Plant description
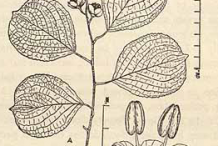
Intellect tree is an unarmed woody, large deciduous twining shrubs that grows about 10 m tall and is found growing in moist deciduous and semi evergreen forests. The base stem of this shrub grows up to 10 centimeters in diameter and 6 meters in length. Being a rambler by nature, it produces many woody branches that cling to surrounding flora for support. The stem has a rough, pale or reddish brown exfoliating bark covered densely with small elongated white lenticels. The inner bark is light and cork like with yellow sapwood. The leaves are simple, broad, and oval, obovate or elliptic in shape, leathery and smooth, alternately arranged on short petioles with toothed margins. They grow on singular stems ranging from light to dark green color.
Flower & Fruit
Flowers are borne in large panicles at the end of branches. Male flowers are minute, whitish green to yellow green. Sepals are nearly circular and toothed. Petals are oblong or obovate-oblong and entire. Female flowers have sepals, petals and disk similar to those of male flowers. Flowers are followed by capsules that are depressed, globose, tri-lobed, bright yellow colored with 1-1.3 cm diameter, containing 3-6 seeds per capsule/ seed pod which are enclosed by an orange-red aril. The seeds are small and oval shaped growing in round pods that gradually change from a light yellow to a deep red color as they mature. They are known to cause yellow orange stains on anything their oils come into contact with. Parts of the plant which are generally used for their economic importance include seeds, bark and leaves.
Botanical description and properties of different plant parts of Celastrus paniculatus
| Intellect tree Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Intellect tree |
| Scientific Name: | Celastrus paniculatus |
| Origin | India |
| Colors | Bright yellow |
| Shapes | Capsules that are depressed, globose, tri-lobedwith 1-1.3 cm diameter, containing 3-6 seeds per capsule |
| Flesh colors | Orange-red |
| Taste | Acrid, bitter |
| Health benefits | Improving Intellect, Dysmenorrhea, Memory loss & Dementia, Neurodegenerative Diseases, Beriberi, Knee Pain, Atherosclerosis, High Cholesterol, Osteoarthritis,Impotence |
| Plant part | Botanical Description/ Properties |
| Bark | Pale yellow corky bark; rough and cracked, exfoliating in small scales |
| Stem | Woody climber |
| Leaf | Ovate, Oblong-elliptic, broad, glabrous, simple, alternate, very variable, slightly serrated, sometimes pubescent beneath along the venation, up to 6 × 11 cm; base cuneate, obtuse or rounded; apex acute, acuminate or obtuse |
| Flower | Unisexual, small, greenish white or yellowish green; panicles large, terminal, pubescent; racemes terminal, compound or supra-decompound, calyx-lobed rounded, ciliated, margin of the disk thin, free. Male flowers are minute, pale green; calyx lobes sub orbicular, toothed; petals oblong or obovate-oblong, entire; disk copular. Female flowers have sepals, petals and disk similar to those of male flowers |
| Capsule | Globose, yellow, transversely wrinkled; trivalved, 3-6 seeded |
| Seed | Grow inside capsules; ellipsoid or ovoid, yellowish or reddish brown in color, enclosed in orange red fleshy aril |
Health Benefits of Intellect Tree
In the Indian traditional system of medicine, called Ayurvedic medicine, Celastrus paniculatus extract has been used to improve intellect, memory and for the treatment of various mental disorders. Seeds of Celastrus paniculatus appear to be protective against cell death from glutamate at very low concentrations, but the maximal protection observed is not too high. Listed below are some of the health benefits of Intellect tree
1. Improving Intellect
Intellect tree is considered beneficial for improving intellect, and is mainly recommended for its memory enhancer action. It helps to improves concentration, alertness, and other cognitive functions. It may act on acetylcholine level in the brain, which enhances the cognition.
