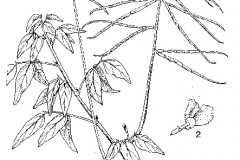
Phasey bean, which is also called cowpea, is a crop that grows in warm weather and is grown for its seeds, which can be eaten. You can eat these seeds fresh, dried, or in a jar. Sometimes the plant is picked from the wild and used as food in the area. This legume also fixes nitrogen, which makes it a popular choice for green manure and an important cover crop in crop cycles.
The plant’s ability to grow quickly on disturbed soils makes it a useful crop in some places, but in others it can be seen as an environmental weed. Even so, phasey bean is still a popular pioneer food that can feed animals quickly. It can even be cut for hay or silage, though some of its leaves may fall off as it dries and is moved around. Overall, phasey bean is a useful crop that can be used in a lot of different ways that can help farms and local communities.
Phasey Bean Facts
| Phasey bean Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Phasey bean |
| Scientific Name: | Macroptilium lathyroides |
| Origin | Mexico, Central America, the Caribbean and South America |
| Colors | Initially green turning to brown or black as they mature |
| Shapes | Pods are linear, sub-cylindrical, glabrous or pubescent. Each pod contains up to 20 seeds. |
| Taste | Mild, nutty flavor |
| Health benefits | Rich in Nutrients, Lowers Cholesterol, Reduces the Risk of Colon Cancer, Regulates Blood Sugar, Respiratory Health, Aids in Weight Loss, Improves Digestion, Promotes Heart Health, Boosts Immune System, Provides Energy, Supports Healthy Bones, Kidney Health |
| Name | Phasey bean |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Macroptilium lathyroides |
| Native | Mexico, Central America (i.e. Belize, Costa Rica, Guatemala, Nicaragua and Panama), the Caribbean and South America (i.e. French Guiana, Guyana, Surinam, Venezuela, Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Argentina and Paraguay) and is naturalized in the tropics and subtropics. It was introduced into India, Australia, Africa and the southern USA |
| Common Names | Phasey bean, phasemy bean, wild bean, wild bush bean, wild pea bean, one leaf clover, quail bean, wild dolly bean, Murray phasey bean, cowpea, pea bean, wild bushbean, wild dolly, scarlet bean |
| Name in Other Languages | Brazil: Feijão-de-rola, feijão-de-rolinha, feijão-de-pombinha, feijão-dos-arrozais Chinese: Da yi dou (大翼豆), Kuān yì dòu (寬翼豆) Colombia: Frijol de los arrozales English: Phasey bean, phasemy-bean, quail bean, wild bean, one-leaf clover; wild dolly; quail bean; cow pea, cowpea, wild bush bean, wild pea bean, scarlet bean, pea bean French: Pois poison, pois zombie, macroptilium à fleur rouge German: Phasemybohne, platterbsenartige Bohne Indonesia: Kacang batang Japanese: Fajiibiin (ファジービーン ), nanban-akabana-azuki (ナンバンアカバナアズキ) Puerto Rico: Habichuela parada, látiros de pasto Portuguese: Feijão, feijão-dos-arrozais, feijão-de-rola, feijão-de-pombinha, feijão-do-campo, figo-de-pombo, feijão-de-rola, Spanish: Habichuela parada, frijol de monte, frijol de los arrozales, pico de aura, Frijolito de los arrozales, Látiros del pasto, Pico de aura, frijolillo de arroz, tacón de campo, frijolillo silvestre, contramaligna, maribari Thai: Thua-phi (ถั่วผี) Tongan: Piinivao, pini Venezuela: Porotillo, porotillo del campo, frijol de monte |
| Plant Growth Habit | Climbing or trailing, herbaceous annual or less commonly short-lived perennial plant |
| Growing Climates | Forests, open scrub, pastures, along roadsides, disturbed areas, waste land, in open fields, cane fields, in open places along streams and rivers |
| Soil | Prefers well-drained soil that is rich in organic matter and requires moderate watering. It can tolerate moderate salinity, but is susceptible to higher levels of available soil manganese and aluminum, responding to lime to reduce available levels |
| Plant Size | Up to 0.5- 2 meters in height |
| Root | Roots of phasey beans are made up of fibers that spread out horizontally in the dirt. These roots can go down to a depth of 2 to 3 feet and spread out from the base of the plant for several feet |
