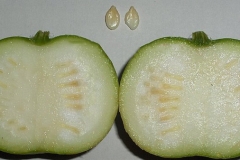
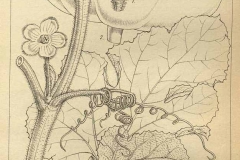
| Indian round gourd Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
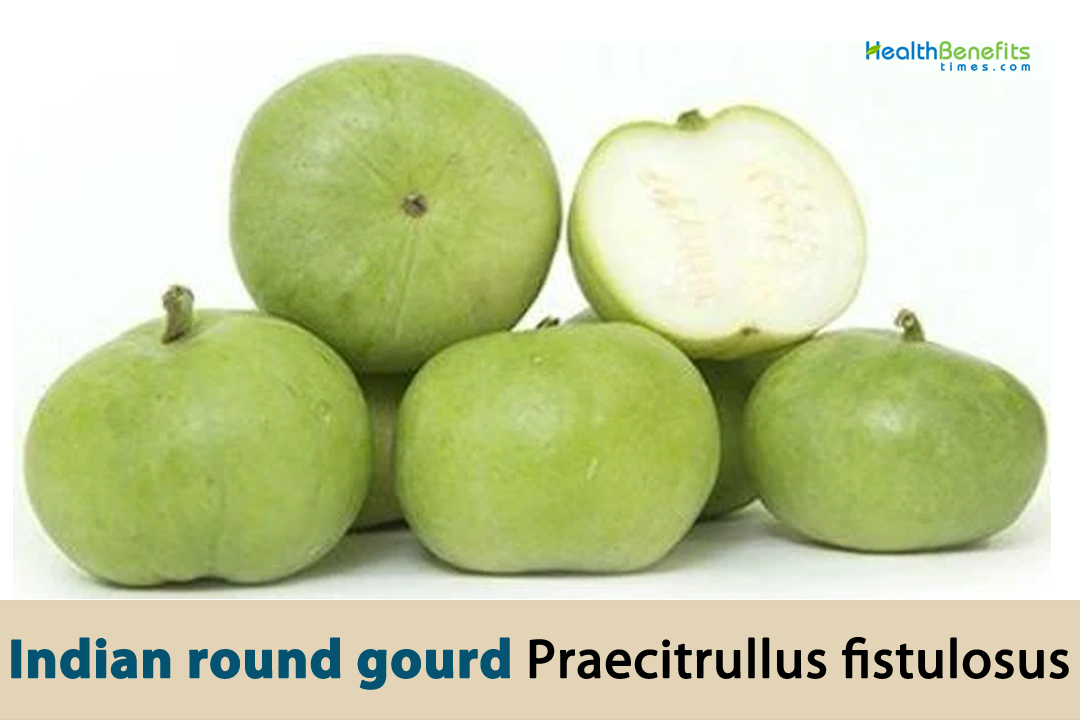
| Name: | Indian round gourd |
| Scientific Name: | Praecitrullus fistulosus |
| Origin | India and today it is popular throughout Asia, Southeast Asia and also in Southern California |
| Colors | Light green, dark green or even pale white |
| Shapes | Elongated, cylindrical, or club-shaped, with lengths typically between 6 to 12 inches |
| Flesh colors | White or pale green |
| Taste | Delicate and slightly earthy flavor |
| Major nutrients | • Dietary Fiber • Vitamin C • Vitamin A • Potassium • Calcium • Magnesium • Antioxidants • Water • Carbohydrate • Protein • Folate (Vitamin B9) |
| Health benefits | Promotes Weight Loss, Bone Health, Eye Health, Cancer, Blood Sugar Control, Moisturizes Skin, Asthma Relief, Battles Fevers, fights Jaundice, Treats Alopecia, Joint Illnesses, Uplifts Immunity, regulates Thyroid, Alleviates Insomnia, Skin Infections, Hair Growth |
| Name | Indian round gourd |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Praecitrullus fistulosus |
| Native | India and has been cultivated since ancient times. Today Tinda is popular throughout Asia, Southeast Asia including India, Sri Lanka, China, Nepal, and Indonesia, and the Middle East, and is also becoming more popular in Southern California |
| Common Names | Tinda, Apple Gourd, Indian Baby Pumpkin, Round Melon, Indian Round Zucchini, Indian Round Squash, Indian Round Cucumber, Indian Round Courgette, Round Bottle Gourd, Indian Apple Gourd, Indian Summer Squash, Indian Pumpkin, Indian Round Gourd Squash, Indian Round Gourd Zucchini, Round Gherkin, Round Tindora, Indian Baby Marrow, Indian Round Courgette Squash, Round Tinda Gourd, Baby Pumpkin Gourd, Round Indian Vegetable, Tinda Squash |
| Name in Other Languages | Angika: Titro Arabic: Kūsah Dā’irīyah Hindīyah (كوسة دائرية هندية), Kusa Hindi Mustadair (كوسا هندي مستدير) Assamese: Kunduli (কুণ্ডুলি) Bengali: Ṭiṇḍā (টিণ্ডা), Dheki (ঢেঁকি) Bhili: Tirika Bhojpuri: Tindoor, Dhera Bodo: Thwisri Burmese: Kyettha Chakma: Ushau Chhattisgarhi: Chilka Bhindi Chinese: Yìndù yuán húlú (印度圆葫芦), Yìndù yuán nánguā (印度圆南瓜) Dutch: Indiase Ronde Pompoen English: Indian Round Gourd, Indian round melon, Round gourd, Round melon, Indian baby pumpkin French: Courge ronde indienne Gaddi: Bedu Garhwali: Kaddu Bhaat Garo: Khing Manda German: Indischer Rundkürbis, Indische Runde Kürbis Gondi: Turri Greek: Indikí strongylí kolokýtha (Ινδική στρογγυλή κολοκύθα) Gujarati: Ṭuṇḍalī (ટુંડલી), Bhinda (ભીંડા), Bhimbi Haryanvi: Tundli Himachali: Tindu Hindi: Tinda (तिन्दा) Italian: Zucca tonda Indiana, Zucchina Indiana Rotonda Japanese: Indo no marui hyōtan (インドの丸いひょうたん), Indo maru kabocha (インド丸カボチャ) Kannada: Donḍekāyi (ದೊಂಡೆಕಾಯಿ), Tindsi (ತಿಂದಸಿ), Kuvale Kashmiri: Tinday Khasi: Soh Phai, Jhadie Kokborok: Mui, Shatu Konkani: Tavshen Undo Korean: Indo dunggeun hobak (인도 둥근 호박) , Minari (미나리) Kuki: Tungkho Kumaoni: Kaddu Bhat, Jhodu Maithili: Tindor Malayalam: Kumpalaṅṅa (കുമ്പളങ്ങ), Vali Pavakkai (വളി പാവക്കായ്) Manipuri: Thambou Nambi Marathi: Dondakaya, Ṭōṇḍalī (टोंडली), Dhemase (ढेमसे) Mizo: Sang-ber Mundari: Kendru Nagamese: Tindli Nepali: Tinma, Tindako Ghiraula, Matyangre pharsi, Tindaa pharsii Odia: Tondoka (ଟଣ୍ଡୋକ) Oriya: Potala Portuguese: Abóbora redonda Indiana, Abóbora