The plant is commonly known as Mrigashringa in Sanskrit where the name is derived from Mriga meaning deer and shringa means horn from the twisted form of the carpels. Apart from that the word Helicteres is derived from, the Greek word helikteres meaning anything twisted / in spiral. Isora is a Japanese name for boys meaning God of the seashore. Helicteres is a large genus of tropical trees and shrubs with axillary flowers and fruits consisting of five twisted carpels. Two varieties of plant are distinguished, variety tomentosa in which the underside of the leaves is glabrous and variety glabrescens in which both sides of the leaves are nearly glabrous.
Plant Description
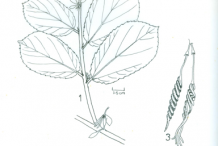
Indian screw tree is a sub deciduous shrub or a small tree that grows about 5–8 m tall. The plant is found growing in dry deciduous, evergreen forests, scrub, dry grasslands on slopes, also in plantations and plains and secondary jungle along roads and forest edges. The plant prefers fertile soils rich in humus. Stem is 1-2 inches in diameter. Bark is pale greyish, finely wrinkled and young parts are covered with stellate hairs.
Leaves
Leaves are simple, alternate, bifarious, 7.5-12.5 cm by 5-10 cm oblong, ovate or obliquely cordate and shortly acuminate, closely dotted on both surfaces with stellate hair. Margin is serrate, scabrous above and pubescent below. Petiole is 6-9 mm long and stipule is subulate 6 mm long. Twigs, petioles and both the upper and lower surfaces of the leaf blade clothed in stellate hairs.
Flower
Flowers are produced along the stems. They occur solitary or in sparse clusters of 2-6 which appear in rainy season. They are red in color and turn pale blue when old or leaden blue when attacked by insects. They are 2.5-3.8 cm long, distinctly bilabitate, pedicles are very short, stellately tomentose, bract small, subulate, hairy, calyx tubular 2 cm long, 2 lipped. Petals are closely hooked together. Staminal column is fused with the gynophores. 10 anthers are present in a ring round the ovary which is conical and placed on curved gynophores. Style is as long as the ovary and deflexed.
Fruit
Fruits are compound pod, twisted like screw with pointed end, signifying the name “Indian Screw Tree”. They are 5.0-6.3 cm long, beaked and cylindrical with 5 follicles spirally twisted like a corkscrew born at the tipofalong gynophore. Raw fruits are greenish in color turning to brown or grey when dried. Each follicle consists of 15-28 seeds placed in a row which are brown black in color, rhomboid, highly polished, rectangle or triangular in shape. When the fruit ripens they untwine and scatter the seeds contained in them. The plant is propagated by seed, but vegetative propagation with stem cuttings is also possible.
It is an ayurvedic herb, distributed widely in forest throughout India. Almost all parts are used traditionally. The fruits are useful in diarrhea, dysentery, wounds, ulcers, hemorrhages and diabetes. Roots and stem barks are considered to be expectorant, demulcent, astringent and anti-glactagogue. Bark is used in diarrhea, dysentery, scabies, and biliousness and is useful in gripping of the bowels. Root juice is used in antidiarrheal and anti-dysenteric formulations. Fried pods are given to children to kill intestinal worms.
History
Indian screw tree is a tropical Asian shrub or medium sized tree found all throughout India from Punjab to Bengal; Jammu to South India. However, it gregariously grows in dry deciduous forests of central and western India up to 1500m on the hill slopes. The plant is commonly grown in dry deciduous, evergreen forests, scrub, dry grasslands on slopes, also in plantations and plains and secondary jungle along roads and forest edges. It is also found in Malay Peninsula, Java, Australia. Today the plant is grown in several parts of the world due to its medicinal values and health promoting benefits.
Ethno-botanical claims and their probable scientific explanations
| Screw Tree Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Screw Tree |
| Scientific Name: | Helicteres isora |
| Origin | Asia including India, South china, Malay Peninsula, Java and Saudi Arabia and also in Australia |
| Colors | Initially greenish in color turning to brown or grey when dried |
| Shapes | 5.0-6.3 cm long, greenish-brown, beaked and cylindrical with 5 follicles spirally twisted like a corkscrew |
| Taste | Sweet, bitter, astringent |
| Health benefits | Beneficial for Abdominal diseases, Eczema, Blood Dysentery, Gastrointestinal problems, Flatulence, asthma, Diabetes, Fever, diarrhea, |
| Plant parts | Disease | Ethno-medicinal use |
| Bark | Diarrhea | Bark boiled with water taken orally thrice per day |
| Fruits | Diabetes | 1 fresh fruits each taken orally |
| Gastrointestinal problems | Approx. 5 g fruit powder with salt is to be taken thrice daily with water | |
| Weakness in new born baby | 1) Fruit paste mixed with mustard oil and turmeric paste is used for massaging in new born baby to cure profound weakness.
