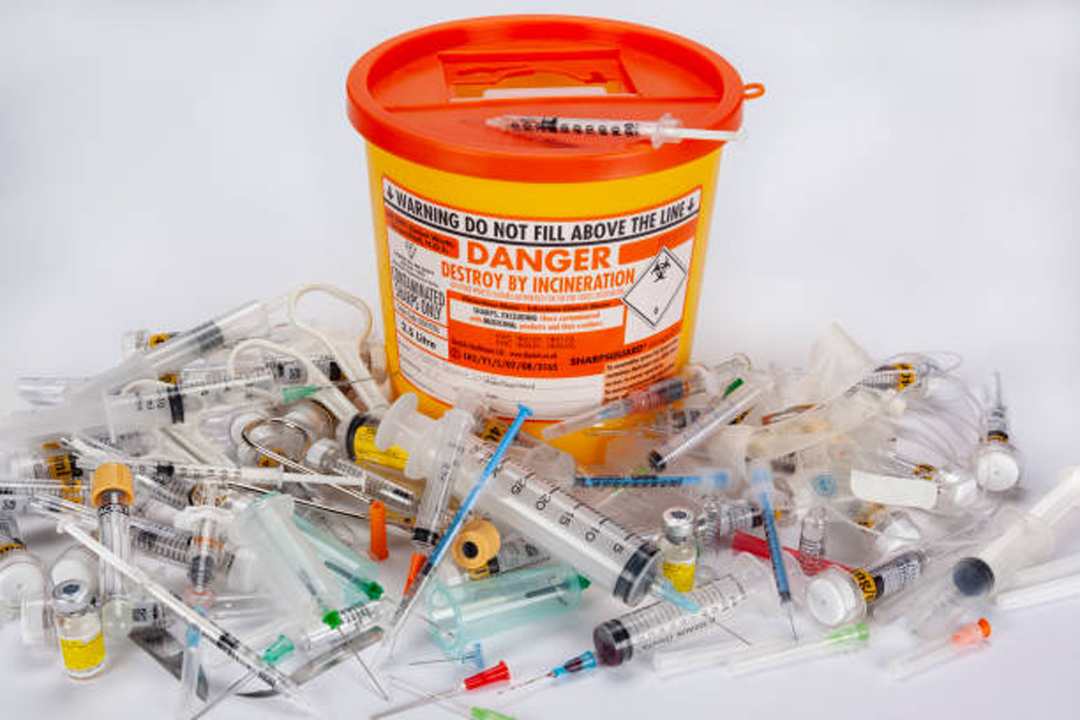
It is estimated that medical facilities such as hospitals create more than 5.9 million tons of waste in the United States each year. Such a huge amount of medical waste requires secure disposal methods to protect the environment from the risks of waste contamination. Medical waste is particularly concerning because it contains infected items, including blood, body fluids, organs, used gauges, and syringes. If not disposed of responsibly, the contaminated medical waste can spread infections, putting our health in danger. With an emphasis on medical waste disposal, here we will highlight its importance, methods, regulations, and more.
Importance of Responsible Medical Waste Disposal
Medical facilities such as hospitals, dental offices, physician’s clinics, blood banks, veterinary facilities, and various research facilities and laboratories contribute to medical waste production in large amounts. As the number of people seeking medical care is on the rise in the United States, so is the medical waste generation. Such trash includes items that are contaminated by infected blood and body fluids. Haphazard disposal of the infected waste can lead to the spread of infections such as HIV, hepatitis, diarrhea, tuberculosis, and more. Therefore, to prevent the epidemic of medical waste contamination, it is important to follow a proper waste management procedure.
Here are some essential tips for responsible medical waste disposal:
- Identification and classification of the waste (hazardous and non-hazardous)
- Segregation of the waste for proper disposal and cross-contamination prevention
- Secure packing and labeling of the waste
- Storage of the waste in a well-ventilated space
- Safe transportation of the waste to the disposal facility
- Application of suitable disposal methods, such as incineration, landfill disposal, chemical treatment, and so on
What are the Methods of Medical Waste Disposal?
Medical waste comprises various types of waste, including sharps disposal, pharmaceutical waste, infectious waste, biomedical waste, general waste, and more. For proper disposal, each category of waste has to be handled differently. Thus, there are different methods of medical waste disposal adapted accordingly. Here are some of the commonly used methods:
Incineration
Incineration is mostly used to dispose of pharmaceutical and pathological waste. This method involves incinerating the waste at a high temperature of over 2,000°F. Incineration is done in a controlled facility where the waste is burned in a regulated environment. It is a highly efficient method that leaves no contamination behind.