Indiana Redonda Punjabi: Tundā (ਤੁੰਦਾ), Tinda (ਤਿੰਦਾ), Indian Roti Kaddu Rajasthani: Tinda Russian: Indiyskaya kruglaya tykva (Индийская круглая тыква), Indiyskiy kruglyy kabachok (Индийский круглый кабачок) Santhali: Thunda Santali: Tindo Sanskrit: Nirvisha Sindhi: Kankuno Sinhala: Kamala Kola (කමල් කොළ), Batu Spanish: Calabaza redonda india, Calabaza India Redonda Swahili: Boga ya duara ya India, Tikiti Maji Mzunguko Tamil: Kovakkai (கோவக்காய்), Mogikai, Thondakai (தொண்டக்காய்) Telugu: Donḍakāya (దొండకాయ), Donda Kayalu (దొండ కాయలు) Urdu: تندا (Tinda) Tagalog: Upo Thai: Fakthong rūp klom Indīa (ฟักทองรูปกลมอินเดีย), Fak Thong Indii (ฟักทองอินเดีย), Indian Round Squash Tulu: Thondekayi, Moraiya Turkish: Hint Yuvarlak Kabak Urdu: Tinda (تِندا) Vietnamese: Bí đỏ Ấn Độ |
| Plant Growth Habit | Tropical or sub-tropical, warm-season, vigorous annual vine |
| Growing Climates | Extend over fences, trellises, or the ground, depending on how they are cultivated |
| Soil | Loose, well drain, and rich in organic matter |
| Plant Size | About 1 to 3 feet (30 to 90 centimeters) tall while the vines can extend anywhere from 10 to 30 feet (3 to 9 meters) or even more in length |
| Root | Typically begins its growth with a primary root, often referred to as the taproot. The taproot extends vertically into the soil and serves as the main anchoring structure for the plant |
| Stem | Typically cylindrical, green, and slightly succulent. The outer surface of the stem is covered with fine, soft hairs, giving it a slightly fuzzy or velvety texture |
| Bark | Does not have a prominent woody stem or bark |
| Leaf | Leaves are arranged alternately along the stem. They are typically large, palmate, and lobed. Margins are typically serrated or toothed, with small pointed teeth along the edges |
| Flowering season | From April to June |
| Flower | Flowers are typically large, showy, and bright yellow in color. They have a distinct trumpet-like shape with five petals that are fused at the base, forming a shallow cup. The petals may have a slightly wrinkled appearance |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Elongated, cylindrical, or club-shaped, with lengths typically between 6 to 12 inches (15 to 30 centimeters) |
| Fruit Color | Light green, dark green or even pale white |
| Fruit weight | About only 3 to 4 ounces |
| Flesh | Crisp and tender when young become slightly fibrous and less tender as they mature and are usually white or pale green |
| Seed | Typically flat, round or oval-shaped and are white or pale cream in color |
| Flavor/Aroma | Mild, vegetal scent with hints of sweetness |
| Taste | Delicate and slightly earthy flavor |
| Plant Parts Used | Delicate and slightly earthy flavor |
| Propagation | By seeds, stem cutting |
| Varieties |
|
| Lifespan | About one year |
| Season | From June, July, and August |
| Major Nutrition |
|
| Available Forms |
|
| Health benefits |
|
Appropriate growing environment for Indian round gourd
Indian round gourd is a popular vegetable in Indian cuisine. To cultivate Indian round gourd successfully, you need to provide the appropriate growing environment. Here are the key factors to consider:
- Climate: The Indian round gourd does best in warm, humid places. For best growth, keep it between 25°C and 35°C (77°F and 95°F). Make sure the plants get a lot of sunshine every day—at least 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight.
