Plant Description
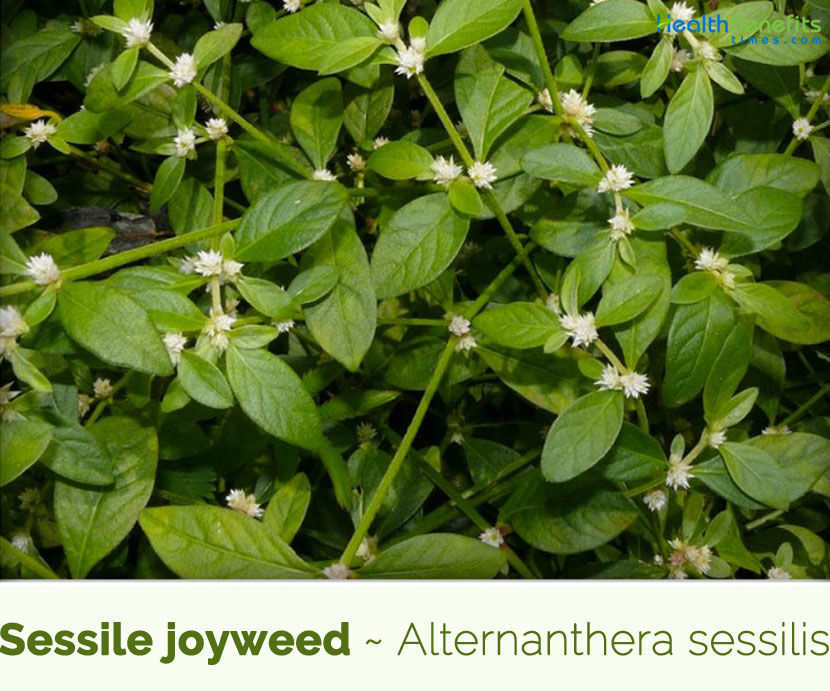
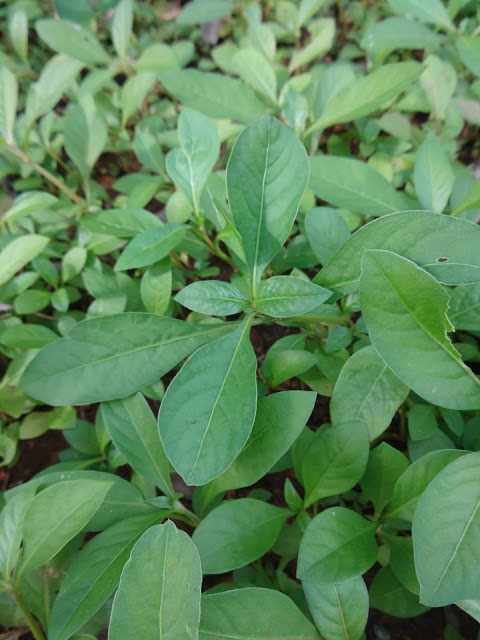
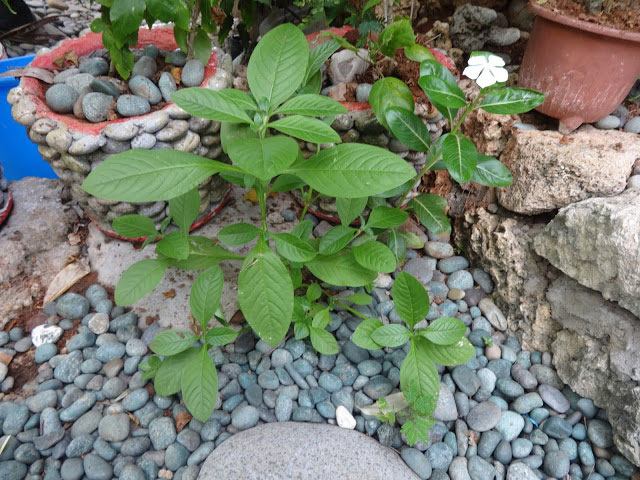
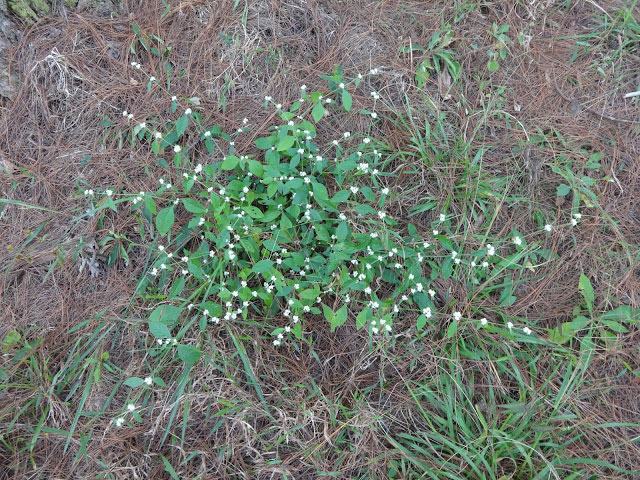
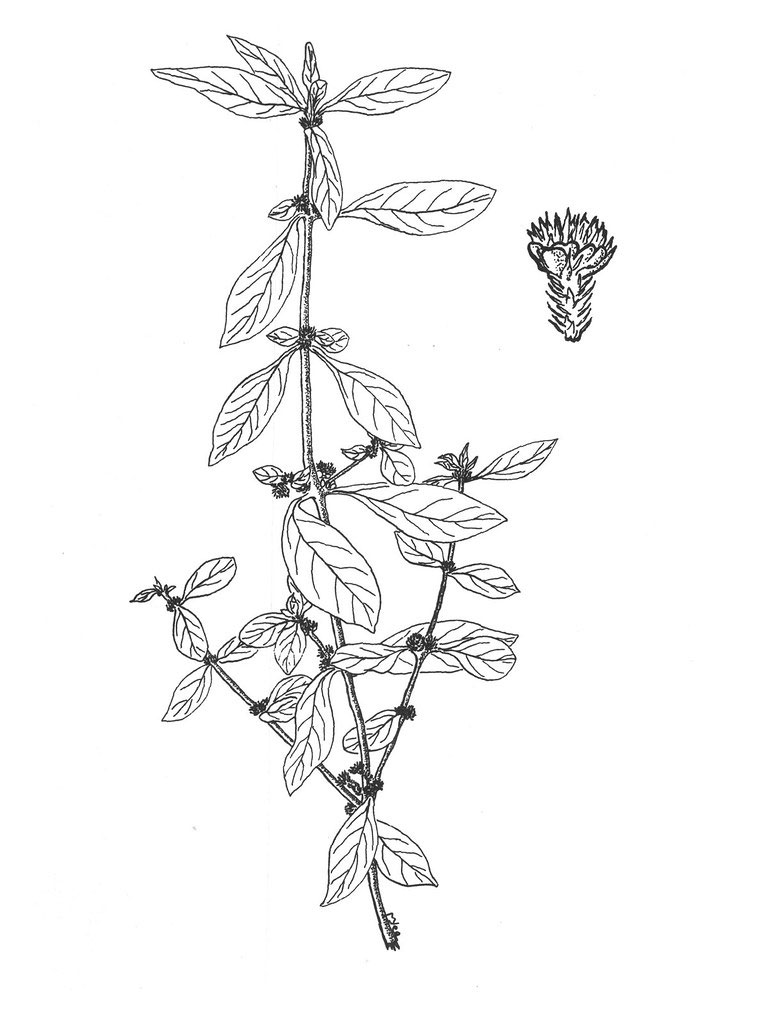
Sessile joyweed is a spreading or prostrate, erect, more or less branched, glabrous, succulent ascending or creeping herbaceous plant that grows about 0.4 to 1.4 meters high. The plant is found growing near ponds, canals, reservoirs, swamps, shallow ditches, and fallow rice fields, ditch banks, along roadsides, and in gardens, floodplain wetlands, margins of rivers, streams, canals, ditches, ponds, reservoirs, tanks, marshes, swamps, wet low-lying ground, ephemeral pools, seasonal pans and damp forest, pathways, wasteland, irrigation canals, ditches, dykes, wet soil, along ditches, seasonally waterlogged roadside depressions, fallow lands, irrigation canals and rice field levees. The plant is adapted to grow on a range of soil types ranging from poor sandy or alkaline soils, to loam or black cotton soils. It is also able to grow in seasonally-waterlogged areas as well as in areas with extreme dry conditions.
