Hog plum, Jamaica-plum, Yellow mombin, Ambarella, Ashanti plum, Golden apple, Hog plum, Jamaica plum, Spanish plum, Thorny hog plum, True ambarella, True yellow mombin, Yellow mombin, gully plum, java plum and hog-plum tree are some of the popular common names of the plant. The plant is used medicinally in traditional medicine against lower back pain, rheumatism, digestive track problems, angina, sore throat, malarial fever, diarrhea, urethritis, gonorrhea, stomach pain, colds, dysentery, laryngitis, ophthalmia, and many others. Root ashes are used in making soap. The wood is used for posts, boxes, matches, general carpentry, tool handles, etc. Seeds are also edible. The pulp can be eaten fresh or made into desserts or juice. The young leaves are consumed raw or cooked.
Hog Plum Facts
| Hog plum Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Hog plum |
| Scientific Name: | Spondias mombin |
| Origin | Amazon in Peru, Brazil, Venezuela, Bolivia, Colombia, the three Guianas, as well as southern Mexico |
| Colors | Initially green and then turns to a light golden-yellow upon ripening |
| Shapes | Ovoid or ellipsoid drupe, 3-4 cm long and 2-2.5 cm in diameter |
| Flesh colors | Orangery-yellow |
| Taste | Sharp, somewhat acid taste |
| Health benefits | Enhances Bone Health, Promotes Muscle Strength, Good for Digestive Health, Improves Hemoglobin Production, Serves as Diuretic and Febrifuge, Role in weight control, Treat anemia, Keep skin healthy, Protects Against Heart Disease, Treat Dysentery, Common Diseases |
| Name | Hog plum |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Spondias mombin |
| Native | Lowland moist forests of the Amazon in Peru, Brazil, Venezuela, Bolivia, Colombia, the three Guianas, as well as southern Mexico, Belize, Costa Rica, and the West Indies. The tree was introduced by the Portuguese in South Asia in the beginning of the 17th century. It has been naturalized in parts of Africa, India, Nepal, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, The Bahamas, Indonesia, and other Caribbean islands. It is rarely cultivated except in parts of the Brazilian Northeast |
| Common Names | Jamaica plum, Spanish plum, ambarella, ashanti plum, golden apple, hog plum, hogplum, jobo, thorny hog plum, yellow mombin, acaiba, acaja, acaja, acajaiba, acaju ajuela, agria, binbish-sheshon, caja, caja-mirim, caja-pequeno, cajazeira, cajazeiro, cajazeiro-miudo, cancharana, cansa boca, canyarana, ciruela amarilla, diji, ciruela, ciruelo, hog plum, hubas, hubo, hubus, imbu, imbuzeiro, itahuba, Jamaica-plum, jobo, jocote, joshin heshon, marope, metsoqui, mombin, mompe, serigiiela, sheshon, sheson, shungi ushun, shungo, shungu, tapareba, tapereba, taperiba, taperiba ubo, tobo de la raontana, tronador, tsiyoroqui, ubos Colorado, ubos, ushum, ushun, uvo, xuxoon), ylopo |
| Name in Other Languages | Afrikaans: Vark pruim Albanian: Kumbul derri Amharic: Hog, pilemi (ፕለም) Arabic: Khinzir albarquq (خنزير البرقوق) Armenian: Khozabuys salor (խոզաբույս սալոր) Assamese: Āmaraā (আমৰা) Amora, Aamrata, Amara, Amora, Omora, Amra-tenga Azerbaijani: Donuz gavalı Bengali: Hōga bara (হোগ বরই), Amara (আমড়া), Aamada, Aamraataka (আম্রাতক), Aamraata (আম্রাত) Brazil: Cajá-mirim, cajazeiro, imbuzeiro, taperebá Bulgarian: Svinska svinya (свинска свиня) Burmese: Hum jee see (Hum ဇီးသီး) Chinese: Zhū lǐ (猪李), Huáng suānzǎo (黃酸棗) Colombia: Jobo Croatian: Svinjska šljiva Czech: Prase švestka Danish: Svin blomme, Gul mombinblomme. Dutch: Hog pruim, Mope English: Hog plum, Jamaica-plum, Yellow mombin, Ambarella, Ashanti plum, Golden apple, Hog plum, Jamaica plum, Spanish plum, Thorny hog plum, True ambarella, True yellow mombin, Yellow mombin, gully plum, java plum, hog-plum tree Esperanto: Hog-pruno Estonian: Karupoeg ploom Filipino: Hog plum Finnish: Sika luumu, Amrapuu French: Prune de porc, Prunier mombin, Mombin, Mombin à fruits jaunes, Mombin franc, Mombin jaune, Prune d’or, Prune mombine, Prunier myrobolan, prunier mombin Fulah: Chaleh, Chali Georgian: Hogi kliavi (ჰოგი ქლიავი) German: Schweinepflaume, Gelbpflaume, Gelbe