- Soil: The dirt should be loose, drain well, and have a lot of organic matter in it. The pH level should be between 6.0 and 7.5. Adding compost or well-rotted dung to the soil can make it better and make it more fertile.
- Spacing: The dirt needs to be loose, drain well, and have a lot of living things in it. It needs to be between 6.0 and 7.5 on the pH scale. If you add compost or dung that has broken down, it can improve the soil and make it healthier.
- Watering: These gourds need to stay moist all the time, especially when they are growing. Deeply water, but don’t let it get too wet, as that can cause root rot. To let the leaves dry during the day, it’s best to water in the morning.
- Fertilization: To give the plants the nutrition they need, use a balanced, slow-release fertilizer or organic compost. Follow the directions on the fertilizer box to add it to the soil before you plant and again during the growing season.
- Support Structures: Use organic soil or a balanced, slow-release fertilizer to give the plants the food they need. Do what it says on the box to add the fertilizer to the soil before you plant and again as the plants grow.
- Pruning and Training: Regularly prune the plants to let more air flow through and keep them from getting too crowded. Train the vines to grow up the support structures so that they are easier to pick and keep pests away.
- Pest and Disease Control: Aphids, whiteflies, and cucumber bugs are some of the most common pests you should keep an eye out for. If you need to, use natural ways to get rid of pests, like neem oil or insecticidal soap. Good cleanliness and enough space between people can also help stop disease outbreaks.
- Harvesting: The Indian round gourd is usually picked when it’s between 4 and 6 inches across. Cut the fruit off the vine with a sharp knife or pruning tools. Fruit grows more when it is picked regularly.
Roots
The Indian round gourd usually starts to grow with a primary root, which is also known as the taproot. This is common for many dicot plants. The taproot goes down into the ground and becomes the main structure that holds the plant in place. To get to water and nutrients in the deeper layers of dirt, it also helps plants grow. Side roots grow from the taproot as the plant grows older. These side roots grow out from the taproot in a horizontal direction and search the dirt for water and food. Side roots are very important for plants because they help them take in water and minerals from the earth around them. This is good for their health and growth as a whole.
To protect the root tip, there is a structure called the root cap. There are many layers of cells that make up the root cap. It protects the root’s growing tip as it pushes through the dirt. It also releases a slimy substance that helps the root move through the dirt and keeps it from getting hurt. The cortex is the area just below the epidermis, which is the root’s top layer. It has cells called parenchyma that store starches and other nutrients. These stored stores are very important for the plant’s growth when it is stressed or doesn’t have enough resources. Roots can sometimes work together with nitrogen-fixing bacteria, like Rhizobium species, to make the plant stronger. These bacteria live on the roots and help change nitrogen in the air into a form that plants can use for growth. This makes the plant’s nitrogen intake better.
Stem
The stem is usually round, green, and a little juicy. It has fine, soft hairs all over it and nodes and internodes. Internodes are the parts of the stem that are between the nodes. Nodes are the points on the stem where leaves, tendrils, and sometimes flowers are connected. Tendrils are one of the things that make the stem stand out. There are thin, coiled structures called tendrils that grow from the nodes and help the plant move and stay upright. They wrap around nearby things, like trellises or other plants, making it possible for the vine to climb and get more sunlight.
