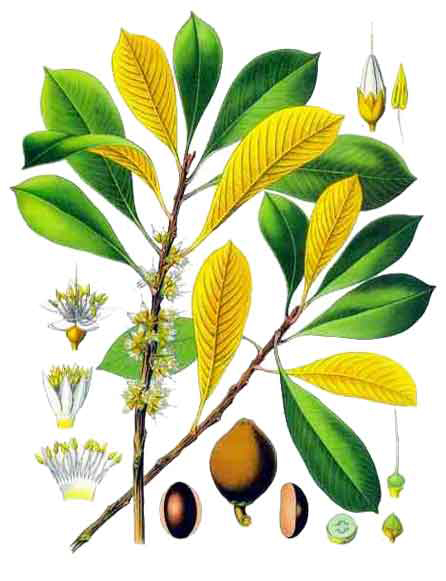
Plant
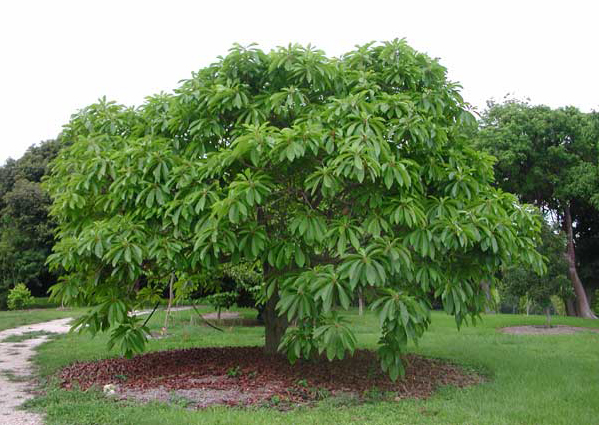
Mamey sapote is an extremely ornamental erect, lactiferous, evergreen tree with a spreading open crown that grows to the height of 15 to 45 meters (49 to 148 ft.) at maturity. Similar to several other fruit trees, grafting is the main technique used for propagating mamey sapote. Additionally, trees propagated by grafting not only have a more rapid growth rate, but also bear fruits sooner compared to those propagated from their seeds. They thrive best in humid tropical or near tropical lowlands with warm temperatures and grow well in well-drained soils, heavy clays to the limestone and infertile sandy soils. It is intolerant of constantly wet or flooded soil conditions which impedes root development and enhances root rots by soil-borne fungi.
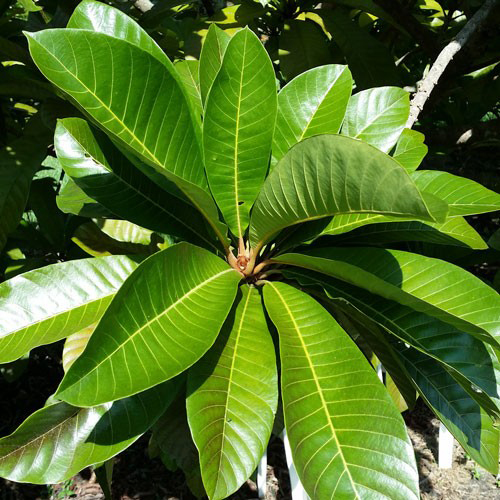
Leaves
The leaves are large, 10–30 cm by 4–10 cm wide, simple, obovate to oblanceolate, with broadly-acuminate apex, tapering base, entire margin, and prominent depressed mid-rib and lateral veins. Upper side of leaves is glossy green while underside is lighter green or brownish and pubescent (hairy) when young but becomes glabrous (smooth) when mature. The leaves are clustered at the ends of the small branches. Depending on the cultivar and recent crop load, trees will drop most of the leaves in late winter or spring, but develop new leaves rapidly.
