It’s Latin name salvia, meaning “health”, “salvation” or “to save”, refers to the plant’s powerful healing properties. The specific epithet miltiorrhiza means “red juice extracted from a root”. It is used in many parts of the world to treat various conditions due to their excellent medicinal values. It is rich sources of tanshinone I, tanshinone II, miltirone and salvianolic acid and a wide range of chemical compounds. The root and rhizome of this plant have been used as traditional Chinese medicines for more than 2 500 years. Root and rhizome has been developed into various kinds of herbal medicine products and used in at least 19 countries or regions for their therapeutic value and market potential in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, neurasthenic insomnia, liver fibrosis and cancer. It has also been used as an ingredient in health supplements and cosmetics.
Red Sage Facts
| Red sage Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Red sage |
| Scientific Name: | Salvia miltiorrhiza |
| Origin | China and Japan |
| Colors | Black or dark brown when ripe |
| Shapes | Nutlets are oval to oblong, 3.2 mm long and 1.5 mm wide |
| Taste | Bitter |
| Health benefits | Prevents Heart attack, Circulatory stimulant, Circulatory congestion, Sedative, Cooling herb, Improve Osteoporosis, Neuro protective Effects, Menstruation and Fertility, Bone Health, Heals Wounds, Antibacterial and Insecticidal Activity, Reduces Risks of Ischemic Stroke, Treats Liver Fibrosis, Improves Vision for Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy, Relieves Menstrual Cramps, |
| Name | Red Sage |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Salvia miltiorrhiza |
| Native | China and Japan and is cultivated for commercial use in northeast China and Mongolia |
| Common Names | Chinese salvia, Redroot sage, red sage, Dan shen, Danshen, Radix, Tan-shen, Tanshen, red-rooted sage |
| Name in Other Languages | Chinese: Dan shen Danish: Kinesisk salvie Dutch: Chinese salie, rode salie English: Chinese salvia, Redroot sage, red sage, Dan shen, Danshen, Radix, Tan-shen, Tanshen, red-rooted sage Finnish: Kiinansalvia German: Rotwurzel-Salbei, Chinesischer Salbei Korean: Dansam Macedonian: Danshen (Даншен) Norwegian: Rødrotsalvie Swedish: Rödrotssalvia Thai: Tạng seī ym (ตังเซียม) Vietnamese: Đan sâm |
| Plant Growth Habit | Hardy, deciduous, perennial flowering plant |
| Growing Climates | Hillsides, stream sides, forests, light woodland, clearings and sunny sides of hills |
| Soil | Prefers moist, sandy and well-drained soil and full or half sun |
| Plant Size | 80 to 100 cm Tall |
| Root | Long, thin, cylindrical, and covered with earthy red skin |
| Stem | Erect, 40-80 cm tall, villous, much branched |
| Leaf | Simple to odd-pinnate; petiole 1.3-7.5 cm, densely retrorse villous, petiolule 2-14 mm; leaflets 3-5(-7), 1.5-8 × 1-4 cm, blades or leaflets circular to broadly lanceolate, pilose, densely so abaxially, margin crenate, apex acute to acuminate. |
| Flowering season | June to September |
| Flower | Flowers grow in whorls, with light purple to lavender blue corollas that are approximately 2.5 cm (0.082 ft) long, with a dark purple calyx |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Nutlets are oval to oblong, 3.2 mm long and 1.5 mm wide |
| Fruit Color | Black or dark brown when ripe |
| Propagation | By seeds or root division |
| Plant Parts Used | Whole plant |
| Available Forms | Extracts, capsules, tablets and teas |
| Taste | Bitter |
| Season | Sep-Oct |
| Health Benefits |
|
Plant Description
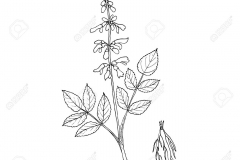
Red sage is a hardy, deciduous, perennial flowering plant that normally grows about 80 to 100 cm tall. The whole plant is covered with dense yellowish pubescence and glandular hairs. The plant is found growing in hillsides, stream sides, forests, light woodland, clearings and sunny sides of hills in the west and southwest provinces of China. The plant prefers moist, sandy and well-drained soil and full or half sun. Roots are long, thin, cylindrical, and covered with earthy red skin. Stems have four prisms and branch on upper part. The herb is propagated by root division in spring. The root is harvested from late autumn through to early spring.
