| Hugas Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Hugas |
| Scientific Name: | Microglossa pyrifolia |
| Origin | Tropical Africa, China, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Cambodia, India, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Thailand, Vietnam, Madagascar, Comoros and Mayotte |
| Shapes | Achene is compressed and 4-angled, with the reddish pappus about 3 millimeters long |
| Health benefits | Fever, headaches, colds, malaria, dermal infections , cough, elephantiasis, wounds, ophthalmia, stomach complaints, jaundice and edemas. |
| Name | Hugas |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Microglossa pyrifolia |
| Native | Tropical Africa, China, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Cambodia, India, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Thailand, Vietnam, Madagascar, Comoros and Mayotte |
| Common Names | Hugas, Maniak and Saroka |
| Name in Other Languages | African: Asibogo Chinese: Guo shan long (过山龙), Li ye xiao she ju, Jiu li ming, Ko shita kiku (小 舌 菊), Màn mián cài (蔓綿菜), Kunori Akira (九里明), Nashi Kanō ko shita kiku (梨叶小舌菊), Xiǎo pán mù (小盘木) Congo: Muntantali East africa: Nyabungu odide Finnish: Pilviripsusäde Japanese: Shimaizuhahako (シマイズハハコ) Kinyarwanda: Umunyaragisaka, Nyakahe Kenyan: Nyabungu odide, Muhinga, Muteei, Olabai-oibor Malay: Ragin Myanman: Bizat, Bezat Nigerian: Anikan segbo, Anikan segbo torisa, Okbakakwu Papua new guinea: Gogo, Pundari Rundi: Umuhe, Muhe Tanzanian: Kichwaghwmbe, Lauhala, Mswaswaki, Uswaswaki Thailand: Khaa bia, tonghung, tonghong Vietnam: Tiểu thiệt |
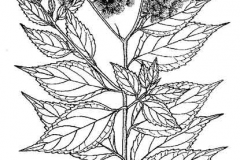
| Plant Growth Habit | Erect or scandent, shrubby and climbing plant |
| Growing Climates | Thickets on slopes, along forest edges, grass land, open forests, forest margins, river forests, stream banks, bush land, wastelands and edges of bamboo plantations |
| Plant Size | Up to 6 m tall |
| Stem | Stem is branched, cylindrical becoming quickly woody. It is speckled, thickly shielded with tiny glandular hairs. |
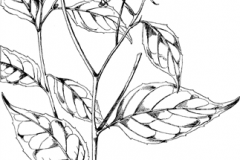
| Leaf | Stalked, ovate-lanceolate, 3.5 to 7.5 centimeters long, pointed at both ends, and obscurely toothed at the margins. |
| Flower | Heads are numerous, less than 1 centimeter across, and clustered on the branches of rounded corymbs. Involucral bracts are lanceolate. |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Achene is compressed and 4-angled, with the reddish pappus about 3 millimeters long, or much longer than the minute achene. |
| Plant Parts Used | Leaves, root, root bark |
| Other Facts |
|
Inflorescence
Inflorescence is a set of yellowish white capitulums organized in a corymbiform panicle within the axils of the leaves or at the end of the axes. Capitulums are about 10-12 mm in length and 5 to 6 mm in diameter. At the base is a campanulate involucre of bracts organized on 4 to 5 rows. Outer bracts are membranous and ovate along with obtuse apex and about 0.7 to 2 mm long. They are enclosed with a thinner tubercular pubescence. Internal bracts are linear to lanceolate, 2 to 5 mm long, glabrous. Basal bracts are persistent. Receptacle of the capitulum is convex.
Flower
Outside of the capitulum are abundant ligulate florets with a filiform ligule 1 mm long. Inside the capitulum of the flower there are tubular florets, along with a tube of 2.5 mm conquered by 5 lobes.
Fruit
Fruit is an obovoid, flattened achene, nearly 1 mm long along with 3 to 4 longitudinal ridges with some fine glandular hairs at the top. Pappus consists of reddish or white bristles organized on 2 to 3 rows. Those from the outside are 1 mm long and from inside are 4 mm long.
Traditional uses and benefits of Hugas
- Decoction of roots is used for stomachache.
- Leaf decoction is used for colds.
- Plant is used to cure fever in babies in Gold Coast.
- In Liberia it is used as a cure for cough.
- It is used in the treatment of cold and headaches in Tanzania.
- Powdered root are used as douse to reduce colds in West Africa.
- Root juice passed through fine linen, is used as eye drops in western tropical Africa.
- Juice of warmed leaves is applied as cure for ringworm of the scalp.
- Tea-like infusion is used for fever with headache.
- Decoction is taken by women during labor.
- Decoction of root bark and also root is used for treating epilepsy in Tanzania.
- Bandages soaked in root decoction are used to cure wounds of incised abscesses.
- Juice from its root is applied to the eyes for cataracts.
- Leaf is applied inside the nose of man and cattle to treat coryza.
- It is also used for backwater fever, dropsy and yellow fever.
- It is used to treat malaria in Africa.
- Pounded roots are soaked in water and used for headache and colds in Kenya.
- Pound leaves are used for treatment of limb fractures.
- It is used for the treatment of wounds and dermal infections in Ghana.
- It is used for elephantiasis, wound and cough in Rwanda.
- Leaves are used for mastitis in Ethiopia.
- Leaf-sap is instilled into the eye for ophthalmia and to kill filarial in Congo.
- It is used in Ivory Coast for numerous stomach complaints, edemas and jaundice.
- The plant is considered as cure for hookworm in E Africa.
- In Peninsular Malaysia a Root decoction is given to treat stomach-ache.
- Vapor produced from heated leaves is blown over sore eyes and spear wounds.
- Bath is used to cure epilepsy, insanity and fits in children.
- Leaf poultice is applied to inflammations, or applied on the chest to reduce pulmonary troubles.
- Powdered root is used locally as a snuff to reduce colds or as a local anodyne.
- Leaves, roots and above ground is used for treatment of meningitis by Bench people.
- Leaves are used for treatment of hard swelling on the skin by Meinit people and for treatment of jaundice and herpes by Sheko people.
References:
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/gcc-26588
https://portal.wiktrop.org/species/show/366
https://plants.jstor.org/stable/10.5555/al.ap.upwta.1_968
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/282143#uses
https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Microglossa_pyrifolia_(PROSEA)