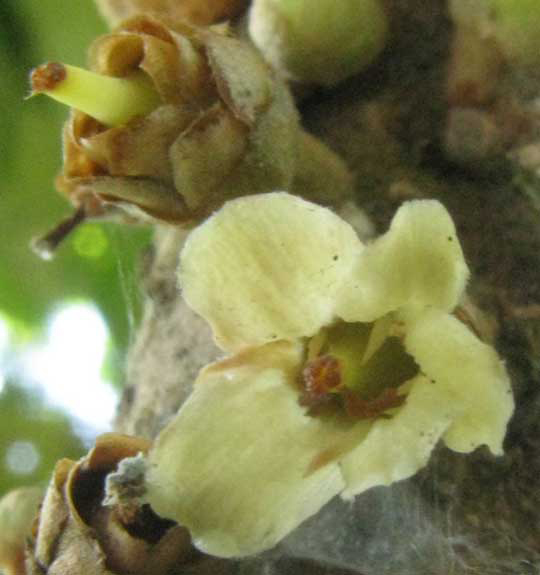
Flowers
Mamey sapote bears small, perfect, whitish, almost sessile flowers along small branches (1/2 to 2 inches; 1.3 to 5.1 cm), and tend to cluster towards the ends of the stems.
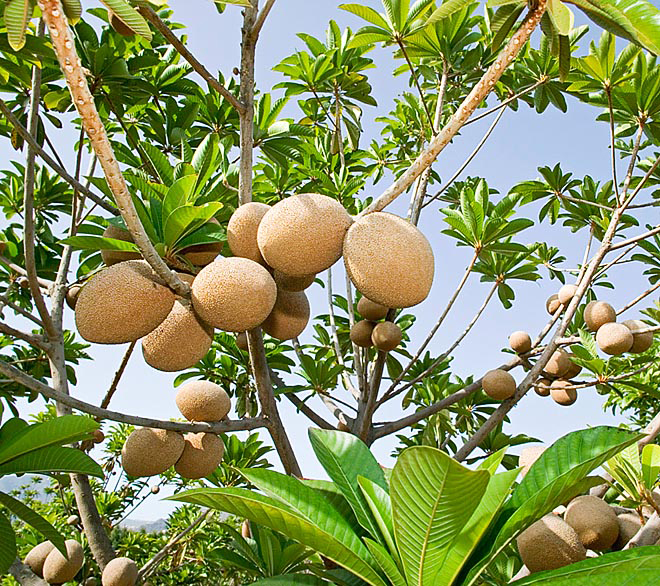
Fruit
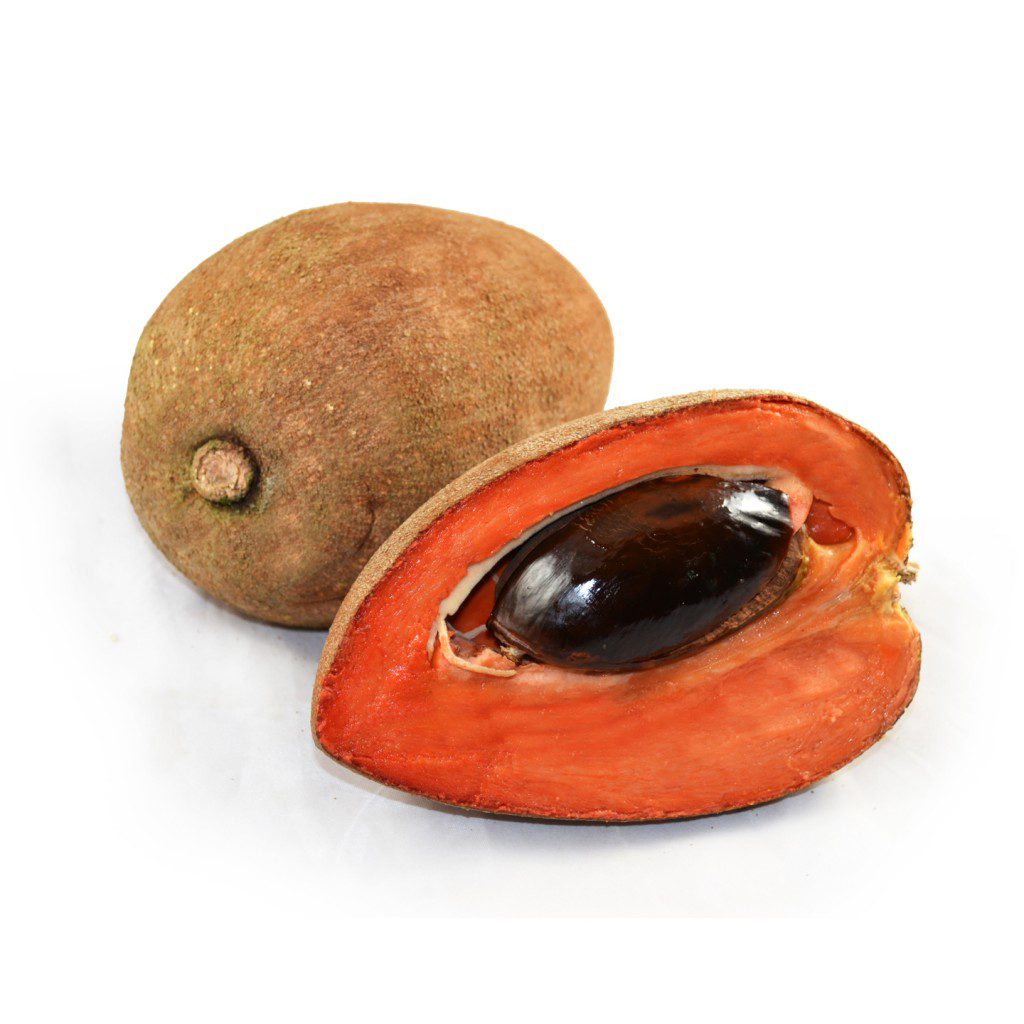
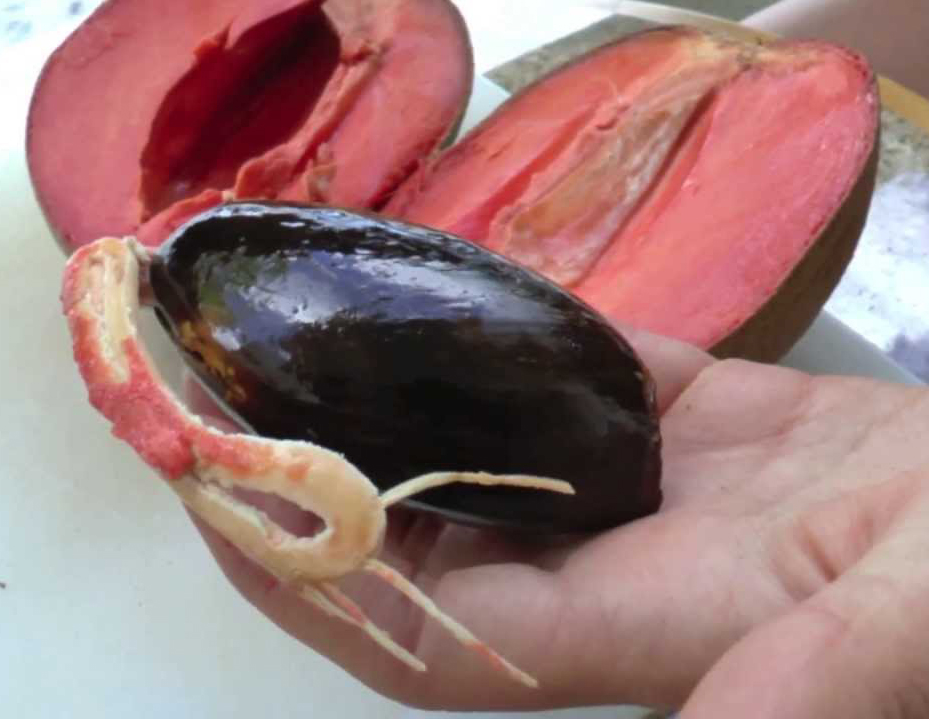
Mamey Sapote is a fruit that is technically a berry, though a very large one. It is ovoid to ellipsoid, 10 to 25 cm (4 to 10 in) long and 8 to 12 cm (3 to 4.5 in) wide, often bluntly pointed at the apex and with a persistent calyx at the base. The skin is thick and woody with a russet brown, somewhat scurfy surface about 1–2 mm thick. The pulp of mature fruits is salmon pink, orange, red or reddish-brown in color, soft and smooth to finely granular in texture, usually low in fiber. The pulp has a sweet, almond-like, unique flavor and sweet taste like a combination of pumpkin, chocolate and almond or akin to a mixture of sweet potato, avocado and honey. Normally, the fruit contains a single, large, elliptical seed but it may have up to four. The seed has a shiny, hard, dark brown surface with a light brown scar (hilum) on the ventral side. Seeds may crack and sprout in over mature fruits. Fruit weight ranges from 0.75 to 6.0 lb. (0.3-2.7 kg).
