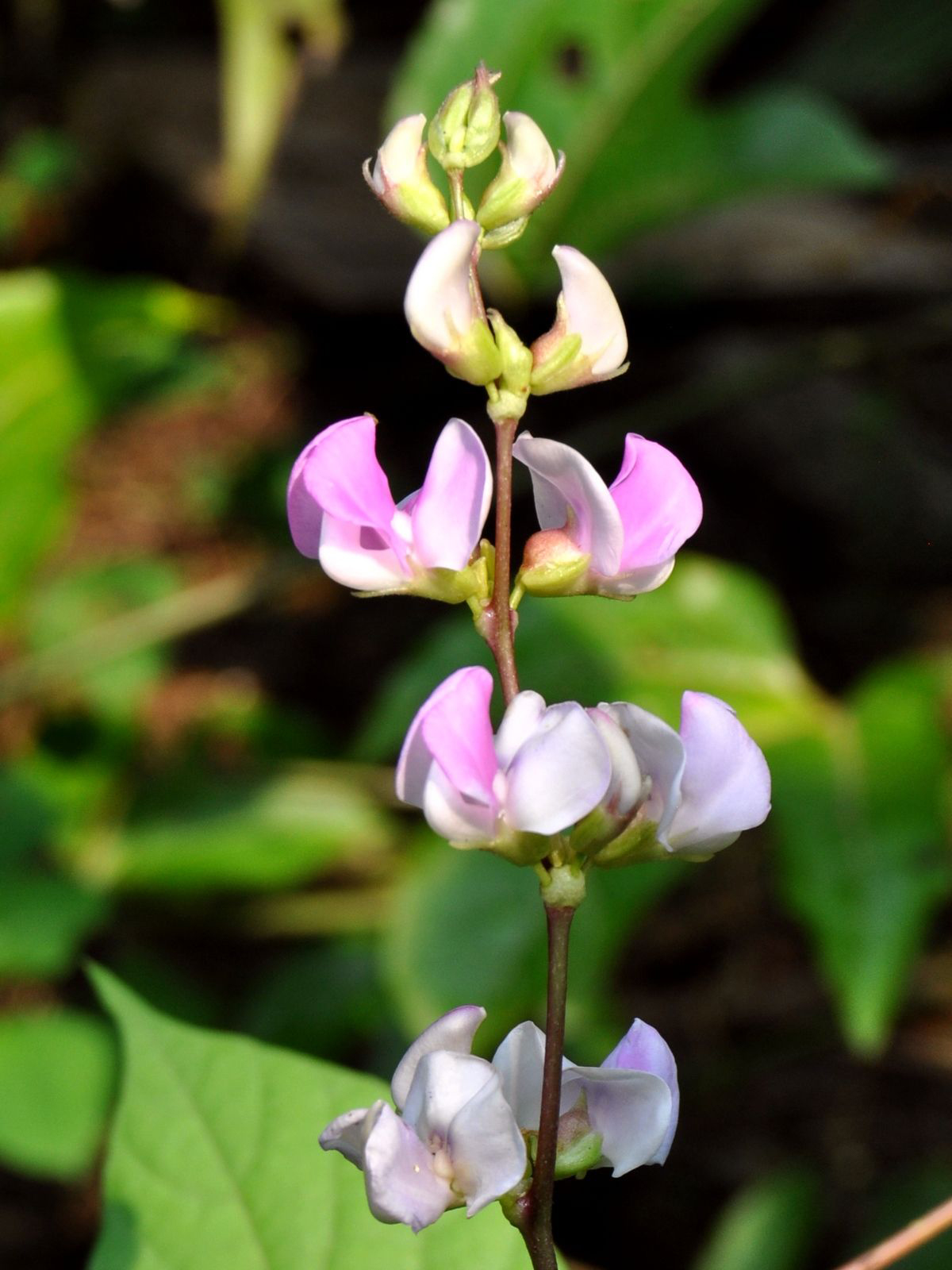
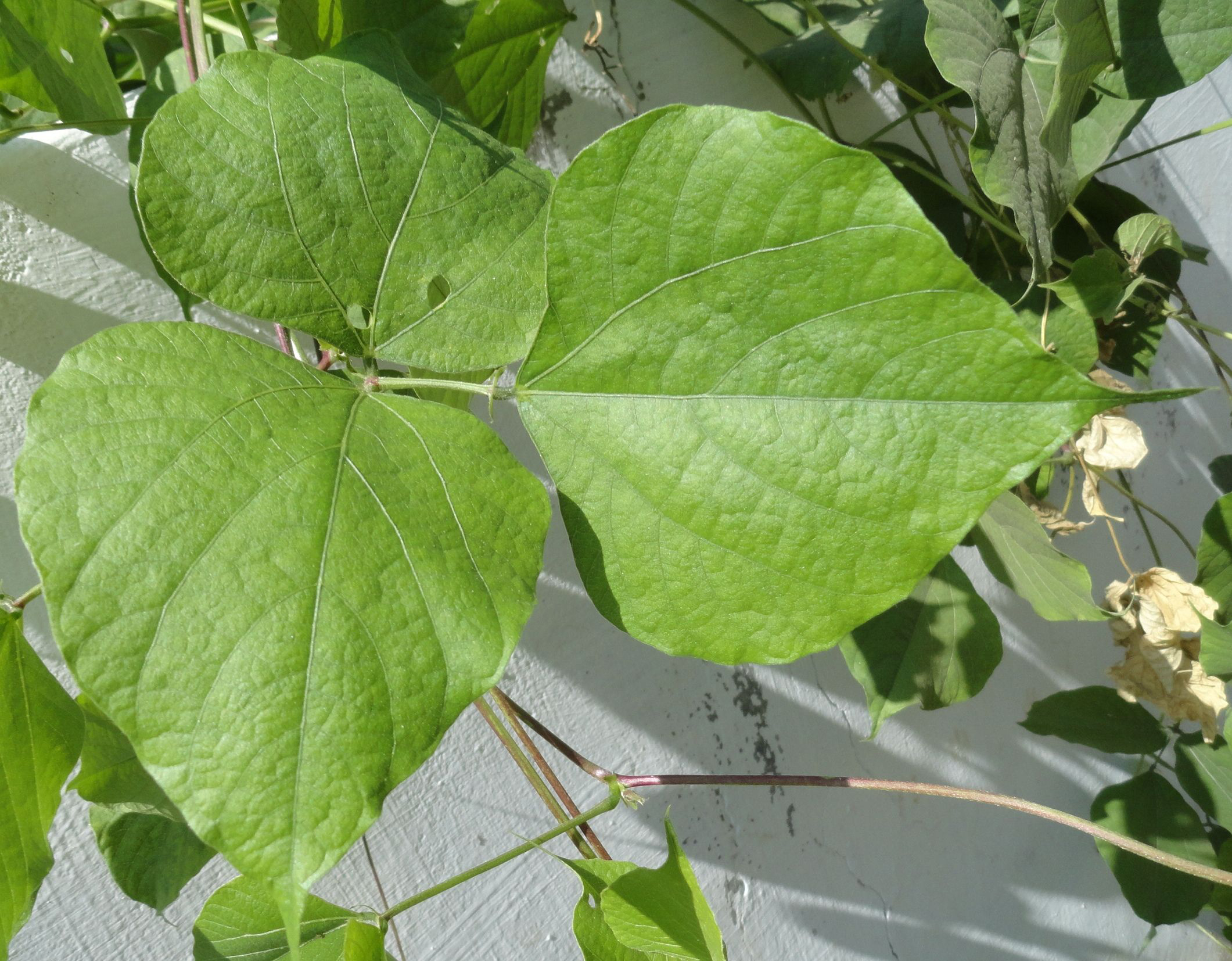
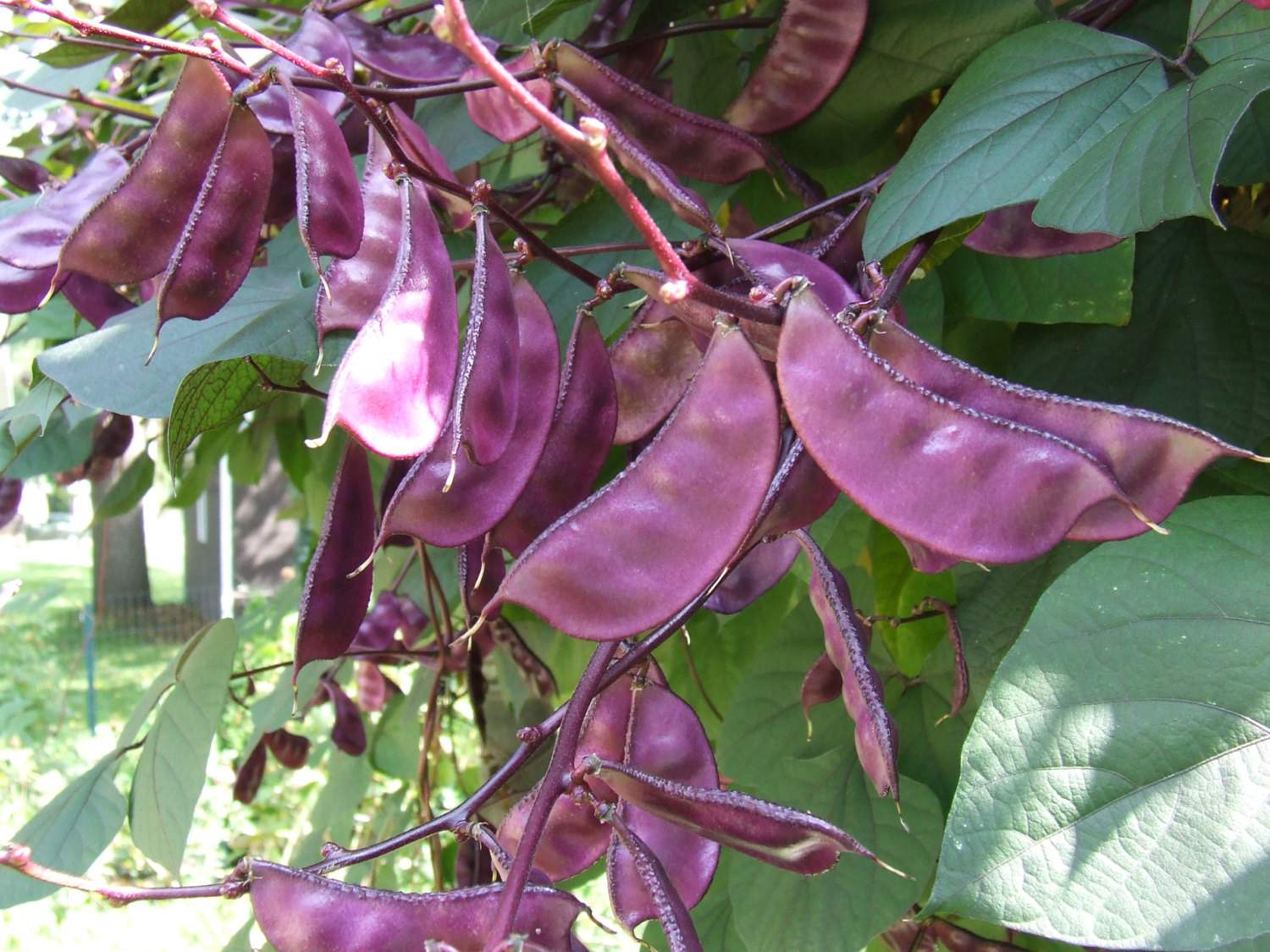
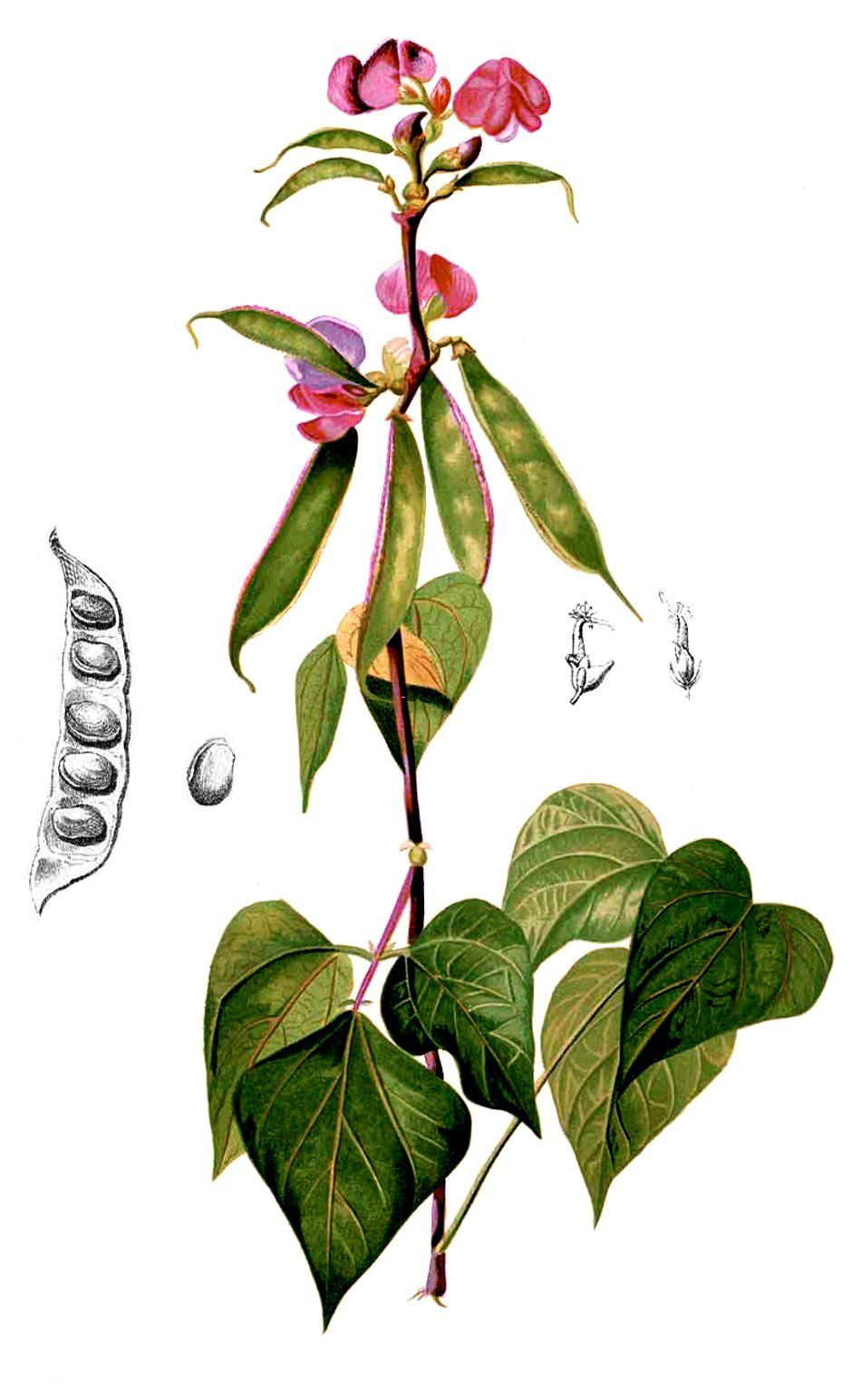
The plant is tropical and widely grown in North Africa and Asia. It is a twining or trailing herb. The pods are 4 to 5 cm long. It is used for vegetable use. It has strong nutty aroma and sweet flavor. There are four varieties of Hyacinth beans such as: White Flower, Purple Flower, Asia Purple and Asia White.
History
Native to Africa, it is cultivated widely in North Africa and Asia for its edible pods. Hyacinth bean made its way to India from Africa in between 1600 and 1500 BC. In 1700’s, Hyacinth beans were introduced to Europe. In 19th century, Hyacinth beans were introduced to America as an ornamental plant. Hyacinth beans were cultivated in Asia and North Africa as a food source.
Plant
The plant of Hyacinth beans is annual or short-lived perennial, twining or trailing herb with thick stem which is about 6 meters long. The plant grows up to 10-15 feet high. The leaves are alternate, trifoliate and 7.5 – 15 cm long. The flowers are purple or white. It requires a well-drained soil.
