Red Bead Tree Facts
| Red Bead Tree Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Red Bead Tree |
| Scientific Name: | Adenanthera pavonina |
| Origin | Southern China and India, and widely naturalized in Malaysia, Western and Eastern Africa |
| Colors | Green turning to dark brown and eventually woody black |
| Shapes | Dehiscent seedpods or fruits that are thin, curved, long and narrow, 15-22 cm long and 2 cm wide |
| Taste | Bitter, Sweet, pungent |
| Name | Red Bead Tree |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Adenanthera pavonina |
| Native | Southern China and India, and widely naturalized in Malaysia, Western and Eastern Africa as well as in most islands of both the Pacific and Caribbean regions |
| Common Names | Circassian bean tree, Circassian-tree, Polynesian peanut, bead tree, coral bean tree, coralwood, false jequirity, false red-sandalwood, false wiliwili, peacock flower-fence, red bead tree, red beantree, red sandalwood tree, red-sandalwood, redwood, saga tree, sandal beadtree, sandalwood-tree, zumbic tree, Acacia Coral, Anikundumani, Bandi guruvenda, Barbados pride, Barricarri, Coral Pea, Coralitos, Curly Bean, Manchadi, Manjadi, Manjetti, Peacock flower fence, Peronías, Peonía, Rakta kambal, Red Lucky Seed, Saga hutan, Saga, Thorligunj, sanderswood, acacia coral, agati, agati petite feuille, coralitos, paina, pitipitio, pomea, popoa |
| Name in Other Languages | Arabic: Mrjan alghaba (مرجان الغابة) Assamese: Ronga-chandan,Chandan,Ku-sandan,Raktchandan Australia: Circassan tree, red beantree, zumbic tree Bengali: Ranjana (রঞ্জনা) Brazil: Carolina, tento-carolina Burmese: Mai-chek Cambodia: Chan’trèi, Phai, Maklam-takai Chamorro: Colales, culalis, kolales, kulales, kulalis Chinese: Hai hong dou (海紅豆), Kǒngquè dòu (孔 雀豆), Xiao zi hai hong dou, Xiang si dou Cuba: Coralillo, coralín, Mato Colorado Divehi: Madoši (މަދޮށި) Dominican Republic: Peronía extranjera Dutch: Koraalboom, rood sandelhout English: Aandal beadtree, Acacia coral, Agati, Bead tree, Circassian bean, Circassian seed, Condori wood, Coral pea, Coral pea tree, Coralwood, Coral wood, Curly bean, Deleite, Dilmawi, False jequirity, False red sandalwood, False wiliwili, Flower-fence, Jumbi bead, Jumbie beads, Peacock Barbados-pride, Peacock flower-fence, Peacock tree, Red bead , Red beadtree, Red bead tree, Red sandalwood, Red sandalwood tree, Red wood, Sandal bean tree, Sandal beadtree, Sandalwood tree, Zumbic tree, Circassian-tree Fijian: Lera, lere ndamu, pomea, vaivai, vaivai ni vavalangi, Lagati, Pitipitio, Popoa, Ranjana French: Arbre à église, Arbre à perles, Agati à petites feuilles, Arbre collier, Bois de condori, Bois de corail, Bois de santal rouge, Bois noir à graines rouges, Bois noir de Bourbon, Bois noir rouge, Corail végétale, Graine de condori, Graine l’église, Graine réglisse, Graine rouge, Oeil de paon, Paina, Pitipitio, Boir Noir a la Graine, Reglisse German: Condoribaum, Indischer Korallenbaum, Rotes Sandelholz, Roter Sandelholzbaum Guam: Colales, culalis, kolales Gujarati: Raktacandana (રક્તચંદન), Badigumchi (બડી ગુમ્ચી) Haiti: Deleite Hindi: Ratan gunj, anikundumani, bandi guruvenda, coralitos, jumble bead, kunchandana, lopa, malatanglin, manjadi, manjetti, peronias, raktakambal, saga, thorligunj, badee gumchee (बड़ी गुम्ची), Rakt chandan (रक्तचंदन), Raktchandan (रक्तचन्दन), Ratangunja (रतनगुंज), Badi Gumchi (बड़ी गुम्ची), Kuchandana (कुचन्दन), Ranjana (रंजना),Rakt chandan Indonesia: Kitoke laut, saga telik, segawe sabrang, Saga pohon, saga Italy: Pavoncina minore, semi di corallo Javanese: Saga telik, Sogok telik Kannada: Aane gulaganji (ಆನೆಗುಲಗಂಜಿ), Doddagulaganji (ದೊಡ್ಡಗುಲಗಂಜಿ), Manchatige (ಮಂಚಟಿಗೆ), Man̄jaḍi (ಮಂಜಡಿ), Manjadi (ಮಂಜಾಡಿ), Manjite (ಮಂಜಿಟೆ), Manjiti (ಮಂಜಿಟಿ) Konkani: Gunja (गूंज),Odlygunji,ओडलि गुंजी, Hodi Manjoti (होडी मंजोटी) Kosraean: Metekam, metkam, metkem, mwetkwem Kwara‘ae: Tatarabebe Laos: lam, Lam ta; Kh’way Lesser Antilles: Arbre à église, corail vegetal, dilmawi, graine réglisse, graine rouge, jumbi bead tree Malagasy: Bonaramena, Conori, Kafe bonara, Oeil De Paon Malay: Saga telik , Segawé sabrang, Kenduri batang, Saga, Pokok