This tree is especially useful in treating gum problems and dental disorders such as bleeding gums, loose teeth, sensitive teeth, cavities, etc. Its tender parts are used as tooth brush. The bark and seed coat are used for strengthening the gum. It is used under the name of Vajradanti, in preparation of various herbal tooth powders along with many other ingredients such as catechu, pomegranate bark, etc. Its fruits are eaten raw and also prepared as pickle. Bark of the tree is used to improve fertility in women. The fruits are edible and used to treat chronic dysentery. They have astringent action. Seeds exhibits purgative action. Its timber is valuable, the fruit is edible, and it is used in traditional medicine. As the trees give thick shade and flowers emit fragrance, it is a prized collection of gardens. Its flower is the provincial flower of Yala Province, Thailand.
Plant Description
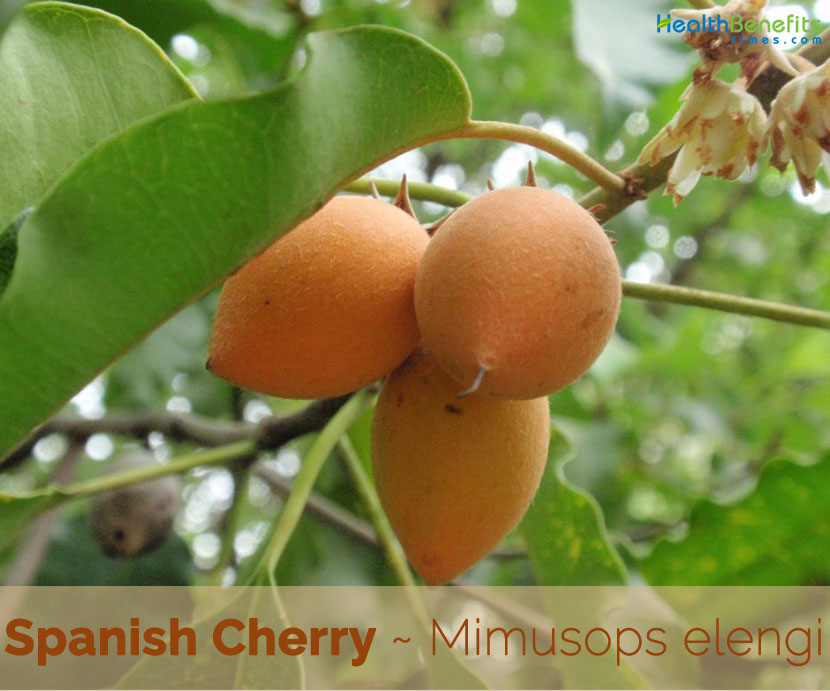
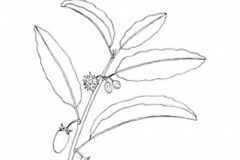
Spanish Cherry is an evergreen, small to medium-sized, much branched tree that grows about 30 m tall with cylindrical trunk 100 cm in diameter. It has a dense, rounded, spreading crown. The tree is found growing in Northwestern Himalayas, Eastern Ghats, Western Ghats, Central Deccan Plateau, East Coast, West Coast, Indo-gangetic Plain, Outlying Islands, maritime habitats along the coast, in coastal vine thickets, lowland inland rain forest, and in rocky localities from sea. The plant tolerates brief periods of water logging but requires fertile soil. It is fairly tolerant of brief light frost. Bark is dark grey, occurs in pieces of 15-25 cm long and 10 -15 cm broad. Externally rough due to the presence of vertical lenticels, cracks and longitudinal fissures. The dried bark is thin and occurs in quills. It is a prized ornamental specimen because it provides a dense shade and during the months from March to July fills the night air with the delicious heady aroma of its tiny cream colored flowers.
Leaves
The leaves are glossy, dark green, oval shaped, 5–14 cm (2.0–5.5 in) long, and 2.5–6 cm (0.98–2.36 in) wide arranged spirally, more or less in clusters at the ends of branches, on grooved, 1–3.5 cm long petiole with minute and caduceus stipules, with wavy margins, light green when young changing to dark glossy green as they mature. They are evergreen or semi-evergreen, depending on the length of the dry season, with some leaf-fall occurring in seasonally dry areas. The lamina is entire, simple, ovate to elliptical or oblong-elliptical, 3.5–4–5 × 7–10.5 cm, base cuneate, apex acuminate, with slightly wavy margins and 10–20 pairs of lateral veins
Flower and Fruits
Flowers are white, star-shaped, sweetly fragrant and showy, but are part-hidden in the foliage. They bloom mainly in the rainy season, with on and off blooms in-between, particularly in irrigated gardens and landscapes. Flowering normally takes place from March-July. Fertile flowers are followed by small egg-shaped, berry-like fruit up to 3 cm (1.2 in) long, with a persistent calyx. Fruits are initially green when young, becoming yellow as get ripe and become dark orange when fully ripe, with a mealy yellow pulp and with one large seed inside, though it is sometimes double-seeded.