Root
Root is cylindrical, 0.1-0.6 cm diameter, cream to grey, numerous roots arising from the main tap root as lateral rootlets; fracture, short; no characteristic odor and taste.
Stem
Stem is cylindric, many-branched and villous in lines and transversely at the nodes. It is solid and thin in dry conditions, the stem is longer, hollow and floating in aquatic conditions, reaching 1 cm in diameter. It is glabrous except for two opposite narrow lines of whitish hairs on the erect parts, and tufts of white hairs at the nodes.
Leaves
Leaves are simple, opposite and decussate; paired blades are generally the same size. Petiole is indistinct, short (1.5 mm) or absent. Laminas are narrow and elongated, very variable in shape and size. Oblanceolate to elliptic-lanceolate or linear-lanceolate, apex acute to obtuse, shortly acuminate, base cuneate to attenuate, 1 to 12 cm long and 0.25 to 3 cm wide; glabrous or nearly so, with sparse hairs mostly found on the lower side, on the midrib.
Inflorescence
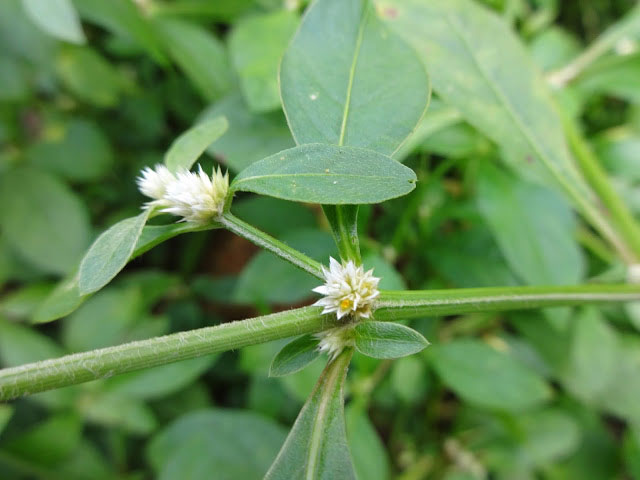
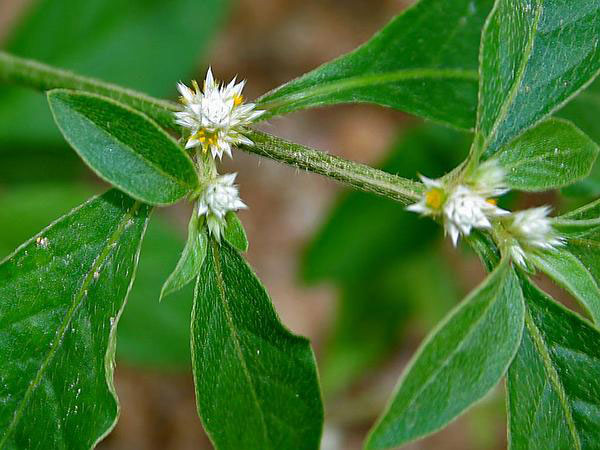
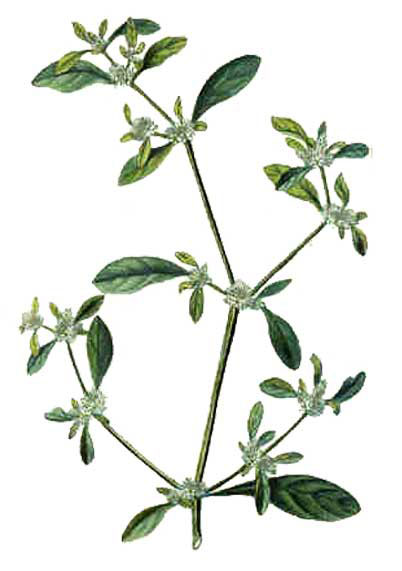
Inflorescences are sessile spikes, in the axils of leaves, isolated or grouped (up to 5), sub-globose, to 1 cm across with segments to 2.5 mm long.
