Plant description
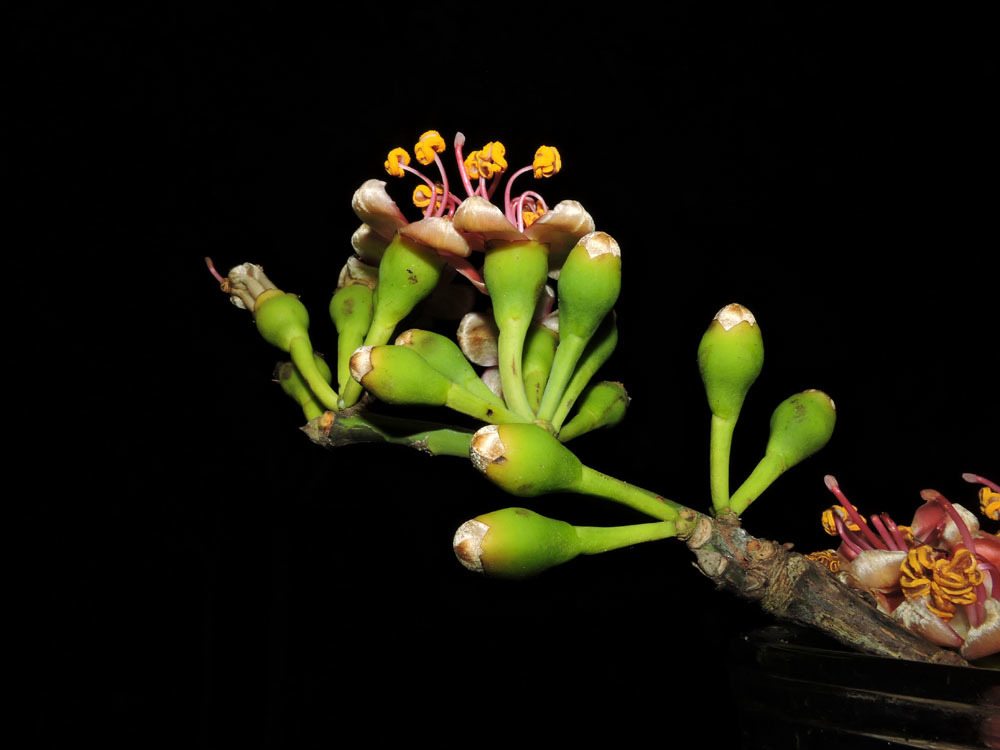
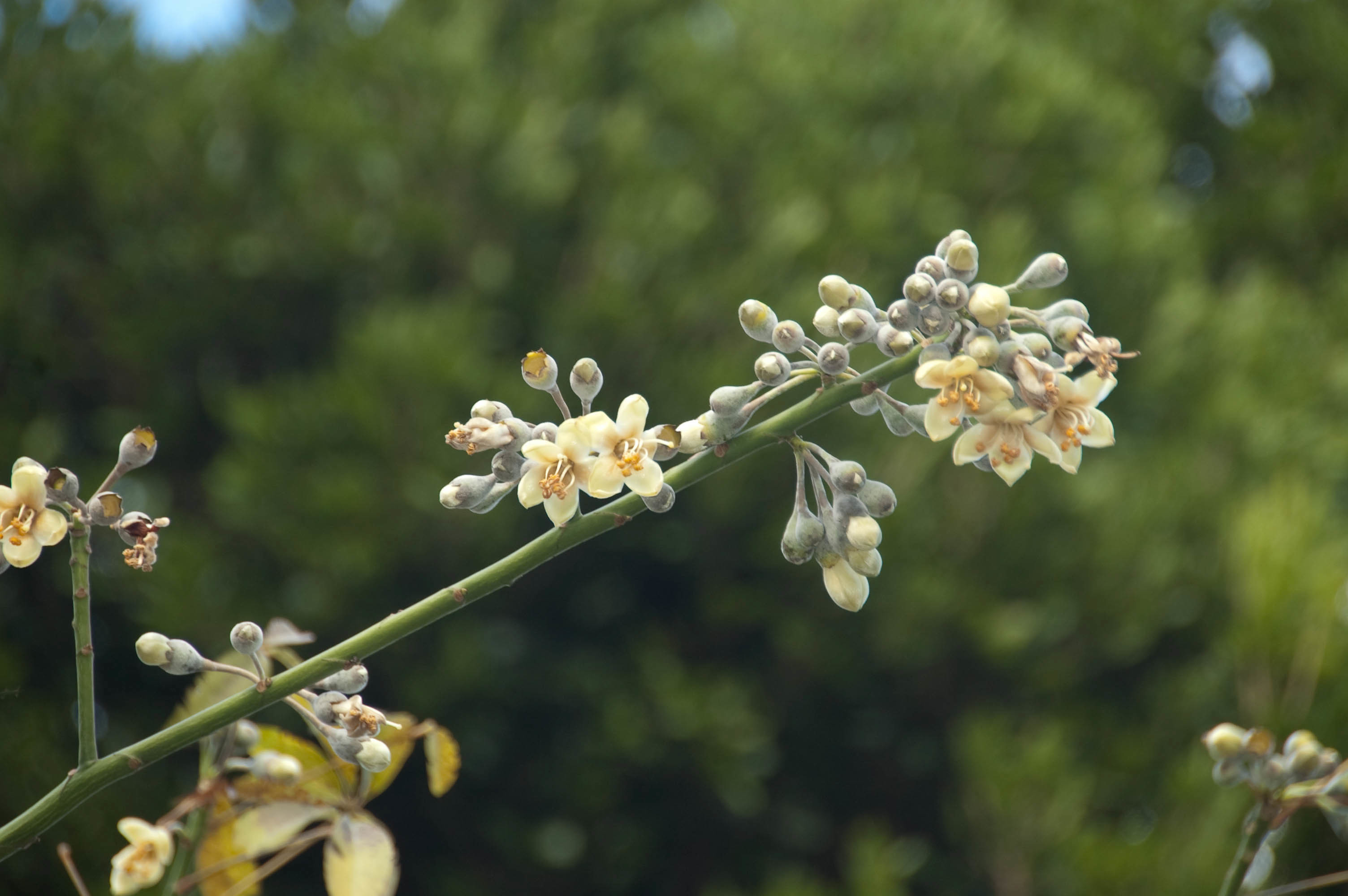
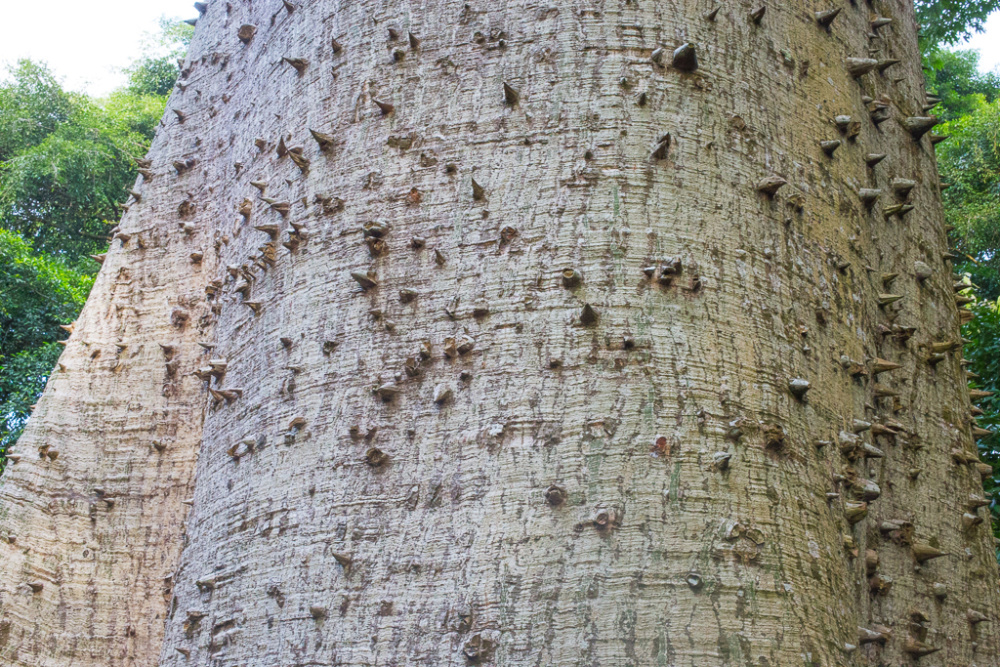
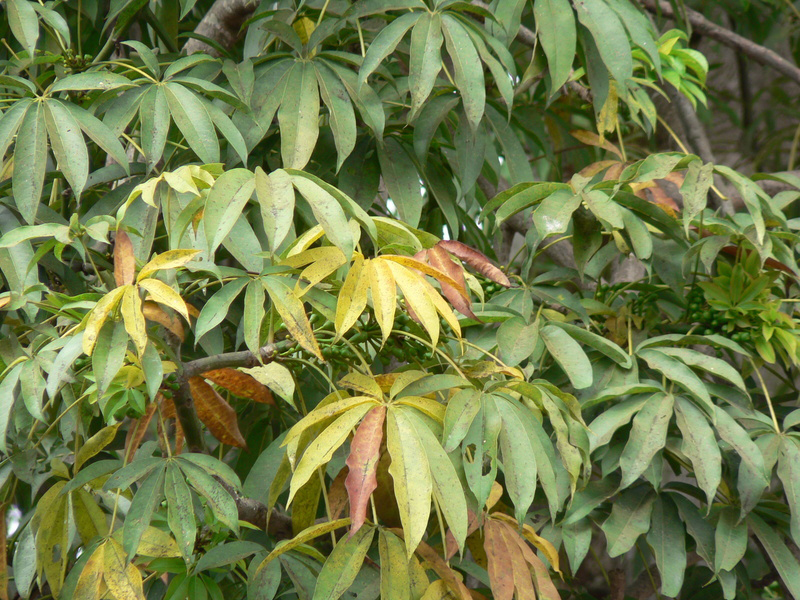
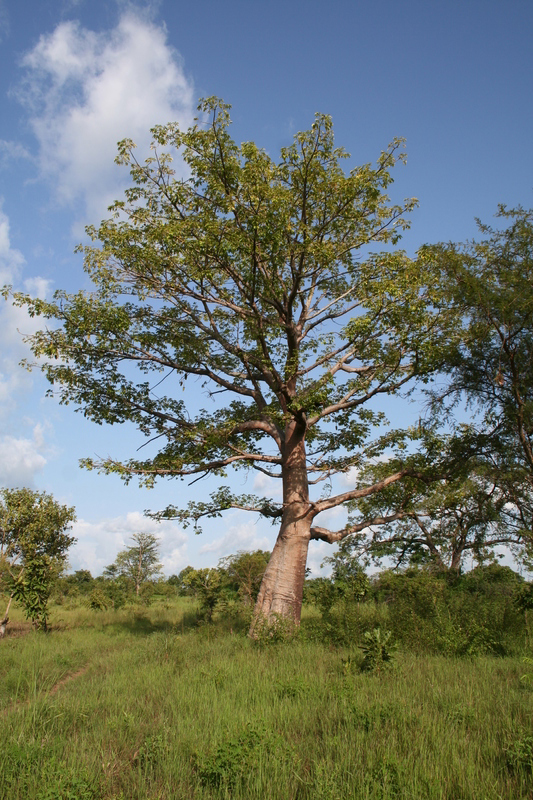
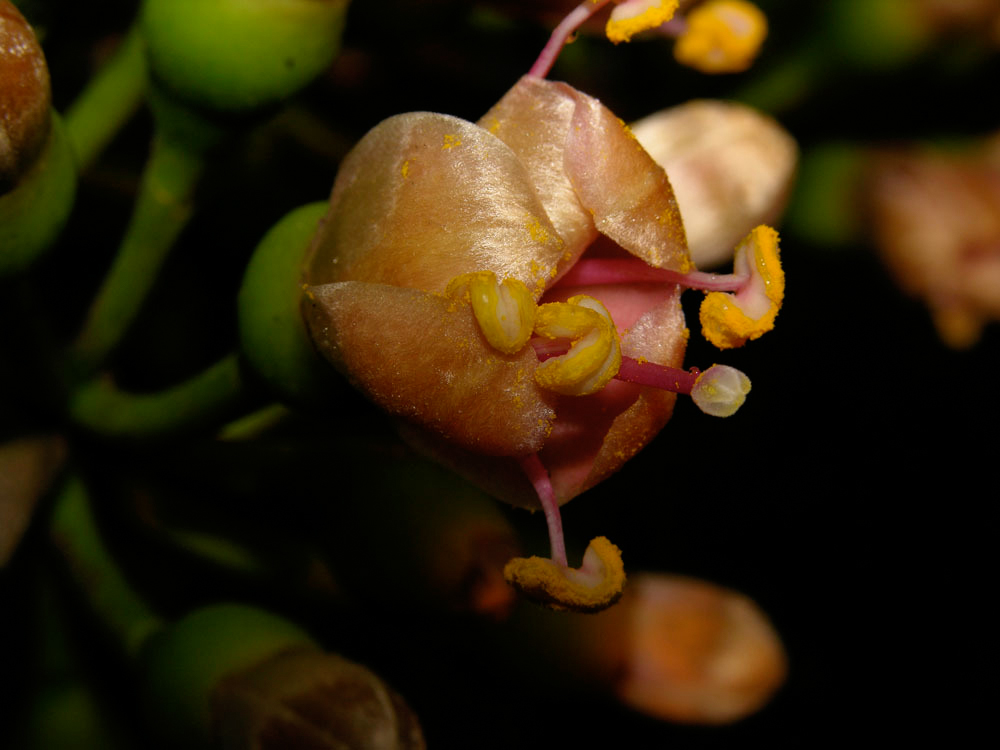
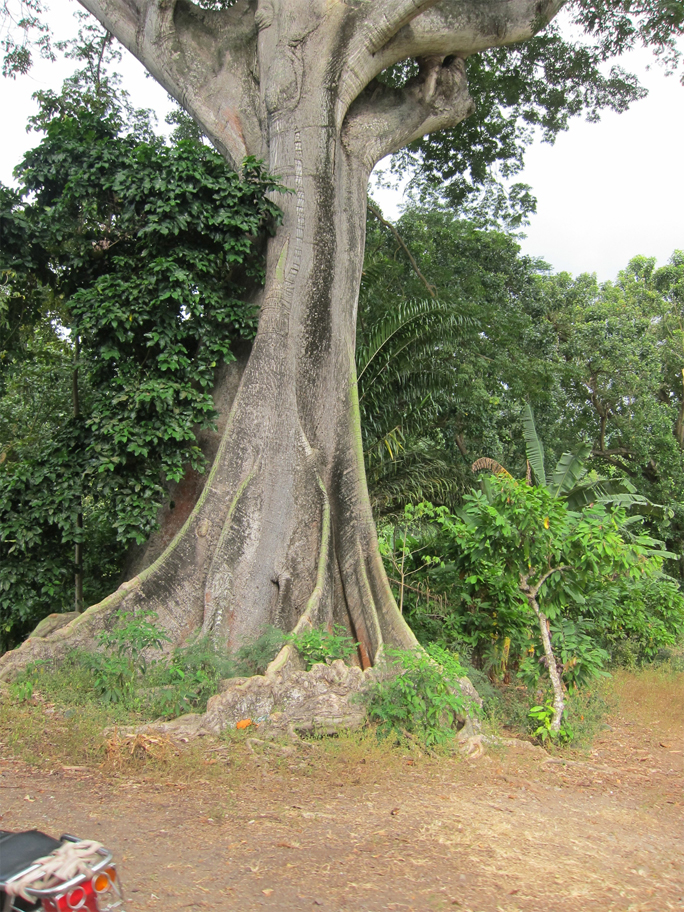