Vascular tubes inside the stem carry water, nutrients, and sugars to all parts of the plant. The xylem and phloem make up the vascular system. The xylem moves water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant, and the phloem moves sugars and other organic substances made during photosynthesis to different parts of the plant. The stem grows at an uncertain rate, which means it keeps getting bigger and making new leaves, tendrils, and flowers all through the growing season. This pattern of growth lets the plant spread and keep making fruit.
Bark
People grow the Indian round gourd for its vines and fruits, which can be eaten. It doesn’t have a woody stem or bark that stands out like trees and bushes do. Instead, its stem is made up of herbs and is pretty soft. This means that it doesn’t have the typical bark structure that you see on hard plants.
Leaves
Along the stem, the leaves are grouped in pairs. This means that each leaf is connected to the stem at a different spot, and as you go up the stem, the leaves switch sides. Most Indian round gourd leaves are big, palmate, and lobed. They have a center point and several deep lobes that spread out from it, making it look like a hand with fingers spread out. The number and depth of the lobes may change based on the type of plant. Most of the time, the ends of the leaves have small, pointed teeth that are serrated or toothed. They are different from some other types of gourds and squash because of this trait. Its leaves have a clear network of veins, like most dicotyledonous plants. From the central midrib, the main veins spread out and split into secondary and tertiary veins. This network of blood vessels moves water, nutrients, and sugars around the leaf.
The leaves’ top side is generally smooth, but the bottom side may have a few hairs or be covered in fine, soft hairs. These hairs can help the leaf keep water in by stopping it from evaporating and protect it from things in the surroundings that could hurt it. The leaves are usually a dark green color, which means they are healthy and photosynthesis is going on. The color green comes from chlorophyll, which is the pigment that absorbs light energy during photosynthesis. There is a thin tube called a petiole that connects each leaf to the stem. The leaf can turn and face the sun in the best way possible thanks to the stalk.
The leaves can be different sizes, but most of them are big, with a lot of surface area for photosynthesis. More sunshine can be used to make energy when the leaves are bigger. The leaves are set up so that they get the most sunlight. Most of the time, they are positioned in a way that lets them absorb the most sunshine for photosynthesis to work well. Photosynthesis is the main job of the leaves. It’s how plants turn light energy into chemical energy (sugars) that they can use to grow and develop. Transpiration, or the release of water vapor, is helped by the leaves. This moves nutrients from the roots to other parts of the plant.
Flowers
Indian round gourd flowers are usually unisexual, which means that each flower is either male or female. Monoecious plants, on the other hand, have both male and female flowers. Every once in a while, there may be bisexual flowers that have both male and female reproductive parts. Most of the time, the flowers are big, showy, and bright yellow. They have a clear trumpet-like shape, with five petals that come together at the base to make a small cup. It’s possible for the flowers to look a little wrinkled. The male flower has a joined corolla (petals), a long tube-like structure called the corolla tube, and a big stamen in the middle. The corolla of a female flower is also joined, and the ovary is a separate structure.
Indian round gourd plants usually have flowers that are both male and female on the same plant. Most of the time, there are more male flowers than female flowers. For food to grow, pollen from male flowers needs to be moved to the stigma of female flowers. Pollinators, like bees and other insects, often make this easier because they bring pollen to flowers when they visit them to get food.
Fruits
Depending on the type, Indian round gourd seeds are usually long, cylindrical, or club-shaped. Their lengths are usually between 6 and 12 inches (15 to 30 centimetres), and their sizes can range from small to middle. When fully grown, the skin on the outside is usually smooth and shiny. Its color can be light green, dark green or even pale white, based on the type and how old it is. The skin is pretty thin, and as it gets older, it may get a little tough. When it’s young, the meat is crisp and tender, and it has a lot of water in it. It can get a little tougher and less soft as it ages, but you can still eat it. The taste is mild and slightly sweet, and the texture is crisp and refreshing. Because it has a mild flavor, it can be used in both sweet and savory recipes.
Seeds
While Indian round gourd seeds can be long, cylindrical, or club-shaped, it depends on the type. To give you an idea of their size, they come in a range of 6 to 12 inches (15 to 30 cm) long. The outside skin is generally smooth and shiny when it’s fully grown. Depending on the type and age, it can be light green, dark green or even pale white. The skin isn’t very thick, and it might get stronger over time. The meat is crisp and soft when it’s young, and it has a lot of water in it. You can still eat it even though it might get a little tougher and less soft over time. What it tastes like is mild and slightly sweet, and the texture is crisp and cool. It can be used in both sweet and savory foods because it doesn’t taste strong.
Types of Indian round gourd
Indian round gourd is a versatile vegetable that comes in various shapes, sizes, and varieties. These variations make it a popular choice in diverse culinary preparations. Here are some common types of Indian round gourds:
- Round or Spherical Indian Round Gourd: This is the traditional round gourd, and it has a shape that is very close to a sphere. It is often used in soups and stews that keep its round shape, like stuffed gourds.