Saga Daun Tumpul Malaysia: Mai-chek, saga daun tumpul, saga tumpul Malayalam: Mancati (മഞ്ചാടി), Sem, Manchadi, Mancati Maori (Cook Islands): Kōviriviri, mata kōviriviri, pitipiti‘ō Marathi: Ratan gunj, Raktacandana (रक्तचंदन), Thorla goonj (थोरला गुंज), Raktachandana (रक्तचंदन) Myanmar: Mai-chek Nauruan: Bin Netherlands: Koraal-boom, sandelhout, rood Niuean: Pomea Oriya: Sokakainjo Other: Dschemudscha Palauan: Telengtúngd, telentundalel Persian: صندل قرمز Philippines: Malatinglin, Alalangat, Alang-langalBaguiroro, Bahay, Casay Pohnpeian: Kaikes Polish: Gruczołkowiec pawi Portuguese: Adenantero, Árvore-coral, Carolina, Falso-sândalo, Olho-de-pavão, Segavé, Tento-carolina, Olho-de-dragão , Tento-vermelho, acácia-coral, acácia-espiral, sándalo-vermelho Puerto Rico: Granate, mato Colorado, palo de mato, peronías chatas Russian: Adenantera pavlin’ya (Аденантера павлинья) Saint Lucia: Dalmawi Samoan: Lōpā, lopa Sanskrit: Ksharaka, kunchandana, Tamraka (ताम्रक), Raktachandana (रक्तचन्दन), Ksharaka, Kunchandana, Tilakah (तिलक) Sinhalese: Mas-moca, madaṭiya (මදටිය) Solomon Pijin: Nodale Spanish: Árbol del coral, Coral, Coralillo, Coralín, Coralitos, Delicia, Mato colorado, Palo de mato, Peonía, Peonía extranjera, Peronías chatas, jumbie bread, madera rosada Swahili: Mshanga Swedish: Korallträd, rött sandelträd Tahitian: La‘au paina, lopa, paina, pitipitio papa‘a Tamil: Anaikuntumani, Anikundumani, Mañcāṭi (மஞ்சாடி), Manjadi, Ani kundamani,Mancati (மஞ்சாடி) Manjati, Tilam (திலம்) Telegu: Baṇḍi gurvina (బండి గుర్విన), Gurivenda, Enugaguruginji, Peddaguruginja (పెద్దగురుగింజ), Bandiguruvenda (బండిగురువెంద) Thai: Ma hohk daeng (มะโหกแดง), Ma hua daeng (มะ หัวแดง), Makl̀ả tācĥāng (มะกล่ำตาช้าง) Makl̀ả t̂n (มะกล่ำต้น), Ma khlam ton Tongan: Lopa Tuvaluan: Lopa United States Virgin Islands: Coquelicot Urdu: Ratangunj USA: Legliz USA/Hawaii: False wili wili Vietnamese: Cây gió, Kiền kiện, Muồng nước, Trạch quạch, Thuốc rắn |
| Plant Growth Habit | Very fast-growing medium-sized to large deciduous, perennial free-flowering tree |
| Growing Climates | Forests and forest edges, woodland, coastal areas, roadsides, dry open forest and disturbed areas, evergreen forests, seasonally dry forests, open savannahs, agricultural land |
| Soil | Succeeds in any moderately fertile, moisture-retentive soil[200 ]. It is found in the wild on a variety of soils, from deep, well-drained to shallow and rocky |
| Plant Size | 6-15 m tall and up to 45 cm diameter, depending on location |
| Trunk | Trunk slightly buttressed, with greyish-brown bark |
| Bark | Bark dark brown to greyish, the inner bark soft, pale brown, and the slash soft, white and fibrous |
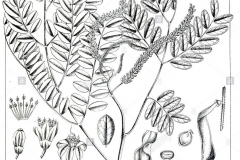
| Leaf | Bipinnately-compound with 2-6 pairs of secondary stalks. Individual leaflets oblong, thin and pale green with unequally-sided base, 9-15 pairs on each secondary stalk. Species is deciduous, shedding leaves for brief periods every 6-8 months in Singapore. They are green when young, turning yellow when old. |
| Flowering season | March – June |
| Flower | Small (2 mm), star-shaped, mature from white to creamy yellow to dull orange, held in 7 – 15 cm raceme inflorescences at tips of new shoots. Flowers open from base to tip of inflorescence, faintly scented like orange blossoms. |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Dehiscent seedpods or fruits that are thin, curved, long and narrow, 15-22 cm long and 2 cm wide with slight constrictions between seeds |
| Fruit Color | Ripening from green to dark brown and eventually woody black as they matures |
| Seed | Shiny scarlet red, hard, lens-shaped, with faint “heart line” around margin, eaten and dispersed by birds |
| Propagation | By seeds |
| Taste | Bitter, Sweet, pungent |
| Plant Parts Used | Root, Heartwood, bark, leaf, Seed |
| Season | May – Aug |
| Precautions | The raw seeds are poisonous. |
Plant Description
