Onion has been valued as a food and a medicinal plant since ancient times. It is widely cultivated, second only to tomato, and is a vegetable bulb crop known to most cultures and consumed worldwide. It is a short duration horticultural crop grown at low latitudes. It is commonly known as “Queen of the kitchen,” due to its highly valued flavor, aroma, and unique taste, and the medicinal properties of its flavor compounds. Onion is used throughout the year, for example in curries, in the form of spices, in salads, as a condiment, or cooked with other vegetables, such as boiled or baked. It is also used in different forms of processed food, e.g. pickles, powder, paste, and flakes, and it is known for its medicinal values.
Plant
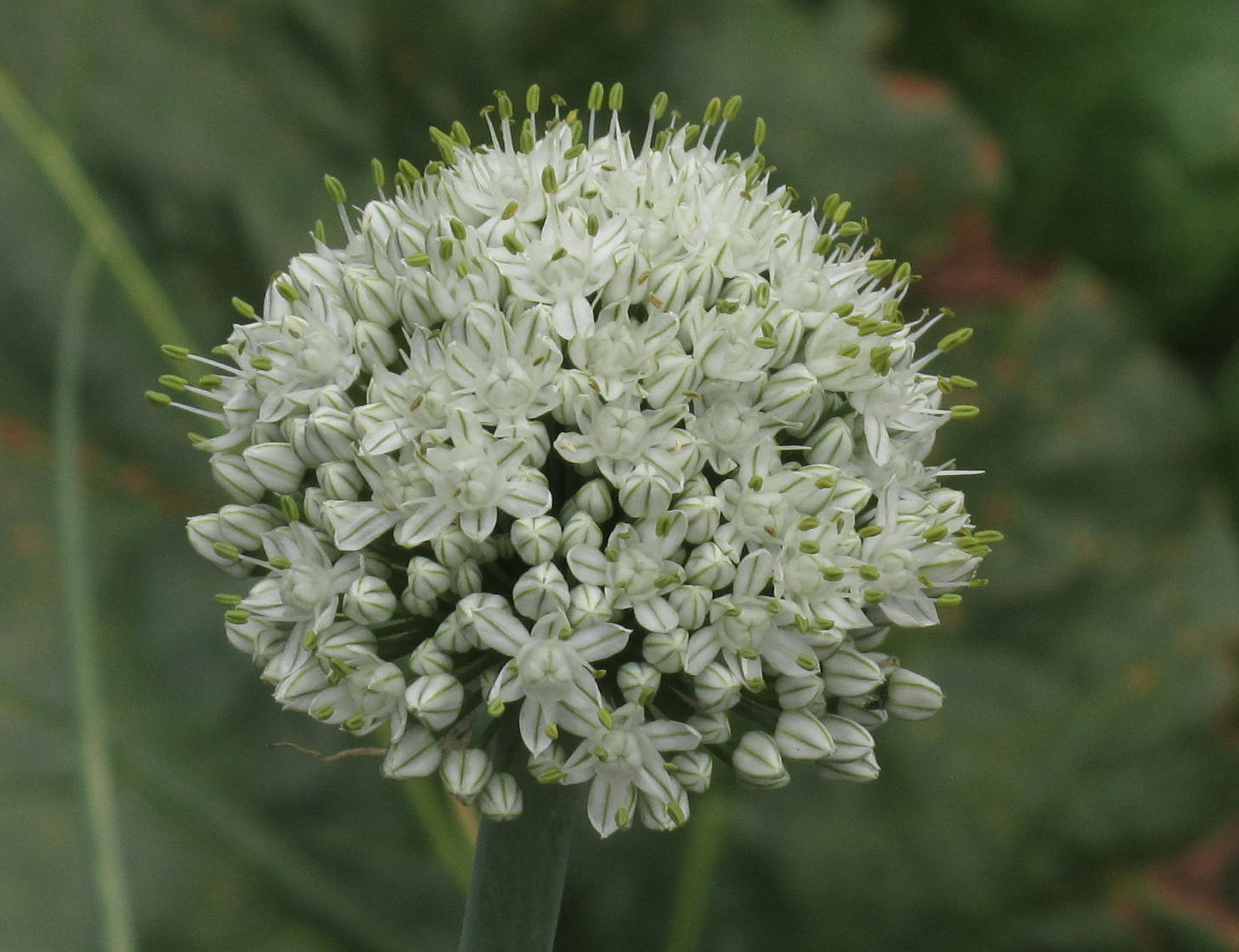
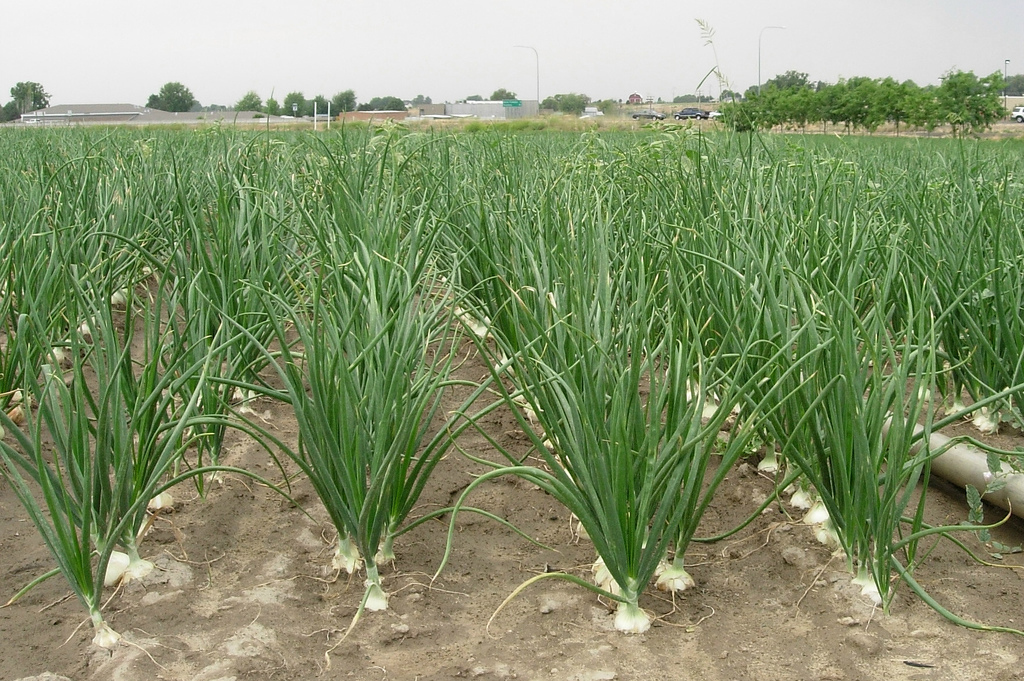
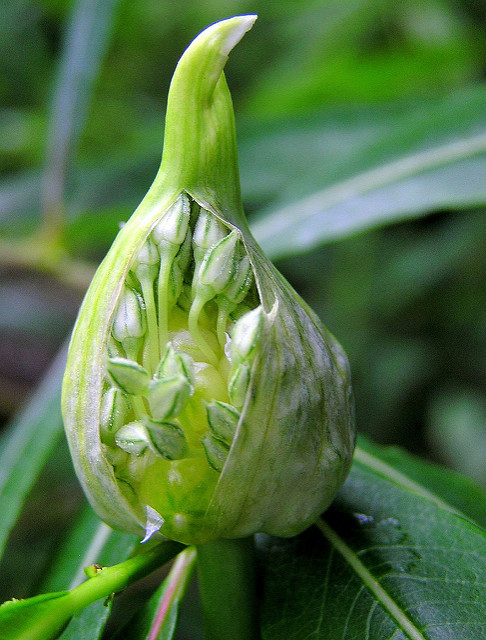
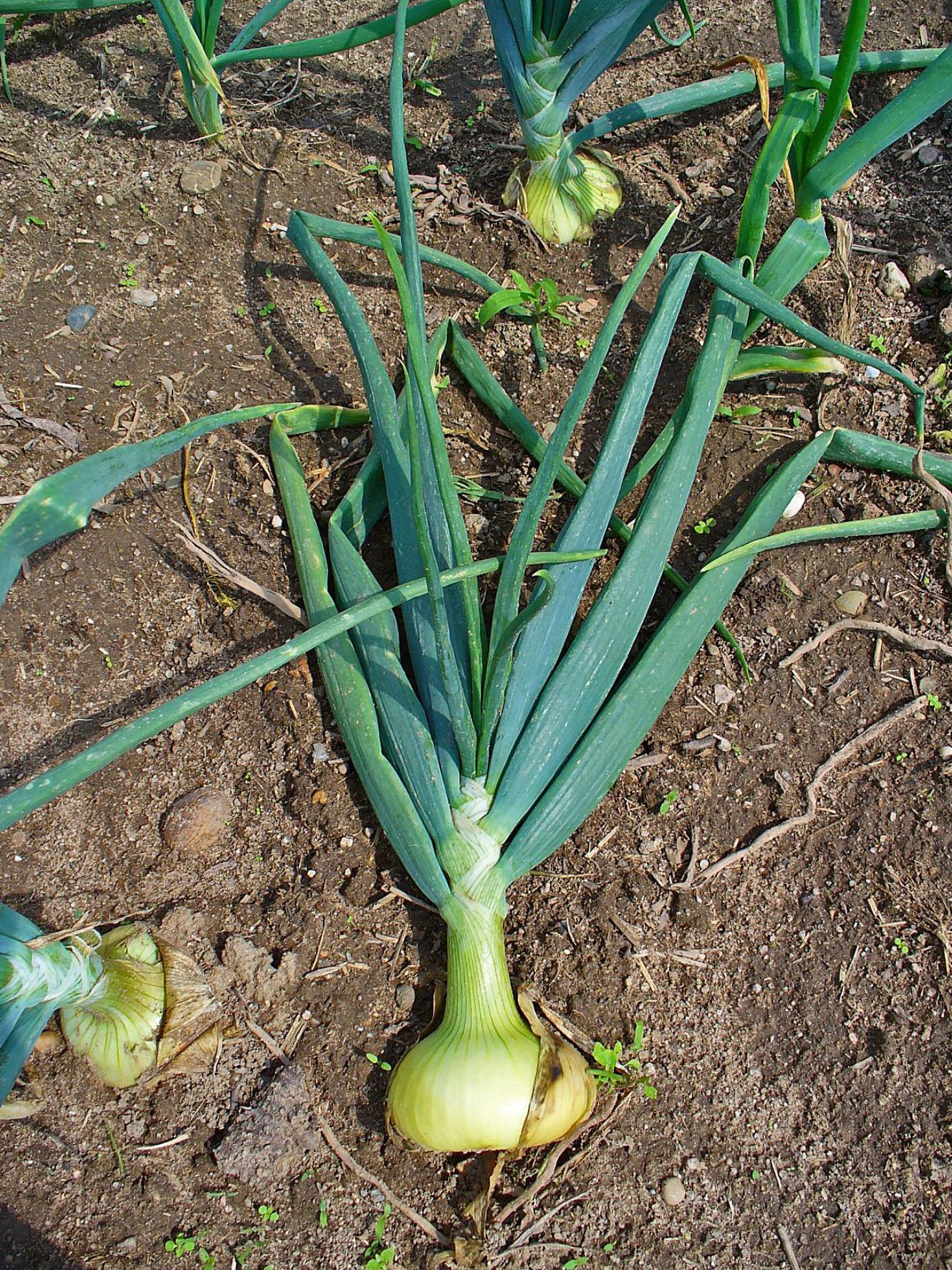
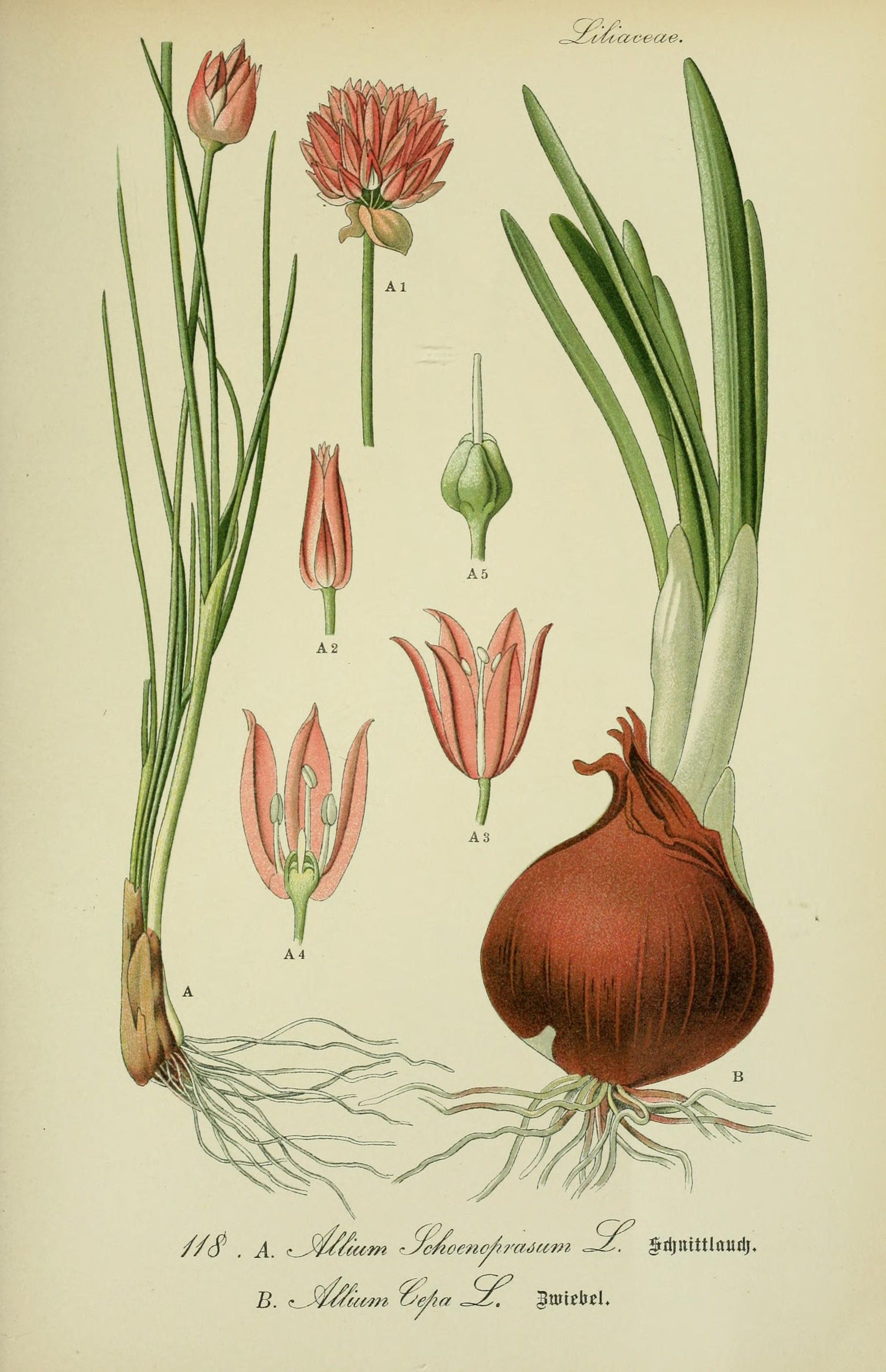
Onion is a biennial 15 to 45 cm (6 to 18 in) tall vegetable which is found growing in cool environment. They require a fertile, well-draining soil such as clay or silt loams with a pH of 5.5–6.5. The plants do not do well in acidic soils. Onions should be set out in full sun for optimum bulb development. Onions are biennial vegetables and if they are left in the ground for a second year, they will produce flowers and set seed. It has adventitious, fibrous roots. The stem of the plant is a flattened disc at the base and the tubular leaves form a pseudostem where their sheaths overlap. Leaves are yellowish-green and grow alternately in a flattened, fan-shaped swathe. They are fleshy, hollow, and cylindrical, with one flattened side and there are 3–8 per plant. Plant produces pink or white flowers clustered on stalks. The bulbs are formed just above the flattened stem of the plant by overlapping leaves. The bulb is made up of several layers, each corresponding to a leaf. They are generally oval but shape can be variable and occur in clusters of 3–18 to a plant. The bulb is protected by a membrane which turns to a papery coat. Seeds are glossy black and triangular in cross section.
