Also called as Flathead grey mullet, Flathead mullet, Black mullet, Striped mullet, Bully mullet, Black true mullet, Bright mullet, Grey mullet, Common mullet, Sea mullet, Mullet, Callifaver mullet, Capitán, Common grey mullet, Flathead greymullet, Formosan gray mullet, Formosan grey mullet and Galapagos mullet. Usually, it schools over sand and mud bottoms feeding on zooplankton.
Description
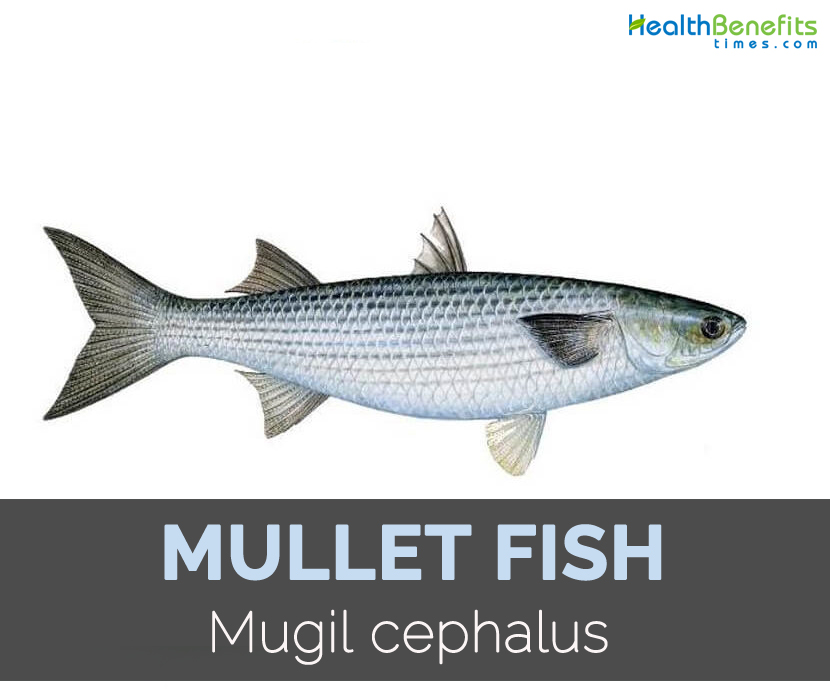
Mullet fish has elongate and robust body with flattened and broad head. Its eyes are covered by well-developed transparent fatty eyelid. Mouths are small with thin lips and open at front having knob at front of lower lips. The outer row of teeth in jaws is simple. Pelvics are inserted behind pectoral base. Scales are moderate to large and rough on body of adults. Scales are in lateral series.
Fish has olive-green back with silvery sides and white belly. It has different lateral horizontal stripes. Commonly, it is 50 cm long and could be upto maximum 100 cm long. The recorded maximum weight is 8 kg.
Lifecycle
Eggs are pale yellow, transparent, spherical and non-adhesive measuring 0.72 mm diameter in average. The eggs hatches after 48 hours of fertilization then release 2.4 mm length larvae. Larvae has no mouth and paired fins. It measures 2.8 mm long at 5 days of age. Jaws become well-defined and fin buds starts to develop. When the larvae become 16 to 20 mm in length, it migrates to estuaries and inshore waters. The adipose eyelid is obvious at 35 to 45 mm and it covers most of the eye by 50 mm. The mullet is regarded as juvenile at this time. Juveniles have the ability of osmoregulation being able to tolerate salinities of 0-35 ppt. It spends the rest of the first year in salt marshes, coastal waters and estuaries. It moves to deeper water in autumn and adults migrate offshore to spawn. After first year of life, it inhabits various habitats such as salt marshes, ocean, fresh water rivers, estuaries and creeks.
Life expectancy
Striped mullet has the lifespan of eight years for female and seven years for male. The record shows that an oldest striped mullet lived for 13 years.
