Leucine is an essential amino acid which is used in protein biosynthesis. It is an amino acid which contains α-amino group (protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), a side chain isobutyl group (making a non-polar aliphatic amino acid) and α-carboxylic acid group (deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions). It is a prerequisite in humans as the body could not synthesize, it should be obtained from diet. The dietary sources are foods which contains protein such dairy products, meats, beans, soy products and other legumes. It is encoded by codon UUA, CUU, UUG, CUA, CUC, and CUG.
Similar to isoleucine and valine, leucine is a branched chain amino acid. Leucin metabolism has primary metabolic end products such as acetoacetate and acetyl-CoA which is one of the two exclusively ketogenic amino acids having lysine being the other. It is a crucial ketogenic amino acid in humans.
Leucine is the branched chain amino acids which are referred as main amino acid due to most popular benefit of BCAAs being mostly due to leucine. It is an activator of protein called mTOR, which promotes muscle protein synthesis by S6K. It is distinct from other two BCAAs isoleucine and valine as leucine is seemed to be fair bit of testing on amino acid in confinement rather than BCAA mixture whereas other two BCAAs are not well studied. Studies evaluating leucine review at muscle protein synthesis when extra leucine is added to diet and it appear that leucine reliably increases muscle protein synthesis after test meals.
Leucine acquires both blood sugar reducing properties which could release from pancreas and can directly vitalizes glucose uptake into cell without insulin. In a cell, leucine arouse uptake of glucose for 45 minutes and hinders itself while in living systems. Isoleucine is more influential hypoglycemic agent but to low inhibitions of its actions.
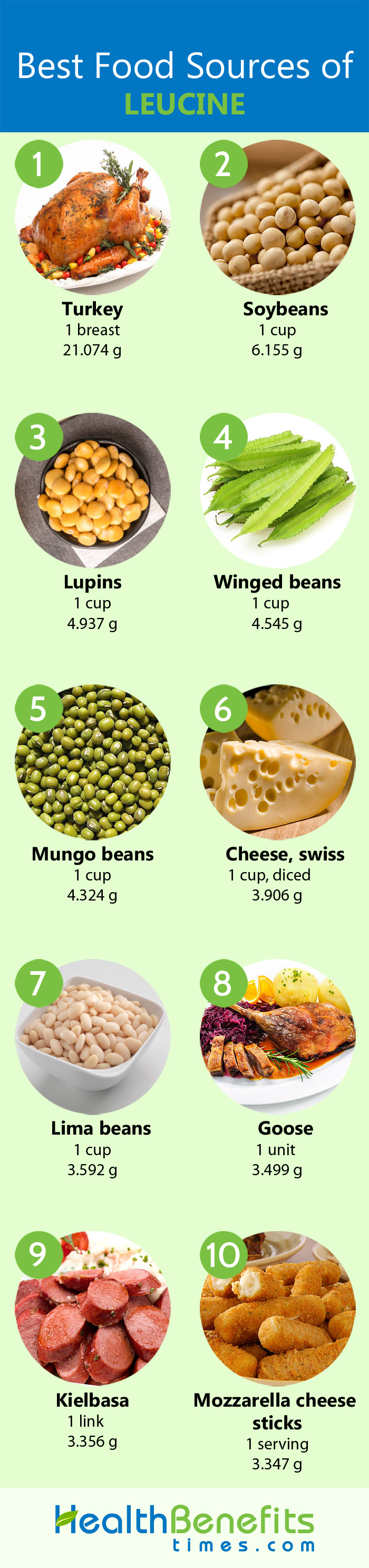
Foods that offer Leucine
| Food name | Weight (g) | Leucine (g) | DV% |
| Turkey | 863 | 21 | 568% |
| Soybeans | 186 | 6 | 162% |
| Spirulina | 112 | 5 | 135% |
| Lupins | 180 | 4 | 108% |
| Winged beans | 182 | 4 | 108% |
| Mungo beans | 207 | 4 | 108% |
| Hyacinth beans | 210 | 4 | 108% |
| Swiss cheese | 132 | 3 | 81% |
| Navy beans | 208 | 3 | 81% |
| Kielbasa | 370 | 3 | 81% |
| Lima beans | 178 | 3 | 81% |
| Adzuki beans | 197 | 3 | 81% |
| Whelk | 85 | 3 | 81% |
| Yardlong beans | 167 | 3 | 81% |
| Monterey cheese | 132 | 3 | 81% |
| Cowpeas | 167 | 3 | 81% |
| Muenster cheese | 132 | 2 | 54% |
| Sardine fish | 149 | 2 | 54% |
| Sorghum grain | 192 | 2 | 54% |
| Salmon | 143 | 2 | 54% |
Health Benefits of Leucine
Let’s know about the health benefits that leucine provides:
- Assist building muscle
L-leucine is well known among athletes and bodybuilders due to its influential effects on gaining muscle. It is one of the essential amino acids included in muscle synthesis, it might trigger muscle building to upgrade workout. Research has shown combined results on promising effects of this amino acid. Leucine is effective to enhance muscle growth and performance when mixed with other amino acids than used alone. Add various protein foods to the diet that helps to maximize leucine effects by offering numerous amino acids as well as essential nutrients to fuel muscle growth.
