Plant Description
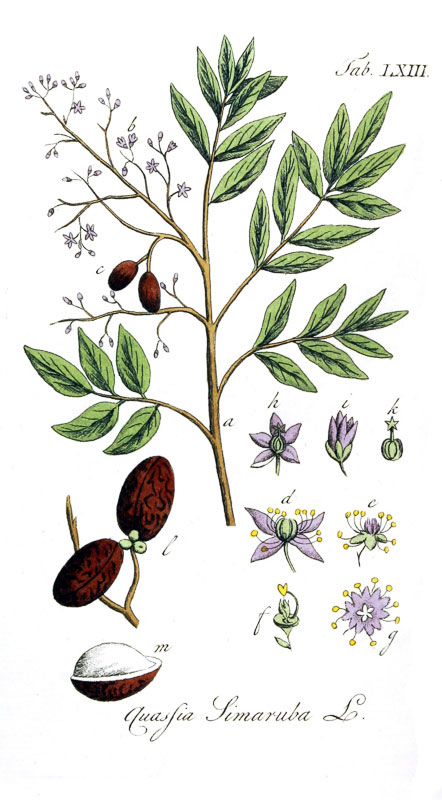
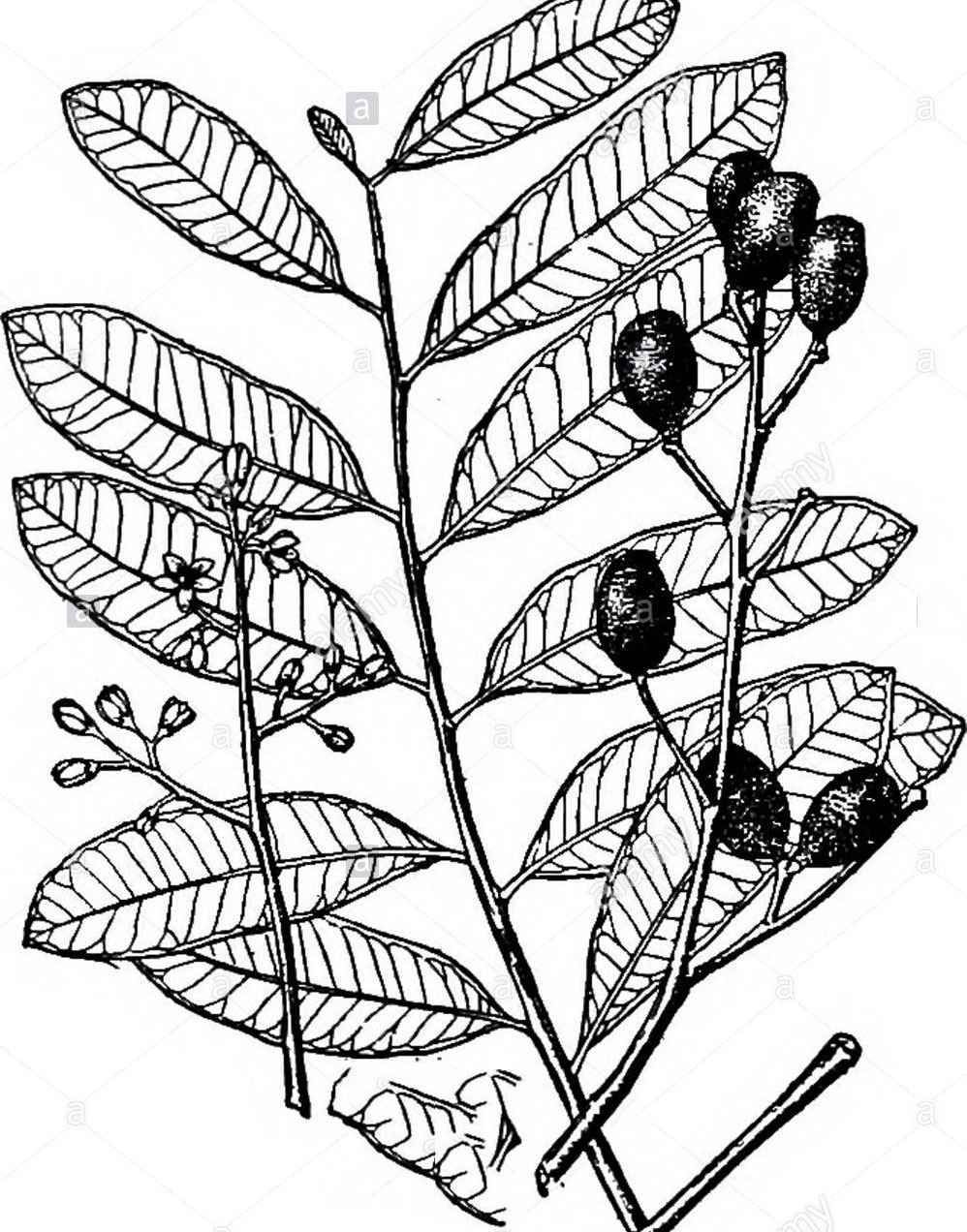
Paradise tree is an evergreen, small to medium-sized tree that grows up to 20 m high, with a trunk 50 to 80 cm in diameter with a narrow crown, well-developed root system, and straight, cylindrical bole. Bark is smooth and green when young, eventually turning light brown to gray, resembling the skin of a cantaloupe. The twigs of tree-of-heaven are alternate on the tree, stout, greenish to brown in color, and lack a terminal bud. They have large V- or heart-shaped leaf scars. The twigs easily break to expose the large, spongy, brown center, or pith.
Leaves
Tree-of-heaven leaves are pinnately compound, meaning they have a central stem in which leaflets are attached on each side. One leaf can range in length from 1 to 4 feet with anywhere from 10 to 40 leaflets. The leaflets are “lance” shaped with smooth or “entire” margins. The leaflets are up to 10 cm in length, dark green above, lighter below, with an entire margin and rounded leaf apex. At the base of each leaflet are one to two protruding bumps called glandular teeth. When crushed, the leaves and all plant parts give off a strong, offensive odor.
Flowers
Flowers are arranged in at branch-ends and in leaf-axils, in panicles. The calyx has 5 unfused, greenish sepals. The flower has 5 free yellowish-white overlapping petals. Male flowers have 10 stamens and no ovaries. Female flowers have 10 nonfunctional stamens and 5 unfused ovaries each with a single locule and seed. Occasionally there are perfect flowers produced on either the staminate or carpellate trees. Flowering normally takes place from
Fruits
Fruit is an oval purple/black drupe at maturity. The fruits can be eaten raw but are of inferior quality. Seeds on female trees are a 1-to-2-inch-long twisted samara, or wing. There is one seed per samara. The samaras are found in clusters, which often hang on the tree through winter. The seed produces edible oil used in the preparation of bakery products and for industrial purposes. Seed shells can be used in the manufacture of particle board, activated charcoal, or as fuel.
