Plant Description
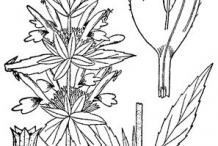
Spotted Beebalm is an aromatic, erect herbaceous perennial plant that grows about 1 feet to 3 feet (0.3m-1m) tall. The plant is found growing in sand prairies, hill prairies, sandy Black Oak savannas, stabilized sand dunes along Lake Michigan, and sandy fields. This species can be found in both disturbed and higher quality sandy habitats. The plant prefers average, dry to medium moisture, well-drained soils in full sun to part shade. It is best in sandy soils with consistent moisture. The plant can tolerate somewhat poor soils and drought. The plant has taproot and hairy rigid stems that are unbranched, reddish, square, obtusely angled, hoary and pubescent.
Leaves
Leaves are opposite, lance-like, up to 3½ inches long and 1 inch across, with shallow teeth and a pointed tip. Bottoms of the leaves are hairy and paler in color from the fine hair. Leaves have short stalks with fine hair, and base of the leaf tapers to the stalk with a wing effect. Smaller leaf growths are frequently seen at the base of the leaf stalk.
Flower
Flowers are quite conspicuous, the corolla being tubular, 3/4 to 1 inch long, yellowish with purple spots. The upper corolla lip is stiff and strongly arched, the lower lip is broader. Both have hair on the outer surface. The two stamens and style are tucked tightly against the inside of the upper lip and are slightly shorter than the lip and thus do not protrude except when the anthers are with mature pollen at which point the anthers are visible. The calyx tube is green, hairy, with 5 small pointed lobes. Even more conspicuous are the whitish to lilac colored bracts that surround the cyme at its base. These growths look like leaves but are called ‘bracts’. The showy bracts remain attractive for a long time after flowering, and each flower is replaced by 4 small nutlets, which are ovoid and smooth, which can ripen and self-sow. Seeds are smooth, brown, oval, just over 1 millimeter long.
Varieties/Types
- Monarda punctata var. arkansana (E.M.McClint. & Epling) Shinners
- Monarda punctata var. correllii B.L.Turner
- Monarda punctata var. coryi (E.M.McClint. & Epling) Shinners
- Monarda punctata var. immaculata (Pennell) Scora
- Monarda punctata var. intermedia (E.M.McClint. & Epling) Waterf
- Monarda punctata var. lasiodonta A.Gray
- Monarda punctata var. occidentalis (Epling) E.J.Palmer & Steyerm
- Monarda punctata var. punctata
- Monarda punctata var. villicaulis (Pennell) E.J.Palmer & Steyerm
Traditional uses and benefits
- Dotted horsemint was used by the Meskwaki to treat colds and catarrh in a mixture with the leaves of Ranunculus delphinifolius and the disk florets of Helenium autumnale.
- The plant, along with other plants were ground into a powder and snuffed up the nostrils to relieve a sick headache.
- Taken with the roots of Asarum canadense, Euphorbia corollata, and Brauneria angustifolia these plants relieved stomach cramps.
- The Delaware washed patients’ faces with an infusion of dotted horsemint to treat skin problems.
- They also used an infusion of dotted horsemint to reduce fevers.
- The Mohegan made an infusion of the plant to reduce fevers as well.
- The Nanticoke used an infusion of the entire plant to treat colds.
- Horse mint was traditionally taken by several native North American Indian tribes to treat nausea and vomiting, and to encourage perspiration during colds.
- It was also applied externally as a poultice to treat swellings and rheumatic pains.
- Nowadays it is used primarily to treat digestive and upper respiratory tract problems.
- Leaves are carminative, diaphoretic, diuretic, emenagogue, rubefacient, stimulant, stomachic and vesicant.
- An infusion of the leaves is used in the treatment of flatulence, nausea, indigestion, catarrh in the upper respiratory tract, and to induce sweating and promote urination.