| Stem | Stem is usually straight and can grow up to 2–3 feet tall. It is often thin and may have small ridges or ribs. The stem also has a layer of fine hairs, or pubescence. |
| Bark | Generally thin and smooth, and may be slightly rough or textured in some varieties. |
| Leaf | Leaves are trifolioate, leaflets entire, ovate to lanceolate, or narrowly elliptic, 3-8 cm long, 1-3.5cm wide. Upper surface of leaves are glabrous while lower surface has adpressed hairs. |
| Flower | The flowers are small, white to pinkish, and arranged in axillary or terminal clusters. |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Pods are linear, sub-cylindrical, glabrous or pubescent. Each pod contains up to 20 seeds. |
| Fruit Color | Initially green turning to brown or black as they mature |
| Seed | Seed are small, black, oblong, smooth, and have a fairly hard feel |
| Flavor/Aroma | Generally mild and not very pronounced. When cooked, they can give off a slightly earthy aroma |
| Taste | Mild, nutty flavor |
| Plant Parts Used | Seed, leaves and roots |
| Propagation | By seed or cuttings |
| Health benefits |
|
Plant Description
Phasey bean is a flexible plant that can rise or trail. It is usually an annual herbaceous plant, but it can also be a short-lived perennial. It can grow from 0.5 to 2 meters tall, but if it is in the shade, it may trail or twine, sending out vines that can grow up to 1.2 meters long.
This plant grows in a wide range of places, including woods, open scrub, pastures, along roadsides, disturbed areas, waste land, open fields, cane fields, and along streams and rivers. It likes well-drained soil that is full of organic matter and needs only a little water. It can handle a modest amount of salt in the soil, but it can’t handle high levels of manganese and aluminum. These amounts can be brought down by adding lime. Phasey bean can grow in a wide range of soils, from sandy to heavy clay. It can also handle a fair amount of dryness. This plant does well in a wide range of conditions, making it a great choice for farmers and growers alike.
Roots
Most of the time, the roots of phasey beans are made up of fibers that spread out horizontally in the dirt. These roots can go down to a depth of 2 to 3 feet and spread out from the base of the plant for several feet. But because the roots aren’t very deep, the plant might be more likely to die in dry circumstances.
Even though the roots of the phasey bean plant are weak, they are very important to the plant’s life. They help the plant get nutrients and water and keep it from falling over. Farmers and ranchers in many parts of the world need the roots very much because of this. By knowing what makes the phasey bean root system different, farmers can better take care of this crop and make sure it keeps doing well.
Stem
Phasey bean plant’s stem is usually straight and can grow up to 2–3 feet tall. It is often thin and may have small ridges or ribs. When the plant is young, it is green, but as it grows, it turns brown. The stem also has a layer of fine hairs, or pubescence, which can help keep water from escaping through the stem’s pores.
The base of a phasey bean plant is used for more than one thing. It gives the plant’s leaves, flowers, and seeds support and is also very important for moving water, nutrients, and other important substances throughout the plant. Vascular tissue, which includes the xylem and phloem and runs through the stem, makes this possible. This tissue lets water and nutrients move from the roots to the rest of the plant. Phasey bean plant’s stem is an important part of its overall structure and function. It helps the plant grow and develop, and it also helps it live and thrive in different environments.
Bark
The bark of a phasey bean plant is usually thin and smooth, but some types have a surface that is a little rough or textured. It is usually brown or gray in color, and as the plant gets older, it may crack or split. The phloem tissue, which is usually lighter in color and moves sugars and other nutrients around the plant, is found in the inner bark.