- Long or Cylindrical Indian Round Gourd: This type is long and circular, making it look like a club. Gourd that has been cut into rounds or strips is often used in this way.
- Bottle Gourd: One of the most popular types of Indian round gourd is the bottle gourd. It looks like a long bottle and has a neck that gets narrower toward the top. This type is commonly used in Indian, Asian, and Mediterranean cooking. It can be added to soups, stews, sauces, and even drinks.
- Doodhi or Lauki: Doodhi, also called Lauki, is a type of Indian round gourd that has pale green skin and white meat. Indian recipes like Lauki ki Sabzi and Lauki ka Halwa are often made with it. This is especially true in North Indian and Gujarati cooking.
- Ridge Gourd: Ridge gourd, which is also called Turai or Tori, is a thin, long type of Indian round gourd that has clear lines running along its length. People from India, Southeast Asia, and China often use it in their cooking. It has a mild flavor and a slightly crunchy texture.
- Snake Gourd: Snake gourd is a type of Indian round gourd that is long, thin, curled, and has a unique snake-like shape. It is used in many Asian dishes, especially those from India and Southeast Asia, and has a mild, creamy taste.
- Opo Squash: Some Indian round gourds look like snakes. The snake gourd is long, thin, bent, and has a unique shape. It is used in a lot of Asian recipes, mostly Indian and Southeast Asian ones. It tastes mild and creamy.
- Ash Gourd: This is an ash gourd, which is also called winter melon. It is a big, long gourd with a waxy, pale green skin. In Asian cooking, it is often used to make both savoury and sweet foods, like soups, curries, and cakes.
- Hulu Gourd: The hulu gourd is a special kind that looks like a bottle or other object. It is often used as a decoration or as a vessel for serving drinks in some countries.
- Bitter Gourd (Bitter Melon): Even though it’s not a real round gourd, the bitter gourd is very similar to Indian round gourds and is often put in the same group. It has a strong bitter taste and is used in many Asian recipes, especially ones that are thought to be good for you.
Health benefits of Indian round gourd
Indian round gourd is a nutritious vegetable that offers several health benefits. Here are some of its health benefits in detail
1. Promotes Weight Loss
Because round gourd is low in calories and high in important nutrients, people who are trying to lose weight and stick to a tight diet plan can eat it regularly. This is especially true for people with diabetes. Round gourd also has dietary fibre that is easily broken down in the gut. This makes you feel full for longer, cuts down on cravings, and speeds up fat burning.
2. Augments Heart Function
Eating round gourd on a daily basis can help keep your heart healthy. Boiling the vegetable makes it easy to add to many traditional Indian recipes. It also improves blood flow to and from the heart, which keeps the heart muscles working at their best.
3. Detoxifies the Kidneys
The excretory system in the body gets rid of waste more easily when you eat Indian round gourd. It increases the production of fluids in the kidneys, which quickly gets rid of toxins and keeps the body’s organs properly hydrated. Juice helps the kidneys and bladder do their normal jobs.
4. Enhances Digestive System
As a result of its high fiber content, round gourd can help keep you from getting constipated, bloated, or stomach cramps after a big meal. Also, because it is a cleanser, it helps control bowel movements, which eases any pain in the gut.
5. Strengthens Respiratory Processes
As its name suggests, round gourd naturally helps loosen and clear out the respiratory system of any extra phlegm or mucus which may be present. This is very good for lung health and keeps asthma and breathing problems at bay.
6. Bone Health
As its name suggests, round gourd naturally helps loosen up and get rid of any extra mucus or gunk that might be in the lungs. This is great for your lungs and keeps asthma and breathes issues at bay.
7. Mitigates Anxiety and Depression
Indian round gourd has a lot of pyridoxine, which is a type of vitamin B6. Pyridoxine helps nerves send impulses and messages smoothly and is also used to make serotonin and dopamine, which control mood. This green vegetable is also full of calcium, magnesium, manganese, and zinc, which are all important minerals that can help your brain work better improve your memory, help you focus, and help with anxiety and sadness.
8. Enhances Eye Health
A type of vitamin B6 called pyridoxine is found in large amounts in Indian round gourd. It is used to make serotonin and dopamine, which control mood, and helps nerves send impulses and messages easily. Calcium, magnesium, manganese, and zinc are all found in large amounts in this green veggie. These minerals are good for your brain and can help you remember things, concentrate, and deal with stress and sadness.
9. Lowers Risk of Cancer
Indian round gourds are full of tannin and cucurbitacin antioxidants, which are very good at reducing inflammation. These helpful organic substances protect body cells from damage caused by free radicals and toxins. In this way, it is a super food that keeps the brain, heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, stomach, and bowels from getting hurt, which in turn stops cancer from happening.
