Plant description
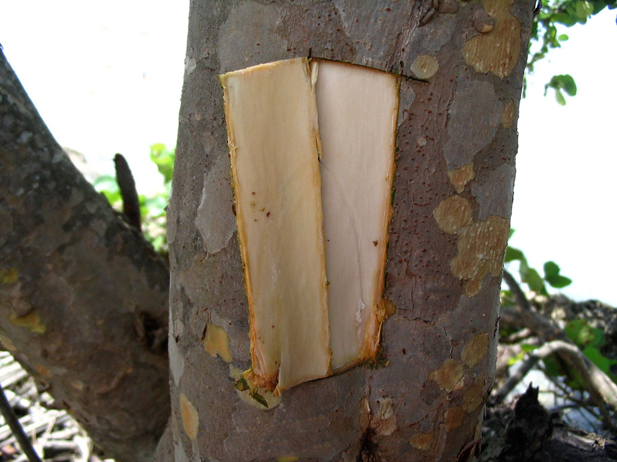
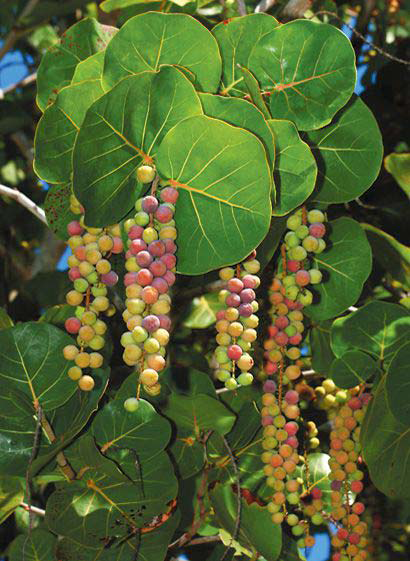
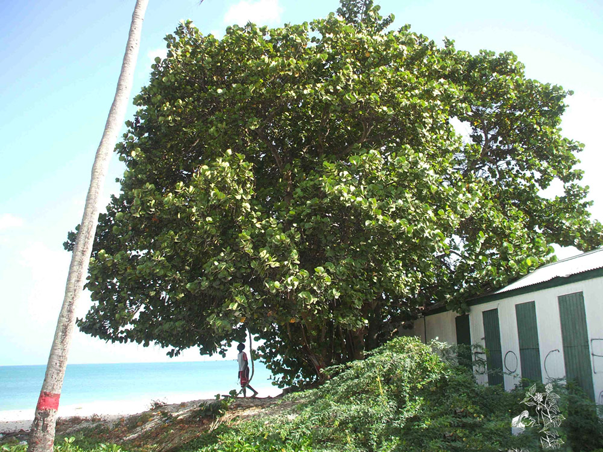
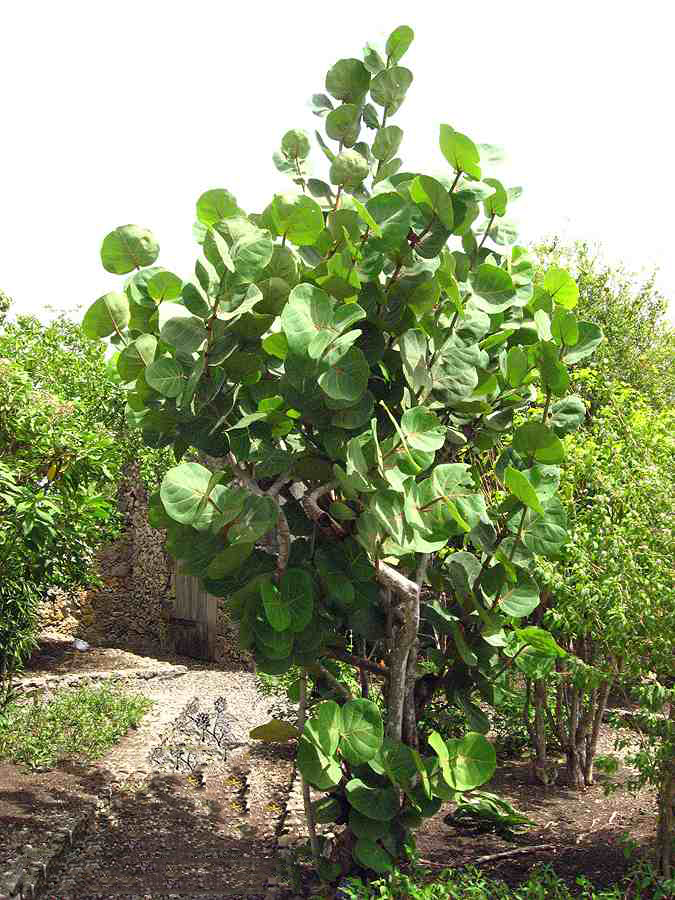
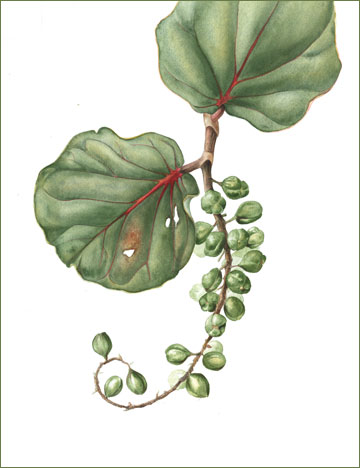
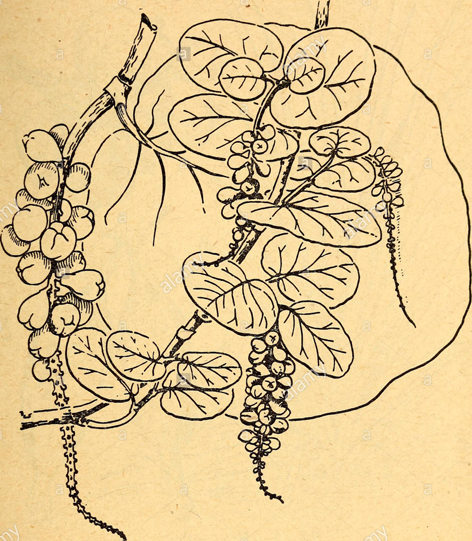
Sea grapes are a sprawling evergreen shrub or small tree that grows about 2–15 m high with a bole of 30–60 cm with spreading or sprawling branches and a sparse crown. The plant is found growing in tropical climatic conditions mainly in the coastal hammocks, coastal scrub, coastal grasslands and beach strands. It is widely tolerant to most soils, provided they are well drained. It grows well in sandy soil but usually grows faster and larger in more fertile soils. Minor element deficiencies may appear in calcareous soils. Barks are smooth grayish to mottled with patches of white, gray, and light brown bark that peels off in flakes, with reddish sap, inner bark is light brown. Twigs are green and puberulent when young, grey at maturity, glabrous or pubescent.
