The Latin word Matrix, means of the womb is where Matricaria is derived from. This is most likely due to the genus’ association with uterine treatments and tonics. The species names Discoidea means without rays. This is in reference to Pineapple Weed’s lack of petals. The flowers and leaves, when crushed, give off a slight aroma of pineapple, as well as the aroma of chamomile, hence the common names. They are edible and have been used in salads (although they may become bitter by the time the plant blooms) and to make herbal tea. Pineapple weed has been used for medicinal purposes, including for relief of gastrointestinal upset, infected sores, fevers, and postpartum anemia.
The cone-shaped flower heads are a valuable part of this plant, as they are used either dried or fresh, most often in pineapple weed tea, which has a clear pineapple scent when brewed. You can also eat the dried or cooked flower heads for an energetic burst, which is why these flowers are often, included in homemade trail mixes. The dense nutrient content of this herb includes myrcene, germacrene, and geranyl isovalerate, as well as various tannins and glycosides.
Pineapple Weed Facts
| Pineapple weed Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Pineapple weed |
| Scientific Name: | Matricaria discoidea |
| Origin | Western North America. It has been introduced to Europe, Asia, Greenland, Iceland, South America, and New Zealand |
| Colors | Dark brown |
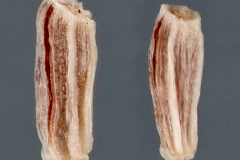
| Shapes | 2 mm long, oblong achene that is broader at the top than the bottom |
| Taste | Sweet like pineapple |
| Health benefits | Treat Insomnia, Act As an Analgesic, Improve Skin Health, Curb Stress and Anxiety, Help Stimulate Breast Milk Production, Improve Immune System, Wound Healing, May lower Fever, Eliminate Parasitic Infection, Promotes Healthy Gut |
| Name | Pineapple weed |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Matricaria discoidea |
| Native | Western North America. It has been introduced to Europe, Asia, Greenland, Iceland, South America, and New Zealand. |
| Common Names | Pineapple Weed, Wild chamomile, Disc mayweed, False chamomile, Rayless chamomile, Rayless mayweed, Rounded chamomile, pineapple mayweed |
| Name in Other Languages | Arabic: Babunj ‘ustuaniun (بابونج أسطواني) Azerbaijani: Ətirli çobanyastığı, Ləçəksiz çobanyastığı Bashkir: Bolan küz̦e (Болан күҙе) Belarusian: ramonak pachučy (рамонак пахучы) Cheyenne: Ónonevonêške-móxêšéne Chinese: Tóng huā mǔ jú (同花母菊), Yě yánggānjú (野洋甘菊) Czech: Heřmánek ter, heřmánek terčovitý Danish: Skive-kamille, Ager-Rævehale, Eng-Rævehale, Gold Hejre, Knæbøjet Rævehale Dutch: Schijfkamille English: Disc mayweed, Pineapple weed, Rayless chamomile, Rounded chamomile, False chamomile, rayless mayweed, pineapple mayweed, wild chamomile Estonian: Lõhnav kummel, ubinheim Finnish: Pihasaunio, Hietakattara, Isorölli, Nurmipuntarpää, Polvipuntarpää, Rikkapuntarpää, Rikkarölli, Pihasaunio French: Matricaire discoid, Matricaire odorante, Matricaire sans ligules, Matricaire discoid, camomille discoid, camomille odorante, matricaire fausse camomille German: Strahlenlose Kamille, Strahllose Kamille, Knopfkamille, Matricaria suaveolens Hungarian: Sugártalan székfű Icelandic: Haliðagras Irish: Lus na hiothlainne Italian: Camomilla falsa, falsa camomilla Japanese: Koshikagiku (コシカギク), oroshagiku (オロシャギク) Kashubian: Pôchnica Korean: Jok je bi ssuk, jogjebissug (족제비쑥) Latvian: Maura kumelīte Lithuanian: Bevainikė ramunė Norwegian: Tunbalderbrå, Engreverumpe, Knereverumpe, Sandfaks, Storkvein, Åkerreverumpe Polish: Rumianek bezpromieniowy, rumianek bezpromienny Portuguese: Porter Romanian: Mușețel aromat Russian: Lepidoteka pakhuchaya (лепидотека пахучая), romashka bezʺyazychkovaya (ромашка безъязычковая), romashka pakhuchaya (ромашка пахучая), Romashka dushistaya (Ромашка душистая), Romashka obychnaya (Ромашка обычная), Romashka romashkovidnaya (Ромашка ромашковидная) Scottish Gaelic: Lus Anainn Serbian: Žuta kamilica Slovak: Rumanček diskovitý Slovene: Vonjava kamilica Spanish: Manzanilla bastarda, Manzanilla, margaza menor Swedish: Gatkamill, Gatkamomill, Krypven, Kvarnven, Kärrkavle, Renkavle, Sandlosta, Storven, Gatkamomill, Pihasaunio, Ängskavle, Gatkamill, Gatukamomill Ukrainian: Khamomila zapashna (хамоміла запашна) Vepsian: Bal’buškhein Welsh: Chwyn Afal Pinwydd, Chwyn Pinafal, Chwynnyn Pinafal |
| Plant Growth Habit | Low-growing erect annual plant |
| Growing Climates | Cultivated and abandoned fields, yards, gardens, roadsides, footpaths, compacted soils in farmyards, waste areas, open areas, bare disturbed areas and rural or urban waste grounds, railroads, irrigation ditches, stream banks, sandbars, cracks in the pavement, rubbish tips, shores, stony slopes of pastures, barnyards, edges of driveways and sidewalks |
