The tree is known for its health benefits when consumed in tea, introduced as an ornamental tree to several countries, also bears edible fruit. It is considered to be one of the most prevalent invaders in Brazilian subtropical forests. The tree is harvested from the wild for local use as a food, medicine and source of materials. It has gained a high reputation for protecting the liver from alcohol damage. The plant is sometimes also grown as an ornamental.
Japanese raisin tree Facts
| Japanese raisin tree Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Japanese raisin tree |
| Scientific Name: | Hovenia dulcis |
| Origin | China, Japan, North Korea, South Korea, Thailand and Vietnam |
| Colors | Green when young turning to purplish to black at maturity |
| Shapes | Drupes, about 7 mm across, containing 2 to 4 seeds |
| Health benefits | Beneficial for asthma, eczema, fibromyalgia, fever, liver diseases, parasitic infestation, hangover treatment and for rectal diseases. |
| Name | Japanese raisin tree |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Hovenia dulcis |
| Native | China, Japan, North Korea, South Korea, Thailand and Vietnam |
| Common Names | Chinese raisintree, Japanese raisintree, Oriental raisin tree, Coral tree, honey tree |
| Name in Other Languages | Abkhazian: Akamfeҭҵla (Акамфеҭҵла) Afrikaans: Japanse rosyntjieboom Arabic: Hūfīniyā Ḥulwat al-thamar (هوفينيا حُلوة الثمر ) Armenian: Konfeti tsarr (Կոնֆետի ծառ) Assamese: Chetia-bola Azerbaijani: Şirin hoveniya Catalan: Arbre de les panses Chinese: Bei zhi ju (北枳椇 ), Guǎi zǎo (拐枣), Jī zhuǎ lí (鸡爪梨), Tián bànyè (甜半夜), Zhǐ jǔ (枳椇), Zhǐ jǔ zi (枳椇子), Zhǐ qízǐ (枳棋子) Czech: Dužistopka sladká Dutch: Japanse krentenboom English: Chinese raisin tree, Japanese raisin tree, Oriental raisin tree, Coral tree, honey tree French: Hovenia à fruits doux, Hovénie sucrée, Raisinier de Chine German: Japanisches Mahagoni, Japanischer Rosinenbaum, Quaffbirne Hebrew: Ets htsimuk hifni (עץ הצימוק היפני) Italian: Albero dell’uva passa, Ovenia dolce Japanese: Kenpo nashi (ケンポナシ ) Korean: Heosgaenamuheosgaenamu (헛개나무헛개나무), heos gae na mu (헛개나무) Mishing: Pinke esing Polish: Howenia słodka Portuguese: Amora-do-mato, Banana-do-japão, Bananinha-do-japão, Caju-do-japão, Caju-japonês, Chico-magro, Gomari, Macaquinho, Mata-fome, Passa-do-japão, Passa-japonesa, Pau-doce, Pé-de-galinha, Tripa-de-galinha, Uva-da-china, Uva-do-japão, Uva-japonesa, Uva-paraguaia, Uva-chinesa, videira-passa-japonesa Russian: Goveniia sladkaia (Говения сладкая), Konfetnoe derevo (Конфетное дерево), Khoveniia sladkaia (Ховения сладкая) Serbian: Hovenija (Ховенија) Spanish: Árbol de las pasas, Pasa japonesa, Sarmiento japonés, hovenia Tamil: Muralimaram Turkish: Hurma, Şeker ağacı Uzbek: Konfet daraxti |
| Plant Growth Habit | Fast-growing, deciduous, annual tree or rarely shrub |