The bark of the phasey bean plant is important to its growth and development in a number of ways. First, it protects the tissues beneath it from damage caused by insects, animals, and environmental stresses like changes in temperature and moisture. Second, the bark helps to control how gases and water move between the plant and the outside world. This makes photosynthesis and water uptake more efficient.
In short, the bark of the phasey bean plant acts as a key layer of defense against outside risks and is also a key part of how the plant works as a whole. As a result, it is an important part of the plant’s structure that needs to be carefully managed and kept for the plant to grow and develop in the best way possible.
Leaves
The leaves of a phasey bean plant are trifoliate, which means they have three leaflets that are connected to a single stem. The leaves have an ovate or elliptical shape and a smooth or slightly serrated edge. They can be between 3 and 10 cm long and 1.5 and 4 cm wide. The top of the leaves is dark green, but the bottom is light green to grayish green. The petiole is thin and long, and it can be up to 10 cm long.
The size and form of the leaves can change depending on the plant’s variety or cultivar and the environment in which it grows. Young plants and seedlings tend to have smaller leaves than full-grown plants. Some types may have leaves that are bigger or smaller than others, or that are a different color.
The leaves of the phasey bean plant are an important source of protein, fiber, and vital minerals for animals that graze. They can be grazed or cut for hay or silage, giving animals high-quality food all year long. Also, the leaves are very important to the total productivity and sustainability of agricultural systems because of how they look and how they grow. Overall, the leaves of the phasey bean plant are a valuable resource for farmers and ranchers. They are a healthy way to feed animals, and they also help keep agricultural ecosystems healthy and productive.
Flowers
The phasey bean plant has small, white or pinkish-white flowers that grow in groups at the plant’s lateral or terminal ends. The flowers look like those of most legumes. They have five petals and ten stems. The base of the petals are joined together to make a small tube, or corolla. The stamens are set up in two groups, with five attached to the base of the petals and five attached to the base of the calyx.
Most of the flowers are self-fertile, which means they can fertilize themselves without help from other things. Cross-pollination can also happen when bees and other animals do their jobs. The plant’s blooming time can be different based on things like its variety or cultivar and the conditions in which it is grown. The plant usually starts to bloom in late spring or early summer, and it can keep blooming all through the growing season. The length of the blooming time can be affected by the temperature, the amount of water available, and the length of the day.
Flowers are very important to a plant’s ability to make more of itself because they make the seeds that are used to grow new plants. In addition, they can provide food for pollinators like bees and butterflies, which can help the plant be more productive and healthy overall. In short, the phasey bean plant’s flowers are important to the plant’s survival and play a key role in how the plant interacts with the ecosystem around it.
Fruit
When the phasey bean plant’s fertile flowers bloom, they are followed by pods that are 2 to 6 cm long and hold one to four seeds. Most of the time, the pods are long and skinny or round and slightly curled. They can be smooth or have a few hairs on them. When they are young, they are green, but as they get older, they turn brown or black. Even though the pods are usually indehiscent, which means they don’t split open when they’re ready, they can sometimes open and let the seeds out.
The phasey bean plant’s fruit is important because it holds the seeds that are used to grow new plants. The pods can also be used to feed animals because they are high in protein and fiber. They can be grazed or cut for hay or silage, giving animals high-quality food all year long.
Overall, the pods of the phasey bean plant are a useful resource for farmers and ranchers because they help the plant reproduce and provide food for the ecosystem around it. The pods are very important to the general productivity and sustainability of agricultural systems because of how they look and how they grow.
Seeds
Seeds of the phasey bean plant are usually small, black, oblong, smooth, and have a fairly hard feel. Most of the time, water can’t get through the seed coat, which can make sprouting hard in some situations.
The plant’s seeds are important for its survival because they are what are used to grow new plants. They can also provide food for animals that graze, since they are full of protein and other important nutrients. The seeds can be eaten or cut to make hay or silage, which is high-quality food for animals all year long.