Leaves
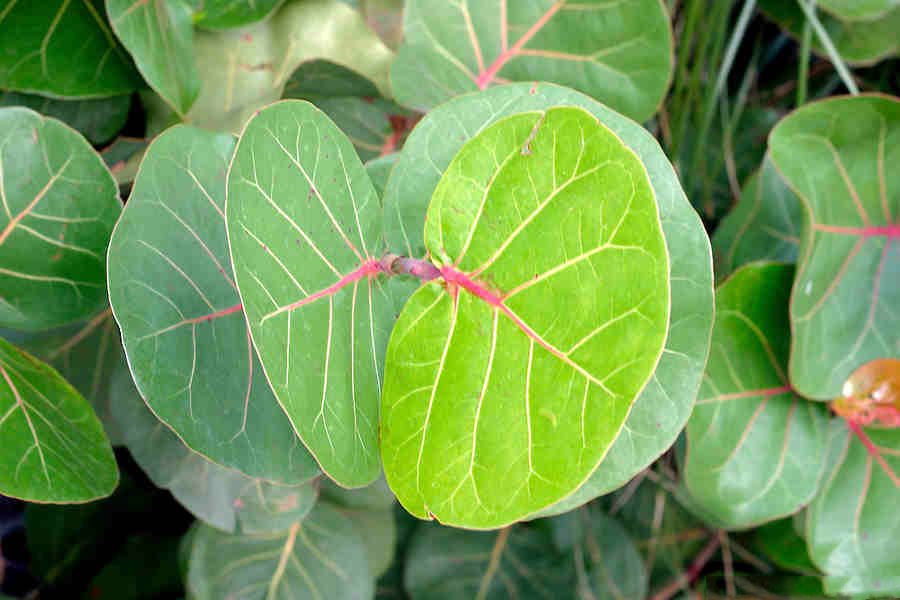
Leaves are alternate, short-petioled, large, leathery, glossy, dark green, broadly bean-shaped, with wavy margins, up to 15 centimeters long, 8 in (20.3 cm) in diameter with a reddish-colored primary vein extending from the base. The entire leaf turns red as it ages.
Flower
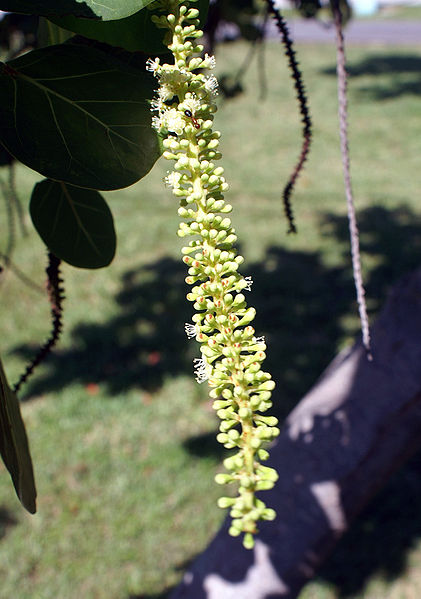
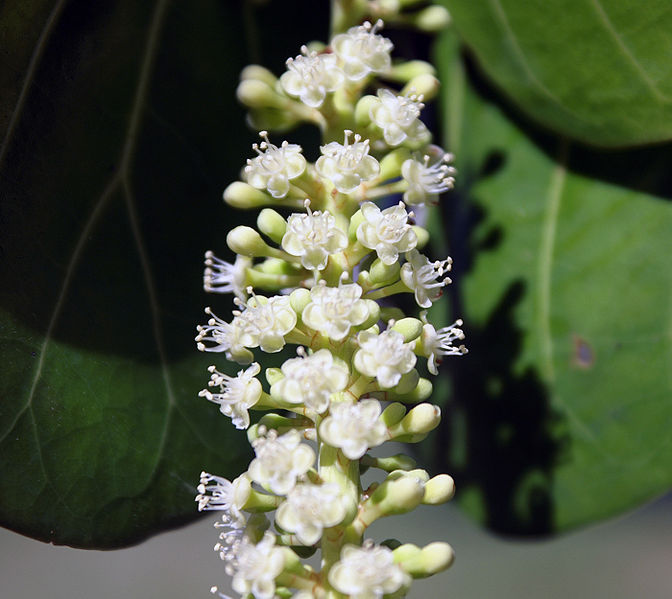
Inflorescences are 10–30 cm, puberulent or glabrous, pistillate pendent in fruit; peduncle 1–5 cm, glabrous. Pedicels are 1–4 mm, glabrous. The flowers are small, white, and fragrant with five petals and eight stamens and bloom mainly in spring but also occasionally throughout the rest of the year, with female and male flowers on different plants.