Leaves
Leaves are simple, opposite and with odd pinnate. Petiole is 1.3-7.5 cm, densely retrorse villous, petiolule 2-14 mm. Leaflets are about 3-7 and are 1.5-8 cm long and 1-4 cm wide, blades or leaflets are circular to broadly lanceolate, pilose, densely so abaxially, margin crenate and apex acute to acuminate. Both surfaces of the leaves are covered densely with white pubescence.
Flower
The inflorescence is terminal and axillary verticillaster, with 3 to 10 flower each round and an alienated raceme arranged by many rounds of flowers and covered with hairs and sticky glands. Flowers grow in whorls, with light purple to lavender blue corollas that are nearly 2.5 cm (0.082 ft.) long, with a dark purple calyx. Flowering normally takes place from June to September.
Fruits
Fertile flowers are followed by 3.2 mm long and 1.5 mm wide, oblong nutlets that are dark brown or black when ripe, and wrapped in persistent calyx.
Health benefits of Red Sage
Danshen is a powerful herb with a lot of properties that could improve your health. It is presently going through trials and may even become the first traditional Chinese remedy to gain approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Below are some of the well-known benefits of Red Sage
1. Prevents Heart attack
The whole herb (rather than isolated constituents) has been used in China to assist patients who are recovering from a heart attack, and it appears to support heart function at this critical time. Clinical research in China, however, has shown that Red sage is most effective when taken as a preventive, rather than as a remedy after the heart attack has taken place. (1)
2. Circulatory stimulant
Red sage has been honored by the Chinese for thousands of years as a circulatory stimulant. Like hawthorn, it is a safe effective remedy for many circulatory problems. It mostly benefits the coronary circulation, opening up the arteries and improving blood flow to the heart, and is thus supportive in treating coronary heart disease. Although it does not lower blood pressure, it relaxes the blood vessels and improves circulation throughout the body.
3. Circulatory congestion
Red sage is used traditionally to treat conditions caused by blood stagnation, mainly those affecting the lower abdomen, such as absent or painful menstrual periods and fibroids.
4. Sedative
The sedative action of Red sage helps calm the nerves, and it is thus helpful in treating angina, a condition made worse by anxiety and worry. Palpitations, insomnia, and irritability also benefit from Red sage’s sedative properties.
5. Cooling herb
Red sage is a soothing remedy that is used to remove “excess heat,” mostly in the heart and liver. It can also relieve inflammatory skin problems, such as abscesses, boils, and sores.
6. Improve Osteoporosis
Clinical trials involving red sage show that it has effectively targeted osteoporosis. It’s supposed that the herb provides strong compounds targeting specific pathways in bone resorption and bone formation.
7. Neuro protective Effects
Research has displayed that acute treatment with herbal extracts containing red sage and cacao has neuro protective effects in stroke models.
When stroke animals received red sage and cacao extracts, they showed a significant reduction in ischemic cell death and better performance in routine motor and neurological tasks.
