Glycine is an amino acid which is a building block for protein. It is regarded as essential amino acid as the body could make it from other chemicals. Typical diet possesses 2 grams of glycine regularly. Its primary sources are protein rich foods such as fish, meat, legumes and dairy. It is used to treat schizophrenia, sleep problems, stroke, metabolic syndrome, benign prostatic hyperplasia and some rare inherited metabolic disorders. It is used to prevent kidneys from harmful side effects of some drugs which are used after organ transplantation and liver from harmful effects of alcohol. It is used to lower chances of psychosis. Other uses include memory enhancement and cancer prevention.
People directly apply glycine to the skin for treating leg ulcers and heal other wounds. It is an amino acid which has single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It has the chemical formula NH2-CH2-COOH. It is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by codons starting with GG (GGC, GGU, GGG, GGA). It is colorless and sweet tasting crystalline solid. It is an achiral proteinogenic amino acid. It could fit into hydrophilic or hydrophobic environments because of its minimal side chain of only one hydrogen atom. It is an earliest amino acids which is to be isolated from gelatin. Its rich sources include silk fibroin and gelatin.
It is simple amino acids in terms of molecular structure and exclusive among standard amino acids. It is essential for normal functioning in humans and could be synthesized by the body from other compounds. It is essential for synthesis of proteins but also purines, ATP, porphyrins, serine and other organic chemicals and a major inhibitory neurotransmitter in central nervous system. Most of the protein possesses small quantities of glycine. Collagen contains about one third glycine. Glycine is an extrusive in gelatin. Alanine and glycine are two small amino acids that form bulk of protein which comprises of spider silk which a strongest material. Glycine units are important for elasticity of spider silk.
History and etymology
French chemist Henri Braconnot discovered glycine in 1820 when he hydrolyzed gelatin by boiling it with sulfuric acid. It is originally called sugar of gelatin but French chemist Jean Batiste Boussingault showed it possesses nitrogen. Eben Norton Horsford, an American scientist and student of German chemist Justus von Liebig gave it name glycocoll yet Swedish chemist Berzelius suggested it glycine. The name is derived from Greek word “γλυκύς” which means sweet tasting. French chemist Auguste Cahours in 1858 determined that glycine is an amine of acetic acid.
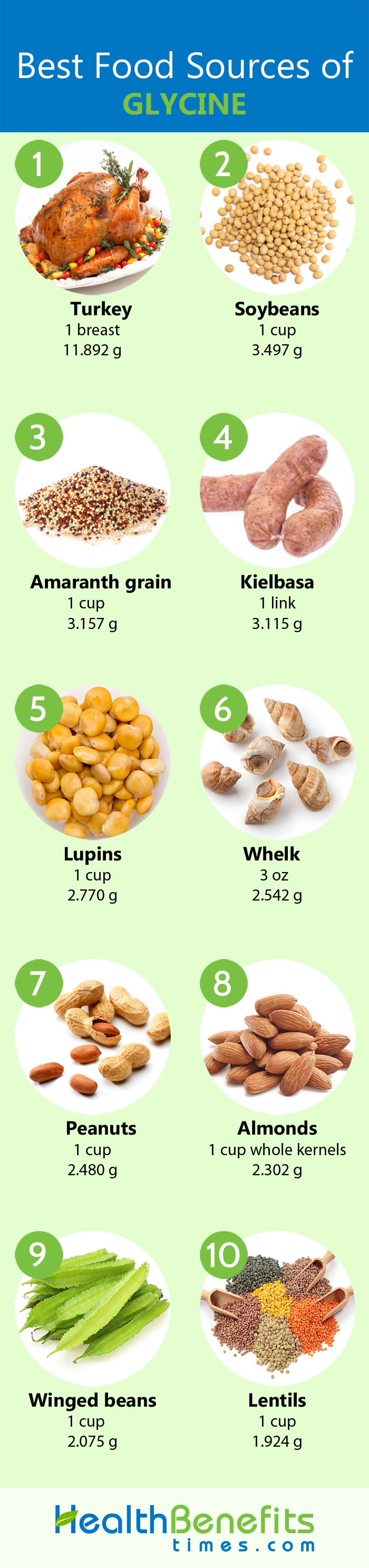
Dietary Sources
| Food name | Weight (g) | Glycine (g) |
| Turkey | 863 | 11 |
| Soybeans | 186 | 3 |
| Amaranth grain | 193 | 3 |
| Kielbasa | 370 | 3 |
| Lupins | 180 | 2 |
| Peanuts | 146 | 2 |
| Mungo beans | 207 | 2 |
| Hyacinth beans | 210 | 2 |
| Almonds | 145 | 2 |
| Winged beans | 182 | 2 |
| Tuna | 146 | 2 |
| Butternuts | 120 | 1 |
| Tilefish | 150 | 1 |
| Lima beans | 202 | 1 |
| Salami | 113 | 1 |
| Buckwheat | 170 | 1 |
| Sesame | 144 | 1 |
| Haddock fish | 150 | 1 |
| Lobster | 150 | 1 |
| Adzuki beans | 197 | 1 |
Health Benefits of Glycine
Here are some health benefits discussed on Glycine:
- Muscle health
Glycine helps to inhibit degradation of valuable protein tissue which forms muscle and enhance muscle recovery. It is called an anti-aging amino acid as it helps to maintain lean muscle mass into old age, prevent loss of cartilage in joints, stimulate secretion of human growth hormone and improve daytime energy, mental capabilities and physical performance.