Bulb
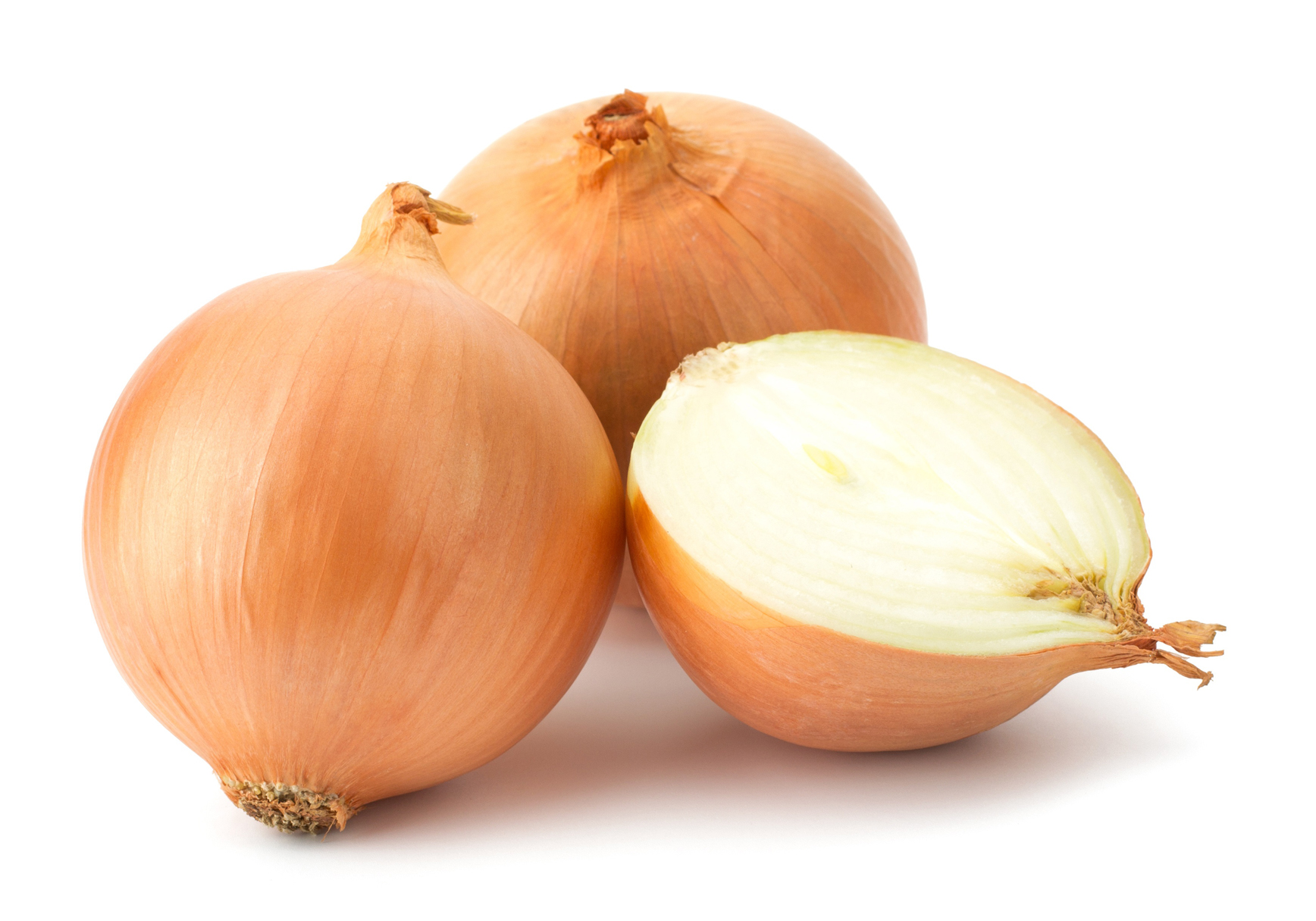
Onion, Allium cepa, is an herbaceous biennial in the family Liliaceae grown for its edible bulb. The bulb is an edible vegetable and is the most commonly used part of the onion, usually consumed after cooking although it can be eaten fresh. The stems and leaves are also edible. Onions are categorized as being either green or dry onions. Green onions are small onions that are harvested before the bulb has matured and the tops are still green. Dry onions, also known as mature onions, are harvested when their shoot has died and layers of papery thin skin cover a firm juicy flesh. Mature bulb of the onion is depressed globose, ovoid or elongate shaped, varying in size from cultivar to cultivar, 5–8 × 3–10 cm. Color of bulb is normally yellowish brown, orangey brown, purplish, red, greyish white or white forming the protective coat. It has sharp, pungent smell and freshly cut onions often cause a stinging sensation in the eyes of people nearby, and often uncontrollable tears. This is caused by the release of a volatile gas, syn-propanethial-S-oxide, which encourages nerves in the eye creating a stinging feeling. This gas is produced by a chain of reactions which serve as a defense mechanism: cutting onion causes damage to cells which discharges enzymes called alliinases. These break down amino acid sulfoxides and produce sulfenic acids. A specific sulfenic acid, 1-propenesulfenic acid, is rapidly acted on by a second enzyme, the lacrimatory factor synthase (LFS), producing the syn-propanethial-S-oxide. This gas diffuses through the air and soon reaches the eyes, where it activates sensory neurons. Tear glands produce tears to dilute and flush out the irritant.
