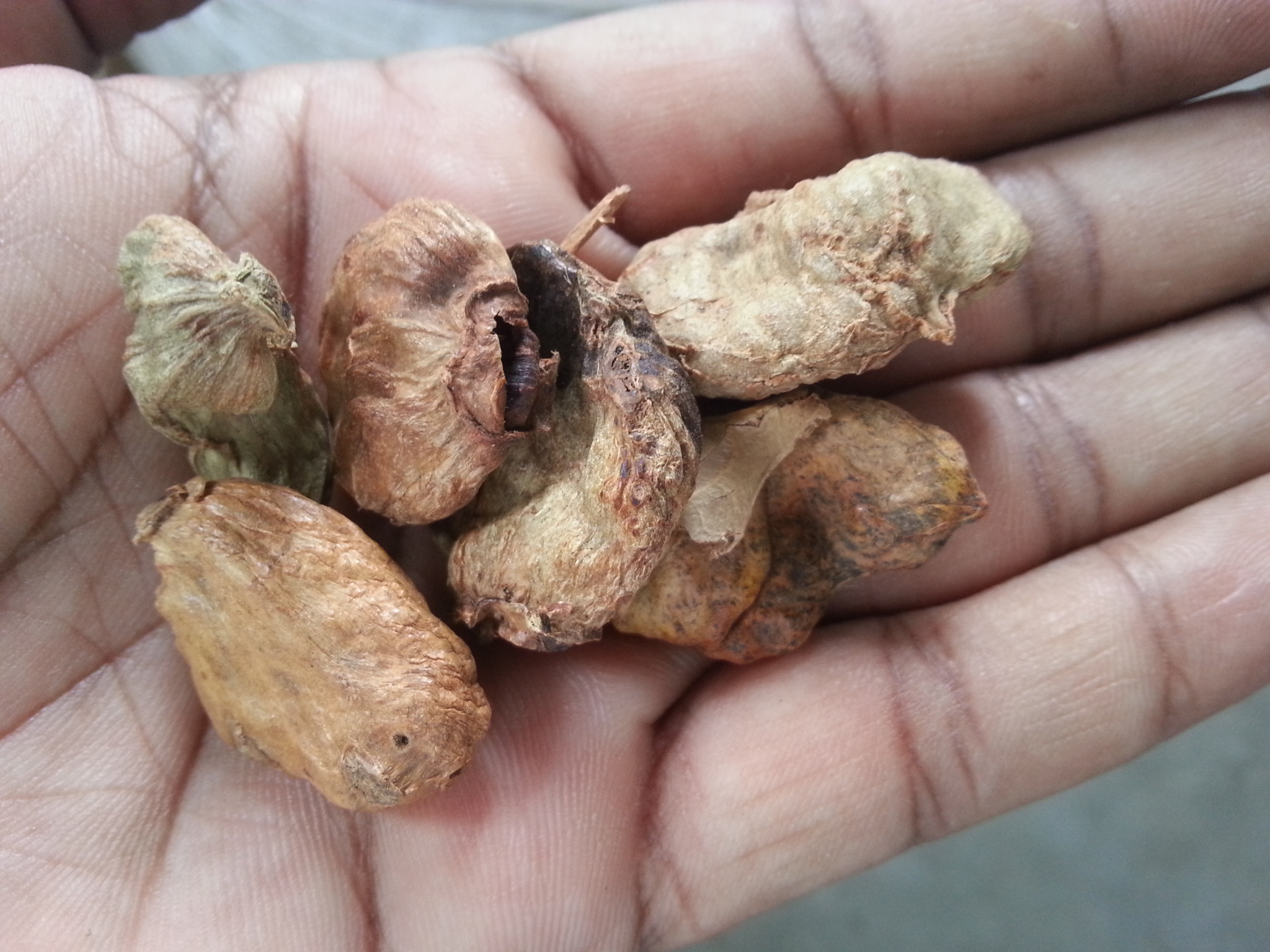
The plant parts such as bark, leaf, root and galls are reported to possess secondary metabolites. Galls are used in folk medicines. It is used in various Ayurvedic formulations such as Dasamularista, Shringyad curna and Chayavanaprasa and use for treating diseases such as tuberculosis, asthma, heart disease, indigestion, liver disorder and fever. Secondary metabolites are tannins, alkaloids, flavonoids and terpenoids. The minor constituents are gum mastic, crystalline hydrocarbon, crystalline acids and resinous substance. Bark contains flavonoids and terpenoids. Leaves and roots contain terpenoids and tannins.
Habit and geographical distribution
It is found in England, Nepal, Myanmar, India, Bhutan, Afghanistan and Pakistan. In Pakistan, it is grown in the Temperate Himalayas Mountains. It is found at an altitude of 600-2500 meters from sea levels. It grows in a tropical climate.