Worldwide Ethno medical Uses
| Paradise tree Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Paradise tree |
| Scientific Name: | Simarouba glauca |
| Origin | Bahamas, Costa Rica, Cuba, EI-Salvador, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, Jamaica, Mexico, Puerto rico, united states of America |
| Colors | purple/black |
| Shapes | Ellipsoid drupe, 2 - 2.5 cm long, with thin hard cuticle and juicy fruit pulp |
| Taste | Bitter |
| Health benefits | Beneficial for fever, malaria, diarrhea, dysentery, intestinal parasites indigestion, anemia, herpes, influenza, polio, and vaccinia viruses |
| Country | Uses |
| Amazonia | For bleeding, constipation, dysentery, fever, malaria |
| Belize | For bowel disorders, diarrhea, dysentery, excessive menstruation, hemorrhages, internal bleeding, skin, sores, stomach disorders, wounds |
| Brazil | For anemia, anorexia, bitter digestive aid, diarrhea, dysentery, dyspepsia, fever, hemorrhages, intestinal parasites, malaria |
| Cuba | For bleeding, colitis, diarrhea, digestive sluggishness, dysentery, malaria, menstrual disorders, parasites, sores, wounds |
| Dominican
Republic |
For colic, diarrhea, gonorrhea, malaria |
| El Salvador | For amebic infections, digestive stimulation |
| Haiti | For aches (body), anemia, dysentery, dyspepsia, fever, menstrual disorders, pain, rheumatism, skin problems, and to increase perspiration |
| Mexico | For amoebic infections, dyspepsia, fever, malaria |
| Peru | For diarrhea, dysentery, fever, intestinal gas, malaria, stomach pains |
| Elsewhere | For bleeding, colds, diarrhea, dysentery, fever, malaria |
Traditional Uses
| Plant Parts | Used For |
| Bark | Anemia, anorexia, bitter, diarrhea, dysentery, dyspepsia, emmenogogue, fever, hemorrhages, internal bleeding, intestinal worms, malaria, skin sores, sores, stomach and bowel disorders, tonic, wounds |
| Leaf | Astringent, colitis, diarrhea, digestive, dysentery, emmenogogue, intestinal worms, malaria, skin
affections |
| Root | Diarrhea, dysentery, flatulence, intestinal worms, malaria, stomach pain, tonic |
Traditional uses and benefits of Paradise tree
- Leaves and bark are used in the treatment of malaria, fevers, and dysentery, to stop bleeding, and as a tonic.
- Leaves and bark have a long history of medicinal use in the tropics, particularly in the treatment of malaria, fevers and dysentery; as an astringent to stop bleeding; and as a tonic.
- They are also used as a digestive, emmenogogue and to treat parasites both within and on the body.
- Studies have shown that the plant is over 90% effective against amoebic dysentery.
- Bark, and its three main quassinoids, has been shown to be an effective treatment against malaria, including strains that have become resistant to drug treatment.
- Research has also shown that the bark has good antiviral properties, effective against herpes, influenza, polio, and vaccinia viruses.
- Quassinoids responsible for the anti-amoebic and antimalarial properties have also been shown to possess active cancer-killing properties.
- Bark is used as a bitter tonic.
- Decoction is taken internally in the treatment of diarrhea, dysentery, malaria, fevers, hemorrhages, intestinal parasites and colitis.
- They are also used as a digestive, emmenogogue and to treat parasites both within and on the body.
- It is used much the same way against Fever, malaria, diarrhea, dysentery, intestinal parasites indigestion and anemia in Brazil.
- Simarouba bark has long been the most highly recommended (and most effective) natural remedy against chronic and acute dysentery in Brazilian herbal medicines.
Ayurvedic Health benefits of Paradise tree
- Malaria : Crush dried 3-4 Paradise tree leaves, 5 cm long sticks, Bark (1 piece for 10 kg body weight and accordingly increases the bark pieces). Put them in 200 ml of water. Boil the mixture at low flame for 10 minutes. Let it stay overnight. The next morning, warm the decoction and filter it. Drink 150 ml of it sip by sip on an empty stomach in the morning, one cup in the evening and one cup in the night for 15 days. Course is repeated once in 6 months. (Note : Do not eat anything for half an hour. )
- Diarrhea: Crush dried 3-4 Paradise tree leaves, 5 cm long sticks; Bark (1 piece for 10 kg body weight and accordingly increases the bark pieces). Put them in 200 ml of water. Boil the mixture at low flame for 10 minutes. Let it stay overnight. The next morning, warm the decoction and filter it. Drink one cup of it sip by sip, 2 times a day.
- Colitis: Crush dried 3-4 Paradise tree leaves, 5 cm long sticks; Bark (1 piece for 10kg body weight and accordingly increases the bark pieces). Put them in 200 ml of water. Boil the mixture at low flame for 10 minutes. Let it stay overnight. The next morning, warm the decoction and filter it. Drink 150 ml of it sip by sip on an empty stomach in the morning, one cup in the evening and one cup in the night for 15 days. Course is repeated once in 6 months.( Note: Do not eat anything for half an hour.)