History
Onions have been used by humans since the Neolithic age, and they are still being used all over the world. Over this long period, there have always been people who have appreciated the use of onions and used them in consider able quantities, but there have also been those who have rejected and detested them (Koch and Lawson, 1996). Onions have been cultivated globally, in at least 175 countries, for around 5000 years. Ancient Egyptians regarded the spherical bulb as a symbol of the universe. The name is probably is taken from the Latin unus meaning “one,” and the Romans introduced the onion to Britain, from where it may have been carried to the Americas. The first known written report about the onion comes from the Sumerians and dates back to 2600–2100 BC. In the Papyrus Ebers, which is based on ancient Egyptian writings and knowledge, we discover that leek played an important role in the kingdom of old Egypt. The great physician Hippocrates suggested onion as a diuretic, laxative, and emmenagogue. He also used onion for the treatment of pneumonia, and, externally, for healing putrid wounds.
Nutritional Value
Apart from their delightful tastes onion is a good source of nutrients, vitamins and minerals. Consuming 160 gram of raw onion offers 0.192 mg of Vitamin B6, 11.8 mg of Vitamin C, 14.94 g of Carbohydrate, 0.206 mg of Manganese, 30 µg of Vitamin B9 and 2.7 g of Total dietary Fiber. Moreover many Amino acids like 0.022 g of Tryptophan, 0.034 g of Threonine, 0.022 g of Isoleucine, 0.04 g of Leucine, 0.062 g of Lysine and 0.003 g of Methionine are also found in 160 gram of raw onion.
Health benefits of Onion
Onion consists of the majority of the nutrition which is needed by the entire body. The water content in onion is nearly 80%. The nutrients present in onions are carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Minerals just like phosphorous, zinc and potassium can be found in onions too. Onion also includes calcium and also vitamins. Following are amongst the advantages of onions.
1. Cancer Prevention
Cancer is normally characterized by uncontrolled growth of cells in the body. It is one of the world’s leading causes of death. Several researches have connected increased consumption of onions to reduced risk of several types of cancers, such as stomach-, breast-, colon- and prostate cancers. (1),(2),(3),(4),(5),(6)
2. Treatment of Anemia
Anemia is a disorder marked by a shortage of red blood cells or of hemoglobin in the blood, resulting in pallor and weariness. Anemic conditions can be cured by eating onions along with jaggery and water, because this adds to the mineral content of the body, especially iron, which is a crucial part of producing new red blood cells. Therefore, anemia, also known as iron deficiency, can be prevented by having a health amount of onions in your diet.(7)
3. Good Oral Health
Onions are often used to avoid tooth decay and oral infections. Chewing raw onions for 2 to 3 minutes can potentially kill all the germs present in the oral area and surrounding places like the throat and lips.(8)
4. Relieving Earache
Onion is found beneficial for earache too. A few drops of onion juice may actually prove hugely beneficial to individuals suffering from acute earache. The ringing sound in the ear may be cured by applying onion juice through a piece of cotton wool.(9)
5. Treating Urinary Disorders
Onion can offer considerable relief for those suffering from a burning sensation during urination. People suffering from this condition should drink water boiled with 6 to 7 grams of onions.(10)
6. Anti-Microbial Effects
We can find several microorganisms around us as well as in our body that normally harms our body. In that case onion extracts and essential oils may suppress the growth of harmful microorganisms, such as bacteria and yeasts. So onion must be included in our regular diet to remain safe from these harmful microorganisms.(11), (12)
7. Relieves Stomach Aches
Onion has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties that give relief to upset stomach and other related gastric disorders. This is due to the saponins that can be found in onions. These saponins have anti-spasmodic abilities that ensure that stomach disturbances do not continue and that your bowels are clear and smoothly functioning.(13)
8. Boosts Sexual Drive
Onions are considered to increase the urge for a healthy sex life. One table spoon of onion juice along with one spoonful of ginger juice, taken three times a day, can boost the libido and sex drive.
