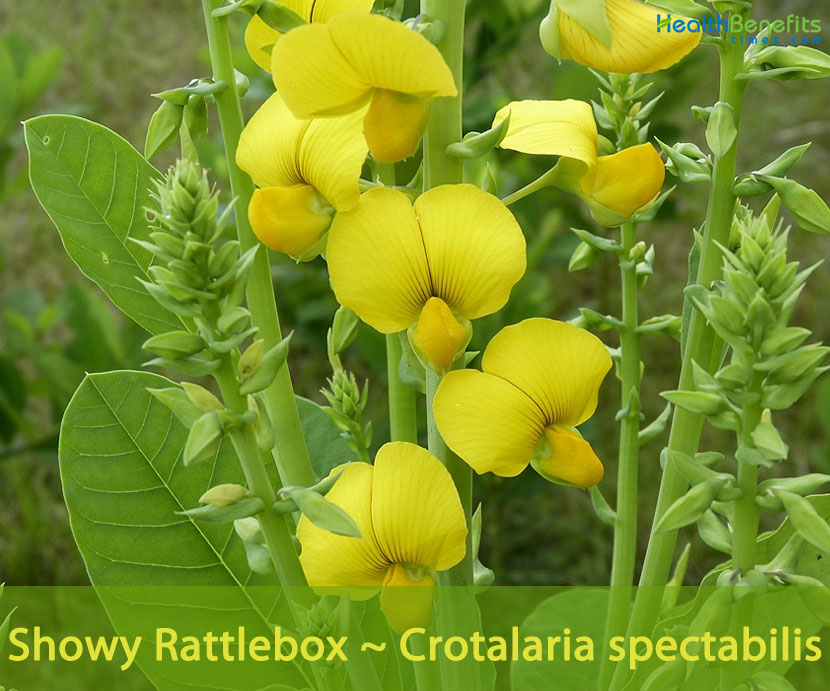
The genus name Crotalaria is derived from the Greek word crotalon, which means castanet and refers to the rattling sound the seeds produce when the dry, inflated pods are shaken. The plant is harvested from the wild for local use as a food and medicine. It is often grown as a soil improver and stabilizer, having the added benefit of being able to reduce soil nematode populations. It is also often grown as an ornamental, valued especially for its long flowering season. As a member of the legume family, it was carried to the United States to be used as a cover crop to help set nitrogen in dry sandy soils. Showy Crotalaria is toxic to livestock, as it consists of high levels of alkaloids, which commonly cause issues in cattle and horses in the southeastern states.
Showy Rattlebox Facts
| Showy rattlebox Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Showy rattlebox |
| Scientific Name: | Crotalaria spectabilis |
| Origin | Tropical Asia, but is now distributed pantropically |
| Colors | Initially green in color, but as they mature, they turn brown to dark brown |
| Shapes | Cylindrical pods (legumes) measuring 4-5 cm long and 1.5-2.5 cm wide, which look inflated |
| Name | Showy Rattlebox |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Crotalaria spectabilis |
| Native | Tropical Asia, but is now distributed pantropically. It has been planted widely and has naturalized in many tropical countries, including South-East Asia and in the south-eastern United States, Hawaii, and Puerto Rico |
| Common Names | Indian rattlebox, Showy crotalaria, Showy rattlebox, Yellow crotalaris, Rattlebox, Showy Rattlepod, Silent rattlepod, Greater rattlepod, Yellow Crotalaris, cat’s bell, rattlepod |
| Name in Other Languages | Assamese: Jhumjhumi (জুমজুমি) Bengali: Pipuli jhunjhun, jhumjhumo (ঝুমঝুমো), pipuli jhunjhun (পিপুলি ঝুনঝুন) Chinese: Da tuo ye zhu shi dou (大托叶猪屎豆), Mei li zhu shi dou (美丽猪屎豆) Cuba: Chicharra, maromera, maruga Danish: Smuk raslebælg Dominican Republic: Maraquita English: Indian rattlebox, Showy crotalaria, Showy rattlebox, Yellow crotalaris, Rattlebox, Showy Rattlepod, Silent rattlepod, Greater rattlepod, Yellow Crotalaris French: Crotalaire remarquable, Cascavelle Jaune, Petit Pois Rond Marron, Pois Rond Marron, Crotalaire remarquable Germany: Ansehliche Klapperhuelse Hawaiian: Kolomona Hindi: Ghungri, Jangalii san (जंगली सन), Jhunjhunia (झुनझुनिया), Dhundhani, Dhundhunia, Sani, showy crotalaria, sonnette, tcha-tcha, Sanni (सन्नी), Ghungri (घुंगरी), Dhundhuni (धुनधुनी), Jhunjhunia (झुनझुनिया) Italian: Crotalaria sericea Japanese: Kurotararia-supekutabirisu (クロタラリア・スペクタビリス) Kannada: Kaadu senabu (ಕಾಡು ಸೆಣಬು) Marathi: Dingala (डिंगळा), Khulkhula (खुळखुळा), dayali (दयाळी), Mizo: Tumthang Nepali: bhuvan jhar (भुवन झार) Palauan: Kuroteraria Polish: Klekotnica okazala Portuguese: Cascabel ornamentale, Chocalho de cobra, Crotalária chocalho, Crotalária espectabilis Russian: Krotaliariia nariadnaia (Кроталярия нарядная) Sanskrit: Ghantarava (घण्टारवा) Spanish: Cascabel ornamentale, Crotalaria amarilla, crotalaria espectabilis Telugu: Pedda giligitcha (పెద్ద గిలిగిచ్చ) Thailand: Mahing men Tongan: Ha‘apai Turkish: Süslü krotalarya USA: Showy rattlebox |