| Spanish Cherry Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Spanish Cherry |
| Scientific Name: | Mimusops elengi |
| Origin | India, Sri Lanka, the Andaman Islands, Myanmar, Indo-China, Peninsular Malaysia to Vanuatu |
| Colors | Green while unripe, get yellow as get ripe and become dark orange when fully ripe |
| Shapes | Ovoid to ellipsoid, fleshy berry, 2–4 cm long, 1–2-seeded and with a persistent calyx |
| Flesh colors | Yellow |
| Taste | Sweet, Astringent, pungent |
| Health benefits | Beneficial for pyorrhea, dental caries, chronic dysentery, constipation, heart diseases, gonorrhea, snakebites, fevers, wounds, scabies, eczema, leucorrhoea, menorrhagia, heat rashes, prickly heat |
| Parts of the Tree | Uses | Action |
| Stem | Destroys protozoa or inhibits their growth and ability to reproduce | Anti-protozoal |
| Bark | Works against microbes | Antimicrobial |
| Bark | Works against virus | Antivirus |
| Bark | Inhibits ulcer formation | Anti-ulcer |
| Leaf | Destroy parasitic worms | Anthelmintic |
| Leaf | Fever reducing Leaf | Anti-pyretic |
| Leaf Bark | Reduce inflammation | Anti-inflammatory |
| Bark | Acting to prevent or counteract the accumulation of lipids in the blood | Anti-hyperlipidemic |
| Bark | Counteracting the accumulation of excess sugar in the blood | Anti-hyperglycemic |
| Leaf, fruit | Inhibits damaging oxidizing agents in a living cells | Antioxidant |
| Leaf | Effective against high blood pressure | Antihypertensive |
| Bark | Preventing the formation of the urinary calculi | Antiurolithiatic |
| Stem bark, Leaf | Controls glucose level | Anti-diabetic |
| Leaf | Pain relieving | Analgesic |
| Bark | Prevent or relieve anxiety | Antianxiety |
| Bark | Prevent or reduce the severity of epileptic fits or other convulsions | Anticonvulsant |
| Bark | Increased passing of urine | Diuretic |
| Stem Bark | Heals wounds | Wound healing |
| Bark | Kills larvae | Larvicidal activity |
| Leaf, Bark, Seed | Kills molluscs (mainly snails and slugs) | Molluscicidal activity |
| Bark | Inhibits formation of ulcer | Anti-ulcer |
| Bark | tonic effect on the action of the heart | Cardio-tonic |
Traditional uses and benefits of Spanish Cherry
- Bark, flowers, fruits and seeds of Spanish cherry are considered astringent, cooling, anthelmintic, tonic, and febrifuge in traditional medicine.
- In Ayurvedic medicine, it is commonly used for treating dental disorders like bleeding gum’s, pyorrhea, dental caries and loose teeth.
- Fruits are used in chronic dysentery, constipation and to relieve burning urination in India.
- Pulverized ripe fruit mixed with water is administered to promote delivery in childbirth.
- Flowers are used against heart diseases, leucorrhoea, menorrhagia and act as antidiuretic in polyuria and antitoxin.
- Flowers are also used as snuff to relive cephalalgia and as lotion for wounds and ulcers.
- Powdered flowers are used in a disease called Ahwa in which strong fever, headache and pain in the neck, shoulders and other parts of the body occurs and as brain tonic.
- Bark is used as a gargle for odontopathy, ulitis and ulemorrhagia.
- Barks are used to increase fertility in women and known to have anti-ulcer activity.
- Tender stems are used as tooth brushes, and in cystorrhea, diarrhea and dysentery.
- Leaves are used medicinally to treat headache, toothache, wounds and sore eyes, and are smoked to cure infections of the nose and mouth in Asia.
- Decoction of the bark, sometimes mixed with the flowers, has been used against fever, diarrhea, and inflammation of the gums, toothache, gonorrhea, wounds and, mixed with tamarind bark, as a lotion for skin complaints.
- Flowers have been used against diarrhea.
- Young fruits have been used in a gargle for treating gum disorders.
- Pounded seeds are used to cure obstinate constipation.
- Bark, as well as the ripe fruit, yields a powerful astringent remedy in Philippines.
- Both are used as a gargle to strengthen the gums.
- They are further used in lotions for ulcers, and in urethral injections for gonorrhea.
- Bark is astringent and tonic and is used in diarrhea and dysentery.
- In Sarawak, the Malays prepare a paste of the leaves with the dry skin of shallot and rub on the nose and forehead to alleviate painful and itchy nose.
- The Melanau boil the leaves with spices that include ketumbar (Coriander sativum), cinnamon bark, cloves, fennel and gadung (Dioscorea hispida) and drink the concoction to treat leprosy and grey hair in young people.
- Liquid from boiling the bark together with the bark of zee-hpyu and shah is held in the mouth to treat thrush, inflamed gums, burns within the mouth, gingivitis, and other gum disorders.
- Liquid from boiling the bark is also used to clean cuts and wounds.
- Used for heart problems, a decoction of the bark is taken, the flowers are inhaled, and the fruit is eaten.
- Fresh flowers are used for treating white vaginal discharge and dental diseases.
- Water from soaking them overnight is given to children for coughs.