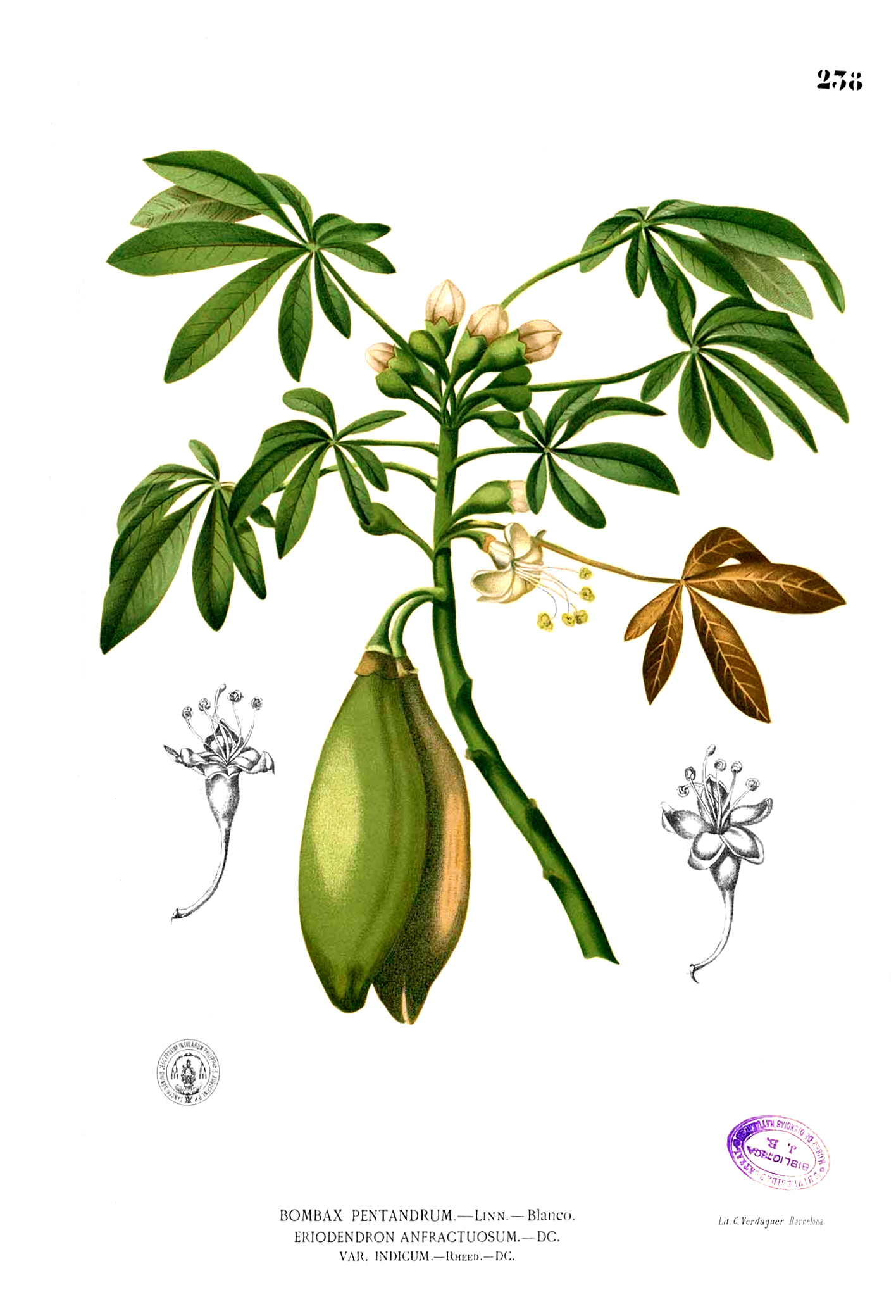
Ceiba pentandra, Kapok , is an erect, buttressed and deciduous tree which reaches to the height of 15 meters. Trunk is cylindric with grey bark which has scattered and large spines. Branches has distinct horizontal whorls. Leaves are palmately compound which consists of 