| Plant Growth Habit | Erect, summer herbaceous, much-branched annual to perennial plant |
| Growing Climates | Montane grasslands, along trails, forest margins, as a weed of cultivated fields, open fields, open ground, roadsides, along railroad tracks, in pastures, wastelands, and disturbed areas |
| Plant Size | Grows up to 2 m in height and 3.5 cm in basal diameter |
| Stem | Stems are green or purplish and may be ribbed. |
| Leaf | Simple, alternately arranged on the stem with persistent stipules. They are obliquely oblong-ovate, acuminate and measuring 3-10 mm long and 2-8 mm wide |
| Flowering season | Between November and January |
| Flower | Flowers are held in a long terminal spike. The bright yellow flowers may have dark lines on the upper petals. Petals are from 0.75-1.0 in. long. |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Cylindrical pods (legumes) measuring 4-5 cm long and 1.5-2.5 cm wide, which look inflated and contain about 22 seeds per pod |
| Fruit Color | Initially green in color, but as they mature, they turn brown to dark brown |
| Seed | Seeds are kidney shaped, 4.5 mm long, small turn brown or black at maturity. They are considered very toxic. |
| Propagation | By Seed |
| Season | December to February |
| Precautions |
|
| Culinary Uses |
|
Plant Description
Showy rattlebox is an erect, summer herbaceous, much-branched annual to perennial plant that normally grows up to 2 m in height and 3.5 cm in basal diameter. The plant is found growing in Montane grasslands, along trails, forest margins, as a weed of cultivated fields, open fields, open ground, roadsides, along railroad tracks, in pastures, wastelands, and disturbed areas. This plant grows best in full sun, is drought tolerant and doesn’t need a lot of water. The plant is supported by a tap and lateral system of stiff, tan roots.
Stem
The plant normally has a single stem. The lower stems are covered with whorled, short, shelf-like old leaf bases and stipule remnants. Leaves and fruiting branches are shed progressively upward after they mature so that foliage and branches are only found on the upper portion of the stem. The mid- and lower stem has a white, brittle, medium-hard wood with a 1.5-mm pith. The upper stem, branches, and foliage are green to yellow-green.
Leaves
Leaves are simple, alternately arranged on the stem with persistent stipules. They are obliquely oblong-ovate, acuminate and measuring 3-10 mm long and 2-8 mm wide. The petiole is 2-8 mm long. The blade is oblanceolate to obovate, and measuring 8-14 cm long and 3-8 cm wide. The narrowest part of the leaf is attached to the stem and the widest part is at the tip. Leaves are generally smooth or hairless above while the lower surface is densely hairy (pubescent).