- Dried flowers, ground together with thanakha, are applied to cure heat rashes and prickly heat.
- Paste of seeds is made with cold water or the ripe fruits are ingested for persistent diarrhea.
- Bark is used in the treatment of diarrhea and dysentery.
- Decoction of the bark, sometimes mixed with the flowers, is used as a gargle to treat gum inflammation, toothache etc.
- It is also used to treat gonorrhea, snakebites, fevers, wounds, scabies and eczema.
- Leaves are used to treat headache, toothache, wounds and sore eyes, and are smoked to cure infections of the nose and mouth.
- Young fruits have been used in a gargle for treating sprue.
- An alcoholic extract of the bark showed anti-ulcer activity against experimental gastric ulcers; this activity was recognized to a decrease in gastric acid secretory activity along with strengthening of mucosal defensive mechanisms.
- Extract of flowers used against heart diseases, leucorrhoea, menorrhagia and act as anti-diuretic in polyuria and antitoxin.
- Ripened fruits facilitates in burning urination.
- Ripe fruit pounded and mixed with water is given to promote delivery in childbirth.
- Powder of dried flowers is a brain tonic and useful as a snuff to relieve cephalalgia.
- Decoration of bark is used to wash the wounds.
- Powder of dried flowers or the juice of flowers is administered through the nostrils to get relief from headache and sinusitis.
- Decoction prepared from the bark is used for gargling to treat disease of the oral cavity like gingivitis, looseness of teeth, oral ulcers.
- Tender leaves or unripe fruits of the plant are chewed to treat bleeding from the gums and gingivitis.
- Cold infusion or decoction prepared from the bark of the stem is given in a dose of 40-50 ml to treat diarrhea and intestinal worms.
- Cold infusion of the bark is given in a dose of 40-50 ml to treat dysmenorrhea and leucorrhea.
- Bark decoction is given in a dose of 30-40 ml to treat fever and general debility.
- Paste of the bark and unripe fruit is applied over the local area to relieve the effect of insect bite and other small animal bites.
- Cold infusion prepared from the dried flowers of the plant is given regularly in a dose of 40-50 ml to strengthen the cardiac muscles and is beneficial in persons suffering from weak cardiac muscles.
- Cold infusion or decoction of the flower acts as a general tonic.
- Leaves are used as nasal drops for treatment.
- Seed fix loose teeth and used as a cure troubles in the head.
- Root is aphrodisiac, diuretic, astringent to the bowel, good for gonorrhea and used as a gargle which cures relaxation of the gums.
- Seed are made into a paste mixed with oil or butter to be used as a suppository in cases of constipation in children.
Other Facts
- Spanish Cherry is usually planted for its timber and as an ornamental and shade tree in gardens and along roads, also in coastal sites in Asia.
- Its wood is luxurious, heavy, hard, strong and durable wood and is well known in Asia.
- Wood is used for heavy general construction, bridge building, boat and shipbuilding, marine construction, flooring, bearings, doors, framing agricultural implements and oil mills.
- It has also been used for poles and piles, furniture, foundation sills, railway sleepers, paving blocks, mine timber, and cabinet work, vehicle bodies and wheels, turnery, tool handles, walking sticks, weaving shuttles, toys, sporting goods and musical instruments.
- Wood is useful in the Philippines and is a favorite for ships’ wheels, marine-spikes, fine tool-handles, etc.
- In Africa the wood is considered good for mortars.
- Good-quality veneer and plywood can be manufactured from the wood.
- Tree also provides good fuel-wood.
- In India bark has been used for tanning, but the tannin content is low.
- Bark is used for toughening and coloring tackle in Ghana.
- Fresh flowers are used for making fragrant garlands, as necklaces for decoration or placed in linen-cupboards.
- Flowers yield essential oil which is used as perfume.
- Seeds are also used for necklaces.
- Seeds yield oil on pressing, which has been used for cooking and illumination.
- Seed oil is also used to make paint and for lighting.
- The essential oil from the bark is also in perfumery.
- Flowers are aromatic and used as fillings in pillows, and for decorations and aesthetics.
- Dried flowers are used as a filling in pillows, strung in garlands or necklaces for decoration, or placed in linen-cupboards.
- Brown dye is obtained from the bark.
- Wood is used for heavy general construction, building purposes, boat and shipbuilding, piles, bridges, agricultural implements and oil mills.
- It is also used for flooring, bearings, doors and framing, poles and piles, foundation sills, railway sleepers, paving blocks, mine timber, furniture and cabinet work, vehicle bodies and wheels, turnery, tool handles, walking sticks, weaving shuttles, toys, sporting goods and musical instruments.
- A good-quality veneer and plywood can be manufactured from the wood.
- Its flower is the provincial flower of Yala Province, Thailand.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=505964#null
https://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/go/140848/
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=24452
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Mimusops+elengi
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=MIEL4
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mimusops_elengi
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl/record/kew-128461
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/15876
https://www.biodiversityofindia.org/index.php?title=Mimusops_elengi
http://www.stuartxchange.org/Kabiki
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/MMOEL
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/34466
https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Mimusops_elengi_(PROTA)