History
Mamey sapote is considered to have originated from Central America – Belize, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua Puerto Rico and Mexico. It was long cultivated by the ancient Mayans in Mexico and has now naturalized in tropical America and the West Indies. The tree is grown in Central America, South America, the Caribbean, and South Florida for its fruit, which is commonly consumed in many Latin American countries.
Nutritional Value
Apart from their sweet taste like a combination of pumpkin, chocolate and almond or akin to a mixture of sweet potato, avocado and honey, mamey sapote is a good source of nutrients, vitamins and minerals. Consuming 175 gram of mamey sapote offers 1.26 mg of Vitamin B6, 40.2 mg of Vitamin C, 56.18 g of Carbohydrate, 0.373 mg of Copper, 9.5 g of Total dietary Fiber and 3.69 mg of Vitamin E. Moreover many Amino acids 0.086 g of Tryptophan, 0.149 g of Threonine, 0.107 g of Isoleucine, 0.128 g of Leucine and 0.128 g of Lysine are also found in 175 gram of mamey sapote.
Health benefits of Mamey sapote
Mamey Sapote is a delicious berry which is ovoid to ellipsoid, 10 to 25 cm (4 to 10 in) long and 8 to 12 cm (3 to 4.5 in) wide, often bluntly pointed at the apex and with a persistent calyx at the base. Apart from its delicate taste it has higher nutritional value and is consumed throughout the world. Listed below are some of the popular benefits of consuming mamey sapote on a regular basis:
1. Weight Management
Selecting nutrient-dense foods that are extremely gratifying for comparatively few calories is a simple way to lose or prevent unwanted pounds. Mamey sapote fills you up and delays the onset of hunger within a few ways. According to the USDA, nearly 30% of the fruit’s carbohydrates come from starch. These complex carbohydrates contribute to long-term satiety because they take longer to digest. More significantly, mamey sapote is a high-fiber food that offers substantial amounts of both types of fiber, soluble and insoluble. Its insoluble fiber takes up space in your stomach to help you feel fuller on fewer calories, while its soluble fiber slows the rate at which digested food exits your stomach.
2. Cardiovascular Health
Mamey sapote is one of the heart-healthy foods. Fruit consists of soluble fiber that helps to promote healthy cholesterol levels, thus reducing your risk of heart disease. Its high potassium content defends cardiovascular health by keeping blood pressure in check and supporting normal heart function. As an excellent source of vitamin C, mamey sapote helps to maintain firm capillaries and blood vessels. Its considerable vitamin E content helps prevent the buildup of plaque in your blood vessels and arteries, which lower your risk of heart attack, stroke as well as coronary artery disease. As antioxidants, vitamins C and E also protect against the kind of free-radical damage associated with heart disease and other chronic illnesses. Vitamin E is mainly beneficial to cardiovascular health, as it helps prevent the oxidation of artery-damaging LDL cholesterol.
3. Increased Immune Function
Mamey Sapote consists of considerable amount of Vitamin C content which helps the body to fight free radical and eliminate them. Vitamin C helps the immune system function effectively. Many instances that trigger immune response that actually result to inflammation. It can be avoided by regular consumption of vitamin C rich foods like mamey sapote.
4. Helps Treat Anemia
Mamey Sapote consists of huge amount vitamin B6 that is needed to create hemoglobin in the blood, which is transported by red blood cells throughout the body to help bring oxygen to cells and to mobilize iron. Anemia results when somebody doesn’t make enough red blood cells, resulting in symptoms like fatigue, aches and pains, and more. Several researches show that consuming plenty of vitamin B6 help lower symptoms of anemia and prevent it from occurring in some instances.
5. Reduces Cholesterol
Research has shown that copper help to reduce the levels of “bad” cholesterol (LDL cholesterol) and help to increase beneficial cholesterol (HDL cholesterol). Regular consumption of Mamey Sapote helps to lowers the chances of cardiovascular diseases like atherosclerosis, heart attacks, and strokes.