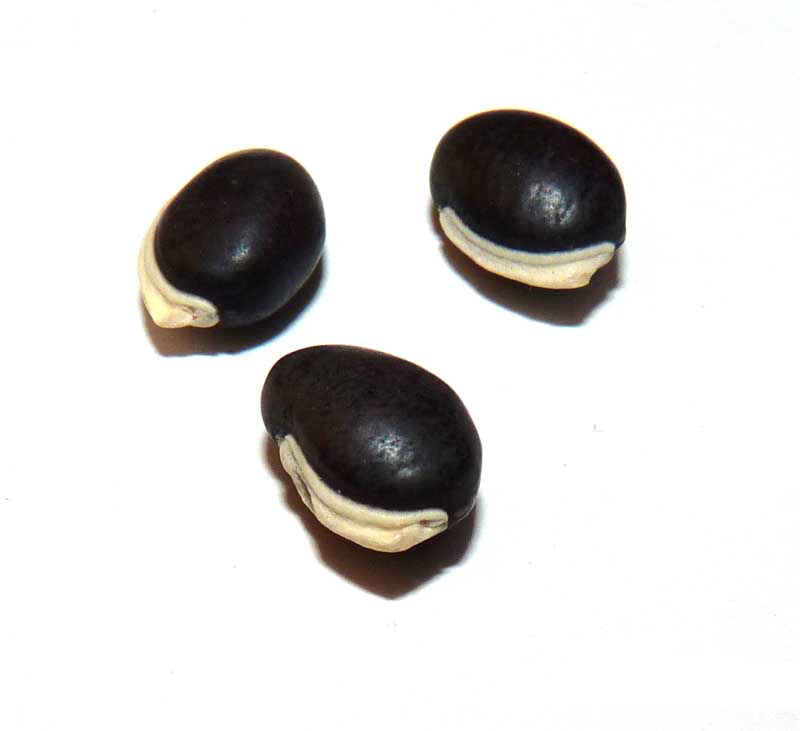
The fruit is a broadly scimitar and smooth pods which is bright purple to pale green. The pods are 4–5 cm long. Each pod contains 4-6 seeds, round to oval and 1 cm long. The seeds are white, cream, pale brown, dark brown, red, black or mottled.
Nutritional Value
The cooked Hyacinth beans without salt provides 227 calories per 1 cup of 194 grams. It contains 111.13% of iron, 73.56% of copper and 50.27% of Zinc. The same amount of serving size of 1 cup provides 159 mg of magnesium, 233 mg of phosphorus, 15.79 g of protein and 78 mg of calcium.
Health Benefits of Hyacinth Beans
Hyacinth Bean contains various nutrients, minerals, vitamins and lipids that help to enhance the overall health. It possess antimicrobial, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, tonic, aphrodisiac, hypocholesterolemic, galactagogue, appetite suppressants and antispasmodic properties that prevents from various types of ailments.
- Brain health
Copper is essential for the brain pathways such as galactose and dopamine which helps to maintain mood, outlook and focus. The low presence of copper leads to fatigue, poor mood, concentration trouble and low metabolic activity. It is also associated in utilizing tyrosinase, ascorbate oxidase, superoxide dismutase and Vitamin C. The antioxidants prevent the damage caused by free radicals and slow down the aging process, neuro-degenerative disease and cancer.
- Cardiovascular health
Vitamin B1 is vital for the production of acetylcholine which is a neurotransmitter that relay messages from the nerves to the muscles. Heart depends on these signals. The proper use of energy helps to provide signals between the nerves and muscles. The studies show that Vitamin B1 helps to counteract heart disease as it maintains the healthy ventricular function and also treats heart failure.
- Prevent cancer
Zinc possesses an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties which helps to counteract oxidative stress and reduce the risk of diseases. Zinc assists the healthy cell division, prevents mutation of cells and prohibits tumor growth. The research shows that the adequate intake of zinc reduced the oxidative stress along with the infections and side effects. It has the ability to promote the immune system.
- Assist respiration
Minerals such as selenium, manganese and zinc assist the people having the lung disorders like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Oxidative stress is the cause for respiratory disorders and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Manganese is able to reduce the oxidative stress as well as inflammation by producing the SOD’s which helps to heal the lungs.
- Supports digestion
Fiber plays a vital role in the digestion. Insoluble fiber provides bulk to the stool and speeds up the time to pass the waste from the body. It helps to prevent bloating, constipation and indigestion. Soluble fiber enhances digestion by absorbing the water to form a viscous substance which is fermented by the bacteria in a digestive tract.
- Treats insomnia
The low consumption and absorption of nutrient is the cause for insomnia. The adequate amount of magnesium helps to increase the sleep, lower levels of cortisol and higher concentrations of melatonin that are related to stress. The research shows that the magnesium supplements reduce the symptoms of insomnia, improve sleep time, sleep efficiency and sleep onset. It also reduces the cortisol.