Flower
Each flower is subtended by a white scarious bract, 0.75-1 mm long with a pointed end, and 2 bracteoles similar to the bract. The perianth consists of tepals, all equal, ovate-elliptic, pointed at the apex, 1.5 to 2.5 mm long, white, glabrous, distinctly mucronate, with a slightly denticulate margin. Five stamens (including 2 without anther) alternate with pseudo-staminodes similar to filaments, but usually a bit smaller. At maturity, they equal the ovary and style. The ovary is compressed, sub-orbicular, with a short style.
Fruit
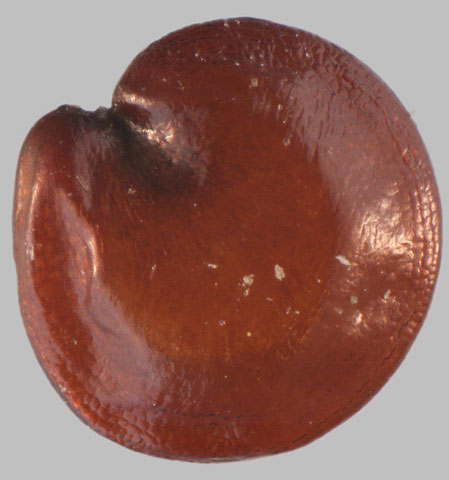
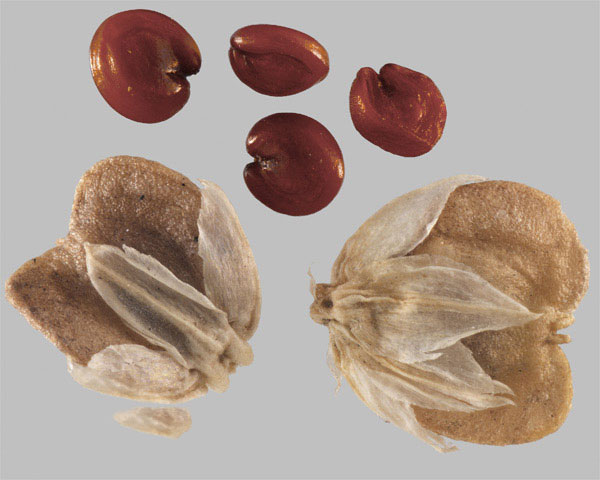
Fertile flowers are followed by indehiscent, a small, flattened, obcordate or obovate utricle, 2-2.5 mm long capsules, enclosing the seed with paler edge. It falls with the tepals. The fruit has no characteristic odor and taste. They are initially green turning to dark brown as they mature. Seeds are lens-shaped, about 0.8-1 mm in diameter, testa bright brown, slightly reticulate.
Health benefits of Sessile Joyweed
Not only the leaves its roots, stem, flower and extract all consists of different medicinal properties. Young leaves consist of anti-fungal and anti-bacterial property. Leaves soothe the wounds and help to subside the acidity level in the body. Listed below is a list of amazing health benefits of Sessile joyweed its roots, stem, flower and extracts if you include in your daily diet.
1. Cures Infertility
If the sessilis leaves are included in the everyday diet it cures the gonorrhea condition. Men’s infertility can be cured. It gives energy to the diabetic people and helps to maintain the sugar level in the blood.
2. Prevents Cancer
It mixes with the blood and removes the toxin and prevents us from cancer. It has the potential to kill germs and heals the wounds.
3. Great for Night Blindness
Alternanthera Sessilis has the greatest ability to improve the vision. Persons suffering from night blindness (Nyctalopia) can eat the raw flower of sessilis continuously will feel the difference in their eye sight. It cools down the body, strengthens the eye nerves, strengthens the muscles and improves the vision power and it acts as the best medicine for eye disease.