Red Bead Tree is a very fast-growing, medium-sized to large deciduous, perennial free-flowering tree with somewhat irregularly rounded crown. The plant normally grows about 6-15 m tall and up to 45 cm diameter, depending on location. The plant is found growing in forests and forest edges, woodland, coastal areas, roadsides, dry open forest and disturbed areas, evergreen forests, seasonally dry forests, open savannahs and agricultural land. Normally plant succeeds in any moderately fertile, moisture-retentive soil. It is found in the wild on a variety of soils, from deep, well-drained to shallow and rocky soil. Its trunk is slightly buttressed with dark brown to greyish brown bark and inner bark is soft and pale brown in color and the slash soft, white and fibrous. The tree is usually only leafless for a few days each year. Its uses include food and drink, traditional medicine, and timber.
Leaves
Leaves are bipinnately-compound with 2-6 pairs of pinnae, each with 9-15 pairs on each secondary stalk. The alternate leaflets 2-2.5 cm long and 3 cm wide are oblong, with an asymmetric base and blunt apex, dull green on topside and blue-green underside. Leaves are green when young turning yellow with age. Species is deciduous, shedding leaves for brief periods every 6-8 months.
Flower
Fragrant and bisexual flowers are borne in narrow spike like racemes, 12-15 cm long, at branch ends. Flowers are small, measuring 2 mm in diameter and maturing from white to creamy yellow to dull orange. Each flower is star shaped with 5 petals, connate at the base and having ten prominent stamen-bearing anthers tipped with minute glands. Flowers open from base to tip of inflorescence. Flowering normally takes place in between March till June.
Fruit
Eventually, the blossoms will be followed by dehiscent seedpods or fruits that are thin, curved, long and narrow, 15-22 cm long and 2 cm wide with slight constrictions between seeds. They ripen from green to dark brown and eventually woody black and twist before splitting to release 8-12 seeds. Showy seeds are 7.5-9 mm in diameter and are vivid scarlet red in color, hard and lens-shaped with faint heart line around margin, eaten and dispersed by birds. Ripened pods remain on the tree for long periods.
These attractive seeds have been used as beads in jewelry, leis and rosaries. They were also used in ancient India for weighing gold. The seeds are curiously similar in weight. Four seeds make up about one gramme. Children love the hard red seeds and few can resist collecting the brightly colored seeds usually littered under the tree. The young leaves can be cooked and eaten. The wood is extremely hard and used in boat-building and making furniture.
Traditional uses and benefits of Red Bead Tree
- The plant is antibacterial and haema-glutinin.
- Decoction of the leaves is used in the treatment of rheumatism and gout.
- The bark is used to treat leprosy.
- Decoction of the bark and leaves is used to treat dysentery, diarrhea and tonsillitis.
- The wood is used as a tonic.
- Pulverized wood, mixed with water, is taken orally for treating migraines and headaches.
- Red Bead Tree leaf extract has antibacterial activity against the intestinal pathogen Campylobacter jejuni.
- High doses of seed extract have an anti-inflammatory effect in studies in rats and mice.
- In India, Malaysia and Indonesia, this species is used in traditional medicine against rheumatism, migraines, headaches and dysentery.
- Plant has been used in traditional medicine for the treatment of asthma, boil, diarrhea, gout, inflammations, rheumatism, tumor and ulcers, and as a tonic.
- Seeds of this plant have been found to be effective in treating cardiovascular diseases during pregnancy.
- Red powder made from the wood is also used as an antiseptic paste.
- The bark was used to wash hair.
- In Ancient Indian medicine, seeds are made into a paste with water and applied externally to cure boils and swellings.
- The ground seeds are used to treat inflammation.
- Decoction of leaves used for chronic rheumatism and gout; also useful for bowel hemorrhage and hematuria.
- Powdered seeds are used externally to hasten suppuration of boils.
- Powdered seeds are also used for headaches.
- Seeds are used for cholera and also used for general paralysis.
- Bark is used in rheumatism, hematuria, ulcers, and gonorrhea.