- The herb is principally used externally as a rubefacient, applied as a poultice it helps to lessen the pain of arthritic joints by increasing the flow of blood in the area and thereby hastening the flushing out of toxins.
- Plant is a rich source of the medicinal essential oil ‘thymol’, which is antiseptic.
- Thymol is also an effective hookworm remedy, but must be ingested in such large quantities that it can prove fatal to the patient.
Herbal Preparations
Spotted bee balm tea
Infusion
- Drink 1/2 cup, or use for a wound wash or steam inhalation.
Spotted bee balm tincture
- 1 part fresh flowers and leaves, chopped
- 2 parts menstruum (50 percent alcohol, 50 percent distilled water)
Or
- 1 part dry flowers and leaves, chopped
- 4 parts menstruum (50 percent alcohol, 50 percent distilled water)
Take 15–25 drops as needed.
Spotted bee balm–infused honey
- 1 part fresh flowers and leaves, chopped
- 3 parts raw, unpasteurized honey
Use as needed.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=32279#null
https://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/go/799/
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=24538
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Monarda+punctata
https://www.cabi.org/ISC/datasheet/115634
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=mopu
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-129232
https://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=MOPU
https://plants.usda.gov/plantguide/pdf/cs_mopu.pdf
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monarda_punctata
http://www.newmoonnursery.com/plant/Monarda-punctata
http://www.illinoiswildflowers.info/prairie/plantx/sp_balm.htm
Comments
| Spotted Beebalm Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Spotted Beebalm |
| Scientific Name: | Monarda punctata |
| Origin | Eastern Canada, the eastern United States and northeastern Mexico |
| Shapes | 4 small nutlets, which are ovoid and smooth |
| Taste | Bitter |
| Name | Spotted Beebalm |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Monarda punctata |
| Native | Eastern Canada, the eastern United States and northeastern Mexico |
| Common Names | Dotted monarda, Horse-mint, Spotted beebalm, Dotted horsemint, American Horsemint, Bee balm, spotted horsemint, Spotted Mint |
| Name in Other Languages | English: Dotted monarda, Horse-mint, Spotted beebalm, Dotted horsemint, American Horsemint, Bee balm, spotted horsemint, Spotted Mint Finnish: Pikkuväriminttu French: Monarde ponctuée German: Monarda, Punktierte Indianernessel, Ojibwa: Kah-be-sah-ne-gwa-y-yok Swedish: Prickig temynta |
| Plant Growth Habit | Aromatic, erect herbaceous perennial |
| Growing Climates | Sand prairies, hill prairies, sandy Black Oak savannas, stabilized sand dunes along Lake Michigan, and sandy fields. This species can be found in both disturbed and higher quality sandy habitats |
| Soil | Easily grown in average, dry to medium moisture, well-drained soils in full sun to part shade. Best in sandy soils with consistent moisture. Tolerates somewhat poor soils and drought. |
| Plant Size | 1 feet to 3 feet (0.3m-1m) |
| Root | Taproot |
| Stem | Hairy rigid stems are unbranched, reddish, square, obtusely angled, hoary and pubescent |
| Leaf | Lanceolate or narrowly oblong, 2-8 cm. and more or less hairy |
| Flowering Periods | July to September |
| Flower | Flowers are tubular, and 13-15 nerved. The corolla is pale yellow, spotted with purple and strongly bilabiate. The upper lip is narrow and entire, and is about as long as the throat and slender tube together. The lower lip is broader. |
| Fruit Shape & Size | 4 small nutlets, which are ovoid and smooth |
| Seed | Smooth, brown, oval, just over 1 millimeter long |
| Flavor/Aroma | Similar to that of oregano |
| Taste | Bitter |
| Plant Parts Used | Leaves, flowering tops, stems |
| Propagations | Seeds or cuttings |
| Varieties/Types |
|
| Culinary Uses |
|
| Other Facts |
|
| Precautions |
|