9. Treatment for Heart Ailments
Onions act as anticoagulants, also known as blood thinners, which in turn avoids the red blood cells from forming clumps. These blocks and clots can lead to heart disorders or cardiovascular diseases.(14)
10. Blood Sugar Regulation
Diabetes is one of the most common diseases, considered mainly by high blood sugar levels. Research done in animals has shown that onions can help to lower blood sugar levels .This has also been shown in humans. Research in diabetics found that 100 grams of raw onions per day led to a considerable reduction in blood sugar levels. Raw onions may be beneficial in the management of both type 1 and 2 diabetes, but more research is needed.(15), (16), (17), (18), (19), (20)
11. Immune System Strength
Onion consists of ample amount of phytochemicals that act as a stimulant to vitamin C within the body. The efficiency of vitamin C, and subsequently your immune system, is increased when you eat onions, since it boosts your immune system against toxins and numerous foreign bodies that can lead to disease and illness.(21)
12. Treatment for Cough
Cough is one of the undesirable problems that are cured by consuming an equal mixture of onion juice and honey. This solution can relive sore throats and coughing symptoms.(22)
13. Bone Health
Osteoporosis is one of the common health problems which are seen mostly in postmenopausal women. Proper and healthy diet is one of the main preventive measures for this problem. Several animal research has shown protective effects against bone deterioration, and may even increase bone mass. Apart from that research in women over 50 years of age discovered that regular onion consumption is connected with increased bone density. From this research study it is confirmed that onions may reduce bone loss in postmenopausal women and must be included in our regular diet.(23), (24), (25), (26), (27), (28), (29)
14. Used as Insect Repellent
Onion juice is one of the best insect repellent available in our home. You can apply onion juice to reduce the pain caused from honeybee stings. Fresh onion juice or paste can be used for external applications for other insect bites and scorpion stings as well. The smell of onions may causes insects to flee, which is why onions can be used as insect repellents as well as a form of sting treatment.(30)
15. Glowing Skin
Onion juice mixed with honey or olive oil is one of the best treatment for treating symptoms or signs of acne. Onions are also notorious anti-inflammatory vegetables, so the active compounds in onions can decrease the redness and swelling which is commonly allied with skin conditions like acne. It helps to reduce the related pain and inflammation of conditions like gout and arthritis.(31)
How to Eat
- Onion bulb is used as vegetable, seasoning and flavoring.
- Bulb is eaten raw or cooked.
- Eaten raw, it can be sliced up and used in salads, sandwich fillings, etc.; it can be baked or boiled as a vegetable in its own right and is commonly used as a flavoring in soups, stews and many other cooked dishes.
- Some cultivars have smaller and hotter bulbs, and are used for making pickles or chutneys.
- Concentrated oils are produced from steam distillation of fresh onion and garlic, and these are used to deliver onion or garlic flavor to processed foods.
- In a number of countries, particularly in Asia, pickled onion and garlic bulbs are consumed.
- Leaves are also raw or cooked.
- Flowers are eaten raw and used as a garnish on salads.
- They can be used either chopped or sliced, in almost every type of food, including fresh salads, or as a spicy garnish.
- Onions are one of the most sought-after ingredients in cooking where they used in curries, stir-fries, soups, stuffing, pastes, dips, sauces, etc., every day in India and Pakistan.
- They are one of the common ingredients in the Chinese “chowmein” (a kind of recipe with chopped onions, chili, cabbage, scallions, sweet bell peppers, and tomato sauce mixture.)
- They are used extensively in the Mediterranean and continental cooking in salads, cheese pizza, burger, soup, tart, rolls, stuffing…etc.