- Powdered seeds are also used for treatment of abscesses.
Ayurvedic Health benefits of Red Bead Tree
- Antiseptic: Sprinkle Red Sandalwood powder on the damaged Skin.
- Boils: Grind Seeds of Red Sandalwood to make a powder. Sprinkle it on the Boils twice a day.
- Inflammation: Sprinkle powdered seeds of Red Sandalwood on the inflamed areas.
- Gout: Prepare a decoction of Red Sandalwood leaves. Drink once a day.
- Rheumatism: Boil leaves of Red Sandalwood in a cup of water. Drink once a day.
- Hair: Make an infusion of Red Sandalwood bark. Wash hair with it.
- Wrinkles: Prepare a mixture of Red Sandalwood, Glycerine and Rose water. Apply it on your face for 20 minutes. Wash after it.
- Burns: Take equal amount of powdered Indian madder, Red sandal wood, Chonemorpha Fragrans. Add adequate amount of Cow’s ghee. Boil for 15-20 Mins. Apply 3-4 times a day.
- Acne: Take equal quantity of Saffron, Turmeric, Neem, Red Sandalwood, Basil and Fuller’s Earth. Mix them in Butter Milk or Milk. Apply on the affected part twice a day.
- Acne: Take 1 teaspoon Neem, 1 teaspoon Red Sandalwood and 1 teaspoon Yogurt. Mix all ingredients. Apply on the face for 20 minutes. Rinse with cold water.
- Acne: Take 1 teaspoon Powdered Indian Madder, 1 teaspoon Red Sandalwood, 1/4 teaspoon Turmeric and 1 teaspoon Snow Lotus. Mix all ingredients. Add water to make a paste. Apply on affected parts for 20 minutes. Wash with cold water.
- Abscess: Take equal quantity of Indian Madder, Red Sandalwood and Snow Lotus. Grind them together. Add 1/4 teaspoon of Turmeric. Make a paste by adding water. Apply on the affected part until it dries. Wash with normal water.
- Eczema: Take one teaspoon powder of each Indian Madder, Red Sandalwood and Snow Lotus. Add half teaspoon of Turmeric. Make a paste by adding water. Apply for 20 minutes and wash.
Culinary Uses
- Young leaves are cooked, eaten and considered as a Famine food.
- Seed can be roasted, shelled and then eaten with rice.
- Seeds are easily digested and are enjoyed by children and adults alike.
- Bright red seeds taste like soya beans and contain 25% oil plus 39% protein.
- Young leaves are cooked and used as a vegetable.
- Flowers are also eaten.
- Roasted or boiled seeds eaten with rice in Java.
Other Facts
- Red Sandalwood or Coral Tree is cultivated for forage, as an ornamental garden plant or urban tree.
- It is a non-climbing species of leguminous tree useful for nitrogen fixation.
- It has many uses including food and drink, traditional medicine, timber, an ornamental garden plant/urban tree and as a shade tree.
- It is also planted along field borders as part of a windbreak.
- The small leaves break down easily, making the species a good green manure.
- It is inter-planted among field and tree crops such as spices, nutmeg, coffee and coconuts.
- Bark is rich in saponins and can be used as soap for washing clothes etc.
- It is also used as a hair shampoo.
- The plant is a source of dyestuffs.
- Red dye is obtained from the shredded bark.
- Dye has been used for dyeing clothes, and is used by the Hindus of India for the sacred mark placed on the forehead.
- Red, glossy seeds are used as toys and for beads in necklaces and other ornaments.
- They were formerly used to weigh gold, silver and diamonds, because they have a narrow range in weight.
- Goldsmiths use the seeds in soldering.
- Wood is heavy, hard, strong, close-grained and durable and is being used for cabinet making, construction, flooring, paving blocks, vehicle bodies and fine art.
- The wood yields very good charcoal.
- This tree is a nitrogen-fixing species commonly used as animal fodder, green manure, and for soil improvement.
- It can be used as a substitute for true red sandalwood.
- It is a popular fuel wood in the Pacific Islands as the wood burns readily and produces significant amounts of heat.
- Red dye is prepared from the wood that is used by the Brahmins in India to dot the forehead red.
- There are reportedly 1600 seeds per pound.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=26447#null
http://www.hear.org/pier/species/adenanthera_pavonina.htm
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxon/taxonomydetail?id=1440
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Adenanthera+pavonina
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/3209
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/ild-2
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=adpa
https://gringlobal.irri.org/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=1440
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Category:Adenanthera_pavonina
https://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?pid=S0102-695X2010000600017&script=sci_arttext
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/245164
https://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Red%20Bead%20Tree.html
https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Adenanthera_pavonina_(PROSEA)
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/ADEPA
http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Adenanthera+pavonina
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adenanthera_pavonina
https://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/go/51496/#b