8. Menstruation and Fertility
Salvia miltiorrhiza is commonly taken for menstrual problems like irregular bleeding. There isn’t actually much hard evidence that it has an effect. It just hasn’t really been studied, so most of the evidence relies on clinical use in traditional medicine and not on severe trials.(2), (3)
Danshen also has estrogen-like effects in rats, which may help improve menopause symptoms.(4)
9. Bone Health
Studies in rodents suggest that compounds in Red sage might allow bones to heal from fractures more quickly. The herb also prevents bone loss in menopausal rats.(5), (6), (7)
10. Heals Wounds
Research has shown that it consists of anti-microbial properties too. These anti-microbial properties can be beneficial to humans and plants alike, since Red sage root could be manufactured into a natural protection for agricultural crops. The tested Red sage root compound demonstrated antimicrobial properties against eight bacterial species and one fungal species.(8), (9)
11. Antibacterial and Insecticidal Activity
Red sage kills certain species of bacteria, including bacteria that are resistant to antibiotics, in dishes. Moreover, it was used to make a silver-based compound that can kill both bacteria and the mosquitoes that spread the Zika virus.(10), (11), (12)
12. Reduces Risks of Ischemic Stroke
Two clinical researches have demonstrated that Red sage root, when combined with other traditional Chinese medicines, can reduce the rate of ischemic stroke as well as the mortality of strokes. Ischemic stroke occurs due to blood clots and is the most common type of stroke in older adults. Red sage extract, combined with other traditional herbs, treat the convalescent phase of ischemic stroke (after the stroke has occurred). (13)
Red sage root is also believed to help prevent stroke recurrence. Naoxintong capsule, which consists of Red sage root, is in Phase IV of clinical trials. The capsule is effective at preventing the recurrence of strokes after the first stroke and decreasing the negative impacts of strokes. These studies, combined with the heart medication studies, show that Red sage root is coming to be recognized as a powerful ingredient in Western medicine.(14)
13. Treats Liver Fibrosis
Research has shown that Red sage root is an effective treatment for liver fibrosis, which is the buildup of scar tissue, due to hepatitis B. Over time, scar tissue can prevent the blood infusion in the liver, hardening the cells. Red sage root compound called salvianolic acid B was shown to inhibit the production of cells, called LX-2, that become scar tissue. Fibrosis has varying levels of severe ness with cirrhosis as the most severe. Applying Red sage compounds during the less severe stages could help prevent degeneration into severe cirrhosis. (15)
14. Improves Vision for Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy
Clinical trial is presently recruiting patients for testing the effects of Red sage root in treating poor vision and blindness, which can stem from diabetes. Degeneration of vision is often caused by bulging or leaking blood vessels. Though this study is evaluating a non-heart condition, the study demonstrates that Red sage root is capable of treating blood-based disorders in other areas of the body.(16)
15. Relieves Menstrual Cramps
Red sage root has been used to treat menstrual cramps for millennia in China; the treatment may soon be available in the United States as well. Red sage root promotes a healthy menstrual cycle when sharp fixed pain and clotting of the blood occur, another form of ‘blood stagnation.’” Research is presently underway examining the efficacy of treatments from two different areas in China. If approved, a Red sage based menstrual drug would be a more natural alternative to Midol.(17)
Traditional uses and benefits of Red sage
- Red sage has long been used in Chinese medicine and recent research has confirmed the validity of its use in the treatment of heart and circulatory problems.
- Root is adaptogen, alterative, anti-cholesterolemic, anti-rheumatic, antiseptic, antispasmodic, astringent, emmenogogue, hepatic, sedative, tonic and vulnerary.
- It acts mainly on the heart energy, removing excess heat and clearing stagnation.
- Its use improves the micro-circulation, increases blood flow to the coronary artery, improves myocardial contraction and adjusts the heart rate.
- It has an antibacterial action, preventing the growth of Pseudomonas, E. coli, Vibrio Proteus, Bacillus typhi, Shigella dysenteriae, Shigella flexneri, Staphylococcus aureus etc.
- It is used internally in the treatment of coronary heart disease, poor circulation, palpitations, irritability, insomnia, breast abscesses, mastitis, ulcers, boils, sores, bruises, menstrual problems and post-natal pains.
- Red sage has been used to improve body function (e.g., promote circulation, blood flow), as well as to treat hemorrhage, dysmenorrhea, miscarriage, swelling, insomnia, and hepatitis.