6. Helps PMS Symptoms
Taking a vitamin E supplement 2-3 days before and 2-3 days after a menstrual period help to reduce the cravings, cramping and anxiety that are related to PMS. Mamey Sapote is one of the best options for vitamin E that help to decrease pain severity and duration, and can reduce menstrual blood loss. It does this by balancing your hormones naturally and it helps to keep your menstrual cycle regulated.
7. Gives skin a Healthy Glow
Pale skin and dark circles are the most common signs of anemia caused due to iron deficiency. Insufficient iron causes hemoglobin levels to decrease, resulting in the subsequent reduction of RBCs. The reduced oxygen flow can deprive your skin of its color, making it look sallow. A healthy dose of iron-rich foods in your daily diet can give your skin a pinkish glow.
8. Bone Health
Potassium present in Mamey sapote is beneficial for improving the health of the bones. There are certain qualities of potassium that help to neutralize numerous acids throughout the body which retain as well as preserve calcium, making it inaccessible to use for bone strength and durability. Additionally, research at the Linus Pauling Institute Micronutrient Information Center claims that consuming fruits and vegetables that have high levels of potassium results in higher mineral density in bones, further strengthening and prolonging the life of your bones!
9. Supports Proper Brain Function
Research have shown that vitamin B3 niacin present in Mamey Sapote help to protect against Alzheimer’s Disease as well as other age related brain disorders that result in cognitive decline.
Furthermore, Vitamin B3 niacin is also correlated with a decreased risk for many problems regarding poor brain function or loss of age-related thinking skills, like memory loss, insomnia, migraine headaches, motion sickness, chronic brain syndrome, depression, and even alcohol dependence.
10. Helps Support Eye Health
Researches have shown that riboflavin deficiency increases the risk for certain eye problems. Vitamin B2 helps to prevent eye disorders like cataracts, glaucoma and keratoconus. Apart from that research has shown a correlation between people who consume sufficiently of riboflavin and decreased risks for eye disorders that can appear as someone ages. Mamey Sapote consists of 0.203 mg of vitamin B2 which is 15.62% of the daily recommended value.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y95Gw0YlCwE
How to Eat
- Ripe fruit pulp is consumed fresh out of hand or spooned out from the half-shell.
- Pulp is made into milkshakes, smoothies, ice cream or frozen as sherbet, sauces and when cooked it is acceptable as apple puree for use in confectionary.
- Fruit is also preserved, made into jams and jelly and the fibrous fruits are set aside for processing.
- Pulp has been imported into Florida by a prominent dairy company for processing and preparing a special “Spanish sherbet”.
- Thick sapote preserve called “crema de mamey colorado” is much relished in Cuba.
- Pulp is occasionally used as filler in making guava cheese.
- Oily large kernel of the seed is also edible.
- Seed kernel can be boiled, roasted, finely ground and mixed with cocoa for making chocolate or made into confectionary.
- Powdered kernel is mixed with parched corn, or cornmeal, sugar and cinnamon and prepared as a nutritious beverage called “pozol” around Oaxaca, in southern Mexico.
- Seed kernel yields 45–60% of white, semi-solid, vaseline-like oil which is edible when freshly extracted and refined.
- Fruit is consumed raw or made into milkshakes, smoothies, ice cream and fruit bars.
- It can be used to produce marmalade and jelly.
Other Traditional Uses and benefits of Mamey Sapote
- It is used widely as a panacea for gastro-intestinal maladies.
- Mamey is used to treat headaches and venereal diseases in southern Cuba.
- Mamey is used as an antiseptic during the Spanish-American war.
- Pulp of the fruit is used as a sedative cataplasm; and an infusion of the bark is prescribed as a pectoral in Antilles.
- Tea of the bark and leaves is administered in arteriosclerosis and hypertension in Costa Rica.
- Milky sap is emetic and anthelmintic and has been used as a poultice to remove warts and fungal growths on the skin.
- Seed infusion is used as eyewash in Cuba.
- Seed coat was used by the Aztecs as a remedy for epilepsy, and in Costa Rica it is considered a cure for colds.
- Pulverized seed coat is reported to be a remedy for coronary trouble and, taken with wine, is said to be helpful against kidney stones and rheumatism in Mexico.
