 Moles are common skin growths that can appear anywhere on the body. While most moles are harmless, some can be cancerous or develop into skin cancer over time. For this reason, many people consider removing moles for cosmetic or medical reasons.
Moles are common skin growths that can appear anywhere on the body. While most moles are harmless, some can be cancerous or develop into skin cancer over time. For this reason, many people consider removing moles for cosmetic or medical reasons.
Understanding Moles
What Are Moles?
Moles are common skin growths that usually appear in childhood or adolescence. They can appear anywhere on the body and vary in color from pink, brown, or black. Moles can be flat or raised, and the texture can range from smooth to rough. Most moles are harmless and do not require any treatment. However, some moles can develop into skin cancer.
Moles are caused by an overgrowth of pigment cells in the skin called melanocytes. The exact cause of this overgrowth is unknown, but genetics and sun exposure are thought to play a role. People with fair skin, light-colored hair, and blue or green eyes are more likely to have moles.
Types of Moles
There are several types of moles, each with its own characteristics:
- Congenital Moles: These are moles that are present at birth. They can be small or large and vary in color and shape. Large congenital moles have a higher risk of developing into skin cancer.
- Acquired Moles: These are moles that develop after birth. They usually appear in childhood or adolescence and can continue to develop into adulthood. Acquired moles can be flat or raised and vary in color.
- Atypical Moles: These are moles that have an irregular shape, color, or texture. They are larger than normal moles and have a higher risk of developing into skin cancer.
- Spitz Nevi: These are moles that are usually pink or reddish-brown and can resemble melanoma. They are more common in children and adolescents.
- Halo Moles: These are moles that have a white ring around them. They are usually harmless but can be a sign of an immune system disorder.
It is important to monitor moles for any changes in size, shape, or color. If a mole becomes itchy, painful, or starts to bleed, it is important to see a dermatologist. They can perform a biopsy to determine if the mole is cancerous and recommend the appropriate treatment.
Pros of Removing Moles
Mole removal is a common procedure that can be done for a variety of reasons. While there are some risks involved with any surgical procedure, there are also many benefits to consider. Here are some of the pros of removing moles:
Cosmetic Benefits
One of the most common reasons people choose to have moles removed is for cosmetic reasons. Moles can be unsightly, especially if they are in a visible location like the face or neck. Removing a mole can improve a person’s appearance and boost their self-confidence. In some cases, removing a mole can also make it easier to apply makeup or shave.
Preventing Skin Cancer
Another benefit of mole removal is that it can help prevent skin cancer. While most moles are harmless, some can turn into cancerous growths over time. By removing a mole, a dermatologist can eliminate the risk of it becoming cancerous. This is especially important for people who have a family history of skin cancer or who have had a lot of sun exposure in their lifetime.
It is important to note that not all moles need to be removed. A dermatologist will evaluate each mole on a case-by-case basis to determine if it is necessary to remove it. In some cases, a mole may be monitored over time to ensure it does not change or become cancerous.
Cons of Removing Moles
While removing a mole may seem like a simple procedure, it is not without its risks and potential downsides. Here are some of the cons of mole removal that you should consider before deciding to go through with the procedure.
Potential Scarring
One of the most common downsides of mole removal is the potential for scarring. Depending on the size and location of the mole, removing it by surgical means may leave a noticeable scar. This is especially true if the mole is large or located in a prominent area, such as the face.
To minimize scarring, dermatologists may use techniques such as shaving the mole or using laser therapy. However, even with these techniques, scarring is still a possibility.
Risk of Infection
Another potential downside of mole removal is the risk of infection. Whenever the skin is broken, there is a risk of bacteria entering the wound and causing an infection. This is why it is important to keep the area clean and dry after the procedure.