| Plant Size | Grows less than 15 cm tall but sometimes grows up to 30 ½ cm tall |
| Root | Root system consists of a branching taproot |
| Stem | Usually erect or ascending, sometimes decumbent, branched from bases |
| Leaf | Stem leaves are alternate; stalk less, hairless, fern-like, 2-3 cm long and 0.6-1 cm wide. Leaf blades are inverted-lance shaped or oblong. They are deeply cut into lobes that are spaced out along the midrib but not cut to the midrib |
| Flowering season | June to September, sometimes into November |
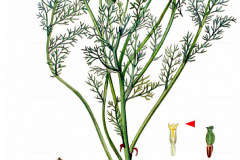
| Flower | Small, yellow disc florets are arranged in cone-shaped heads that are 5 to 10 mm across. Ray florets are absent. Each head is surrounded by several overlapping bracts that have papery margins |
| Fruit Shape & Size | 2 mm long, dark brown, oblong achene that is broader at the top than the bottom |
| Fruit Color | Dark brown |
| Flavor/Aroma | Strongly of pineapple |
| Taste | Sweet like pineapple |
| Propagation | By Seeds |
| Season | Seed set begins in July, normally within 40-50 days of flowering |
| Health Benefits |
|
Plant Description
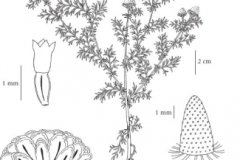
Pineapple weed is a low-growing erect annual plant that normally grows less than 15 cm tall but sometimes grows up to 30 ½ cm tall. The root system consists of a branching taproot. Stems are erect to semi-erect, ascending, smooth, and branched. Mature plant tends to be bushy when not subjected to competition. The plant is found growing in cultivated and abandoned fields, yards, gardens, roadsides, footpaths, compacted soils in farmyards, waste areas, open areas, bare disturbed areas and rural or urban waste grounds, railroads, irrigation ditches, stream banks, sandbars, cracks in the pavement, rubbish tips, shores, stony slopes of pastures, barnyards and edges of driveways and sidewalks.
Leaves
Stem leaves are alternate; stalk less, hairless, fern-like, 2-3 cm long and 0.6-1 cm wide. Leaf blades are inverted-lance shaped or oblong. They are deeply cut into lobes that are spaced out along the midrib but not cut to the midrib; the lobes do not form separate leaflets (pinnatifid). The lobes may themselves be divided into lobes (bipinnatifid), which may be again divided into lobes (tripinnatifid). Basal leaves are transient and usually disappear by flowering time. Leaves are odorless when crushed.
Flowers
From the axils of the upper leaves, there develops flower heads on stalks about ½–1½ inches long. The flower head of each stalk is about 1/3 inches across, and consists of numerous greenish yellow disk florets and no ray florets. Each disk floret has 4 tiny lobes at its apex. The base of the flower head has several overlapping green semi-translucent bracts that are lanceolate or ovate with papery upper margins. The top of the flower head is shaped like a dome or blunt cone. At the base of the flower head the part of the stem on which the disk flowers are borne (the receptacle) is smooth, not bristly or chaffy. Both the foliage and flower heads have a pineapple-like odor when they are bruised or crushed. The blooming period occurs in between June to September, sometimes into November.
Fruits
Fertile disk floret is replaced by a 2 mm long, dark brown, oblong achene that is broader at the top than the bottom. The achenes are without awns or tufts of hairs. This plant spreads by reseeding itself.
Health benefits of Pineapple weed
The dry flower of pineapple weed is commonly consumed as herbal tea and use as topical medication. If you grow this flowering plant in your garden, pineapple weed could become an effective insect repellent. Aside from that, the health benefits of pineapple weed could be seen in the list below.
1. Treat Insomnia
Since ancient time, pineapple weed is well known for its sedative effect. There are a lot of health benefits of herbal tea before bed particularly tea like pineapple weed tea. That is why it is highly recommended for those with sleeping disorder like insomnia. Consume a cup of warm pineapple weed tea before bed. If before you usually wake up tired because of the lack of sleep, after drinking pineapple weed regularly, instead of tired you will feel fresh every time you wake up in the morning.
2. Act As an Analgesic
For pain relief, both topical and internal, drinking this tea and applying the cold tea to the painful area are both great options. The active compounds can quickly numb the area and provide relief from your chronic or acute pain.