Reproduction
These are catadromous i.e. it spawns in saltwater and spends most of its lives in freshwater. Adult mullet migrates far offshore to spawn in large aggregations during autumn and winter months. In Gulf of Mexico, it is observed spawning 65 to 85 km offshore in water over 1000 meters deep.
The fecundity is estimated to be 0.5 to 2 million eggs per female which depends on the size of an individual. In 4th year, female reaches sexual maturity i.e. between 40 to 42 cm. Males mature in third year when reaching 33 to 38 cm size. The spawning size of females is minimum 31 to 34 cm.
Spawning occurs from mid-October through late January in deep offshore waters with peak spawning that occurs in November and December. Then larvae and prejuveniles migrate to inshore estuaries where it inhabits shallow and warm water.
Food Habits
Being diurnal feeders, it consumes dead plant matter, zooplankton and detritus. They has thick walled gizzard like segments in its stomach along with long gastrointestinal tract which enables them to feed on detritus. Ecologically, it is an important link in energy flow within estuarine communities. It feeds by sucking up top layer of sediments and removing microalgae and detritus. It picks some sediment that function to grind food in gizzard like portion of stomach. Primarily, larvae of striped mullet feed on microcrustaceans.
Predation
Its major predators are larger fish, marine mammals and birds. Cynoscion nebulosus (spotted seatrout) feeds on mullet measuring upto 13.8 to 35 cm long. Often sharks feed on large mullet off the coast of Florida. Striped mullet are also preyed by aquatic birds, pelicans and dolphins. Humans are also considered to be significant predators of striped mullet.
Health Benefits of Mullet fish
Let us discuss the health benefits of mullet fish:
- Nutrition
Besides delicious flavor, mullet is loaded with nutrients which are useful for the body for supporting daily nutritional needs. Moreover, mullet could promote one’s appetite.
- Source of power
Carbohydrate content found in mullet is used as a power source that could achieve regular nutritional needs of the body. Carbohydrates play a vital role in metabolic processes in the body. Additionally, mullets have fat, protein and carbohydrate that serve as a source of body required for the body.
- Skin and hair health
Mullets have fatty acid content which is essential to maintain healthy hair and skin. It also prevents drying and flaking.
- Accelerate healing of sounds
The protein content in mullet are useful to promote the healing of wounds. Protein has a role of regerenerasi cells in the body.
How to Eat
- It is dried, salted and smoked.
- Mullet is used to make as Taiwanese Wuyutsu, Greek avgotaraho, Korean myeongran jeot, Italian bottarga, Japanese karasumi, Turkish Haviar and Egyptian batarekh.
- Mullet is consumed baked, fried or canned.
- Mullet is used in stews and chowders.
- It could be steamed, poached, sautéed, broiled and microwaved.
- It is marinated to the salad dressing.
- Add it to salad greens and pasta.
- Grill or broil it with seasoned salt and lime–butter.
Other Facts
- It could measure reach 2.5 feet in length and weighs from 2 to 3 pounds.
- The body is covered with large scales.
- Mullet has triangular shaped mouth and small head.
- Teeth are compact, miniature and arranged in several rows.
- The shape of lower jaw resembles spade.
- With two dorsal fins, first dorsal fin has five sharp spines and second dorsal fin has eight soft rays.
- It is also called happy mullet or jumping because it jumps and effectively skips across water surface.
- In wild, mullets could survive up to 16 years.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=170335#null
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flathead_grey_mullet
http://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Mugil_cephalus/
http://www.foodreference.com/html/art-mullet.html
http://www.softschools.com/facts/animals/mullet_facts/1272/
Comments
comments
| Mullet Fish Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Mullet Fish |
| Scientific Name: | Mugil cephalus |
| Origin | Native to perennial Hawaiian streams |
| Colors | Olive-green |
| Shapes | Flat head, torpedo, 135 cm |
| Calories | 140 Kcal./cup |
| Major nutrients | Selenium (79.09%) Isoleucine (63.58%) Lysine (63.37%) Tryptophan (58.86%) Threonine (57.50%) |
| Health benefits | Nutrition, Source of power, Skin and hair health, Accelerate healing of wounds |