Chemical Disinfection
For chemical and liquid waste, the chemical disinfection method is preferable. This method decontaminates the waste through chemical treatment. The trash is treated with disinfecting chemicals such as chlorine and sodium hydroxide, among others. It is carried out on-site before sending the waste to the disposal facility.
Autoclaving
Autoclaving is a thermal disinfection method used mainly for sharps. In this process, the waste is sterilized using steam to get rid of contaminating agents. For proper decontamination, the autoclaving container has to be the right size, fitting the amount of waste you generate. It is an on-site process and is done before the waste is transported to the disposal center.
Land Disposal
Landfill disposal is typically used for decontaminated medical waste that has been treated and sterilized. Waste that has undergone suitable decontamination methods can only be disposed of in landfills. This method is mostly used for liquid waste and general waste.
Microwave Irradiation
Microwave treatment is somewhat similar to autoclaving. It utilizes heat to disinfect the medical waste. It is commonly used for dry or solid waste. The waste undergoes a microwaving process, which gets rid of the microorganisms in the waste efficiently before the final disposal.
Color Codes Used for Medical Waste Disposal Containers
You must have noticed colored trash bins in hospitals. These bins are color-coded for a specific purpose. The different colors of the bins indicate different types of medical waste that go into them. Here is what the color codes represent:
- Red container: It contains biohazardous trash such as blood, body fluids, sharps, and contaminated PPE.
- Yellow container: It contains chemo waste, including PPE, IV bags, chemo drugs, sharps, and other items used for the chemo.
- Blue container: It contains hazardous trash, including pills, injectables, and antibiotics.
- Black container: It contains highly toxic hazardous waste, such as radioactive items, cleaning solvents, and hazardous pharmaceutical items.
Conclusion
Safe and responsible medical waste disposal can protect us from potential health hazards due to waste contamination. Therefore, to ensure proper medical waste management, it’s essential to stick to the waste handling and disposal guidelines. Such regulations not only protect us from health risks but also help keep our environment clean and trash-free.
FAQs
What method is best for medical waste disposal?
Incineration is considered the best method for securely disposing of medical waste. This method involves the complete combustion of the waste for its final disposal. Incineration is a commonly used method for medical waste management because of its safety, efficiency, and reliability. Besides, it not only gets rid of waste efficiently but also generates heat energy that can be utilized for other beneficial purposes.
What precautions should be taken during medical waste disposal?
Here are some of the essential precautions you should follow for your safety while dealing with medical waste disposal:
- Make sure to wear sterile PPE gear, such as gloves, masks, boots, and suits, before handling the medical waste.
- Look for biohazard symbols in the waste that you accumulate and place them separately.
- Use puncture-resistant and leak-proof containers to collect sharp waste (needles and glass).
- Collect the medical waste in containers specially designed for medical waste.
- Close the lid of the container securely after collecting the waste.
- Label the containers and specify the type of waste they hold, such as solid waste, liquid waste, and sharps.
- Store the waste containers or bags in a well-ventilated area to avoid foul odors.
How do I pack medical waste?
Here are some of the important steps to follow while packing the medical waste:
- Identify the waste: Check and classify the type of medical waste, i.e., sharps, liquid, and solid, and store them in separate bags.
- Follow the requirements: Comply with the state-level requirements for the thickness of the bag and its weight limit for waste collection.
- Use specific containers: Place the bag in a specially designed medical waste collection container. Tie the bag properly and securely close the lid of the container.
- Label the containers: Ensure the container is labeled properly with suitable details, such as the type of waste inside and the waste generator’s name and address.
How do I dispose of medical waste generated from households?
Before the disposal, make sure to disinfect the sharps (needles, lancets, syringes, etc.) in a solution of bleach and water. Keep the disinfected sharps in a puncture-resistant bag or container. Likewise, pack other infectious medical waste (used gauze, bandages, gloves, etc.) in a leak-proof plastic bag. For proper disposal, contact your local hospital or pharmacy to inquire about the medical waste collection service provider in your area.
How do you treat liquid biomedical waste?
The liquid form of biomedical waste is disposed of after disinfecting and neutralizing the waste. It is disinfected using bleach or other EPA (Environmental Protection Agency)-registered chemical disinfectants. The treated waste is then disposed of in the sanitary sewer drain.
What is the red dustbin used for in hospitals?
The red dustbin in a hospital is used to store biomedical waste generated in the hospital. The waste that goes into these containers is needles, surgical knives, cotton dressing, sanitary napkins, body fluids, tissues, etc. These are all non-recyclable wastes that undergo incineration for final disposal.