5 to 8 leaflets, acuminate, glaucous and 6-18 cm long. The flowers are 5-merous, creamy white, numerous and about 3 cm long and is clustered on branchlets. The capsules are dehiscent, pendulous, oblong-ellipsoid measuring 7-15 cm in length. The fruit is green which turns brown when matured. It has brown seeds which is smooth, compressed-globose and embedded in fine and silky hairs.
Fruit
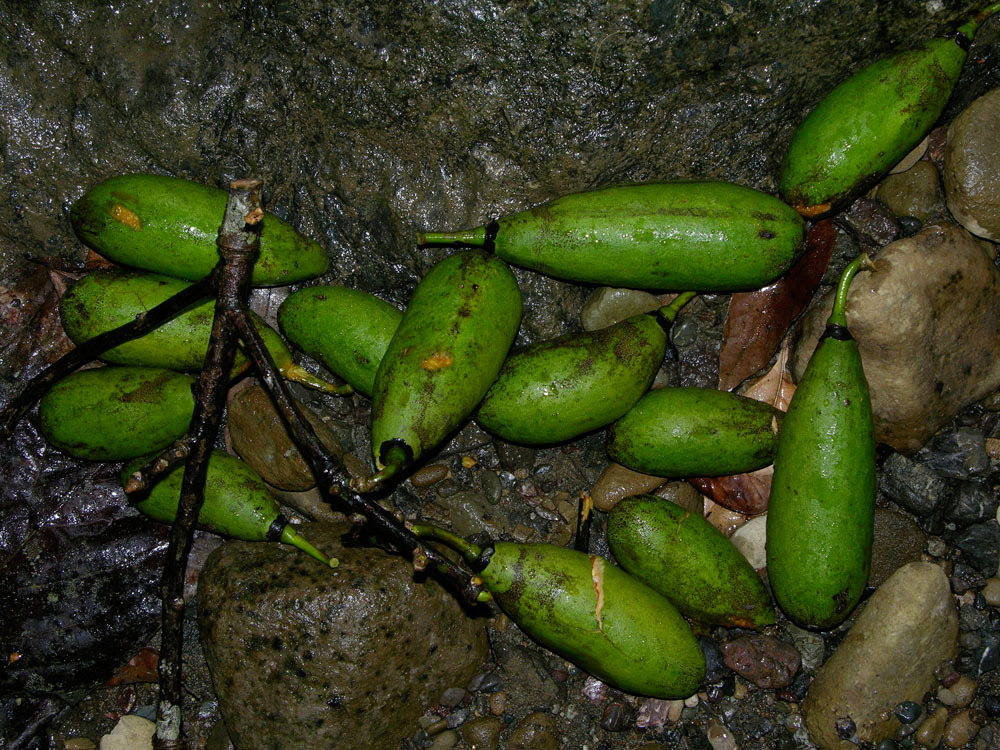
The fruit is a leathery, pendulous, ellipsoid capsule which is 10-30 cm long and 3-6 cm wide. The capsules split into 5 valves disclosing grey woolly hairs which embed 120-175 seeds.