3. Improve Skin Health
Pineapple weed does have certain antimicrobial and antibacterial properties, as well as antioxidants that can help to improve the appearance and health of the skin. Apply small amount of the tea or extracted oil on the site of psoriasis, eczema, insect bites and even wrinkles. It can help minimize their appearance and speed healing.
4. Curb Stress and Anxiety
The aromatic compounds found in pineapple weed have been connected to lower levels of stress and anxiety, due to the herb’s sedative effects. You can drink this herb in tea form or eat the dried flower heads to help balance your mood and prevent depressive episodes.
5. Help Stimulate Breast Milk Production
Pineapple weed can help to stimulate the production of breast milk. For new mothers, this can be important, as many women struggle to produce enough milk for their child. However pineapple weed should not be used by pregnant women, although it is safe for breast-feeding mothers.
6. Improve Immune System
The primary activities of this herb, when ingested, affect the digestive system, which is where a large amount of immune activity occurs. It can help to balance the bacterial levels in your micro flora environment, and also soothe upset stomachs. This can also improve your digestive efficiency and prevent symptoms of constipation, bloating and cramping.
7. Wound Healing
Applying pineapple weed tea or oil to wounds can help to speed the healing process and possibly protect the injuries from infection. Due to the analgesic properties, it can also remove the pain of fresh wounds, when used in small quantities.
8. May lower Fever
Traditional use of pineapple weed included the treatment of fevers. It is believed that this tea can stimulate the immune system and induce sweating, which will help to release toxins from the body and stimulate the recovery process.
9. Eliminate Parasitic Infection
Pineapple weed has strong anthelmintic properties, meaning that it may be particularly good at eliminating any parasitic infections or intestinal worms that may have taken up residence in your body. This can improve your nutrient uptake, and ensure proper growth and development, particularly in areas of the world where parasitic infections are more widespread.
10. Promotes Healthy Gut
It has been mentioned several times in some previous points that the anti-microbial and anti-bacterial agents of pineapple weed could help improving immunity system by making sure the gut is in healthy condition. Furthermore, pineapple weed is also able to improve digestion by preventing constipation, cramping and bloating. When your gut is healthy, metabolism could be significantly improved because nutrient will be optimally absorbed.
Traditional uses and benefits of Pineapple weed
- Pineapple Weed has been used for several uterine conditions, as a sedative, antispasmodic, and anthelmintic (wormer).
- Pineapple weed has been used for medicinal purposes, including for relief of gastrointestinal upset, infected sores, fevers, and postpartum anemia.
- Pineapple weed has many of the same benefits as chamomile, namely being good for relaxation and promoting sleep, and as an excellent digestive aid.
- It is also helpful for treating colds and is a mild pain reliever.
- Infusion of herb is used for upset stomach, intestinal pains or menstrual cramps due to its antispasmodic and anti-inflammatory properties.
- The tea [flowers] is reputed to be soothing for a cold and helps aid digestion and calm an upset stomach.
- The tea is good for colds and urinary tract infections.
- Decoction of herbs and flowers used for diarrhea.
- Tea is ideal brew for those troubled by insomnia or bad nerves.
Culinary uses
- Greens can be washed and eaten, and both the flowers and the whole plant can be steeped to make tea, described as excellent by one field guide.
- The flowers can be eaten raw or in salads, or to make jellies, syrups and cordials.
- Leaves and flowers can be used to make a fragrant tea.
Other Facts
- Seed production per plant can average from 850 to 7,000 seeds.
- This plant is also considered an effective insect repellent.
- The flowers and leaves, when crushed, smell of pineapple, giving this plant its common name.
- The 1,000 seed weight is 0.13 g.
Pineapple weed Side Effects
There are very few side effects of pineapple weed, although allergic reactions, skin inflammation and stomach upset have been reported. Some of the common side effects are mentioned below
1. Gastrointestinal Problems
Internal consumption of this herb (both in tea form and when eating flower heads) is not known to be toxic, although in large quantities, it can cause stomach upset, diarrhea and nausea. The moderate use of this herb is enough to benefit from its various properties.
2. Skin Irritation
Topical application of this potent oil can cause skin inflammation, redness, and itching, particularly for people with sensitive skin. Applying a small amount of this oil to a patch of skin and waiting a few hours to see if a reaction occurs is the best way to avoid this side effect.
3. Allergic Reactions
One of the most common reports regarding pineapple weed is allergic reactions on the skin, lips, tongue, gums, throat, and stomach. If you are allergic to other members of the Asteraceae family, such as daisies or sunflowers, you may experience a negative reaction when using this herb.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=501470#null
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/MATMT
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Matricaria_discoidea
https://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Pineapple%20Weed.html
https://accs.uaa.alaska.edu/wp-content/uploads/Matricaria_discoidea_BIO_MADI6.pdf
http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=1&taxon_id=242331665
https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q1144217
https://www.illinoiswildflowers.info/weeds/plants/pineapple_weed.htm
https://plants.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=MADI6