| Growing Climates | Plains, mountains, secondary forest, roadsides, disturbed areas, forest gaps/edges, regenerating forests, cliff bases, suburban woodlots and thickets |
| Soil | Grow in almost any well-drained soil in full sun or partial shade. Not for poorly-drained areas or compacted soil, Japanese Raisin tree prefers adequate soil space for root exploration. It has a moderate drought tolerance |
| Plant Size | Can reach 40 to 50 feet in height but is most often seen at 30 to 35 feet |
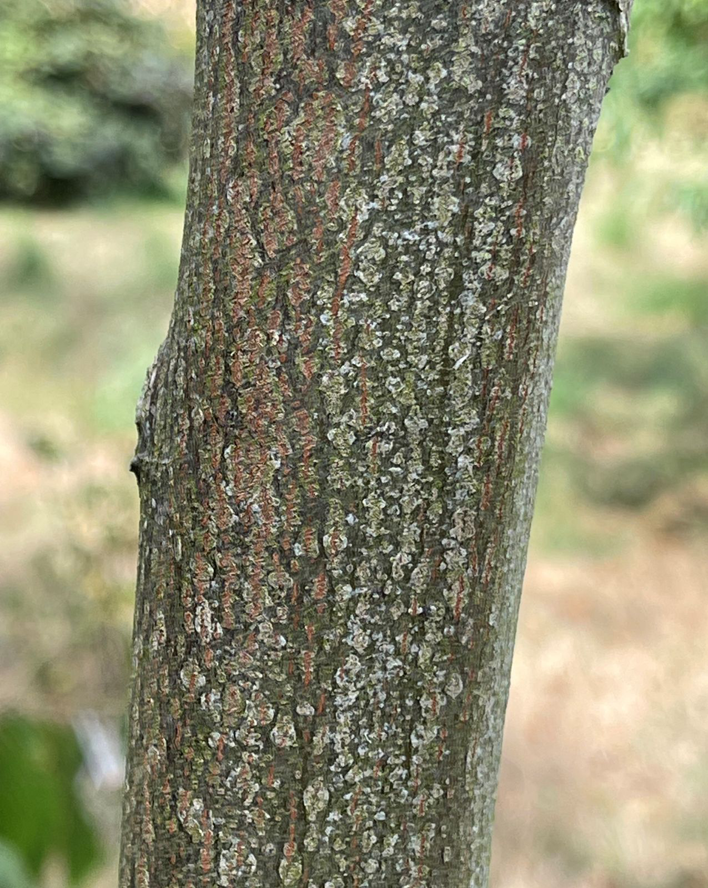
| Bark | The bark is rigid and light gray with brown valleys |
| Branchlets | Branchlets brown or black-purple, glabrous, with inconspicuous lenticels. |
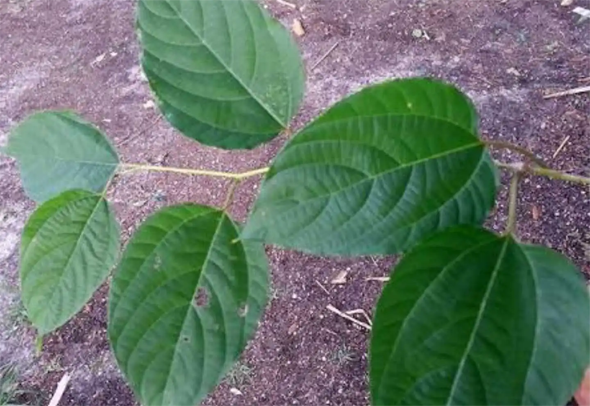
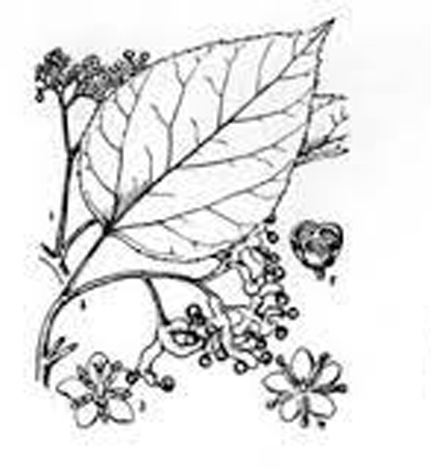
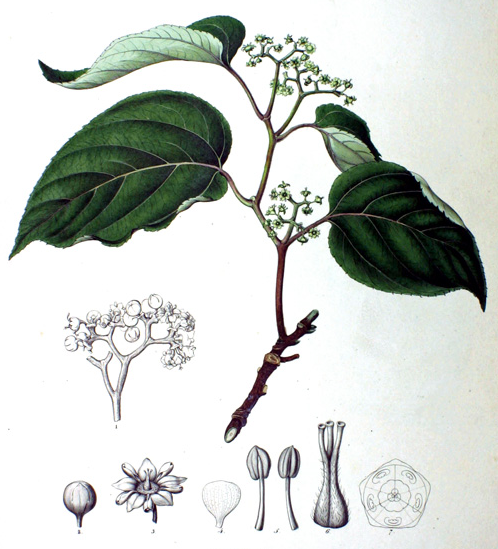
| Leaf | Leaves are simple, alternate, spiral, glabrous or glossy and smooth. Leaf blade is ovate, broadly oblong or elliptic-ovate, 7-17 cm long and 4-11 cm wide. Their real shape can only be revealed by spreading them wide. |
| Flowering season | May-July |
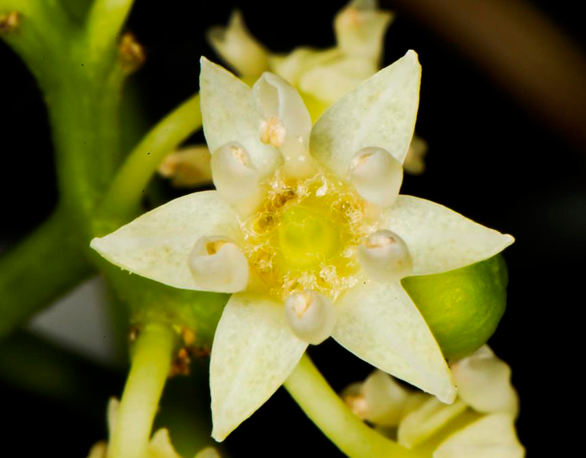
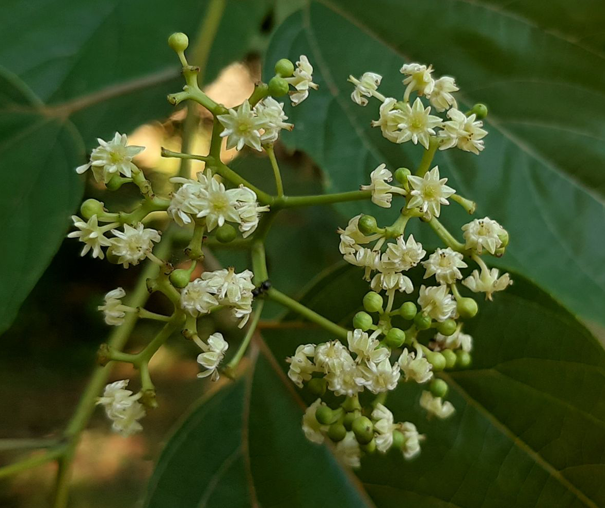
| Flower | The small flowers have a cream-like color and bloom at the end of spring. They are 0.5-0.6 cm across, white, pubescent; pedicels 0.2-0.4 cm long; bracteoles are lanceolate, subulate and deciduous. Calyx lobes is 0.2-0.3 cm long, glabrous within; petals 0.15-0.2 cm long, cuneate, obtuse, glabrous |