- Dysentery: Crush dried 3-4 Paradise tree leaves, 5 cm long sticks; Bark (1 piece for 10 kg body weight and accordingly increases the bark pieces). Put them in 200 ml of water. Boil the mixture at low flame for 10 minutes. Let it stay overnight. The next morning, warm the decoction and filter it. Drink one cup of it sip by sip, 2 times a day.
- Cancer: Crush dried 8 Paradise tree leaves, 10 cm long sticks, Bark (2 piece for 10 kg body weight and accordingly increase the bark pieces). Put them in 200 ml of water. Boil the mixture at low flame for 10 minutes. Let it stay overnight. The next morning, warm the decoction and filter it. Drink 150 ml of it sip by sip on an empty stomach in the morning, one cup in the evening and one cup in the night. (Note: Do not eat anything for half an hour.)
- Blood Cancer: Crush dried 8 Paradise tree leaves, 10 cm long sticks, Bark (2 piece for 10kg body weight and accordingly increase the bark pieces). Put them in 200 ml of water. Boil the mixture at low flame for 10 minutes. Let it stay overnight. The next morning, warm the decoction and filter it. Drink 150 ml of it sip by sip on an empty stomach in the morning, one cup in the evening and one cup in the night. (Note: Do not eat anything for half an hour.)
- Ulcers: Crush dried 8 Paradise tree leaves, 10 cm long sticks, Bark (2 piece for 10 kg body weight and accordingly increase the bark pieces). Put them in 200 ml of water. Boil the mixture at low flame for 10 minutes. Let it stay overnight. The next morning, warm the decoction and filter it. Drink 150 ml of it sip by sip on an empty stomach in the morning, one cup in the evening and one cup in the night. (Note: Do not eat anything for half an hour.)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Crush dried 8 Paradise tree leaves, 10 cm long sticks, Bark (2 piece for 10 kg body weight and accordingly increase the bark pieces). Put them in 200 ml of water. Boil the mixture at low flame for 10 minutes. Let it stay overnight. The next morning, warm the decoction and filter it. Drink 150 ml of it sip by sip on an empty stomach in the morning, one cup in the evening and one cup in the night. (Note: Do not eat anything for half an hour.)
Culinary Uses
- Fruit can be consumed raw.
- Oil is largely used in the preparation of bakery products in Central America.
- It can be used in the manufacture of vanaspati, vegetable oil and/or margarine in India.
- The oil is free from bad cholesterol.
Other facts
- Seed produces edible oil used in the preparation of bakery products and for industrial purposes.
- Seed shells can be used in the manufacture of particle board, activated charcoal, or as fuel.
- Wood is used for interior construction, boxes and crates, furniture, veneer, etc.
- It is also used for fuel.
- Tree has a well-developed root system and an evergreen, dense canopy – it efficiently checks soil erosion, supports soil microbial life, and improve groundwater availability.
- It is shade tolerant and occurs as an under-storey tree, particularly under the canopy of large fruit trees where birds perch and deposit the seeds.
- Pulp and leaf litter can be economically used in the manufacture of vermi compost.
- Oil obtained from the seed can be used for industrial purposes in the manufacture of bio-fuels, soaps, detergents, lubricants, varnishes, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals etc.
- Seed shells can be used in the manufacture of particleboard, activated charcoal or as fuel.
- Freshly cut, the heartwood is whitish or cream colored with occasionally a yellow or greenish cast – when dry it becomes a uniform cream color with occasional oily streaks; it is not distinguished from the sapwood.
- It works easily and machines to a smooth clean surface; it is easy to finish and to glue.
- Wood is used for interior construction, boxes and crates, furniture components, veneer and plywood, pattern making, millwork, particleboard and fiber board.
- Wood is used for fuel, especially because it burns readily when still green and freshly cut.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=28844#null
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=33957
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Simarouba+glauca
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=SIGL3
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Simarouba_glauca
http://www.narc.gov.jo/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=33957
https://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Paradise%20Tree.html
http://www.rain-tree.com/Simarouba-Monograph.pdf
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/246716
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/SMBGL