2. Memory loss & Dementia
Intellect tree is one of the best memory booster herb, which improves recall powder and retention span. Generally, it is used as brain tonic for increasing memory. Seeds and oil both are effective in forgetfulness and memory disorders. Intellect tree should be used in dosage of 5 to 15 drops in milk. Seeds can be taken in powdered form in dosage of 1 gram with milk.
According to research study, it increases glutathione and catalase levels and decreases malondialdehyde in the brain, which might be responsible for its antioxidant, neuro-protective and cognitive-enhancing actions.
3. Neurodegenerative Diseases
Intellect tree might have neuroprotective effects, which might be due to its antioxidant action, which helps reducing oxidative damage of the neurons.
Nootropic effect of Intellect tree is well-established in Ayurveda and it is widely used for this purpose. Actually, it acts as nervine stimulant according to Ayurveda. It encourages alertness, improves concentration, reduces rate of cell death of neurons, improves ability of thinking and reasoning and helps tackling stress disorders.
4. Atherosclerosis
Intellect tree seeds have anti-lipidemic effects and help to reduce atherogenic index. Its use reduces total cholesterol and anti-inflammatory property helps reducing inflammation of blood vessels, which helps stopping or slowing down the progress of atherosclerotic lesions.
5. High Cholesterol
Intellect tree significantly lowers the elevated cholesterol and LDL cholesterol, which helps in preventing cardiac diseases and atherosclerosis.
6. Osteoarthritis
Intellect tree Seeds possess significant antinociceptive characteristic and anti-inflammatory property, which helps reducing joint inflammation and joint pain. In osteoarthritis, 1 grams seed powder is recommended and taken with cow’s milk. It has thermogenic action, which also induces heat sensation in the body, so its use is suggestible in winters. In other seasons, Safed Musli, Ashwagandha, Gokshura, Mulethi, etc. are more advisable.
7. Impotence
Seeds of Intellect tree have powerful aphrodisiac, erectogenic and stimulant action. For improving male performance, it should be used along with milk.
8. Dysmenorrhea
Roasted seeds of Intellect tree along with China rose flower powder are used to promote easier menstruation and reduce menstrual cramps. It is also a good ayurvedic herbal remedy for primary and secondary dysmenorrhea.
9. Beriberi
Intellect tree Oil consists of a good amount of Vitamin B1 (thiamine). Beriberi occurs due to nutritional deficiency of Vitamin B1 (thiamine). Thus, it is used in dosage of 15 drops thrice a day added in the milk.
10. Knee Pain
Intellect tree seeds are traditionally used for knee pain treatment. It decreases pain, joint crepitation, inflammation and stiffness. It also improves joint movement and strengthens the joints. It is best to use during the winter season it has very hot potency.
Its optimum dosage (500 to 1000 mg twice daily) can be used during winters. It has very hot potency and one can experience excess heat sensation in the body. Its lower dosage with milk is suggestible in summers.
Traditional uses and benefits of Intellect tree
- A seed consists of fatty acids and alkaloids, and have sedative and antidepressant actions.
- Seeds are used to sharpen the memory and the seed oil is used as a tonic for memory loss in ayurvedic medicines.
- Seeds are acrid, bitter, hot, appetizer, laxative, emetic, aphrodisiac, powerful brain tonic and causes burning sensation.
- Oil enriches blood and cures abdominal complain.
- Seeds are bitter, expectorant, brain and liver tonic, cure joint-pains, paralysis and weakness in Unani system of medicine.
- Oil is good for cough and asthma and is used in leprosy, cures headache and leucoderma.
- Crushed seeds, a decoction of the seeds or the fixed oil from the seed are applied as a poultice, or taken internally.
- Crushed Seeds are applied to relieve fevers, joint and muscular pains, and paralysis.
- Oil from the seed is a powerful stimulant and is used in the treatment of beriberi.
- Seed oil is a major component in various products to relieve rheumatic and muscular pains.