Seed
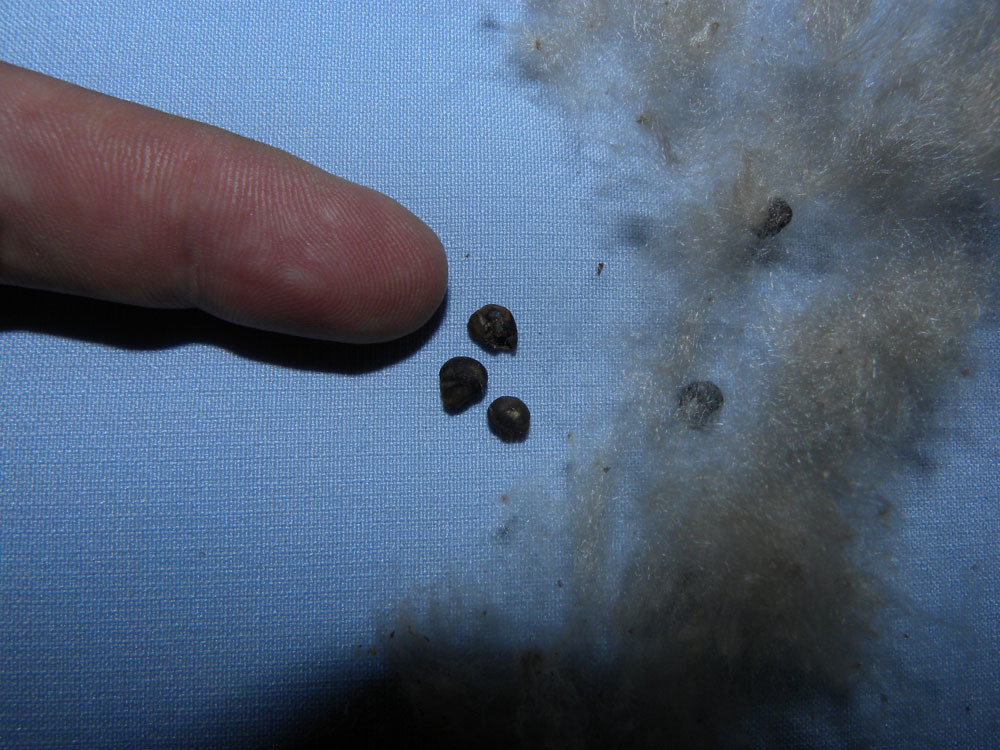
Seeds are black or dark brown which is covered with wool.
Traditional uses
- Use the plant to provide relief from cough and as hair shampoo.
- The flower decoction is used in French Guiana for constipation.
- Latex is used to treat dysentery, diarrhea, and menorrhagia and provided with milk as cooling laxative for incontinence in children.
- People in Singapore use the pounded leaves with onion and little turmeric and water to treat coughs.
- Infusion made from leaves is used in Java for hoarseness, coughs, urethritis and intestinal catarrh.
- Tender leaves are used to treat gonorrhea in India.
- Leaves are used to clean hair in Java.
- Leaves decoction is used in Senegal, West Africa for inflammation of conjunctivitis.
- Leaves are used to treat lumbago and fatigue.
- In Nigeria, leaves are used as laxative and its infusion is used as a cure for colic.
- Wet poultice of pulped leaves is used in Guinea for maturate tumors.
- Bark is used in Philippines as aphrodisiac and vomitive.
- Brew the bark into decoction for febrile catarrha and used for type 2 diabetes and headaches.
- Bark is used with nutmegs, areca nuts and sugar candy in Java.
- The bark decoction is used in Mexico for diuretic, emetic, antispasmodic properties.
- In Congo, bark decoction is used to provide relief from diarrhea, stomach complaints, blennorrhoea, asthma, heart trouble, hernia.
- Nigerians use the Kapok oil for treating rheumatism.
- In Senegal, decoction of branch bark and stem is used as a gargle for gingivitis and inflamed gums.
- Kapok is used to lower fevers, control bleeding and relax spasms.
- Leaves are used for treating hoarse throats, lumbago, fatigue, coughs, diarrhea and scabies.
- Tender shoots decoction is used as contraceptive.
- Warm the young leaves and combine with palm oil and consume it for heart problems.
- Drink the leaf sap for mental illness.
- The juice extracted from bruised young branches is used for tumors, sprains, sores, whitlows, abscesses.
- Apply the leaf sap for skin infections.
- The leaves macerations are used in baths for treating fevers, fatigue, headache, stiffness of limbs and bleeding of pregnant women.
- Use the bark and leaves for treating bronchial congestion.
- Use it externally for treating headaches and fevers.
- Stem bark decoction is used for hernia, diarrhea, stomach problems, heart problems, gonorrhea, fever, oedema, rickets and asthma.
- Apply the decoction on swollen fingers, sores, wounds, leprous macules and furuncles.
- Flowers are used for constipation.
- Bark decoction is used for catarrh.
- Use the tender fruits as emollient.
- Bark infusion is used as mouthwash in Liberia.
- Bark is used for diarrhea and fevers in Cambodia.
- Bark is used by Malays for colds and asthma in children.
- Roots are used for fevers, dysuria, and gonorrhea in India.
- The compressed fresh leaves are used for dizziness.
- The plant is used in Malaya and India for bowel complaints.
youtube.com/watch?v=piAaKMMQc64
Culinary uses
- Eat young leaves, petals and immature fruits as vegetables.
- Cook or consume young capsules fresh.
- Seeds are roasted or added to soups.
- Inner parts of young capsules are consumed as vegetables in Thailand.
- In West Africa, young leaves are consumed as soup herb.
- It is also consumed in the form of sprouts.