- Assist levels of energy
Iron helps to transport the oxygen to the cells. It helps to body to absorb nutrients and digest proteins from the food. The low presence of iron results sluggish, trouble being active and cause exhaustion. The symptoms of iron deficiency are mood change, low concentration and muscle co-ordination problem.
- Gum health
Vitamin D, Calcium and phosphorus is essential for maintaining bone health by supporting jaw-bone mineral density, tooth enamel and holds teeth in place. Vitamins and minerals help to cure tooth decay. Children require the foods rich in calcium and phosphorus which helps to form the hard structure of the teeth. Along with phosphorus, Vitamin D is essential to balance the calcium in the body and enhance it absorption for the formation of tooth. Vitamin D reduces the gum inflammation that is related with periodontal gum disease.
- Enhance mood
The protein foods contain the amino acids that are essential to balance hormones, control mood and treats anxiety. Protein assists the function of neurotransmitters and harmonizes the hormones such as serotonin and dopamine which helps to calm us. Proteins balance the glucose and prevent irritability, mood chance and cravings which are associated with the fluctuation of blood sugar level.
- Prevent cramps
Hyacinth beans contains adequate amount of potassium which reduce the muscle cramps and improves the strength of muscles. The deficiency of potassium is the cause of muscle cramps. The potassium soothes the muscles by balancing the fluid levels. Low level of potassium leads to cramps, general pains and muscle spasms. It helps to breakdown the proteins and carbs which the muscle depend upon for the repair and energy.
Traditional uses
- In Peninsular Malaysia, the leaves are used with rice flour and turmeric as a poultice for eczema.
- An infusion made from leaves is used to treat gonorrhoea.
- In Indo-China, the leaves are used for colic.
- In Philippines, the leaves are used for leucorrhoea and menorrhagia.
- In East Africa, the crushed leaves are used to cure headache.
- Leaves are used to treat stomach disorders.
- Green leaves with vinegar are used to cure snakebites.
- In Rwanda, a decoction made from leaves is used to cure heart problems.
- In Democratic Republic of Congo, an infusion made from leaves is used to treat sore throat andtonsillitis.
- In Asia, the flowers are used as antivinous, emmenagogue, alexiteric and carminative.
- In Indo-China, the flowers are used as the treatment for leucorrheoa and menorrhagia.
- In Assam, the pods juice is used to treat an inflammation of ear and throat.
- The mature seeds are anthelmintic, aphrodisiac, antispasmodic, digestive, astringent, depurative, febrifuge and stomachic.
- The decoction is used to treat sunstroke, vomiting, nausea, enteritis, diarrhoea, alcoholism, abdominal pain and arsenism.
- The Chinese use the boiled ripe seeds as a carminative and tonic.
- In India, the seeds are used to stop nose bleeding.
- In Senegal, the seed is used as stomachic, antispasmodic and as a treatment for sunstroke and cholera.
Comments
| Hyacinth beans Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Hyacinth beans |
| Scientific Name: | Lablab purpureus |
| Origin | Africa and is cultivated widely in North Africa and Asia for its edible pods. |
| Colors | Bright purple - pale green |
| Shapes | Broadly scimitar, long, flat, smooth; Length: 4–5 cm |
| Taste | Sweet |
| Calories | 227 Kcal./cup |
| Major nutrients | Iron (111.13%) Copper (73.56%) Zinc (50.27%) Isoleucine (45.28%) Vitamin B1 (43.67%) |
| Health benefits | Brain health, Cardiovascular health, Prevent cancer, Assist respiration, Supports digestion |
| More facts about Hyacinth beans | |
| Rank | Scientific Name & (Common Name) |
|---|---|
| Kingdom | Plantae (Plants) |
| Subkingdom | Tracheobionta (Vascular plants) |
| Superdivision | Spermatophyta (Seed plants) |
| Class | Magnoliopsida (Dicotyledons) |
| Subclass | Rosidae |
| Order | Fabales |
| Family | Fabaceae/ Leguminosae (Pea family) |
| Genus | Lablab Adans. (Lablab) |
| Species | Lablab purpureus (L.) Sweet (Hyacinthbean) |
| Synonyms |
|