2) Fruits are fried in mustard oil, used on new born baby to remove body pain. |
|
| Post- Delivery weakness | Fruit powder along with other herbs and spice mixed sweet dish is given to women after child birth. It may be given to them during pregnancy. | |
| Sores of ear | Fruits are made into liniment for sores of ear | |
| Seeds | Dysentery | 5 g seed powder boil with water; taken twice a day |
| Root | Diabetes | Fresh root juice taken twice a day |
| Cuts and wounds | Fresh root paste with turmeric paste is applied externally | |
| Diarrhea | Root decoction | |
| Leaves | Scabies | Paste is applied externally twice per day till cure on infection area of scabies |
| Skin infections
|
Fresh leaf paste applied thrice a day | |
| Snake bite | Fresh leaf paste applied on affected area |
Traditional uses and benefits of Screw Tree
- Different parts of the plant are traditionally used in the indigenous medicine system to cure various ailments.
- Fruits are used to prepare medicines for children.
- Roots and the bark are used as an expectorant, demulcent, constipating and lactifuge and useful in colic, scabies, gastropathy, diabetes, diarrhea and dysentery.
- Fruits are used as astringents, refrigerant, stomachachic, antispasmodic, haemostatic and vermifuge.
- They are also used in griping of bowels, flatulence, colic, diabetes, diarrhea and dysentery.
- Root juice and fruits are topically applied to cure snake bite.
- Fruit powder mixed along some other herbs and spices is given to new mothers as laddoo (Indian sweet dish) in order to cope with post-delivery weakness.
- Stems of this plant are used as anti-helminthic, colic.
- Fruits are used as colic, anticonvulsant and abdominalgia.
- Root juice is said to be useful in diabetes, emphysema and snakebite.
- Leaf paste is claimed to be effective against various skin ailments such as eczema and scabies.
- Fruit pod extracts are found to be anti-dysenteric, vermifuge (colic).
- It is also used in flatulence, stomach ache, gout and as astringent.
- Fruits are fried in mustard oil and used to apply on the body of new born babies to relieve pain.
- Root decoction/juice and the paste are stated to be traditionally used in ISM against diabetes, diarrhea, emphysema, stomach afflictions and asthma.
- Extract is used as anthelmintic; for treatment of gastro-spasm on Java Island; and as an antispasmodic, antipyretic, anti-diarrheic and anti-dysenteric in Saudi Arabia.
- Fruits are used in diarrhea as well as constipation of new born baby.
- Aqueous extract of its root, one teaspoonful is given for 3-7 d for the treatment of dog-bite in Utter Pradesh.
- Tribals of Singbhum district of Bihar use the fruits as an amulet in neck to treat disease of malnutrition, which is locally known as Dubli disease among children.
- Powdered seeds are used to cure ulcers in ears, dysentery and stomachache.
- Seed powder is used as an aphrodisiac to improve the quality of the sperms, their total count.
- They are also used for improving physical stamina and strength.
- It is extensively used for general physical strengthening, anti-aging, blood sugar stabilization, injury healing, and urinary tract rejuvenation.
- It also enhanced brain functioning potency, bone healing, and kidney rejuvenation.
- It is use to maintain physical, sexual and mental strength and to maintain youth and long life.
- It is also effective in treating kidney, and lower back pain, threaten abortion, leucorrhoea, seminal debility efficient in treating dryness of the lungs and throat, consumptive diseases (lingering cough, dry cough), tuberculosis and blood- tinged sputum.
- Bark and fruits are used for anti-galactogogue, soothing, demulcent, expectorant, and useful in respiratory troubles, dysentery, diarrhea, diabetes, stomachache and scabies.
- Paste made of stem bark of Grewia tiliaefolia and Helicteres isora together with tuber of Amorphophallus paeoniifolius are applied for bone setting.
- Roots are used in cough, asthma and root paste are warmed and applied on boils.
- Mixture of water extracts of roots of Celastrus paniculatus, Helicteres isora, Imperata cylindrica and Rhynchosia minima given as an antidote for snake poison.