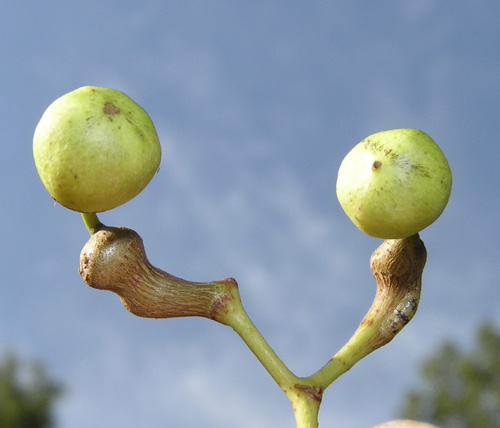
| Fruit Shape & Size | Drupes, about 7 mm across, containing 2 to 4 seeds. |
| Fruit Color | Green when young turning to purplish to black at maturity |
| Propagation | Propagate by seed, or take greenwood cuttings in early summer, or hardwood cuttings in late autumn |
| Plant Parts Used | Fruits, peduncles |
| Available Forms | Eaten fresh, dried, tea, powder or capsules |
| Season | August to October |
Plant Description
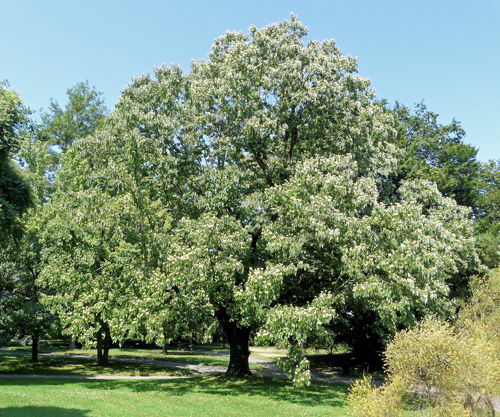
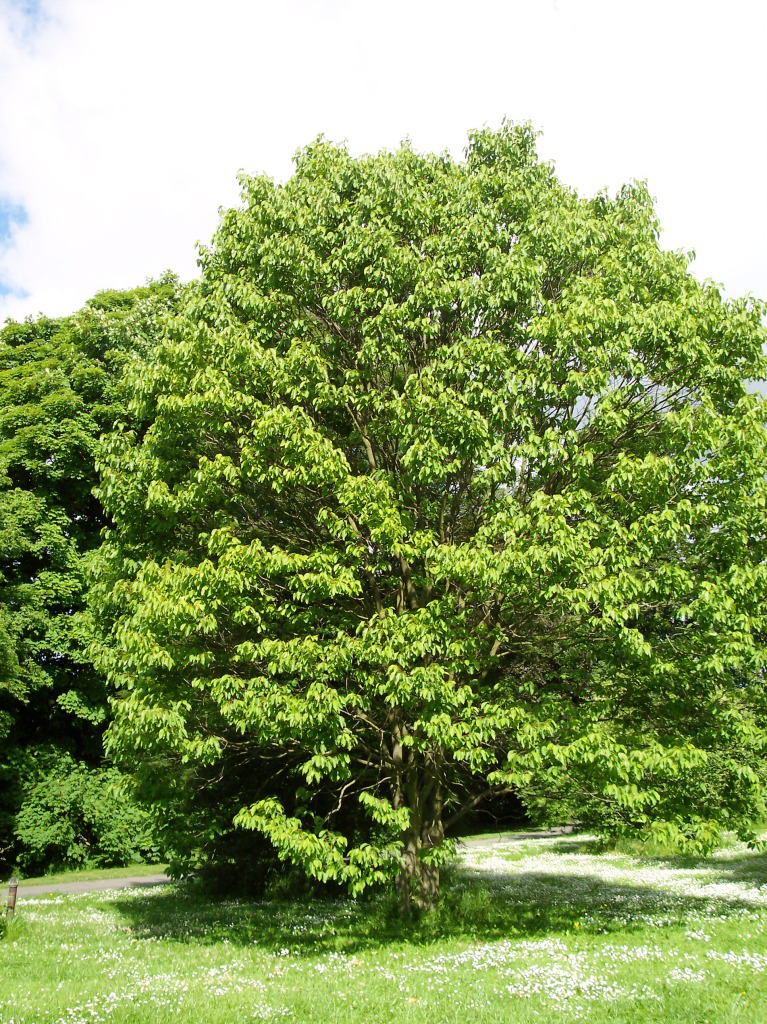
Japanese raisin tree is a fast-growing, deciduous, annual tree or rarely shrub with a fairly open, upright, oval crown. The plant normally can reach 40 to 50 feet in height but is most often seen at 30 to 35 feet tall. The plant is found growing in plains, mountains, secondary forest, roadsides, disturbed areas, forest gaps/edges, regenerating forests, cliff bases, suburban woodlots and thickets. It grows in almost any well-drained soil in full sun or partial shade. It is not for poorly-drained areas or compacted soil, Japanese Raisin tree prefers adequate soil space for root exploration. It has a moderate drought tolerance. Branchlets are brown or black-purple, glabrous, with inconspicuous lenticels. The bark is rigid and light gray with brown valleys.