- It has also been used for treating heart disease, including conditions like atherosclerosis, thrombosis and hypertension.
- It is often used as a treatment for high blood pressure by opening up the arteries and improving blood flow.
- The herb may be useful in treating osteoporosis.
- It has been used to lessen stress and ease anxiety which in turn has a favorable effect on angina pectoris that is worsened by anxiety and stress.
- It is also used for menstrual disorders, diabetes, chronic liver disease, and insomnia caused by a rapid heartbeat and tight chest.
- It is regarded as antibacterial and anti-inflammatory and has been used as a remedy for skin conditions such as acne, psoriasis, and eczema.
- It is also used to relieve inflammation, lessen bruising and to speed up wound healing.
- Herb might be useful in lowering “bad” cholesterol (LDL) and increasing the production of “good” cholesterol (HDL).
- It is known to inhibit bacteria such as Staphylococcus (Staphylococcus aureus) and Tuberculosis (Mycobacterium tuberculosis).
Ayurvedic Health benefits of Red sage
- Heart Enlarged: Take 10 drops of extract or tincture.
- Liver Diseases: Take 1 to 2 g powder of Yellow Dock root, Dandelion root, Red sage, Sarsaparilla, and Pau de Arco. Mix each Herb into a wide mouth jar. Shake it up and your perfect formula for liver detoxification is ready. Prepare the tea and add 2-3 full drops of the Milk Thistle Seed extract to the tea. Let it cool and drink. Take this tea twice a day.
- Buerger’s Disease: Mix 1 teaspoon each of Dong Quai and Red Sage. Consume it with a glass of water, twice daily.
- Debility: Ginseng Korean, Polygonatum, Chinese Knotweed, Dong Quai, Schisandra, Wild Yam, Chinese Licorice, Goji Berry, White Peony, Hoelen, Eucommia, Glehnia, Cornus Officinalis, Citron, Paeonia Suffruticosa, Red Sage and Bupleurum in conjunction are beneficial for Energy, Stamina and improve overall feeling of well-being. OR You may buy the formula, containing the above mentioned Herbs. Capsule form is readily available. Consume 1 capsule per day.
Dosage and Administration
As a tea (infusion): Add 1/2 or 1 teaspoon of the dried herb to one cup of boiling water, steep for 15 mins and then strain. For therapeutic reasons 1 cup, three times daily is often recommended. The tea can also be used as a gargle and mouthwash as required.
As a tincture: Take 30-60 drops, in water or juice three times daily.
As a fluid extract: Take 15-30 drops, in water or juice three times daily.
For all commercial preparations containing the herb, the manufacturer’s instructions should be followed.
Precautions
- Red sage may potentiate the effects of the anti-coagulation drug warfarin, possibly causing bleeding complications.
- Other adverse effects may include allergic reactions, dizziness, headache, or gastrointestinal upset.
- It’s recommended that you don’t use it for more than a three-week period without taking a one-week break.
- Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should not use red sage, as there isn’t enough evidence to support its safety.
- People suffering from Haemoptysis, Hematuria and Hyper menorrhea should avoid taking this herb.
- Excess intake may cause dizziness, headache, dry mouth, weakness, numbness, dyspnea, anxiety, nausea, vomiting, tachycardia, and gastrointestinal disorders.
- If you take pharmaceutical medications or have a health condition, speak to your doctor before using red sage therapeutically. The herb can interact with heart medications and blood thinners.
- Tinctures made from the herb can cause upset stomach and minor skin reactions.
- This herb may cause allergic reactions, manifested as body itching, rash, hives, chest tightness, and some also sees choking sensation in chest and short of breath, difficulty breathing, and even chills, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, irritability, pale complexion, cold extremities, sweating, declining blood pressure, and even faint due to shock.
References:
http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=2&taxon_id=200020230
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Salvia+multiorrhiza
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salvia_miltiorrhiza
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?402704
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-183206
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/SALML