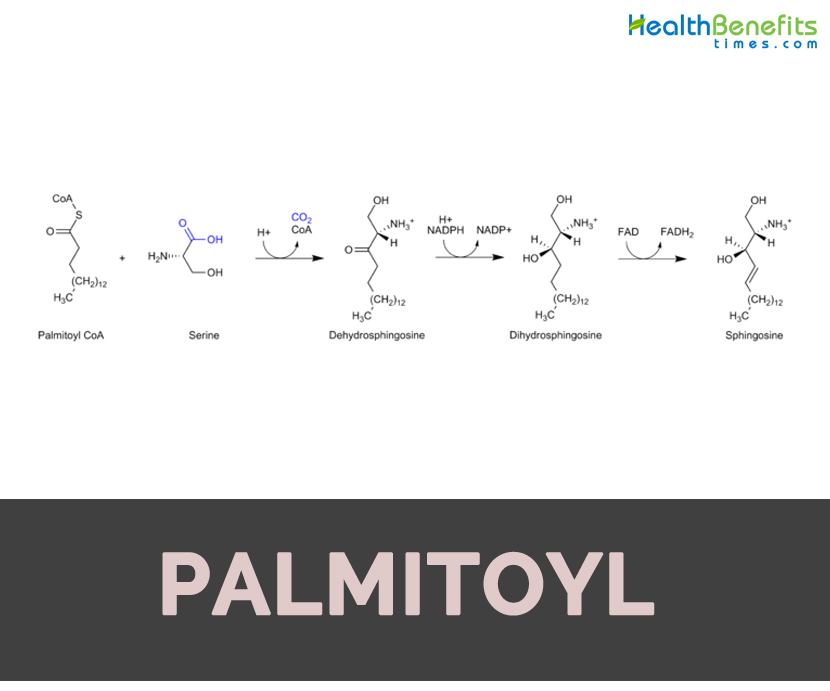
 Palmitoyl-CoA is a part of carnitine shuttle system that transports other fatty acyl-CoA molecules into the mitochondria for β-oxidation. It is a long chain fatty acyl-CoA which results from formal condensations of carboxyl group of hexadecanoic acid along thiol group of coenzyme A. It derives from coenzyme A, a hexadecanoate and hexadecanoic acid.
Palmitoyl-CoA is a part of carnitine shuttle system that transports other fatty acyl-CoA molecules into the mitochondria for β-oxidation. It is a long chain fatty acyl-CoA which results from formal condensations of carboxyl group of hexadecanoic acid along thiol group of coenzyme A. It derives from coenzyme A, a hexadecanoate and hexadecanoic acid.
It is a conjugate acid of a palmitoyl-CoA(4-). It yields 14 pairs of hydrogen atoms and 8 acetyl-CoA molecules by seven cycles through β-oxidation system. It could be oxidized in TCA cycle for the synthesis of fatty acid and cholesterol and used for formation of ketone bodies in liver. β-Oxidation of an acyl-CoA along an uneven number of carbon atoms yield propionyl-CoA during acetyl-CoA acyltransferase reaction of last cycle. Two high energy bonds are employed in activation of fatty acid molecule. Mole of fatty acyl-CoA which cycles through reactions 1 to 4 forms 1 mol of FADH2, 1 mol of acetyl-CoA and 1 mol of NADH. On last pass of even chain length fatty acid, 2 mol of acetyl-CoA are created and final pass of odd chain length molecule release 1 mol of propionyl-CoA.