- Root extract of Woodfordia fruticosa along with extract of Helicteres isora is given as antidote in snakebite.
- Fruits or roots of Helicteres isora, seeds of Pongamia glabra and stem bark of Tinospora cordifolia mixed and crushed into powder and consumed to cure diabetes.
- Seed decoction or the aqueous extract of the seeds are used in dysentery and stomach pains.
- Paste of dried leaves, pepper and coconut oil is used in the treatment of skin ailments including eczema.
- Fruits are soaked in boiling oil and this oil is applied externally in stomach complaints of children.
- Fruit powder in beneficial for diarrhea and dysentery.
- It is considered that twigs placed on the door of the hut of a pregnant woman are beneficial for relieving the labor pains.
- Tribal use to hang a dry fruit in black thread on neck of children against pain, a fruit hung around the neck of a patient as a postpartum remedy.
- Fresh fruits are made into garland and tied as necklace for scabies.
- Fruits are tied to the waist of children to cure muscular pain, fever and swelling.
- Roots along with leaves of Phyllanthus reticulatus are pounded and the extract is given orally in insect bite.
- Fruits of Gardenia latifolia along with leaves of Jasminum auriculatum, stem bark of Helicteres isora pounded and the extract given orally for tympany.
- Roots along with those of Coccinia grandis and leaves of Jasminum auriculatum pounded and the extract given orally for tympany.
Ayurvedic Health benefits of Screw Tree
- Ear Drops: Crush the pods of Screw Tree. Heat it in castor oil. Strain and use it as ear drops.
- Fever: Consuming 10-20 ml of decoction prepared from equal amount of Devil’s Horsewhip and fruit of screw tree is beneficial for overcoming fever.
- Diarrhea: Make a decoction with bark and pods of Screw Tree. Drink 5 ml of it once a day.
- Asthma: Drink 3 ml bark decoction of Screw Tree twice a day.
- Skin Diseases: Crush the leaves of Screw Tree to make a paste. Apply it on damaged or infected skin.
- Urinary Disorders: 15-20 ml of Root bark decoction along with rock sugar is beneficial for urinary disorders.
- Abdominal diseases: Prepare a seed decoction of Screw Tree. Have 4 ml of it once a day.
- Colic pain: Roots of tree are chewed in dose of 5 grams per day for three days.
- Eczema: Paste prepared from root bark and fruit is beneficial for eczema.
- Blood Dysentery: 1-1 fruits of Screw Tree are soaked in water and are then mashed and filter the juice. Consuming the juice is quite beneficial for blood dysentery.
- Cut and wounds: Fresh root paste with turmeric paste is applied externally.
- Gastrointestinal problems: Fruit powder 5 g is taken thrice daily with water.
- Skin infections: Fresh leaf paste applied thrice a day.
- Abdominal pain: 10-15 ml Screw tree’s plant decoction is quite beneficial for abdominal pain.
- Flatulence: 500 mg of powder when taken with Himalayan black salt is beneficial for overcoming flatulence.
- Snakebite: Fresh leaf paste applied on affected area.
- Weakness in new born baby: Fruit paste mixed with mustard oil and turmeric is used for massaging in new born baby to cure profound weakness.
- Worm Infestation: 500 mg of Fruits of screw tree is fried and is given to kids with worm infestation. It helps to eliminate the worms from the body.
- Abdominal Pain: 1-2 gram of fruit powder when taken regularly helps to prevents abdominal pain.
- Dysentery, stomach ache
- The fruit paste or powder is taken in dose of 5 grams twice a day for three days.
- Bark boiled with water taken orally thrice per day.
- Seed powder, 5 g boiled in water is taken twice a day.
- Diabetes
- One fresh fruit taken orally.
- Fresh root juice taken twice a day.
- Scabies
- The root or bark paste is applied topically for scabies.
- The Paste is applied externally twice per day till cure on infection area of scabies.
Other facts
- Barks give a coarse fiber and wood used for fuel.
- Fiber is extracted from the young branches to make ropes to tie the cattle.
- It is used as cordage for making cots, tying cattle and ploughs.
- In India it is known as “kaivun fibre” and is used for making ropes and sacks and as supplementary raw material for paper making.
- H. isora is not only used for fiber and medicine but also for fodder, fuel and gunpowder in India.
References:
https://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/go/204328/
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-2843218
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Helicteres_isora
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4025269/
https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Helicteres_isora_(PROSEA)