4. Regulates Nervous System
Sessilis will improve the sleep condition too. It can regulate the central nervous system. It cures many nerve related disease, improves the memory power, it cools and relaxes the eye and brain.
5. Reduces Body Heat
Equal amount of sessilis extract with gingelly oil and 20 g of licorice, water lily and cumin seeds all these are grinded with cow’s milk and are boiled at low flame and filter it. Apply this filtrate on your hair 4 days once and wash it this therapy will acts as a medicine to reduce the body heat and improves to grow hair, reduce the internal fever, body pain, leg pain, head ache, eye irritation and stomach pain.
6. Cures Piles
People suffering from piles can make a soup with sessilis, garlic and pepper to make a full stop for the disease condition. 25 gm. of sessilis extract mixed with equal amount of carrot extract along with little salt also help to cure piles.
7. Irritation during Urination
Extract butter milk with 2 liter of buffalo’s milk and mix the roots of sessilis and drink that buttermilk which cures the irritated urination.
8. Cures Jaundice
People suffering from jaundice can grind the sessilis leaves and extract 20 ml boil this with brown sugar and mix it with cow milk and drink for a certain period will helps to cure them. The Naturopathic doctors include sessilis in their medicinal formula for curing hepatitis, chest cold, and asthma and for liver disease.
9. Helps Weight Loss
Sessilis with pepper eaten with rice will reduce the body weight. For body weight gains eat sessilis with cooked dhal and ghee.
10. Hair Growth
Equal amount of sessilis extract and bhringraj (Eclipta prostrata) extract boiled in gingelly oil and allow it cool down and store it in a container for eye irritation and for hair growths apply this on the hair.
11. Improves Health Condition
Alternanthera Sessilis will help to reduce the following diseases conditions like body heat, eye irritation, knee pain, white discharge, helps recovering from loss of appetite, liver diseases. The extract and oil from sessilis help to reduce the body heat during summer season and helps to prevent headache. Since the sessilis leaves can boost the milk production in breast feeding women, it is used in Thailand.
Traditional uses and benefits of Sessile Joyweed
- It is used as a topical treatment for the common skin problem cane vulgaris.
- In folklore, A. sessilis was used for treating sick individuals.
- It is “used for the treatment of biliousness, dyspepsia associated with sluggish liver, chronic congestion of liver, acute and chronic pyelitis, cystitis, gonorrhea, and strangery and snake bite in Sri Lanka.
- It is used for treatment of gastrointestinal problems in India and Sri Lanka.
- It is used as a treatment for headaches and vertigo in Nigeria.
- It is also used to treat hepatitis, bronchitis, and asthma in Taiwan.
- Root is used for hazy vision and night blindness, postnatal complaints, prolapsus and fistula ani, diarrhea, fever with intense thirst, dog, jackal and lizard bite also, and an unspecified plant part is used for dysentery.
- Broth of the plant is cooked with meat and taken for tuberculosis in China.
- Decoction with wine is used for internal injuries.
- It has been used for the treatment of dysuria and hemorrhoids.
- It is used for simple stomach disorders, diarrhea, and dysentery and as a plaster for diseased or wounded skin parts and against fever.
- Decoction with some salt is taken to stop vomiting blood in Ghana.
- Pounded plant is used against headache and vertigo, and leaf sap is sniffed up the nose to treat neuralgia in Nigeria.
- Paste is used to draw out spines or any other object from the body and it is also used to cure hernia.
- Leafy twigs, ground to a powder, are applied against snakebites in Senegal and India.
- It is used to treat hepatitis, tight chest, bronchitis, asthma and other lung troubles, to stop bleeding and as a hair tonic in Taiwan.
- Juice of the plant is used to treat white discharge in the urine.
- Plant is used in mixtures with other medicinal plants, to treat hepatitis, tight chest, bronchitis, asthma, and lung troubles, to stop bleeding and as a hair tonic.
- It is also applied externally in the treatment of scabies, cuts and wounds, boils; and as a cooling agent to treat fever.
- Mixed with corn flour and baked, it is eaten to treat menstrual disorders.
- Juice of the root is used in the treatment of dysuria, fevers and bloody dysentery.