10. Blood Sugar Control
Indian round gourd may help keep blood sugar levels in check, according to some studies. It’s good for people with diabetes or who are at risk of getting it because it has a low glycemic index, which means it affects blood sugar more slowly.
11. Asthma Relief
It is used in some ancient medicines to help people with asthma. It may help lower inflammation in the airways and make breathing easier because it is anti-inflammatory.
12. Pregnancy and Lactation
Indian round gourd has a lot of vitamin B9, which is important for the growth of the baby while the mother is pregnant. It can also help nursing moms make more milk, which can help them breastfeed.
13. Naturally Moisturizes Skin
The Indian round gourd naturally contains Vitamin E, which is a moisturizing and smoothing vitamin that also fights free radicals. Putting the vegetable’s gel extract on sunburns and rashes calms down the irritated and dry skin, leaving it soft and saturated with moisture.
14. Battles Fevers
If you rub the leaves of a round gourd on someone who has a high fever, they feel better right away. The leaves lower the person’s body temperature and tiredness. Furthermore, because fevers mess up the body’s regular metabolism, round gourd leaves help get rid of extra water and salts to keep the electrolyte balance in check.
15. Fights Jaundice
Cucurbitacins, which are found in round gourd leaves, are very important for supporting the body’s defense system and liver function. The leaves of the round gourd also have a lot of vitamin C, which helps people with jaundice by increasing their defenses and antioxidant defenses. As an Ayurvedic treatment for jaundice, the leaves of a round gourd are crushed with coriander seeds and then eaten twice a day.
16. Remedies Heart Ailments
People think that round gourd juice is one of the best ways to treat heart problems like chest pain, palpitations, high blood pressure, coronary heart disease and irregular heartbeats. A dose of two cups of round gourd juice is given to people with heart problems in traditional Indian medicine to improve blood flow and make it easier for them to do normal in-person activities.
17. Treats Alopecia
When made and used on people who were losing a lot of hair, round gourd gel improved blood flow and nerve function in the head, which led to faster hair growth. Alopecia is marked by noticeable bald spots and hair loss that is too much. The high carotene content in gel extract fights these effects, stopping hair loss and making hair stronger and smoother.
18. Recovers Joint Illnesses
Round gourd juice is a good anti-inflammatory that heals joint problems like fractures, gout, osteoporosis and arthritis and eases pain in muscles and bones. It also has a lot of magnesium, calcium and phosphorous, which are three important minerals for building strong bones. This increases bone strength and helps muscles and joints get back to being flexible.
19. Uplifts Immunity
Round gourd is a powerful way to boost your immune system when you are sick because it is full of vitamin C, antioxidants, and carotenoids. When someone is sick, their organs don’t work as well as they should. Eating round gourd vegetables gives vitamin C to their blood cells, which is then sent to other organs to help them get back to working at their best. It also helps you feel better when you’re tired.
20. Regulates Thyroid
For some people, their thyroid hormone levels change and go above the standard range, which is called hyperthyroidism. Large amounts of iodine and zinc are found in round gourd. Iodine helps lower high thyroid hormone levels, and zinc is essential for enzymes to work properly, which improves thyroid concentrations.
21. Alleviates Insomnia
Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), which is found in large amounts in round gourd juice, helps the brain work properly and let’s nerve signals travel without any problems. Having a glass of gourd juice can lower the activity of neurotransmitters and help you fall asleep when you have trouble sleeping or can’t sleep at all.
22. Combats Skin Infections
Sticky substances are found in the round gourd leaf leftovers. This helps calm down the skin spots that are very red. It also effectively gets rid of any boils, pus, or carbuncles on skin areas that are irritated by allergies, fungus diseases, pollution, or the sun.
23. Promotes Hair Growth
There are many vitamins and minerals in round gourd that are good for hair and make it strong. When used as a gel, it also goes deep into the head to protect follicles and keep hair thick and stable. If you want to grow your hair long and strong, round gourd is a great choice.
24. Tackles Excessive Dandruff
Round gourd has potent chemicals that can reduce the intensity of flakiness and dandruff on the scalp of hair. It can also shelter the roots of the hair strands, known as follicles, from the dirt and fungus particles that trigger dandruff. Round gourd gel obtained from the flesh, when applied routinely to itchy and peeling scalp and dry hair, can significantly revamp the appearance of dull hair, giving it an incredible sheen.
Culinary uses of Indian round gourd
Indian round gourd is a versatile vegetable used in various culinary dishes across different cuisines. Here’s a list of culinary uses for Indian round gourd:
- Curries: It is often added to curries, either by itself or with other veggies. It takes on flavors well and gives the curry a mild, slightly sweet taste.
- Stir–Fries: For a quick and healthy side meal, you can stir-fry sliced or diced gourd with spices and other foods.
- Soup: You can mix it into soups to make them creamier and give them a mild flavor. To make it taste better, add herbs and spices.