Overall, the seeds of the phasey bean plant are a useful resource for farmers and ranchers because they help the plant reproduce and give it nutrients. Because each seed is different and grows in a different way, they are very important to the total productivity and sustainability of agricultural systems.
History
The Phasey bean plant is thought to have come from the Americas, and its beans were first grown by local peoples because they were so healthy. Beans were a key source of protein and other important foods for these early societies.
In the 1600s, Spanish explorers found the Phasey bean and brought it to Europe, where it quickly became a famous food crop and was grown on a large scale. The Spanish also spread the Phasey bean to Africa and Asia, where it became even more popular.
Later, in the 19th century, the Phasey bean was brought to North America to feed cattle. Farmers quickly chose this plant because it was easy to grow and had a lot of health benefits. Phasey beans are now grown all over the world, including the US, South America, Africa, and Asia.
Even though Phasey beans are grown all over the world, they are still an important part of many traditional meals. Beans are a main food in many parts of the world. They are an important source of protein and other important nutrients. The plant is also valuable because it helps keep the earth healthy and because it contains nitrogen, which can be used to fertilize crops.
Overall, the Phasey bean has been grown and eaten for a long time, and it is still an important part of the world’s food system. It has a lot of nutrients, is easy to grow, and can improve the health of the soil. This makes it a useful resource for farmers and ranchers all over the world.
Varieties of Phasey Bean
There are many varieties of phasey bean, which differ in their color, size, and flavor. Some of the most common varieties include:
- Purple flowered Phasey bean: The purple flowers on this variety are bigger and more showy than those on other types.
- Wild Type Phasey bean: The wild type version is known for how quickly it grows and how many seeds it makes.
- Low-growing Phasey bean: This type is shorter and bushier than other types, which makes it a good choice for a ground cover.
- Trailing Phasey bean: This type has long, hanging stems that can get as long as a few feet. It’s often used as a cover crop or a crop to feed animals.
- Perennial Phasey bean: This type of plant is an annual, which means it can live for more than one year. It works well in agroforestry systems and as a crop to protect the land.
- High-yielding Phasey bean: This type is often chosen as a forage crop because it produces a lot of seeds.
- Black-eyed pea: This type of phasey bean is the most well-known because of its creamy white color and black spot on one end.
- Cream pea: This type has seeds that are creamy white and are often used in soups and stews.
- Crowder pea: This type has seeds that are close to each other and look wrinkled because of this.
- Purple hull pea: The pods and seeds of this type are purple, and it is often used in salads and casseroles.
Health benefits of Phasey bean
Listed here are some of the health benefits of Phasey bean
1. Rich in Nutrients
The Phasey bean is a very healthy food because it has a lot of protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. It is a great source of many important nutrients, such as iron, potassium, calcium, and vitamin C, which are all needed for good health.
The Phasey bean is a good addition to any diet because it is full of healthy nutrients. It is especially good for people who want to get more plant-based protein and other important nutrients. The Phasey bean is a tasty and healthy food that can be used in many different dishes. It has a unique taste and can be used in many ways in the kitchen.
2. Lowers Cholesterol
There is soluble fiber in the Phasey bean, which has been shown to help lower cholesterol levels. The bean’s soluble fiber binds to bile acids in the gut, which are then passed out of the body. This helps lower the amount of “bad” LDL cholesterol in the blood.
Studies have shown that eating Phasey beans regularly can help lower cholesterol and lower the risk of getting heart disease. Adding this healthy food to a well-balanced diet is a good way to support heart health and general wellness.
3. Reduces the Risk of Colon Cancer
The Phasey bean has a lot of fiber, which may lower the risk of getting colon cancer. Fiber is known to help people have normal bowel movements and cut down on how long waste stays in the colon. This process cuts down on exposure to dangerous toxins and cancer-causing chemicals that can build up in the colon and make it more likely that a person will get cancer.
When eaten regularly, Phasey beans and other foods high in fiber can help keep your digestive system healthy and lower your risk of colon cancer. Adding these foods to a balanced diet and living in a healthy way can help improve general health and lower the risk of chronic diseases.