During biosynthesis of creatine, glycine provides muscles having direct source of fuel for repairing damage and grow back stronger. It provides energy to cells as it converts nutrients from diet and feeds hungry muscle tissues and increase endurance, performance and strength. It is beneficial for hormone production and regulation, assist body to naturally synthesize steroid hormones which regulate ratio of fat to muscle mass and control energy expenditure.
- Enhance digestion
Amino acids such as proline and glycine helps to rebuild tissue which lines digestive tract, keep foods particles and bacteria inside gut where it belong and allow tiny openings for forming to pass particles to bloodstream where it trigger inflammation. It helps to form two most essential substances which makes gut lining: gelatin and collagen. Gelatin and collagen helps people with food allergies and sensitivities. It could soothe lining of GI tract in people having inflammatory bowel disease and indigestion, IBS, leaky gut syndrome, ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s and acid reflux.
It acts as a metabolic fuel in GI tract. It is required to manufacture bile, creatine phosphate, nucleic acids and porphyrins used for breaking down nutrients from diet. Glycine helps to stabilize level of blood sugar leading to more lasting energy and prevent fatigue and sugar cravings.
- Strengthen immunity
Glycine helps in forming glutathione which is an antioxidant used for preventing cellular damage and various signs of aging. Deficiency of glutathione in elderly people is occurred due to marked reduction in synthesis and supplementation with glutathione precursor’s cysteine and glycine fully restores glutathione synthesis. This promotes concentration and reduces level of oxidative stress and oxidant damages which result to aging. Some studies show that glycine helps to prevent cellular mutations that results cancer.
- Brain health
Glycine is helpful to support cognitive performance and central nervous system as it regulates metabolic synthesis of some nutrients which the nerve and brain use for energy. It helps to regulate nerve impulses throughout the body by balancing level of electrolyte such as chloride, calcium and potassium. Glycine has role in both neurotransmitter and nerve functions to help promote sleep, bodily sensations, mental performance, memory, moods and behavior.
Glycine lowers hyperactivity in brain and has a role in treatment or preventing mental disorders such as schizophrenia, learning disabilities, epilepsy, manic depression and bipolar disorder. Some studies shows that glycine helps to lower psychotic symptoms, seizures, strokes when used with other supplements as a part of holistic treatment plan for cognitive/mental illness.
- Sound sleep
Glycine has role in central nervous system and digestive system, it boost energy levels, prevent fatigue and balance blood sugar. It is used to calm nervousness or anxiety which keeps up at night and gets in way of good sleep. It directly brings nutrients to cells or tissues for energy at all times of day. Glycine supplements helps to improve sleep quality, improve performance of memory recognition tasks and lower daytime sleepiness.
It also helps to carry out biosynthesis of heme which is a component of hemoglobin that produce and maintain red blood cells. Red blood cells carry oxygen to the body; provide tissue, support cellular functions, brain and heart with energy. Glycine helps to improve energy in athletes, counteract fatigue caused by anemia and helps to regulate level of blood sugar.
Possible side effects of Glycine
It causes uncommon side effects such as vomiting, nausea, soft stools, mild stomach upset.
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycine
https://www.britannica.com/science/glycine-amino-acid
https://bodynutrition.org/glycine/