Leaves
Leaves are simple, alternate, spiral, glabrous or glossy and smooth. Leaf blade is ovate, broadly oblong or elliptic-ovate, 7-17 cm long and 4-11 cm wide. Their real shape can only be revealed by spreading them wide. Leaves are papery or thickly membranous. Leaf margin is irregularly serrate or coarsely serrate, apex shortly acuminate or acuminate. They are green and glabrous (hairless) on upper side, pale green and glabrous to thinly pubescent (hairy) on nerves beneath, becoming deep brown when dry. Leaf stalk (petioles) is 2.5-6 cm long. Leaves do not change color in fall and drop while they are still green.
| Leaf arrangement | Alternate |
| Leaf type | Simple |
| Leaf margin | Serrate |
| Leaf shape | Ovate, elliptic (oval) |
| Leaf venation | Pinnate, reticulate |
| Leaf type and persistence | Deciduous |
| Leaf blade length | 4 to 8 inches |
| Leaf color | Green |
| Fall color | No color change |
| Fall characteristic | Not showy |
Flower
The flowers are able to pollinate themselves and can be found on terminal cylindric racemes or panicles. The small flowers have a cream-like color and bloom at the end of spring. They are 0.5-0.6 cm across, white, pubescent; pedicels 0.2-0.4 cm long; bracteoles are lanceolate, subulate and deciduous. Calyx lobes is 0.2-0.3 cm long, glabrous within; petals 0.15-0.2 cm long, cuneate, obtuse, glabrous; stamens 0.12-0.2 cm long; anthers dorsifixed; disc saucer-shaped; lobes linear; style 3-cleft and elongate. They are grouped in large clusters, even if the individual flowers are small. Sometimes the flowers only emerge at the end of summer if the weather is cold, which can hurt the fruit production. Flower-stalks start swelling unevenly after the decay of the flower into a fleshy, knotted mass, red, and sweet to the taste. They are chewed by the Japanese and Chinese. Flowering normally takes place in between May-July.
| Flower color | White/cream/gray |
| Flower characteristics | Showy |
Fruits
Fertile flowers are followed by red/brown drupes, about 7 mm across, containing 2 to 4 seeds. Plants begin to produce fruit after three or four years. The fruit is sweet, fragrant and is edible raw or cooked and have a pear-like flavor. When dried the fruits look and taste like raisins. The fruit is sweet and can be used in candies or to make a honey substitute. It can also be made into juice or fermented to make wine and vinegar.
In reality, they are not actually fruits but oversized flower stalks. The seed pods at the end are the actual fruits of the plant, which are not edible. The stem peduncle that supports the seed pod becomes red or brown as the fruit matures and can be consumed when it falls naturally to the ground. They have high sugar content and a taste similar to a pear. While the peduncles are not bigger than a raisin, the tree produces them in large numbers. The brown seed pods fruits are discarded.
| Fruit shape | Round |
| Fruit length | Less than .5 inch |
| Fruit covering | Fleshy |
| Fruit color | Red |
| Fruit characteristics | Attracts birds; showy; fruit/leaves a litter problem |
Health benefits of Japanese raisin Tree
Hovenia Dulcis or Japanese raisin Tree is popular for its medicinal properties making it widespread for dealing with hangover. It is a key source of dihydromyricetin that is used as a hangover medication by a lot of medical practitioners in the sub eastern countries. Some of the most acknowledged medical benefits of Japanese raisin Tree are listed below
1. Treats drunkenness
Japanese raisin Tree has long been used in Korean and Chinese traditional medicine to relieve intoxication after excessive drinking. Research has concluded that it lowers the blood alcohol level of mice. This recommends that it could help people metabolize alcohol more rapidly and efficiently, which could possibly relieve both drunkenness and hangovers.
Another research found that it prevents alcohol-induced muscle relaxation in rats. This suggests that it could be used to combat the lack of coordination commonly associated with drunkenness. There are no studies of these effects of Japanese raisin Tree on humans, but eating the fruit seems to be safe.
2. Treats hepatitis C
Research published in the American Journal of Chinese Medicine found that it can prevent liver damage from hepatitis C. Research looked at the effects of Japanese raisin Tree in mice infected with hepatitis C and found reduced levels of fibrosis and necrosis of the liver.