- Prevention of muscle loss
As people get older, lot of changes takes place in the body. Sarcopenia is the gradual deterioration of skeletal muscles which is one of the noteworthy effects of advanced age. It causes weakness and lowers stamina resulting decline in physical activity. Leucine helps to reduce deterioration of muscle to lower the aging effects. Study shows that it promotes muscle synthesis in older adults with intake of recommended amount of protein per meal. Another study conducted on human model also showed similar results that report that supplementation of leucine helps to limit weight loss caused due to malnutrition in elderly participants.
- Enhance performance
Besides its use for bodybuilding purpose, athletes use leucine for improving physical performance. Study shows that taking supplementation of leucine for six weeks improve both endurance as well as upper body power in competitive canoeists. Other study shows that supplementation of leucine promoted lean tissue mass and enhanced functional performance in older adults.
- Assist fat loss
Leucine is helpful for those who are trying to build muscle and at the same time shed some extra body fat. Several studies have shown its powerful effects on fat loss. An animal model shows that supplementing low dose of leucine to rats for six weeks resulted increase in fat loss in comparison to control group. Leucine is shown to lower accumulation of fat during aging and prevent development of diet associated obesity.
- Recovery of muscles
Sore muscles and cramp are annoying which is experienced by many people after they hit gym. With an intense workout, these muscle aches make one completely throw off schedule and delay fitness goals. Studies have shown promising results on the ability of leucine in recovery of muslces. Review showed that intake of leucine after working out helps to stimulate recovery of muscles and muscle protein synthesis. Other studies show that supplementation of this amino acid promoted recovery and enhance high intensity endurance performance in male cyclists after training.
- Stabilize blood sugar
High blood sugar is also termed as hyperglycemia can wreak havoc on health. It causes symptoms such as fatigue, increased thirst and unintentional weight loss. If left untreated, high blood sugar could cause more serious problems such as kidney problems, nerved damage and prone to skin infections.
Research shows that leucine helps to maintain normal level of blood sugar. Study conducted on human shows that leucine taken with glucose helps to stimulate secretion of insulin and lower blood sugar levels in participants. Leucine helps to facilitate signaling of insulin and uptake of glucose to normalize blood sugar levels.
- Lowers risk of atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis indicates hardening of arteries which is associated to high low density lipoprotein levels and high density lipoproteins helps to lower chances of atherosclerosis due to its reverse role in cholesterol transport. Supplementation of leucine in rat studies lower LDL by 41% and increase HDL by 40%. Its supplementation lowers atherosclerotic lesions by 58%. Chronic inflammation and high cholesterol levels are associated to atherosclerosis. Supplementation of leucine lowers liver cholesterol by 52% and lowers inflammation.
References:
https://www.nutritionexpress.com/article+index/protein/showarticle.aspx?id=807
https://examine.com/supplements/leucine/
https://www.britannica.com/science/leucine
http://www.aminoacidsguide.com/Leu.html
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leucine
http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Leucine
https://www.selfhacked.com/blog/leucine-health-benefits-side-effects/