4. Regulates Blood Sugar
Because it is high in fiber and protein, the Phasey bean is a great food for controlling blood sugar. The fiber in the bean makes it take longer for the body to absorb carbs. This keeps blood sugar levels from going up and down quickly. Also, the protein in the bean helps control blood sugar by making insulin more likely to be released.
Adding Phasey beans to a healthy diet can be a good way to help control blood sugar, especially for people who have diabetes or are at risk of getting it. The Phasey bean is a healthy food that tastes great and is good for you. It can be used in many different meals.
5. Respiratory Health
In Ayurvedic medicine, the Phasey bean has been used for a long time to treat respiratory diseases like coughs, colds, and bronchitis. People think that the bean has an effect that helps open and get rid of phlegm from the lungs.
The Phasey bean is a natural treatment for lung health that has been used for hundreds of years. It is a valuable addition to any natural medicine cabinet because of its unique qualities and possible health benefits. Before using the Phasey bean as a medicine, you should talk to a medical professional, just like you would with any other natural cure.
6. Aids in Weight Loss
Because it is low in calories and high in fiber, the Phasey bean can help people who want to lose weight. The fiber in the bean makes you feel full and can lower your overall calorie intake. The bean’s low number of calories also helps you eat less.
Adding Phasey beans to a balanced meal can be a good way to help you lose weight in a healthy way. The Phasey bean is a healthy food that can be enjoyed as part of a healthy lifestyle. It has many possible health benefits and can be used in many different ways in the kitchen.
7. Improves Digestion
Because it has a lot of fiber, the Phasey bean is a great food for keeping your bowels moving and avoiding constipation. Fiber makes stools bulkier and stimulates the digestive system, which helps people have good bowel movements. Also, the fiber in the bean helps healthy bugs grow in the gut, which can improve the digestive health of the whole body.
Adding Phasey beans to a healthy, well-balanced diet can help with digestion and help keep you normal. The Phasey bean is a healthy food that can be used in many different recipes. It has many possible health benefits and tastes great.
8. Promotes Heart Health
The Phasey bean is a great food for heart health because it is high in fiber and antioxidants. Antioxidants help lower inflammation and oxidative stress in the body, both of which can lead to heart disease. Fiber can help lower blood pressure and lower the chance of heart disease by lowering cholesterol levels and improving blood flow.
Adding Phasey beans to a healthy diet can help keep your heart healthy and lower your risk of getting heart disease. The Phasey bean is a healthy food that can be enjoyed as part of a healthy lifestyle. It has many possible health benefits and can be used in many different ways in the kitchen.
9. Boosts Immune System
The Phasey bean is a healthy food that has vitamin C and antioxidants that can help boost the defense system. Vitamin C is important because it helps the body make white blood cells, which are a key part of fighting off diseases and infections. Antioxidants in the bean also help protect against free radicals, which can hurt cells and harm the immune system.
Adding Phasey beans to a healthy diet can help keep your immune system healthy and lower your risk of getting sick or getting an infection. The Phasey bean is a healthy food that can be used in many different recipes. It has many possible health benefits and tastes great.
10. Provides Energy
The Phasey bean has a lot of complex carbohydrates, which give you energy that lasts all day. Simple carbohydrates are digested quickly and can cause a spike in blood sugar levels. Complex carbohydrates, on the other hand, are eaten slowly and provide a steady stream of energy that can help keep you active both physically and mentally.
Adding Phasey beans to a well-balanced diet can be a good way to get more energy and feel less tired. The Phasey bean is a healthy food that can be used in many different recipes. It has many possible health benefits and tastes great.
11. Supports Healthy Bones
The phasey bean has a lot of calcium and phosphorus, which are two important nutrients for bone health. Calcium is needed to build and keep strong bones, while phosphorus is needed for bone tissue to grow and fix itself.
Phasey beans can help support bone health and lower the risk of osteoporosis if they are part of a well-balanced diet. The Phasey bean is a healthy food that can be used in many different recipes. It has many possible health benefits and tastes great.