Fruit
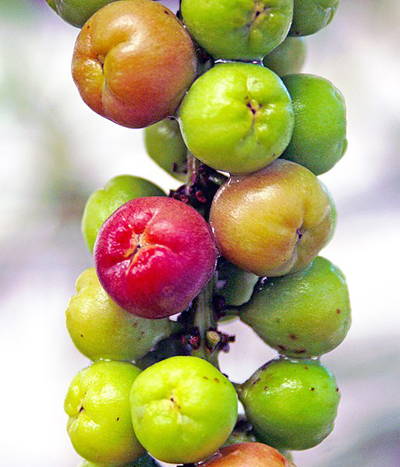
The flowers on female plants are followed by globose to pear-shaped fruit about 3/4 inches in diameter. The fruit has the size of a large marble but a bit tougher than the ordinary grape and it has one large seed. The fruit remain green and hard for a long time but eventually one by one they change to their mature deep purple color when ripe. It is produced in large clusters resembling grapes. Edible pulp which varies from acid to sweet and insipid surrounds a single, large, pointed seed which may account for 2/3 of the fruit volume. Fruit normally ripens unevenly in individual racemes and readily drops from the tree. Most fruit matures during the summer, but in some years some fruit may mature in late fall because of late bloom. Fruit is produced only on female trees but a male tree must be present for pollination. Assurance of a productive female tree with good quality fruit needs vegetative propagation. Large tree generally produces several thousand fruit per season, more than enough for individual use.
History
The Plant is indigenous to Mexico, northern South America, the Caribbean and southern Florida. It is now found pantropically and has been introduced to Taiwan, Australia and the Philippines. In its native tropical range from Argentina north throughout the West Indies and in Florida, it occurs on sandy coasts, coastal hammocks, coastal scrub, coastal grasslands and beach strands. It thrives in full sun to partial shade. It is drought tolerant and highly tolerant of salt spray and salty soils as well as strong sun and wind. It is often planted as a windbreak near beaches and as a hedge. It is sensitive to frost.
Health Benefits of Sea Grape
The fruit is loaded with numerous important vitamins and minerals essential for the proper functioning of the entire body. Listed below are few of the popular health benefits of consuming Sea grapes
1. Strengthen Bones and Joints
Sea Grapes consist of good amount of protein, calcium and polyunsaturated fatty acids found in omega3 group (DHA, EPA, ALA), effective in calming inflammation and reduce the symptoms of arthritis.
2. Helps Strengthen Eyesight and the Heart
Sea Grapes consists of unsaturated fatty acids AA, LA, DHA, EPA and ALA that help to strengthen eyesight and memory, reduce cholesterol, increase the elasticity of blood vessels, prevent oxidation, maintain collagen structure of the arteries, preventing cardiovascular diseases such as stroke, atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction.
3. Helps Prevent Hypertension and Diabetes
Sea Grapes are a wonderful source of calcium, potassium and vitamin C and are effective in reducing blood pressure due to the ability to promote excretion and maintain normal blood pressure for people with high blood pressure. In addition to vitamin C, Sea Grapes also help control sugar level and activity of free radicals, reduce intracellular accumulation of sorbitol and inhibit the binding of glucose and protein, reducing complications of diabetes.
4. Helps Prevent Constipation
Sea Grapes contain very low calories and sugar, allowing good bacterium to digest food and excrete waste quickly which is effective in preventing constipation.
5. Helps Prevent Goiter
100g of Sea Grapes consists of about 1.8mg Iodine. Consuming 30gr of Sea Grapes a day can provide adequate Iodine required for thyroid, help prevent goiter.
6. Helps Generate Beautiful Skin and Silky Hair
Fat found in Sea Grapes helps protect cell membranes, improve elasticity and lower the permeability of the vessel wall to reduce the symptoms of dry skin. Rich with vitamin A, C Sea Grapes are capable of producing collagen and antioxidants and are considered as natural cosmetics that help improve skin, hair and slow the aging process.