- Stuffed Dishes: An empty gourd can be filled with a mix of herbs, spices, other veggies, or ground meat before it is cooked.
- Fritters: Gourd slices or grated can be mixed with gram flour (besan) and spices to make fritters. The fritters should then be fried until they are golden brown.
- Chutney: When mixed with coconut, mango, and spices, Indian round gourd can be used to make unique chutney.
- Salads: You can add grated or thinly sliced Indian round gourd to salads to give them a nice crunch and mild flavor.
- Pickles: Spices, vinegar, and oil can be used to make a tangy and savoury sauce for Indian round gourd.
- Parathas: For stuffed parathas, grated or finely chopped gourd can be added to the dough to make it taste better and keep it from drying out.
- Baked Dishes: It can be added to baked goods like casseroles and gratins to give them a different texture and taste.
- Smoothies: You can add it to baked goods like gratins and casseroles to change the way they taste and feel.
- Dosa: Indian round gourd can be used to make dosa batter. It gives the batter a mild flavour and a soft texture.
- Pulao: Diced Indian round gourd can be added to rice recipes like pulao to make them more filling and healthy.
- Biryani: It can be added to vegetable biryani recipes to make the dish taste and feel better overall.
- Chai: “Lauki ki chai” is a type of tea made in some countries by simmering Indian round gourd with milk and spices.
- Daal: When you add Indian round gourd to lentil soup, you get a healthy and filling meal. It takes on the flavors of the spices and makes the structure nice.
- Pasta Sauce: Indian round gourd that has been grated can be added to pasta sauces, especially thick ones, to make them more interesting.
- Dumplings: Whether it’s by itself or with other veggies and spices, it can be used to fill dumplings or momos.
- Bharta: Gourd should be roasted or grilled, then mashed. Spices, herbs, and oil should then be added to make a bharta.
- Stuffed Parathas: For a filling and tasty meal, stuff Indian round gourd with spices and maybe some cheese into parathas.
- Chapati/Roti: Grate Indian round gourd into the dough for chapati or roti to make them taste and feel better.
- Samosas: For samosas, a popular Indian snack, fill them with a mix of Indian round gourd, spices, and other veggies.
- Tacos: Indian round gourd that has been sautéed or grilled can be used as a filling for veggie tacos. Salsa and other toppings can be added to go with it.
- Omelets: If you dice or grate Indian round gourd, you can add it to omelets or boiled eggs to make them healthier and more interesting.
- Sandwiches: Along with other veggies, spreads, and condiments, sliced or grated Indian round gourd can be used to fill a sandwich.
- Casseroles: You can add Indian round gourd to casseroles, lasagnas, or baked pasta recipes to make them taste better and be healthier.
- Pizzas: If you slice or dice Indian round gourd very thinly, you can put it on pizza. It gives the pizza a mild, slightly sweet taste.
- Sushi Rolls: For meatless sushi rolls, fill them with thin strips of Indian round gourd that have been blanched.
- Stews: You can make a hearty and healthy meal with Indian round gourd by adding it to veggie stews or ragouts.
- Kebabs: To make vegetable burgers that you can grill or bake, mix minced Indian round gourd with herbs, spices, and other things.
- Sautéed Side Dish: Indian round gourd slices can be cooked with garlic, herbs, and spices to make a tasty side dish to go with your main meal.
- Bread: Slices of Indian round gourd can be cooked with garlic, herbs, and spices to make a tasty side dish for your main food.
- Smoothie Bowls: For a healthy and delicious breakfast, put thinly sliced or diced Indian round gourd on top of smoothie bowls.
Different uses of Indian round gourd
Indian round gourd has several non-culinary uses as well. Here are some non-food applications of Indian round gourd:
- Crafts: The tough skin is often used to make things. It can be cut, painted, or decorated to make jewelry, masks, and other items for decoration.
- Containers: A lot of things are made from the tough skin. Jewelry, masks, and other decorative items can be made from it by cutting, painting, or decorating it.
- Musical Instruments: To improve the sound of traditional instruments like sitars, banjos, and some percussion instruments, gourds are sometimes used as resonators.
- Sponges and Scrubbers: The inside is made of fibre that can be used to clean as a natural sponge or brush.
- Decorations: Gourds that have been dried out can be used to decorate gardens and houses. To make one-of-a-kind home art, you can paint, carve, or leave them as they are.
- Candles: You can hollow out gourds and use them as natural candleholders, which looks nice and homey.
- Plant Containers: Gourds that have been cut in half or hollowed out can be used to plant small herbs, succulents, or decorative plants.
- Birdhouses: Dried gourds can be used to make birdhouses, which birds can use to nest in fields and other outdoor areas.
- Educational Tools: Gourds are sometimes used in schools to show how plants grow, how biology works, and how to make traditional crafts.