- Seeds are toasted in Java, Celebes and Peninsular Malaysia.
- Oil is extracted from seeds.
- Add dried stamens to hot and sour soup and curries.
- Use the wood ashes as the substitute for salt.
Precautions
- The fiber is irritating to eyes, throat and nose.
- The exposure to kapok dust for long periods causes chronic bronchitis.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=21595#null
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Ceiba+pentandra
https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Ceiba_pentandra_(PROTA)
http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Ceiba+pentandra
http://www.tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Ceiba+pentandra
https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/0cd2/008fed719c3c9a5cecac105583ebebd6c234.pdf
http://www.stuartxchange.org/Buboi.html
http://herbs-treatandtaste.blogspot.com/2012/04/kapok-tree-saved-from-being-endangered.html
Comments
| Kapok Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Kapok |
| Scientific Name: | Ceiba pentandra |
| Origin | Tropical America and Africa – Mexico, Central America, northern South America and the Caribbean, and tropical west Africa. |
| Colors | Green turning brown |
| Shapes | Capsule, oblong-ellipsoid |
| Name | Kapok |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Ceiba pentandra |
| Native | Tropical America and Africa – Mexico, Central America, northern South America and the Caribbean, and tropical west Africa. Now introduced elsewhere in the tropics, in Asia and the South Pacific. |
| Common/English Name | Ceiba, Cotton Silk Tree, Corkwood, Cotton Tree, Cottonwood Tree, Java Cotton, Kapok, Java Kapok, Kapoktree, Kapok Tree, Silk Cotton Tree, White Silk Cotton Tree, Silk- Cottontree, White-Flowered Silk-Cotton Tree, White Silk-Cottontree |
| Name in Other Languages | Arabic: Rum (Chad), Shajaret Al Kutun; Australia: Paina; Bambara: Bàna, Bànan (Mali); Benin: Gounma (Bariba) Araba; Bolivia: Hoja De Yuca, Toborochi (Spanish); Brazil: Arvore-Da-Lã, Barriguda De Espinho, Arvore-Da-Seda, Mai-Das-Arvores, Paina-Lisa, Samaúma-Cabeluda, Paineira, Samaúna Da Várzea, Sumaúma, Samaúma-Lisa, Sumaúma-Barriguda, Sumaúma-Branca, Sumaúma-De-Macaco, Sumaúma-Da-Várzea, Sumaúma-Rosada, Sumaúma-Verdadeira (Portuguese); British West Indies: Corkwood; Burmese: Thinbawle; Cameroon: Douma (Sangmelima, Ebolowa), Dum (Yaounde), Bouma (Douala), Djam (Bangangte), Nkouma, Nfuma, Ogouma; Caribbean: Koemaka, Makau; Central African Republic: Bouma (Lissongo), Fromager (Local French); Chamorro: Algidon, Algodon Di Manila, Algodon De Manila, Atgidon Di Manila, Atgodon Di Manila; Chinese: Ji Bei, Ji Bei Mu Mian Zhua Wa Mu Mian, Ji bei (吉贝), Zhua wa mu mian (爪哇木棉), Ji bei mian (吉貝棉), Ji bei mu mian(吉貝木棉); Colombia: Ceiba Blanca, Bonga, Ceiba De Lana (Spanish); Congo: Bosengo, Bokuma, Mofumo; Cook Islands: Mama‘U, Mama‘U, Mama‘U, Tumu Mama‘U, Vavai (Maori); Cote I’voire: Cote D’ivoire: Gbi (Abe), Enivé (Abure), Akuondi, Gna (Akan-Asante), Muong, Nguéhié, Won (Akye), Egniè, Enia, Egnien, Enya (Anyi), Egna, Etchui (Avikam), Angbo, Gniè, Gna, Gnien, Nyé (Baule), Guima (Brong), Guê Dan), Banatan, Bantignei, Bantan, Bantiguehi (Fula-Fulfulde), Gué, Molongué (Gagu), Diô, Do, Tiô, Go, Tshyo, Djô (Guere), Go (Kru-Bete), Ton’ko, Ton’go, Toonko (Kulango), Dangué, N-Gué, Allotegue, Ague, Anié (Kyama), Bana, Bana-Bandan (Manding-Maninka), Tshyo (Ngere), Ghê (Mano), Eguina, Enyam’gua, Eniémé, Enyan’gua (Nzema), Sérigné (Senufo-Tagwana),Tiu (‘Onele’); Chuukese: Kkóton, Kkaton, Koton; Curaçao: Ceiba; Dahomey: Guénesso (Baseda), Gbê (Busa), Guma (Batonnun), Bantan (Dendi), Bentan Habu, Gué Dehunsu, Dehon, Patin Dehun (Fon), Linihi, Rinihi (Fula-Fulfulde), Gpati Dêkrun,Adjoro Hun, Hun-Ti (Gbe-Fon), Hunti (Vhe), Hunsufu (Hweda), Igi Èégun, Igi