter, the outer margins narrowly keeled, spineless, or with two rows of divergent prickles up to 2.5-3.5 mm long, somewhat curved to nearly straight with short hook at tip |
| Name | Spotted medick |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Medicago arabica |
| Native | Mediterranean region and introduced in North and South America and Australia |
| Common Names | Spotted bur-clover, Spotted medic, Spotted medick, Spotted-leaf medic, Burclover, Spotted Bur Medick, Spotted Burclover, Southern burr clover, Spotted burrclover, Spotted burr-clover, Calvary Clover, Cogweed |
| Name in Other Languages | Albanian: Jonxha me njolla, jonxhë Arabic: Qisas earabia (فصة عربية) Armenian: Arrvuyt arabakan (Առվույտ արաբական) Bulgarian: Arabska lyutserna (арабска люцерна) Catalan: Herba de la taca Chinese: He ban mu xu (褐斑苜蓿) Croatian: Arapska vija Czech: Tolice arabská Danish: Plettet Sneglebælg, Plet-sneglebælg Dutch: Gevlekte, Gevleker rupsklaver. English: Spotted bur-clover, Spotted medic, Burclover, Spotted Bur Medick, Spotted Medick, Southern burr clover, Spotted-leaf medic, Calvary clover Esperanto: Arabia medikago Estonian: Araabia lutsern Finnish: Araapian mailanen, Laikkumailanen. French: Luzerne d’ Arabie, Luzerne tachetée, Luzerne Tachee, Luzerne maculée Georgian: Ionja (იონჯა) German: Arabischer Schneckenklee, Gefleckter, arabische Luzerne, gefleckter Schneckenklee, Luzerne, Arabische Hungarian: Arab lucerna Italian: Medica maculate, erba-medica araba, Japanese: Montsuki umagoyashi, Montsukiumagoyashi (モンツキウマゴヤシ) Latvian: Ar Netherlands: Rupsklaver, gevlekte Norwegian: Flekksnigleskolm, Flekksneglebelg Occitan: True, treulé Persian: یونجه عربی Polish: Lucerna Arabska Portuguese: Herba-medica, Luzerna-arábica, Alfafa-de-folhas-manchadas, erva-médica, luzerna-da-arábia Russian: Liutserna araviiskaia, Lyutzerna Araviiskaya, lyutserna arabskaya (люцерна арабская), lyutserna araviyskaya (люцерна аравийская) Serbian: Vija (вија), pegava vija (пегава вија) Scottish Gaelic: Meidic bhreac Slovak: Tolica arabská Slovenian: Arabska meteljka Spanish: Carretón, Herba de la taca, Mielga pintada, Trébol carretilla, Trébol de carretilla, Trébol manchado, trébol de manchado, alfalfa Silvestre, medicago de Arabia, caretilla, hualputra, Carretón manchado Swedish: Fläcklusern Turkish: Benli yonca Ukrainian: Lyutserna arabsʹka (люцерна арабська) Upper Sorbian: Arabiska šlinčina Vietnamese: Linh lăng Ả Rập Welsh: Llys y Meheryn, Maglys Amrywedd, Maglys Brith, Meillion Calfari, Meillion Gragenog |
| Plant Growth Habit | Native, prostrate or sprawling herb |
| Growing Climates | Moist stream banks, grasslands, places, thin pasture, lawns, meadows and fields and disturbed areas including waste lots, roadsides |
| Soil | Light, sandy and gravelly soils, particularly near the coast |
| Plant Size | 2–6 cm |
| Stem | Decumbent or spreading, longitudinally ridged, sparsely hairy, hairs simple and multicellular-glandular |
| Leaf | Leaves alternating along the stems are pinnately compound, with 3 leaflets each 0.4-4 cm long and 5–45 mm wide. Margins are toothed towards the tips. Upper surface is hairless, usually with a dark patch near the middle, lower surface is sparsely appressed-hairy |
| Flowering season | April and August |
| Flower | Inflorescence of 1 to 5 pea-like flowers is in a reduced, axillary raceme on a stalk 1-3 cm long on fairly short peduncles arising from the leaf axils. The stalks are shorter than the leaves. Corollas are pea-like, yellow, about 5 mm long, the banner erect, much longer than the wings and keel |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Barrel-shaped pod with 3 to 5 spirals, round, 4-8 mm in diameter, the outer margins narrowly keeled, spineless, or with two rows of divergent prickles up to 2.5-3.5 mm long, somewhat curved to nearly straight with short hook at tip |
| Fruit Color | Green when young turning to brown as they mature |
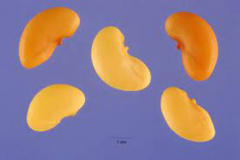
| Seed | Kidney-shaped, 3 mm long and 1.5–1.8 mm wide, glossy reddish brown, with stalked hilum close to midpoint and adjacent micropyle just outside the hilum |
| Propagation | By Seed |
Plant Description
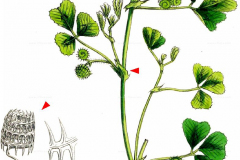
Spotted medick is a native, prostrate or sprawling herb that normally grows about 2–6 cm tall. An annual, it is often found low to the ground mixed in with the grass. The plant is found growing in moist stream banks, grasslands, places, thin pasture, lawns, meadows and fields and disturbed areas including waste lots and roadsides. The plant grows in light, sandy and gravelly soils, particularly near the coast. Stems are decumbent or spreading, longitudinally ridged, sparsely hairy, hairs are simple and multicellular-glandular. The plant has one leaf per node along a hairy stem that is often red-streaked.
Leaves
Leaves alternating along the stems are pinnately compound, with 3 leaflets each 0.4-4 cm long and 5–45 mm wide. Margins are toothed towards the tips. Upper surface is hairless, usually with a dark patch near the middle, lower surface is sparsely appressed-hairy, tips squared off or notched with a terminal tooth, stipules strongly toothed and hairy on lower surface.
Flowers
Inflorescence of 1 to 5 pea-like flowers is in a reduced, axillary raceme on a stalk 1-3 cm long on fairly short peduncles arising from the leaf axils. The stalks are shorter than the leaves. Corollas are pea-like, yellow, about 5 mm long, the banner erect, much longer than the wings and keel. Calyces are sparsely white-hairy, 2-3 mm long, the lanceolate, long-pointed teeth slightly longer than the tube. Flowering normally takes place in between April and August.
Fruits
Fertile flowers are followed by pod spirally coiled through 3 to 5 spirals, round, 4-8 mm in diameter, the outer margins narrowly keeled, spineless, or with two rows of divergent prickles up to 2.5-3.5 mm long, somewhat curved to nearly straight with short hook at tip, aging pale brown. Seeds are kidney-shaped, 3 mm long and 1.5–1.8 mm wide, glossy reddish brown, with stalked hilum close to midpoint and adjacent micropyle just outside the hilum.
Other Facts
- For millennia people have used those plants for soap.
- They’ve also been used as a fish poison making it easy to catch the fish.
- A cover crop controls soil erosion and replenishes nutrients.
- It is planted after the primary cash crop has been harvested.
- The plant is an excellent green manure and has been the subject of studies about its use as a cover crop in large-scale farming.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=503718#null
http://www.hear.org/pier/species/medicago_arabica.htm
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxon/taxonomydetail?id=23555
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/MEDAB
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Medicago_arabica
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/33024
https://www.feedipedia.org/content/spotted-medick-medicago-arabica
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/ild-8482
https://gobotany.nativeplanttrust.org/species/medicago/arabica/
http://www.worldfloraonline.org/taxon/wfo-0000213417
https://plants.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=MEAR