- Oil is an ingredient of many more herbal medicines, claiming to enhance the nervous and mental system.
- Leaves can be an ingredient, together with ‘adas-pulasari’ of a prescription against dysentery.
- Leaf sap has been used as an antidote for opium poisoning.
- Root is used as an antimalarial and antipyretic.
- Wood is used in the treatment of tuberculosis.
- Juice from the bark is used in the treatment of indigestion.
- Stem bark is used as an anti-dysenteric and a decoction of the stem as a diuretic in the treatment of kidney disorders.
- Fruits are considered anti-flatulent, a blood tonic and a relief for fainting.
- Ayurvedic doctors of Bastar region in Chhattisgarh, used to prescribe Celastrus seeds to the patients suffering from forgetfulness in the dosage of one seed daily in their diet and then gradually increasing it up to 100 seeds per day in India.
- Traditional healers have used Intellect tree oil for centuries to increase mental acuity, improve memory and intellect as well as retention and recalling power; and to alleviate mental fatigue, stress and minor joint pains.
- Seeds are used to heal indolent ulcers and sores, as well as infectious skin conditions such as scabies in the form of a poultice.
- Application of the oil on the head acts as a brain stimulant to improve memory.
Ayurvedic Health benefits of Intellect tree
- Cough: Take some seeds. Powder them. Take a pinch with slightly warm water daily for 7 days
- Dysentery: Take some seeds. Powder them. Take a pinch with slightly warm water daily for 7 days
- Stomach ache: Take some seeds. Powder them. Take a pinch with slightly warm water daily for 7 days
- Wounds: Take some seeds. Powder them. Mix with coconut oil. Apply it on wounds. OR grind the seeds. Boil them. Wash wounds with it twice a day.
- Analgesic: Massage using Intellect tree oil on the painful areas.
- Abortifacient: Prepare a decoction using bark of Intellect tree. Drink a cup of it twice a day.
- Vitiligo: Add 1 tsp seed powder of Intellect tree in a cup of water. Boil. Drink it twice a day.
- Rheumatism: Massage using seed oil of Intellect tree over painful Joints.
- Alzheimer: Take equal quantity of Intellect tree, Butterfly Pea, Indian Pennywort, Bacopa Monnieri and Withania Somnifera. Grind them together. Have 1/4 teaspoon with lukewarm water daily.
- Weakness, Migraine, Epilepsy: Chew Intellect tree seeds (10-12 seeds) on an empty stomach and drink some water.
- Headache and Arthritis: Mix 1 drop each of almond oil and Intellect tree oil and take with a batasha on an empty stomach, followed by a cup of milk. It can also be used to massage on affected area. This oil can also be used to massage babies.
- Erectile Dysfunction: As a stimulant, apply the oil on penis on erectile failure.
- Memory, Intellect and Concentration: Add Intellect tree oil (2-4 drops) in milk and drink on an empty stomach in the morning.
- Cold and Cough: Take nasya by instilling a few drops of the oil into nostrils to ward off mucous secretions in colds and cough.
- Headache: Paste prepared from leaves of Intellect tree when applied over forehead is considered beneficial for relieving headache.
- Eye disorders: Intellect tree oil when massaged over foot is considered beneficial for all the eye related disorders.
- Abdominal disorders: Consuming a glass of milk along with 1-5 drops of Intellect tree oil is beneficial for abdominal disorders.
- Piles: Paste prepared from Intellect tree root, rice water and black pepper powder when applied is considered beneficial for piles.
- Urinary disorders: Consuming lassi along with 2-5 drops of Intellect tree oil is beneficial for overcoming urinary disorders.
- Eczema: Paste prepared from Intellect tree root powder and godhan ark when applied over eczema is considered beneficial.
References:
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-2707638
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Celastrus_paniculatus
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEPA7
http://www.ijpbs.net/vol-3/issue-3/pharma/33.pdf
https://hort.purdue.edu/newcrop/CropFactSheets/peng.html