- Decoction of the leaves is drunk for treating itchy and overheated skin.
- It is used to relieve headaches and dizziness and the leaf sap is sniffed up the nose to treat neuralgia in Nigeria.
- Sessile joyweed is used to treat snakebites and to stop the vomiting of blood in various regions of Africa.
- Decoction with some salt is taken to stop vomiting blood in Ghana.
- Paste of the herb is used to draw out spines from the body.
- Plant is used for the treatment of biliousness, dyspepsia and sluggish liver in Sri Lanka.
- Alternanthera sessilis is used in local medicine in Taiwan, along with other medicinal plants, to treat hepatitis, tight chest, bronchitis, asthma and other lung troubles.
- It is used as a cholagogue (a medicinal agent which promotes the discharge of bile from the system), and febrifuge (reduces fever) in India.
- People in Thailand and Sri Lanka use the plant as a galactagogue.
- Leaves are boiled and ingested to treat hypertension.
- Topical application of leaf paste is used for drawing foreign object such as spines, stings from the body.
- Leaves powder is also applied externally on snakebites.
- Fresh leaves are applied over eyes for styes, conjunctivitis and chronic inflammation of the eyelid.
- Topical application of leaf paste is used for drawing foreign object such as spines, stings from the body.
- Soup prepared from fresh plant is helpful in increasing breast milk and toning up of the liver.
- Fresh leaves juice (1 tablespoon) mixed with garlic clove are folk remedy for asthma, chronic cough, and intermittent fever.
- The herb is used to fight depression in Taiwan.
- It is used to relieve tiredness, laziness, and sleepiness in Bangladesh and other parts of Asia.
- This herb is consumed to improve male sexual potency in Pakistan.
- It is used to treat low sperm count in Bangladesh.
- It is also used for treatment of anemia, diabetes, hypertension, piles, and blood disorders and against worm infection.
- Roots used by the Bantar of Morang for stomachache in Nepal.
- Decoction is recommended as an herbal remedy to treat wounds, flatulence, nausea, vomiting, cough, bronchitis, diarrhea, and curative, protective or promote purposes.
- It is used as a local medicine often in mixtures with other medicinal plants, to treat hepatitis, tight chest, bronchitis, asthma and other lung troubles.
- Leaves and shoots boiled and drunk as an anti-hypertensive remedy.
- The plant is used to treat gonorrhea, low sperm count and leucorrhea in Noakhali district of Bangladesh.
- The plants are used by folk medicinal practitioners for treatment of severe pain in several areas of Faridapur and Rajbari districts of Bangladesh.
Home remedies using Sessile joyweed
- Grind the leaves to a very fine paste and take 2 tsp. every day for 45 days. Steamed leaves taken with a little butter every day for 45 days also helps to cure various eye problems.
- Regular consumption of sessile joyweed flower is also said to improve eyesight. Night blindness can be cured by regular consumption of raw sessile joyweed flowers.
- Soak a handful of fresh sessile joyweed flowers, in half a liter of coconut oil. Having a tsp. of this every morning leads to increased energy
- Mix two ounces of the juice of this plant with 4 ounces of goat or cow’s milk. This mixture helps in building strength and vitality.
- Boil together about a liter of fresh Sessile joyweed juice with 250 ml of sesame seed oil. Once the juice is absorbed into the oil, reduce the mixture to about 250 ml, Cool and strain. Massaging this oil to the head gives good eyesight and memory.
- Soup prepared using the Sessile joyweed leaves, garlic and pepper is very effective in curing piles. Another home remedy for piles drinking a mixture of 25 gm of Sessile joyweed juice mixed with equal amount of carrot juice, and a pinch of rock salt.
Culinary Uses
- In Southeast Asia young shoots and leaves are ingested as vegetables.
- It is used in many different foods in Africa, such as soups, relish, and sauces.
- In certain regions of South East Asia, the leaves and young shoots are consumed as vegetables.
- In Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu, the leaves, flowers and tender stems are consumed as vegetables.
- It is used in salads, soups and cooked as a potherb.
- Leaves and tender tops are consumed raw or cooked.