In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent infection. If you notice any signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or discharge, be sure to contact your dermatologist right away.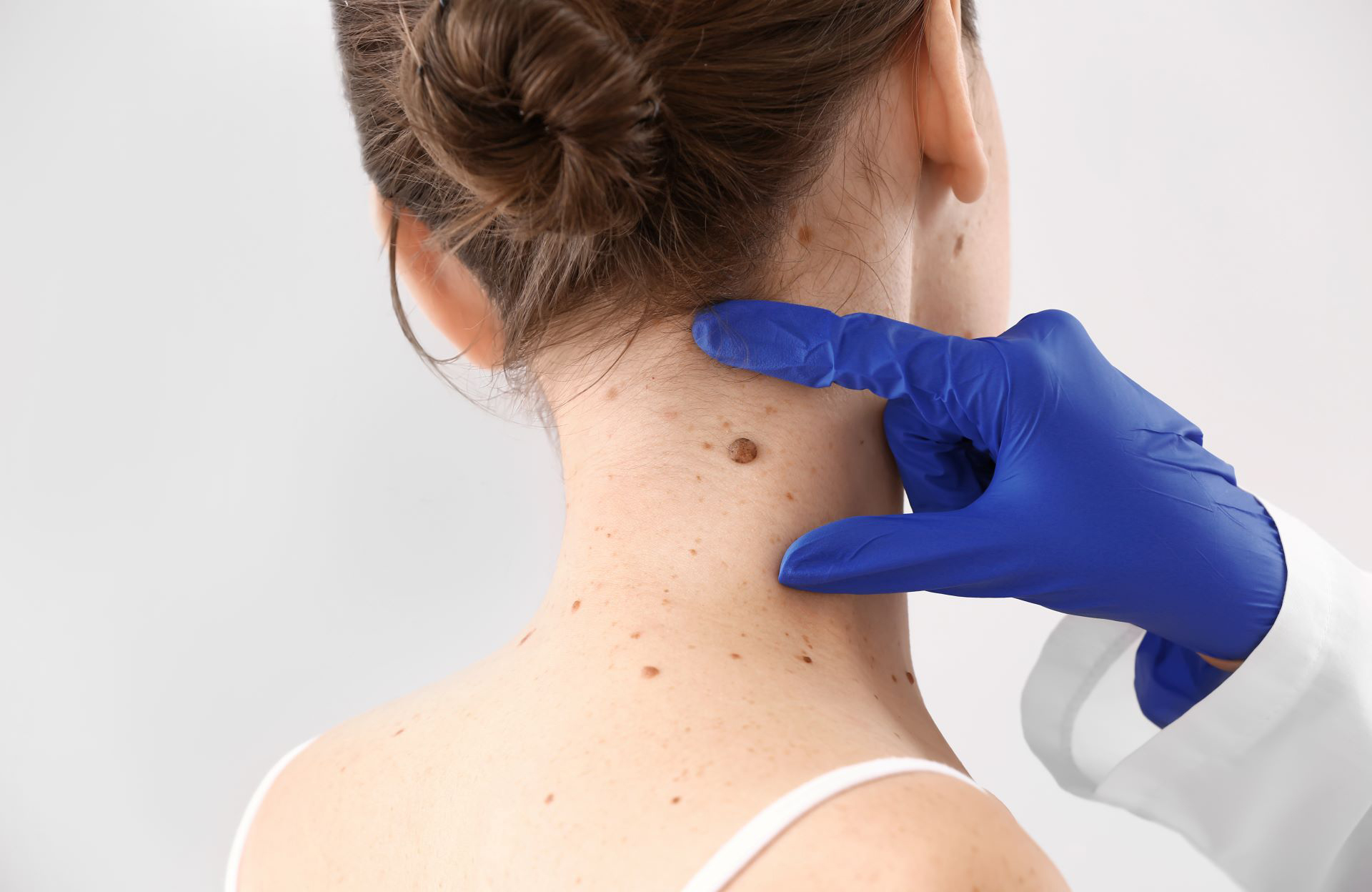
When to See a Dermatologist
If you have a mole that is causing concern, it is important to see a dermatologist. Dermatologists are trained to identify and treat skin conditions, including moles. Here are some signs that indicate it is time to see a dermatologist:
Signs of Malignant Moles
Malignant moles, or melanomas, are a type of skin cancer that can be deadly if left untreated. It is important to see a dermatologist if you notice any of the following signs:
- A mole that is asymmetrical
- A mole that has an irregular border
- A mole that has multiple colors or shades
- A mole that is larger than a pencil eraser
- A mole that is evolving or changing in size, shape, or color
If you notice any of these signs, it is important to see a dermatologist as soon as possible. Early detection and treatment of melanoma can save lives.
Mole Changes
Even if a mole does not show signs of malignancy, it is still important to see a dermatologist if it changes in any way. Changes to a mole can indicate a problem, so it is important to have it checked out. Some changes to watch for include:
- A mole that becomes itchy or painful
- A mole that bleeds or oozes
- A mole that crusts or scabs
- A mole that becomes raised or develops a lump
- A mole that develops a rough or scaly texture
If you notice any of these changes to a mole, it is important to see a dermatologist. They can examine the mole and determine if it needs to be removed or biopsied.
Removal Methods
Moles can be removed through various methods, including surgical excision and laser removal. Here are the pros and cons of each method:
Surgical Excision
Surgical excision involves cutting out the mole and stitching up the wound. This method is typically used for larger moles or those that are suspected to be cancerous.
Pros:
- It is an effective method for removing moles
- The mole can be sent to a lab for testing to determine if it is cancerous
- The wound typically heals well with minimal scarring
Cons:
- It can be more invasive than other methods
- There is a risk of infection or bleeding
- The wound may take longer to heal than other methods
Laser Removal
Laser removal involves using a laser to break up the pigment in the mole. The mole will then scab over and fall off.
Pros:
- It is a quick and relatively painless method
- There is no cutting involved
- There is minimal scarring
Cons:
- It may not be as effective as surgical excision for larger or deeper moles
- It may require multiple treatments
- It can be more expensive than other methods
Overall, the method of mole removal will depend on the size, location, and suspected cancerous nature of the mole. It is important to consult with a dermatologist to determine the best method for each individual case.
Post-Removal Care
After mole removal, it is important to take proper care of the wound to promote healing and prevent infection. The healing process can take several weeks, and it is important to follow the dermatologist’s instructions carefully.
Healing Process
The healing process for mole removal can vary depending on the size and location of the mole. In general, it takes about 7-14 days for the wound to heal. During this time, it is important to keep the area clean and dry to prevent infection. The dermatologist may recommend applying an antibiotic ointment to the wound to prevent infection and promote healing.
In some cases, the dermatologist may use stitches to close the wound. If this is the case, the stitches will need to be removed after about 7-10 days. The dermatologist will provide instructions on how to care for the wound and when to return for a follow-up appointment.
Preventing Infection
Preventing infection is an important part of post-removal care. The dermatologist may prescribe an antibiotic ointment to apply to the wound, and it is important to follow their instructions carefully. In addition, keep the wound clean and dry, and avoid touching the area with dirty hands.
If the wound becomes red, swollen, or painful, or if there is pus or drainage from the wound, it may be infected. Contact the dermatologist immediately if any of these symptoms occur. They may prescribe antibiotics to treat the infection.
It is also important to avoid exposing the wound to sunlight until it has fully healed. Sun exposure can cause scarring and discoloration of the skin. If you must be in the sun, cover the area with clothing or a bandage and apply sunscreen to the surrounding skin.