12. Kidney Health
Ayurvedic custom says that Phasey bean may be good for the health of your kidneys. It is thought to help keep kidney stones from forming and help the kidneys work better generally.
Even though more study is needed to fully understand the possible benefits of Phasey bean for kidney health, adding this healthy food to a balanced diet may be a good way to support overall health and well-being.
Traditional uses and benefits of Phasey bean
- It has a lot of vitamins, which can help stop cancer and heart disease from happening.
- It has a lot of fiber, which can help with digestion and lower the risk of getting colon cancer.
- In traditional medicine, Phasey beans have been used to treat stomach problems, fever, and lung illnesses, among other things.
- The powder made from the ground seeds is used to treat urinary tract infections, swelling, and high blood pressure.
- The leaves are often used to treat skin diseases like eczema and psoriasis because they are thought to help reduce inflammation.
- The roots can also be used to treat joint pain and gout because they can reduce inflammation.
Culinary Uses
Here are some of the ways in which Phasey bean is used in cooking:
- Soups and stews: People often put Phasey bean beans in soups and stews. They make the dish feel heartier and are a good source of protein.
- Salads: Phasey beans that have been cooked and chilled can be added to salads to make them more tasty and healthy.
- Side dishes: You can make a side dish with phasey beans by sautéing them with herbs and spices or mixing them into rice or other grains.
- Snacks: As a healthy food, roasted Phasey beans are a good source of protein and fiber.
- Fermented Foods: Phasey bean is used in some countries to make fermented foods like miso, tempeh, and natto.
- Baked Goods: Phasey bean flour can be used instead of wheat flour in baked foods like bread, cakes, and cookies to make them gluten-free.
Other Uses of Phasey bean
- Forage Crop: Phasey bean is often used to feed animals because it is a good source of protein and other important nutrients.
- Soil Conservation: The roots of Phasey bean can fix nitrogen in the soil, which makes it a valuable crop for protecting land and farming in a sustainable way.
- Traditional Medicine: In traditional medicine, Phasey bean has been used to treat stomach problems, fever, and infections of the lungs, among other things.
- Green Manure: Phasey bean can be used as a green waste crop, which means it can be used to add organic matter to the soil and make it more fertile.
- Fuel Source: The Phasey bean plant’s dried roots can be used as fuel. This is a source of energy that keeps on giving.
- Ornamental Plant: Because Phasey bean has pretty flowers, it is often used as an ornamental plant in fields and parks.
- Cover Crop: As a cover crop, phasey bean keeps the soil from washing away, stops weeds from growing, and makes the soil more fertile. It is also used to help other crops grow better when they are planted next to each other.
- Bio-control Agent: The Phasey bean has compounds in its seeds that are poisonous to insects and other pests. This makes it a possible bio-control tool.
- Bioremediation: Because Phasey bean can take in heavy metals and other pollutants from the earth, it could be used to clean up polluted soils through bioremediation.
- Feedstock: Phasey bean has a lot of protein and oil, which makes it a good material for making energy.
- Traditional Dye: In the past, the leaves and roots of the Phasey bean were used to make dyes of different colors, from green to brown.
- Medicine: Some study shows that Phasey bean may be useful as an anticancer drug because it can stop cancer cells from growing.
References:
https://www.feedipedia.org/node/627
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Macroptilium_lathyroides
http://www.hear.org/pier/species/macroptilium_lathyroides.htm
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxon/taxonomydetail?id=23072
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=503647#null
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/PHSLY
https://keyserver.lucidcentral.org/weeds/data/media/Html/macroptilium_lathyroides.htm
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/ild-2785
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/230285
https://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Phasey%20Bean.html
http://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Macroptilium_lathyroides_(PROSEA)
https://apg.pir.sa.gov.au/gringlobal/taxon/taxonomydetail?id=23072
https://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Macroptilium+lathyroides
https://plants.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=MALA9