- It is used in sauces and soups, stir fried, added to omelets, or made as a relish.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=20773#null
https://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/go/31894/
http://www.hear.org/pier/species/alternanthera_sessilis.htm
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/4404
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=ALSE4
http://issg.org/database/species/ecology.asp?si=767&fr=1&sts=&lang=EN
http://www.iucngisd.org/gisd/species.php?sc=767
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=2713
https://nas.er.usgs.gov/queries/FactSheet.aspx?speciesID=227
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-2631425
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alternanthera_sessilis
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/32910
https://www.prota4u.org/database/protav8.asp?g=pe&p=Alternanthera+sessilis+(L.)+DC.
http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Alternanthera+sessilis
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/ALRSE
http://www.stuartxchange.org/BungaBunga.html
http://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Sessile%20Joyweed.html
https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Alternanthera_sessilis_(PROTA)
Comments
| Sessile joyweed Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Sessile joyweed |
| Scientific Name: | Alternanthera sessilis |
| Origin | Throughout the tropical and subtropical regions of the Old World |
| Colors | Green when young turning to dark brown as they mature |
| Shapes | Indehiscent, a small, flattened, obcordate or obovate utricle, 2-2.5 mm long capsules |
| Taste | Sweet, acrid |
| Health benefits | Cures Infertility, Prevents Cancer, Great for Night Blindness, Regulates Nervous System, Reduces Body Heat, Cures Piles, Irritation during Urination, Cures Jaundice, Helps Weight Loss, Hair Growth, Improves Health Condition |
| Name | Sessile joyweed |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Alternanthera sessilis |
| Native | Throughout the tropical and subtropical regions of the Old World. It has been introduced to the southern United States, and its origins in Central and South America are uncertain |
| Common Names | Creeping chaffweed; dwarf copperleaf; khaki weed; rabbit weed; rabbit-meat |
| Name in Other Languages | Arabic: Laqmah al-ḥamal (لَقْمَة الحَمَل), Luwayq (لُوَيْق), Nammūl Assamese Sakraj, Matikaduri, Menmeni, Mati-kaduri Bengali: Sanchesak, Salincha Sak, Chanchishak, Haicha, Kekrak shak Cambodia: Cheng bângkong, phak phew Chinese: Lian zi cao (莲 子草), Bai Hua ZI, Shui Niu Xi, Jie jie huo, Man tian xing English: Rabbit meat, Sessile joyweed, dwarf copperleaf, joyweed, Tangle Mat, sessile alligator weed, sessile flower globe amaranth, carpet weed, water Amaranth, Brede Chevrette Fiji: Galuti French: Alternanthère sessile, Brède chevrette, Brède emballage, Herbe d’emballage, Illécèbre sessile, serenti, magloire German: Sitzendes Papageienblatt, Garnelenkraut Ghana: Tosre, Abanase-abanase Gujrati: Jalajambo, Pani ki Bhaji Hawaiian: Palewāwae Hebrew: Nitzan machsif, בִּצָּן מַכְסִיף Hindi: Geluti, Gudrisag, Ponnaganni, Garundi Indonesia: Bayem kremah, daun tolod, kremah, kremek, tolod Illocano: Abisrana Irula: Ponnankanni dagu Japanese : Aruterunantera sesshirisu (アルテルナンテラ・セッシリス), Hoshi no geitou (ホシノゲイトウ), Tsuru no geitou (ツルノゲイトウ), turu-nogeito Kannada: Honagone soppu, Honugonesoppu Laos: Khaix ped Malay: Daun tolod, Rumput Aur, Karemah Bukit, Keremuk, Daun Keremak Malaysia: Akar rumput, bayam pasir, bayam tana, carpet weed keremak, kelama hijau, kerak-kerak paya, keremak, kerumak bukit paya Malayalam: Kozhuppa, Ponamgani, Kozhuppacheera, Meenamgani, Ponnamkannikkeera, Ponnankanni Manipuri: Phakchet Maori (Cook Islands): Mata kura Marathi: Kanchari Marquesan: Ti Myanmar: Pazun-sar, pazun-za Nepali: Bhirangijhar (भिरिंगी झार), Sarhanchi sag, aankhe Jhar (आँख्ले झार), Bhaale Bhringaraaj (भाले भृंगराज), Bisaaune Jhaar (Bisaaune Jhaar), Jibre Paate (जिब्रे पाते), Dube Jhaar (दुबे झार) Oriya: Matsagandha, Salincha Saaga, Madsagandha Pakistan: Bengroo, Waglon Palauan: Eluached, okula beluu lechad, sechal Panay Island: Lupo Philippines: Bonga-bonga Portuguese: Bredo d´água, Periquito-sessil, Periquito violacea, Perpétua Russian: Al’ternantera sidyachaya (Альтернантера сидячая) Samoan: Vao sosolo Sanskrit: Matsyagandha, Bahli, Matsyaduni, Gandali, Lonika Gartkalambuka Sierra Leone: Datawuli Sinhalese: Mukunuwanna, Mukunu wenna Spanish: Colchon de nino, coyuntura, hierba de perico, paja blanca, sanguinaria, santoma cimarrona Sri Lanka: Mukunuwanna Surinam: Santi wiwiri, Wet’ede, Weti hede, Witti hede Tagalog: Bunga-bunga Taiwan: Periquito-sessil, Horngtyang Wu Tamil: Ponankani, Ponnaankannikkeerai, Poonnankannikeerai, Ponnangaani Telugu: Ponnaganti Koora, Ponnagantikura Thai: Phak pet thai (ผักเป็ดไทย), phakpet khaao Tongan: Fisi‘i‘ano, brede embellage Unani: Machhechhi, Paanachooni Visayan: Karitana Zambia: Mkungira |
| Plant Growth Habit | Spreading or prostrate, erect, more or less branched, glabrous, succulent ascending or creeping herbaceous plant |
| Growing Climates | Near ponds, canals, reservoirs, swamps, shallow ditches, and fallow rice fields, ditch banks, along roadsides, and in gardens, floodplain wetlands, margins of rivers, streams, canals, ditches, ponds, reservoirs, tanks, marshes, swamps, wet low-lying ground, ephemeral pools, seasonal pans and damp forest, pathways, wasteland, irrigation canals, ditches, dykes, wet soil, along ditches, seasonally waterlogged roadside depressions, fallow lands, irrigation canals, rice field levees |
| Soil | Adapted to grow on a range of soil types ranging from poor sandy or alkaline soils, to loam or black cotton soils. It is also able to grow in seasonally-waterlogged areas as well as in areas with extreme dry conditions |
| Plant Size | About 0.4 to 1.4 meters high |
| Root | Cylindrical, 0.1-0.6 cm diameter, cream to grey, numerous roots arising from the main tap root as lateral rootlets; fracture, short; no characteristic odor and taste |
| Stem | Generally prostrate, creeping, often rooting at the nodes, sometimes floating or ascending at the tips, cylindrical and slightly hairy, with numerous, erect branches |
| Leaf | Simple, opposite, shortly petiolate or sessile, broadly lanceolate or spatulate to almost linear, 0.6-5 cm long, and 0.3-1 cm wide. They are attenuated at the base, and the apex is acute to blunt, with entire, glabrous or pilose (thin, fine, articulate hairs) margins |
| Inflorescence | Inflorescence an axillary, sessile, subglobose head 5 mm in diameter, solitary or in clusters of up to 5 |
| Flower | Bisexual, regular, 5-merous; tepals free, equal, ovate to elliptical, up to 2.5 mm long, white to pinkish, 1-veined; stamens united at base into a very short cup, 2 without anthers; ovary superior, strongly compressed, 1-celled, style very short. |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Indehiscent, a small, flattened, obcordate or obovate utricle, 2-2.5 mm long capsules, enclosing the seed |
| Fruit Color | Dark brown |
| Seed | Dark-brown to black, disc-shaped and shiny, about 0.8-1 mm in diameter |
| Propagation | Seed, rooting at nodes |
| Taste | Sweet, acrid |
| Plant Parts Used | Leaf, Stem, Root, dried whole plant |
| Other facts |
|
| Health Benefits |
|