7. Helps Prevent Obesity
Sea Grapes consists of less amount of sugar but rich in calcium, zinc, iron, vegetable protein, vitamin C and polyunsaturated fatty acids are considered the nutritious and safe food for overweight and dieting consumers.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Bf17G00HVtM
Traditional uses and benefits of sea Grapes
- Leaves bark and roots were traditionally used by the Native Americans to make medicinal teas.
- Both the juice and decoctions of wood, bark, and roots of the sea grape are astringent and were used to treat diarrhea, dysentery, hemorrhages, and venereal diseases.
- Juice and decoction are applied externally for rashes and other skin afflictions.
- Tea made from the leaves was used to treat hoarseness and asthma, and to bathe wounds.
- Resinous gum of the bark was also used against throat ailments.
- Root decoction was used against dysentery.
- Whole plant produces an astringent juice which is used to treat diarrhea and dysentery.
- Decoction of bark is used for intestinal disorders.
- Decoction made from leaves helps in curing asthma, hoarseness and also to clean the wounds.
- Sea grapes help in digestion and also help in proper functioning of the liver.
- These fruits help in reducing the overall glucose content present in the body.
- It also helps in decreasing the cholesterol content in the body.
- It helps in counter balancing the blood pressure of the body.
- Alcohol added to tea made from bark of sea grape is taken for ulcers in Yucatan.
- Decoction of leaves used for menopausal symptoms, diarrhea, tumors, anemia, skin irritations, asthma in Dominican Republic.
- Fruit is also effective against diabetes.
- It increases immune response, can treat meningitis and reduces the level of cholesterol in the blood.
- Drink made from boiling all the parts of the plant together are used to treat diarrhea.
- Leaves can be used as a compress for boils.
- Putting the leaves on a person’s head is said to stop headaches.
Culinary uses
- Fruit is edible; the pulp can be eaten fresh or made into jams, jellies or fermented to make wine.
- Fruits are eaten and a beverage is made that is used as medicine on the island of Trinidad.
Other facts
- Sea-grape is used as hedges and as an ornamental street tree in coastal cities throughout the tropics.
- It is also used as windbreak and is planted along the sea-shore to stabilize the sandy soils.
- Wood is used for furniture, carvings and for fuel.
- Resin of the bark is used in tanning and yields a red dye.
- Plant is also valued for honey production.
- In Jamaica and Cuba it is in demand for cabinet making and furniture.
- Wood of the sea grape is occasionally used for firewood, making charcoal and even cabinetry.
- Sap of the sea grape is used in the West Indies and Jamaica for dyeing and tanning of leather.
- It is sometimes used as a subject for bonsai.
- Plants are used to form hedges and also grown in the streets of the cities coming under the coastal regions.
- These plants act as barriers of wind near the coasts and also as hedges surrounding shopping centers and also the parking areas.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=21039#null
https://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/go/1869/
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=10993
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=COUV
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-2729556
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/14655
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coccoloba_uvifera
http://www.floridaplants.com/horticulture/seagrape.htm
Comments
| Sea Grape Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Sea Grape |
| Scientific Name: | Coccoloba uvifera |
| Origin | Tropical America and the Caribbean |
| Colors | Green turning shiny rose-purple when mature |
| Shapes | Round, berry-like fruits (2 cm wide) are tightly packed in long hanging chains. |