Flower
The inflorescence is 15-50 cm long which is rather lax and with many-flowered raceme. The bracts are persistent, cordate, measuring 10-20 mm long and 5-10 mm wide, and acute or acuminate. The pedicel is 8-13 mm long. The bracteoles are 1-2 mm long and lance-shaped. The hairless sepal is bell-shaped, measures 11-14 mm long, and with 5 unequal lobes which are longer than the tube. The petal is yellow. The wings are obovate-oblong, and measuring 9-18 mm long and 5-9 mm wide. The keel measuring 10-14 mm long and 4-9 mm wide is rounded about the middle, with a short, incurved and twisted beak. The 10 stamens are united into one group by their filaments. The anthers are dimorphic, with 5 long, basifixed anthers on a short filament that alternate with 5 rounded dorsifixed anthers which are on a long filament. The ovary is narrowly oblong and hairless. Flowering normally takes place in between November and January.
Fruit
Fertile flowers are followed by cylindrical pods (legumes) measuring 4-5 cm long and 1.5-2.5 cm wide, which look inflated, that darken at maturity. Fruits are initially green in color, but as they mature, they turn brown to dark brown with 20-24 seeds. When mature, seed may break free inside the pods and create a rattling sound when shaken; hence the name rattlebox. Seeds are kidney shaped, small, and brown to black at maturity measuring about 3.5 mm long and 4 mm wide, with the radicular side incurved. Seed are considered very toxic.
Traditional uses and benefits of Showy Rattlebox
- The seed and other above-ground parts consist of the pyrrolizidine alkaloid monocrotaline, which has been shown to lower blood pressure but is also toxic.
- In herbal medicine, extracts of the whole plant are used to treat impetigo and scabies.
- It is used as an antiseptic for cuts, and to treat intestinal worm.
Other facts
- The plant is grown as a green manure and also to stabilize the soil.
- The stem yields a fairly strong, durable fiber.
- Showy Rattlebox has been planted as an ornamental and for erosion control.
- It is often responsible for livestock poisonings in south Alabama.
- The green pods we called poppers.
Different Control Methods
Biological
No widespread biological controls are utilized for showy rattlebox.
Chemical
There are a number of chemical control options for showy rattlebox. These include both preemergence and postemergence herbicides in pasture and/or hay, corn, and soybeans. In pasture and/or hay, diuron can used for preemergence control while dicamba, hexazinone, triclopyr, triclopyr mixes, 2, 4-D, or 2, 4-D mixes can be used for postemergence control. In corn, atrazine can be used for both preemergence and early postemergence control of showy rattlebox. Other postemergence options in corn include dicamba, clopyralid, glyphosate, or 2, 4-D. Ametryn, linuron, or paraquat can be used postemergence directed in corn. In soybeans, flumioxazin or metribuzin can be used for preemergence control. Acifluorfen can be used for postemergence control, while fomesafen, glyphosate, Lactofen, or paraquat can be used postemergence directed control of showy rattlebox.
Mechanical
Small patches of showy rattlebox can be mechanically removed by hand. Remove plants prior to fruit ripening to avoid seed dispersal. Hand removal can be slow and labor intensive. In pastures, clipping can be an effective method of weed management to minimize exposure of grazing animals to plants that are toxic. Repeat as necessary to minimize likelihood of consumption by livestock and seed production. Care should be taken to prevent contamination of forages that will be fed as hay or silage to livestock with showy crotalaria. In feed grain crops, such as corn or soybean, care should be taken to avoid contamination of harvested grains with showy rattlebox seed. Sanitation should be used to prevent the movement of seed on tillage or harvest equipment from one field to other fields.
Physical
Physical controls are not widely used for showy rattlebox
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=26580#null
http://www.hear.org/pier/species/crotalaria_spectabilis.htm
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxon/taxonomydetail?id=12384
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/16161
http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Crotalaria+spectabilis
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=Crsp2
http://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Showy%20Rattlepod.html
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/ild-6024
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/229376
https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Crotalaria_spectabilis_(PROSEA)
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/CVTSP
https://www.gri.msstate.edu/research/invspec/factsheets/2P/Showy_rattlebox.pdf