- Onions are a staple in Indian cuisine, used as a thickening agent for curries and gravies.
- Sliced onions are battered and deep-fried and served as onion rings in North America.
Other Traditional uses and benefits of Onion
- Onion bulb is antiseptic, anthelmintic, anti-inflammatory, carminative, diuretic, expectorant, stomachic, febrifuge, hypoglycaemic, lithontriptic, antispasmodic, hypotensive and tonic.
- Both garlic and onion are shown to have applications as hypoglycaemic antithrombotic, hypolipidaemic, anti tumour, antiarthritic and antimicrobial agents.
- In the Errachidia province in southeastern Morocco, A. cepa is one of several plants used to treat diabetes and hypertension.
- Allium cepa is used for chilblains and to remove thorns and splinters in traditional phytotherapy in the Marche, Abruzzo and Latium regions in Central Italy Guarrera.
- When used regularly in the diet, onions offset tendencies towards angina, arteriosclerosis and heart attack and also useful in preventing oral infection and tooth decay.
- Baked onions are used as a poultice to eliminate pus from sores and warmed onion juice can be used as eardrop to treat earache.
- Fresh onion juice is a very useful first aid treatment for bee and wasp stings, bites, grazes or fungal skin complaints.
- It also aids in the formation of scar tissue on wounds, therefore speeding up the healing process, and has been used as a cosmetic to remove freckles.
- Onion juice scrubbed into the skin is said to encourage the growth of hair and to be a remedy for baldness.
- Bulbs of red onion cultivars are used to make a homeopathic remedy particularly in the treatment of people whose symptoms include running eyes and nose.
- It is beneficial for hypertension, appetite loss, arteriosclerosis, dyspeptic complaints, and tendency to infection, fevers and colds, cough/bronchitis, inflammation of mouth and pharynx and common cold.
Other Uses
- The juice of the plant is used as a moth repellent and can also be rubbed onto the skin to repel insects.
- Onion water extract is said to the resistance of other plants to diseases and parasites.
- It has been used to polish glass and copperware and to prevent rust on iron.
- A yellow–brown dye is obtained from the outer skin of the bulbs.
Precautions
- Raw onions may cause irritation to skin, mucus membranes and eyes.
- Eating onions can lead to bad breath and an unpleasant body odor.
References:
http://www.uaex.edu/publications/pdf/FSA-6014.pdf
http://www.aces.edu/pubs/docs/A/ANR-1085/ANR-1085.pdf
https://www.reneesgarden.com/seeds/onions/Onion%20Planting%20Guide.pdf
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Onion
http://www.burpee.com/gardenadvicecenter/vegetables/onions/all-about-onions/article10242.html
Comments
| Onion Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Onion |
| Scientific Name: | Allium cepa |
| Origin | Central Asia |
| Colors | Yellowish brown, orangey brown, purplish, red, greyish white or white (Bulb) |
| Shapes | Depressed globose, ovoid or elongate, varying in size from cultivar to cultivar, 5–8 × 3–10 cm.(Bulb) |
| Calories | 64 Kcal./cup |
| Major nutrients | Vitamin B6 (14.77%) Vitamin C (13.11%) Carbohydrate (11.49%) Manganese (8.96%) Vitamin B9 (7.50%) |
| Health benefits | Cancer Prevention, Treatment of Anemia, Good Oral Health, Relieving Earache, Treating Urinary Disorders, Anti-Microbial Effects, Relieves Stomach Aches, Boosts Sexual Drive, Treatment for Heart Ailments, Blood Sugar Regulation, Immune System Strength, Treatment for Cough, Bone Health, Used as Insect Repellent, Glowing Skin |
| More facts about Onion | |
| Rank | Scientific Name & (Common Name) |
|---|---|
| Kingdom | Plantae (Plants) |
| Subkingdom | Tracheobionta (Vascular plants) |
| Superdivision | Spermatophyta (Seed plants) |
| Division | Magnoliophyta (Flowering plants) |
| Class | Liliopsida (Monocotyledons) |
| Subclass | Liliidae |
| Order | Liliales |
| Family | Liliaceae (Lily family) |
| Genus | Allium L. (Onion) |
| Species | Allium cepa L. (Garden onion) |
| Synonyms |
|