Roots, stem and leaves
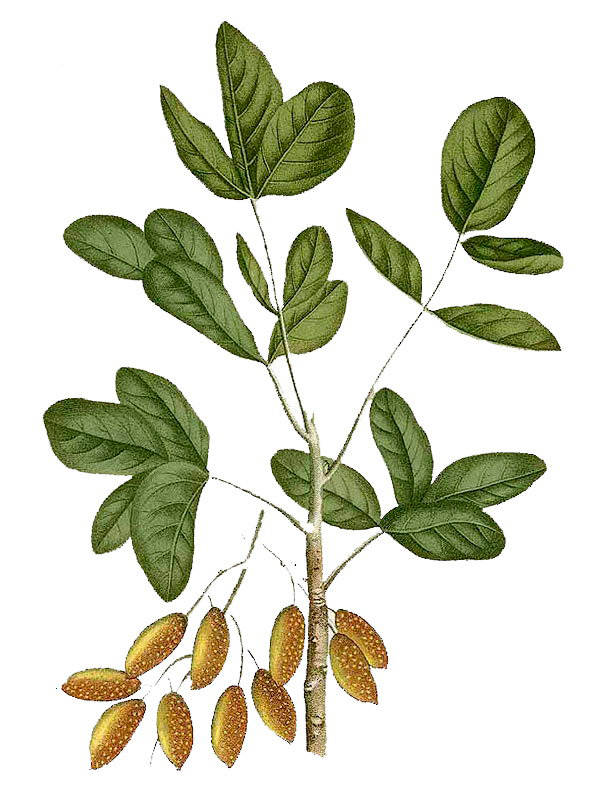
It is a deciduous multi-branched tree with dark gray and blackish bark and usually grows to 18 meters. Leaves are 20 to 25 cm long with or without leaflets. Leaflets are 4 to 5 pairs, coriaceous, lanceolate, pari or imparipinnate and base oblique. Leaves are dark green that turns bright red in autumn.
Flower and fruit
Flowers are in lateral panicles. Male is a compact pubescent and female lax and elongated. Plant bears flowers and fruits in spring with large clusters of yellowish-brown colored fruit in winter.
Medicinal uses
- Galls are used for treating cough, dysentery, asthma, liver disorders and snake bites.
- The plant is used for treating various diseases such as coughs, dyspeptic vomiting, appetite, phthisis, dysentery and asthma.
- Take roasted galls with honey for diarrhea and cough asthma in northern areas of Pakistan.
- In Pakistan, galls are also used for hepatitis and other liver problems.
- Use the galls with other drugs for scorpion sting and snake bites.
- Boil bark in water and extract is used for hepatitis and jaundice.
- Stem resin is used to heal wounds.
- In India, galls are used for treating respiratory ailments.
- In India, it is used as a remedy for chronic bronchitis, vomiting, psoriasis, fever and promotes appetite.
Culinary uses
- Cook young shoots and leaves as vegetable.
- Roast the seeds and consume as confectionery.
References:
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Pistacia+chinensis+integerrima
http://old.worldagroforestry.org/treedb/AFTPDFS/Pistacia_integerrima.PDF
https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/9bb6/78be01f5bb701c979ea22f8c5dbc53cd21da.pdf
https://www.actascientific.com/ASNH/pdf/ASNH-03-0226.pdf
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1319610310000748
Comments
| Pistacia integerrima Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Pistacia integerrima |
| Scientific Name: | Pistacia integerrima |
| Origin | Asia |
| Colors | Purple to blue |
| Shapes | Globular, 4-6 mm diameter |
| Taste | Slightly bitter |
| Name | Pistacia integerrima |
|---|---|
| Native | Asia |
| Common/English | Crab’s claw, zebrawood |
| Names in Other Languages | English: Zebrawood, Pistanchio tree; Pakistan: shnai, khanjar, thoak; India: kakroi, kakra, kakring, kakar singhi, kakkar, kakarsinghi; Ayurvedic: Karkarashringi, Shringi; Unani: Kaakarasingi; Latin: Pistacia integerrima; English: Crab claw and zebra wood; Urdu: Kakarasingi; Hindi: Kakadasrngi; Pushto: Shanai; Panjabi: Kakar, Kakarsingi; Bengali: Kankihasringi; Kashmiri: Kamaladina |
| Plant Growth Habit | Multi-branched, single stemmed, deciduous tree |
| Plant Size | 25 m tall |
| Bark | Dark grey or blackish |
| Leaf | Alternate, pinnate, 25 cm long |
| Flowering Season | March-May |
| Flower | Reddish or yellow or brownish, unisexual, dioecious, 0.2 cm diameter |
| Fruit shape & size | Globular, 4-6 mm diameter |
| Fruit color | Purple to blue |
| Taste | Slightly bitter |
| Fruit Season | June-October |