| Taste | Varies from acid to sweet and insipid |
| Health benefits | Strengthen Bones and Joints, Strengthen Eyesight and the Heart, Prevent Hypertension and Diabetes, Prevent Obesity, Prevent Constipation, Prevent Goiter, Generate Beautiful Skin and Silky Hair |
| Name | Sea Grape |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Coccoloba uvifera |
| Native | Coastal beaches throughout tropical America and the Caribbean, including southern Florida, the Bahamas, Barbados and Bermuda |
| Common Names | Bay Grape, Bow Pigeon, Caracas Kino, Coccoloba Kino, Columbian Kino, Hopwood, Horsewood, Jamaican Kino, Mangrove Grape, Platterleaf, Pigeon Wood, Sea Grape, Seaside Grape, Seaside Plum, Shore Sea-Grape, Shore Grape, South American Kino, West Indian Kino, Wild Grape, Wild Mangrove Grape, Wild Seaside Grape |
| Name in Other Languages | Brazil : Cocoloba, Uva-Do-Mar, uva de praia British West Indies : Bow Pigeon, Hopwood, Horsewood, Mangrove Grape, Pigeonwood, Seaside Grape, Seaside Plum, Wild Grape, Wild Mangrove Grape, Wild Seaside Grape Central America : Uva, Uva Caleta, Uva De La Mar, Uva De Playa, Uverillo, Uvero English: Jamaican kino, Platterleaf, Sea-grape, Shore sea-grape, common seagrape, Kino, seaside grape, shore grape, Uva de playa, baygrape Finnish : Norsunkorva French : Raisin Marine, Raisinier, Raisinier Bord De Mer, Raisinier Des Bords De Mer, Raison De Mer, cipo branco de pernambuco, Coccoloba uvifera, Kino, uva da praia French Guiana: raisin du bord de la mer French West Indies : Bois Baguette, Bois Rouge Montagne, Raisinier À Grappes German : Meertraube, Seetraube, Gemeine Seestraube, Meertrau benbaum, Strandtraube, Coccoloba uvifera, Gewöhnliche Guyana Arawak: matora Guyana Creole: sea grape, seaside grape Honduras: Papaturro Mexico: niiche Netherlands: zeedruif, gewoone Portuguese : Cipo Branco De Pernambuco, Uva- Da-Praia, cocoloba, uva do mar Puerto Rico : Cucubano, Gateado, Uva-Del Mar, Uvero, Uvillo; Spanish : Arahueque, Cumare Blanco, Manzano, Micongo, Nula, Palo Mulato, Papatón, Uva Caleta, Uva De La Playa, Uva De La Costa, Uva De Mar, Uverna, Papaturro; Uvero, Uvero De Playa, Uvero Macho, Zapatero Surinam : Dreifi , Droifi, Zeedruif, Zee-Druif, Matora, sistridroifi Swedish: Havsdruva Trinidad: Cuchape, Uvero Del Monte Venezuela: Uvero De Playa |
| Plant Growth Habit | Sprawling evergreen shrub or small tree |
| Growing Climates | Tropical climatic conditions mainly grows in the coastal hammocks, coastal scrub, coastal grasslands and beach strands |
| Soil | Widely tolerant to most soils, provided they are well drained. It grows well in sandy soil but usually grows faster and larger in more fertile soils. Minor element deficiencies may appear in calcareous soils. |
| Plant Size | 2–15 m high with a bole of 30–60 cm |
| Bark | Smooth grayish to mottled with patches of white, gray, and light brown bark that peels off in flakes, with reddish sap, inner bark is light brown |
| Twigs | Green and puberulent when young, grey at maturity, glabrous or pubescent |
| Leaf | Alternate, short-petioled, large, leathery, glossy, dark green, broadly bean-shaped, with wavy margins, up to 15 centimeters long, 8 in (20.3 cm) in diameter |
| Inflorescences | Inflorescences 10–30 cm, puberulent or glabrous, pistillate pendent in fruit; peduncle 1–5 cm, glabrous. Pedicels 1–4 mm, glabrous |
| Flowering season | January to august |
| Flower | Small, white, and fragrant with five petals and eight stamens and bloom mainly in spring |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Globose to pear-shaped fruit about 3/4 inches in diameter and size of a large marble but a bit tougher than the ordinary grape |
| Fruit Color | Green turning shiny rose-purple when mature |
| Propagation | Seeds and stem cuttings |
| Taste | Varies from acid to sweet and insipid |
| Plant Parts Used | Leaves, bark, roots, fruit |
| Season | March to October |
| Health Benefits |
|