- Seed kernel is regarded as a digestive; the oil is said to be diuretic.
- Seed kernel oil is used as a skin ointment and tonic, and as a hair dressing believed to stop falling hair in Santo Domingo.
- Oil from the seed is used as a skin tonic, to prevent baldness, to reduce muscular pain and to treat rheumatic ailments in Guatemala and El Salvador.
- Two or three pulverized kernels are combined with 10 oz. (300 g) castor oil for application to the hair in Mexico.
- The oil is used as a sedative in eye and ear ailments.
- Seed residue after oil extraction is applied as a poultice on painful skin afflictions.
Other Facts
- Tree is used as shade for coffee.
- Tree provides fine-grained, compact, hard, heavy, strong, easy to work and fairly durable reddish-brown timber but is rarely misused as timber.
- Wood is used for furniture, but commonly serves for building carts, and for shelving and house frames.
- Nectar of the flowers is collected by honeybees.
- Seeds contain white semi-solid oil called sapuyucol or zapoyola, which was used in olden times to fix paintings and colors on gourds and other handicrafts.
- The edible vaseline- like oil from the seed kernel is occasionally used in making soap and is considered to have a greater potential in the soap industry, in cosmetics and pharmaceutical products.
- Seeds have served as a source of Noyeau scent in perfumery.
- During the nineteenth century, the seeds were used as a linen starch in Costa Rica.
- Thick, yellow gum from the bark is melted with fat and applied to the feet to combat chiggers and used to rid animals of fleas and ticks in Mexico and Jamaica.
Precautions
- The milky latex of the tree is extremely irritant to the eyes and caustic and vesicant on the skin.
- Leaves are supposedly poisonous and the seeds are reported to have incredible properties due to its HCN content.
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pouteria_sapota
http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/mg331
http://healthyliving.azcentral.com/health-benefits-mamey-sapote-15963.html
https://www.slowfoodusa.org/ark-item/pantin-mamey-sapote
http://www.localharvest.org/mamey-sapote-C13452
https://www.hort.purdue.edu/newcrop/morton/mamey.html
https://www.healthaliciousness.com/fruits/mamey.php
http://www.capetrib.com.au/mamey.htm
http://www.australiantropicalfoods.com/index.php/exotic-fruits/mamey-sapote/
http://www.virtualherbarium.org/tropicalfruit/mameySapote.html
http://www.rarefruitclub.org.au/Level2/Mamey.htm
Comments
| Mamey Sapote Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Mamey Sapote |
| Scientific Name: | Pouteria sapota |
| Origin | Central America –Belize, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua Puerto Rico and Mexico. |
| Colors | Russet-brown |
| Shapes | Berry, sub globose, ovoid to ellipsoid, 10 to 25 cm (4 to 10 in) long and 8 to 12 cm (3 to 4.5 in) wide |
| Flesh colors | Deep orange, salmon-pink or reddish brown |
| Taste | Sweet like a combination of pumpkin, chocolate and almond or akin to a mixture of sweet potato, avocado and honey. |
| Calories | 217 Kcal./cup |
| Major nutrients | Vitamin B6 (96.92%) Vitamin C (44.67%) Carbohydrate (43.22%) Copper (41.44%) Total dietary Fiber (25.00%) |
| Health benefits | Weight Management, Cardiovascular Health, Increased Immune Function, Helps Treat Anemia, Reduces Cholesterol, Helps PMS Symptoms, Gives skin a Healthy Glow, Bone Health, Supports Proper Brain Function, Helps Support Eye Health |
| More facts about Mamey Sapote | |
| Rank | Scientific Name & (Common Name) |
|---|---|
| Kingdom | Plantae (Plants) |
| Subkingdom | Tracheobionta (Vascular plants) |
| Superdivision | Spermatophyta (Seed plants) |
| Division | Magnoliophyta (Flowering plants) |
| Class | Magnoliopsida (Dicotyledons) |
| Subclass | Dilleniidae |
| Order | Ebenales |
| Genus | Pouteria Aubl. (Pouteria) |
| Species | Pouteria sapota (Jacq.) H.E. Moore & Stearn (Mammee sapote) |
| Synonyms |
|