- Herbal Poultices: In traditional Chinese medicine, gourd poultices can be put on the skin to help with some skin problems and small wounds.
- Natural Sponges: If you dry and clean the inside of a gourd, you can use it as a natural sponge for cleaning and bathing.
- Costumes: Gourds can be used to make masks, costumes, and other props for plays, fairs, and other cultural events.
- Art and Sculpture: Because gourds have different sizes and textures, artists can use them to make sculptures and other three-dimensional art.
- Traditional Rituals: Gourds are used in traditional ceremonies and rituals in some countries to represent fertility, plenty, and safety.
- Gourd Lamps: Dried gourds can be made into lampshades or lanterns with great detail, and when lit, they give off beautiful patterns of light.
- Cultural and Religious Artifacts: Masks, totem poles, and other religious and cultural items, like decorations used in ceremonies and practices, are often made from gourds.
- Toys and Games: Toys, singing instruments, and game pieces made from dried gourds can be made for kids to play with and enjoy.
- Shakers and Maracas: When you fill gourds with seeds or other small things, you can use them to make shakers and maracas for dance and music shows.
- Gardening Tools: Cut out the tough shell of a gourd and use it as a small scoop, tool, or gardening container.
- Natural Sponge Gourd: The fibre inside of fully grown gourds can be used as a natural cleaner or sponge to remove dead skin or clean.
- Insect Traps: Containers in the shape of gourds can be turned into bug traps, which are often used in farming to get rid of pests without using chemicals.
- Decoration for Festivals: Gourds are often used as decorations at different celebrations and gatherings. They are often painted or decorated with complicated patterns.
- Traditional Medicine Storage: In traditional medicine, dried gourds are sometimes used to store medical herbs and powders.
- Arts and Crafts: People often use gourds in arts and crafts projects, like painting, cutting, and decorating them to make one-of-a-kind items that can also be used.
- Pottery and Ceramics: The textures and forms of gourds can give pottery and ceramics artist’s ideas for making vases, bowls, and other containers.
- Ornamental Gourds: Different kinds of gourds, like ornamental or “bottle” gourds are grown just to look nice because of their unique shapes and sizes.
- Traditional Instruments: Traditional rhythmic instruments like the kalimba (an African thumb piano) and the marimba (a South American instrument) are incomplete without gourds.
- Natural Bird Feeders: By hanging hollowed-out gourds outside, you can use them as bird feeders that give bird’s food and look nice in your yard.
- Traditional Containers: Because of their natural shape and sturdiness, gourds have been used for a long time as traditional containers for liquids and grains.
- Ink and Paint Containers: Some cultures store ink, paint, or natural dyes in gourd cases that are used for art and calligraphy.
- Sculpture Bases: When making three-dimensional art, gourds can be used as stable bases for shaping clay, papier-maché, or other materials.
Side effects of Indian round gourd
Indian round gourd, like many other foods, is generally safe to consume in moderation as part of a balanced diet. However, there are a few potential side effects and considerations to keep in mind:
- Bitter Taste and Toxins: Natural chemicals called cucurbitacins can make some Indian round gourds taste bitter. This is because large amounts of these chemicals can be harmful. If you eat gourds that have a lot of cucurbitacin in them, you might get stomach pain, sickness, vomiting, and diarrhea. It’s important to pick gourds that aren’t too bitter, and you should never buy gourds that are bitter.
- Allergic Reactions: People who are allergic to gourds, cucumbers, or other vegetables that are linked to Indian round gourd may have allergic reactions like itching, hives, or swelling after eating it.
- Gastrointestinal Distress: Indian round gourd can cause stomach problems like gas, bloating, and indigestion if eaten in large amounts, especially when it is raw or not fully ripe. These signs are less likely to happen if you cook or steam the gourd.
- Kidney Stones: Indian round gourd has a lot of oxalates, which can make kidney stones more likely in people who are already more likely to get them. People who have had kidney stones in the past might need to reduce the amount of oxalate they eat. This includes gourds.
- Blood Sugar: Some studies show that Indian round gourd may help control blood sugar levels. However, people with diabetes should closely watch their blood sugar when adding it to their diet because it might affect how their diabetes drugs work.
- Interaction with Medications: Some medicines, like those for diabetes and high blood pressure, may not work well with Indian round gourd. If you are taking medicine, talk to your doctor to make sure there aren’t any bad reactions.
- Over-hydration: Because Indian round gourd is mostly water, eating too much of it, especially in its raw form, can make you too thirsty, which can throw off your body’s chemical balance. This doesn’t happen very often, but it can happen to people with certain health problems.
References:
https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/10.1079/cabicompendium.97683433
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-2409649
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tinda
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/CITFI
https://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Praecitrullus+fistulosus
http://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Tinda.html
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/249171