However, with the new hepatitis C drugs, you and your doctor may want to consider other more evidence-based and possibly safer ways to treat hepatitis C.
3. Hangover cure
Many people have hangovers after they drink to the point of intoxication. The exact cause of hangovers is unknown, although there are most likely several contributing factors. Typically, hangovers begin when the alcohol concentration in your blood begins to fall. Your hangover peaks when your blood alcohol level reaches zero. For many people, this hangover peak happens at right about the time they wake up in the morning.
However, there are many factors that contribute to a hangover that wouldn’t be affected by H. dulcis. This includes low blood sugar, dehydration, and gastrointestinal upset. Drink fluids, rest, and consider having a couple of glasses of water between drinks next time.
4. Treats alcohol withdrawal syndrome
Some people believe that hangovers are partially caused by a sort of mini-withdrawal from alcohol. For people with alcoholism, however, alcohol withdrawal syndrome is a serious, even life-threatening condition. There are currently no prescription medications without significant side effects that can be used to treat alcohol withdrawal.
Research has suggested that dihydromyricetin, a derivative of Japanese raisin Tree, has the potential to treat alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Research conducted with rats found a reduction in withdrawal symptoms including anxiety, tolerance, and seizures. Rats taking dihydromyricetin were also less likely to voluntarily consume alcohol, suggesting that it may also reduce alcohol cravings.
5. Protect Liver from Damage
Japanese raisin tree consists of ingredients that protect your liver from the damage caused by alcohol intake. This is one of the surprising medical benefits of Japanese raisin tree. Traditionally, it has been used by a lot of physicians to treat liver related diseases and to detoxify the liver. Taking it in your diet not only helps in aiding hangover, but also helps in eliminating all the alcohol induced toxins from the liver. So if you are more concerned about your liver damage caused due to alcohol consumption, try adding any form of Japanese raisin tree to your diet. You could never go wrong with this.
Traditional uses and benefits of Japanese raisin tree
- Fruit is antispasmodic, febrifuge, laxative and diuretic.
- Seeds are diuretic and are used in the treatment of alcohol overdose.
- Seeds are used to relieve intoxication due to wine.
- Stem bark is used in the treatment of rectal diseases.
- It has been used in traditional Chinese, Korean, and Japanese medicines to treat fever, parasitic infection, as a laxative, and a treatment of liver diseases, and as a hangover treatment.
- It prevents the production of histamine and various other compounds that cause allergies in the body, while acting like a bronchodilator.
- Japanese raisin tree is effective against asthma, eczema, fibromyalgia and other similar problems.
- The Japanese raisin tree might also be a cure for fever, since it is known to reduce inflammation.
- It also treats gastric issues, reducing spasms.
- In general, it can relieve numerous types of digestive and stomach problems, regardless of their cause.
- It has a detoxifying effect by boosting the rate of toxin elimination from the body, while it reduces swelling and relieves abdominal and intestinal pain.
Culinary Uses
- Fruit can be consumed raw or cooked.
- They can be dried when they have the sweet flavor and texture of raisins and can be used similarly.
- The fruit is sweet and fragrant with a pear-like flavor.
- The fleshy peduncle, which is sweet and aromatic, is eaten.
- An extract of the seeds, bough and young leaves can be used as a substitute for honey and is used for making wine and candy.
Other Facts
- The wood is hard and fine grained it is good for building construction and fine furniture.
- The leaves are eaten by cattle.
- The tree is cultivated for its fleshy peduncles which taste like Bergamot pear.
- The wood can be used to make musical instruments and ships.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=28554#null
http://www.hear.org/pier/species/hovenia_dulcis.htm
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxon/taxonomydetail?id=19387
https://pfaf.org/user/plant.aspx?LatinName=Hovenia+dulcis
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/27697
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/HOVDU
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/281904
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hovenia_dulcis
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-2853957
http://www.worldfloraonline.org/taxon/wfo-0000725083
https://temperate.theferns.info/plant/Hovenia+dulcis
https://www.texasinvasives.org/plant_database/detail.php?symbol=HODU2
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/ST296
http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=1&taxon_id=200013347
https://plants.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=HODU2