Àràbà, Ogufé (Yoruba- Nago); Danish: Kapoktræ, Silkebomuldstræ; Democratic Republic of Congo: Ntunturu (Yanzi); Dutch: Kapokboom; Finnish: Capoc, Kapokkipuu, Seiba; Fijian: Semar, Vauvau Ni Vavalangi; French: Bois Coton, Capoc, Coton, Faux Contonni, Capoquier, Cotonnier De l’Inde, Fromager, Faux Cotonnier, Fromager Commun, Fromager Des Antilles, Fromager D’indo- Malaisie, Fromager Inerme Du Golf De Guinée, Faux Kapokier, Kapokier, Kapokier A Fleurs Blandes, Kapokier De Java, Kapokier, Kapokier Du Togo; French Guiana: Cotonnier Grand Bois; French West Indies: Arbre À Cotton, Fromagier; Gabon: Nkouma, Nfuma, Ogouma; Gambia: Bantehi (Fula-Pulaar), Bosanobo (Diola-Flup), Bantalŋforo, Bantaŋ (Manding-Mandinka), Betenbi, Bentenki (Wolof); German: Baumwollbaum, Kapokbaum, Fuma, Wollbaum; Ghana: Onyima (Akan-Asante), Leno, Sokpe (Adangme), Enyaa (Anyi), Onyima (Asante),Enya (Anyi-Aowin), Nye (Baule), Ekile, Danta, Sdanta-Pu (Brong), Gbang (Bimoba), Goni, Gongu (Dagaari), Gumbihi, Gunga, Guna, Gunguma- Gumdi Gungumli (Dagbani), Onyãã, Ayigbe Ogbedei, Onyina, Onyãá, Ayigbe, Onyãí (Fante), Ofu, Atepre, Wudese (Gbe-Vhe), Gung (Grusi), Kàkílíyà, Kakre (Guang-Gonja), Rimi (Huasa), Kpugbum, Bufo-Sõgbum (Konkomba); Kekyafu (Krachi), Gonga (Nankanni), Gunga (Mampruli), Enyenna, Enyaa (Sehwi), Enyensa (Nzema), Kuŋ-Kumuŋ, Kuŋkomo (Sasaala), Onyã-Hene, Onyina (Twi), Ofua, Vule, Ofwho, Atepre, Be (Vhe), Enyena, Onyina (Vulgar), Onya, Onyina (Wasa); Greek: Kapόk (Kαπόκ); Guinea: Kö-Porõ Kö (Baga), Banda (Kissi), Bantignei, Bantignei Bentégniévi (Fula-Pulaar), Uyé (Kpelle), Bara (Kono), Banan (Manding-Bambara), Ban-Bandan, Bana, Bandan (Manika), Kondé (Susu), Bantan (Pular), Am-Polon (Temne); Guinea-Bissau: Brêgue (Biafada), Psáhè, Rumbum (Balanta), Cob-Be (Bidyogo), Bantanhe (Fula-Pulaar), Poilão, Polom (Crioulo), Péntia (Mandyak), Bantaŋ(-Ô) Bantango, Bintaforo (Manding-Mandinka), Pèntè, Pentene (Mankanya) Metchene, N’teme, N’tene (Pepel); Guyana: Kumak, Kumae, Kumaka (Macushi), Silk Cotton Tree (Creole), Wiring (Wapisiana); India:- Bengali: Schwet Simul, Setsimul; Hindu: Hattian, Safedsemal, Katan, Saphed Simal, Safed-Semal; Kannada: Apurani, Buraga, Biliburaga, Dudi, Elava, Bilibaralu, Apoorni, Bilibooruga, Booruga, Bili Booruga, Doodi, Dudi, Doodihatthi, Marali; Malayalam: Ilavu, Nakuli, Mullillapappula, Panja, Pannimaram, Panni, Panniyala, Pula; Manipuri: Moreh Tera; Marathi: Pandhari, Safetasavara, Salmali, Shamieula, Samali, Saalmali, Safedsavara; Mizoram: Japanpang; Sanskrit: Chirayu, Kutashalmali, Kutasalmali, Moch, Kutsitashalmali, Rochana, Shvetasalmali, Salmali, Sthirayu, Svetashalmali; Tamil: Ilavam, Pancu, Karukkanam, Panji, Ilavu, Ulagamaram, Panjimaram, Ilavumaram, Ilavam Pinchu, Acikai, Apurani, Akikai, Ayika, Calamali, Ayikam, Calamirittiran, Callakimaram, Callaki, Camani, Canamali, Camani, Canamali, Canamalikam, Canamali, Canamalikamaram, Cilesmavarttani, Caranamalam, Cilettumavarttani, Cirancivi, Ciracivi, Citalicimitta, Citakapi, Cittanmuki, Cukumaranul, Cittanmukimaram, Cukumaratuli, Cukumaratuvi, Icanam, Emanarvalli, Ilavam, Ilakumaram, Ilavamaram, Iyamanarvalli, Irakaputpam, Kantapalam, Kantapalamaram, Katicakali, Kariyacu, Kukkati, Katicakalimaram, Matacaram, Pancu, Purani, Piccila, Putpapani, Terrukam,Terru, Tolam, Tulakikam, Tolaya, Tulakikamaram, Tulani, Tulam, Tulavirukkam, Tulini, Tuli, Tulipalai, Mocacani, Turanimoca, Mocacanimaram, Mocani, Mocai, Mocaniriyacam, Nariyilavamaram, Nattilavu, Nariyilavu, Tuyarkantam, Ulakumaram, Ulavamaram; Telugu: Kadami, Tella Buruga, Tellaburaga, Booruga, Thellabooraga; Urdu: Smabal; Indonesia: Randu (Sundanese), Randu (Java), Kapeh Panji, Kapuek, Panji (Sumatra); Italian: Albero Del Kapok, Pianta Del Kapok; Japanese: Kapokku (カポック), Kiwata Kapokku (キワタカポック); Kosraean: Cutin, Kuhtin; Khmer: Koo, Kor; Laotian: Kokuiyu, Nguiz Baanz; Liberia: Dan: Gwe, Gwèh; Kru-Guere: Dju; Mano: Geh, Guéh; Mende: Nguwa; Mali: Dámu (Dogon), Bantignei, Bantiguehi (Fula-Pulaar), Bana(n) (Manding-Bambara), Bana, Bana-Bandan (Maninka); Malaysia: Kabu-Kabu, Kabu Kabes, Kekabu, Kapok-Kapok, Kapok, Mengapas, Randu; Marquesan: Uruuru, Puatio, Uruuruvaikirita; Marshallese: Bulik, Kotin; Mexico: Pochote, Pochota, Pochote, Yaxché (Spanish); Nauruan: Duwoduwo; Niger:- Fula-Fulfulde: Bantiguehi, Songhai-Zarma: Forgo; Nigeria: Ukem Akabi, U-Muum, Ù-Mùùm, Àrù-Mùùm (Abua), Rum (Arabic-Shuwa), Bokum (Bokyi), Úkúm (Anaang), Gbée, Gbiê-Li (Busa), Úkím (Efik), Okha (Edo), Bantahi, (Fulfulde), Gehi, Gyehi (Gwari), Rimi, Rini, Rimin, Masar (Hausa), Úkím (Ibibio), Agwu, Agwugu (Igala), Afalafase (Ijo), Ogungbologhá (Ijo-Izon), ẽgungun (Isekiri), Torn (Kanuri), Ahe (Isoko), Kúci (Nupe), Konngô, Gbê-Siê, Vàmbè (Shanga), Araba, Okha (Vulgar), Óháhèn (Urhob), Okho (Yekhee), Àràbà, Ogungun (Yoruba); Niuean: Vavae; Palauan: Kalngebard, Kalngebárd, Kerrekar Ngebard; Peru: Ceibo, Huimba; Philippines: – Bontak: Sanglai, Bikol: Boboi, Kayo, Bisaya: Boi-Boi, Doldol, Daldol, Kapoc, Kayo, Cebu Bisaya: Bulak-Dondol, Dondol, Dogdol, Gapas, Ifugao: Gataova, Iloko: Basanglai, Kapas-Sanglai, Dondol, Kulak, Pampangan: Bulak-Kastila, Bulak, Kasanglai, Pangasinan: Kapas, Sambali: Kapak, Kapas, Sulu: Kapoc, Kapuk, Tagalog: Balios, Bulak- Kahoi, Boboi, Bulak, Buboi, Bulak-Sina, Tinggian: Sanglai; Pohnpeian: Koatoa, Cottin, Koatun; Portuguese: Barriguda, Paina, Mafumeira, Polão, Poilão, Sumauma De Terra Firme, Sumauma Da Mata, Sumaumeira; Samoan: Vavae, Vavae, Vavae Papalagi; Senegal: Kidem (Banyun), Gi-Ndii (Bedik), A-Ndín (Basari), Busana, Busanay, Étufay (Diola), Bâtigéhi, Bâtinévi (Fula-Pulaar), Kantaŋ (Mandinka), Bamâri, Batân (Manding-Bambara), Buday, Budey (Non), Bana-Bâdâ, Bana, Bâtân, Bana-Bandan, Busana (Maninka), Len (Serer-Non), M-Buday (Serer), Bêtéńé (Wolof), Bêtanô (Soce); Sierra Leone: Banta (Fula-Pulaar), Poloŋe, Polon-De (Bulom), Sona (Gola), G-Banda (Kono), G-Banda (Kissi), Kstin-Tri (Krio), Kutene (Limba), Gbandaŋ (Manding-Mandinka), N-Gukhs(I) (Loko), Banda (Maninka), Nguwa (Mende), Konde-Na Kundi-Na, (Susu-Dyalonke,) Konde (Susu), Am-Poloŋ, G-Banda (Vai); Spanish: Árbol Capoc, Ceibo, Ceiba, Pochote Sumauma Kapok, Arbol De Seda, Capoquero, Arbol De La Seda, Mosmote, Ceiba Juca, Peem, Yuca; Sri Lanka: Elavam, Kottapulung, Imbul, Pulung, Pulunimbal (Sinhalese); Surinam: Kumaka (Arawak), Kankantrie, Jumbi Tree, Silk (Creole), Kankantrie, Katoenboom (Dutch), Koddobakkoe, Fuma; Swahili: Mbuyu, Msufi; Swedish: Kapok; Tahitian: Pacae, Komiro, Vavai; Thai: Nun, Ngui Noi, Ngao(ง้าว), Nun Tale, Ngio noi (งิ้วน้อย), Ngio sai (งิ้วสาย), Ngio soi ( งิ้วสร้อย), Nun (นุ่น); Togo: Aloe, Eloe (Gbe), Bubumbu, Bufu (Bassari), Huti, Vuti, Wuti (Gbe-Fon), Lovi (Gen), Botu-Kocholemotu Botu,Botu, Botu-Kisemto, Kolombolu Kom, Kpong (Kabre), Igboa, Ju, Juna (Kposo), Bahun, Gomu-Schiere, Ubombě (Moore- Nawdam), Bagbasse, Komu (Tem), Agú, Oguvé (Nago), Aloe, Eloe, Evu, Ewu, Vu, Wu, Wudese, Wuti (Vhe), Huti, Vuti, Wuti (Yoruba-Ife ); Upper Volta: Pi (Bobo), Banda( Dyula), Bantan, Bantignei (Fula-Fulfulde), Banan (Manding-Bambara), Rimi( Hausa), Bantan, Bonetan (Songhai-Zarma), Gunga (Moore), Belon (Kirma), Blo (Turuka); Venezuela: Ceiba Yuca, Ceibo Jabillo (Spanish); Vietnamese: Bông Gòn; West Cameroons: Bŭma, Kabò (Duala), Buma, Wuma (Kpe), Bum (Lundu); Tongan: Vavae; Yapese: Batte Ni Gan‘ Ken; Yoruba: Araba (Nigeria), Egun, Ogungun |
| Plant Growth Habit | Erect, deciduous, buttressed tree |
| Plant Size | 15 m high |
| Leaf | 6-18 cm long |
| Flower | Creamy white, about 3 cm long |
| Fruit shape & size | Capsule, oblong-ellipsoid, 7–15 cm |
| Fruit color | Green turning brown |
| Seed | Brown, compressed-globose |