Mombinpflaume, Gelbpflaumenbaum Greek: Gouroúni damáskino (γουρούνι δαμάσκηνο) Gujarati: Hōga plama (હોગ પ્લમ), Ambaada (અંબાડાં) Haitian: Monben bata Hausa: Hog plum, isada Hebrew: שזיף חזיר Hindi: Hog ber (हॉग बेर), Ambari (अम्बाड़ी), Pitan (पीतन), Metula (मेटुला), Pashu-haritaki (पशु हरितकी), Bhringi-phal (भृङ्गी फल), Ambara (अम्बाड़ा), Amra (अमरा) Hungarian: Disznó szilva Icelandic: Svínafruma Igbo: Nugulunguwo Indonesian: Prem babi Irish: Pluma muc Italian: Prugna di maiale Japanese: Buta ume (豚梅), Subonjiasu, Suponjiasu. Javanese: Hog plum Kannada: Hāg plam (ಹಾಗ್ ಪ್ಲಮ್), Amate (ಅಮಟೆ), Muthiga,Amte,Poondi,Ambatte Mara,Amategayi Gida,Vrykshamla,Marahunsie,Kodalimavu,Goddada Kayi,Gooddamate,Kadambatte Karbi: Chiming Kazakh: Soşqa örik (шошқа өрік) Khasi: Dieng-sohpier Konkani: Ambado (आंबाडो), Ambade (आंबाडे) Korean: Dwaeji maehwa (돼지 매화) Kurdish:H çikilî Lao: Hog plum Latin: Prunus sexdecim Latvian: Vepris plūme Lithuanian: Serno slyva Macedonian: Sliva od slivi (слива од сливи) Malagasy: Hog plum Malay: Hog plum Malayalam: Hēāg plaṁ (ഹോഗ് പ്ലം), ampaḻaṁ (അമ്പഴം) Ampazham x, Ambazham, Pithanam, Mampuli, Kattambazham Maltese: Għanbaqar tal-hog Manipuri: Eikhoi Maori (Cook Islands): Māpēra, māpera, marbel Marathi: Hog plam (हॉग प्लम), Dholamba (ढोलआंबा), Amada (अमडा), Khatamba (खटांबा), Ambada (अंबाडा), Ranamba (रानआंबा) Mishing: Dorge Mongolian: Gakhain chavga (гахайн чавга) Nepali: Hag ber (हग बेर), Amaro (अमारो) Norwegian: Hog plum Oriya: ହଗ୍ ପ୍ଲମ୍, Ambaada Palauan: Mesehezl, mesehzl Pashto: د هګ بیر Persian: آلو گراز Polish: Sliwka wieprzowa Portuguese: Ameixa de porco, Cajarana, Cajazeira, Cajazinho, Cajá, Cajá-mirim, Imbu, Taperebá, Tepereba, Acaiba, Acaja, Acajaiba, Cajá mirim, Cajá miudo, Cajá pequeno, Cajazeiro, Cajazeiro-miudo, Imbuzeiro, Taperiba, mandiplo Punjabi: Hauga palama (ਹੌਗ ਪਲਮ) Romanian: Prun de porumb Russian: Svin ya sliva (свинья слива), Mombin zholtyy (Момбин жёлтый) Sanskrit: Metula (मेटुला), Aamraata (आम्रात), Pitan (पीतनः), Amraatakah (अम्रातकः) Serbian: Svinja šljiva (свиња шљива) Sindhi: هاگ پلايم Sinhala: Hog plam (හොග් ප්ලම්) Slovenian: Svinjska sliva Spanish: Ciruela de cerdo, Ubos, Choco, Ciruela agria, Ciruela amarilla, Ciruela de jobo, Ciruela de monte, Hobo blanco, Jobo, Jobo blanco, Jobo espinoso, Jobo gusanero, Jobo hembra, Jocote, Jocote amarillo, Jocote de jobo, Jocote montañero, Jocote montero, Marapa, Jobo, Wild Plum, hobo, mango ciruelo, hogolum, jocote de chancho Sudanese: Hog plum Suriname: hoo-boo, mopé Swahili: Amra Swedish: Hog plum, Gult balsamplommon, Svinplommon Tahitian: Vi popa‘a Tajik: Oluca (олуча) Tamil: Paṉṟi piḷam (பன்றி பிளம்), Kincam (கிஞ்சம்), Ambazham, Pulima (புளிமா) Telugu: Hāg plaṁ (హాగ్ ప్లం), Adhvamu (అధ్వము), Adavimamidi (అడవిమామిడి), Ambalamu (అంబాళము) Thai: Phlạm h̄mū (พลัมหมู), Makok farang, Makxk (มะกอก) Turkish: Domuz eriği Ukrainian: Svynyacha slyva (свиняча слива) Urdu: ہوگ بیر Uzbek: Cho’chqa olxo’ri Vietnamese: Lợn mận, Cóc Thái Welsh: Eirin mochyn Wolof: Nimkom, Nimkoum, Ninkon, Ninkong Yoruba: Agbalumo Zulu: I-hog plum |
| Plant Growth Habit | Small, elegant, deciduous tree |
| Growing Climates | Along roadsides, fence rows, pastures, forests in the coastal, moist limestone, lower mountain regions, evergreen lowland forest or semi-deciduous forest |
| Soil | Prefers a medium to heavy, well-drained, fertile soil |
| Plant Size | Up to 20 m (66 ft.) high and 1.5 m (4.9 ft.) in girth |
| Bole | Bole can be 60 cm or more in diameter with a thick, corky bark |
| Bark | Greyish-brown, thick, rough, often deeply grooved, with blunt, spine like projections |
| Leaf | Alternate, compound, comprising five to nine pairs of leaflets, once pinnate with an odd terminal leaflet. Stipules are absent and rachis is about 30-70 cm long. |
| Flowering season | January to May |
| Flower | Inflorescence is branched, terminal panicle with male, female and hermaphrodite flowers |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Ovoid or ellipsoid drupe, 3-4 cm long and 2-2.5 cm in diameter |
| Fruit Color | Initially green and then turns to a light golden-yellow upon ripening |
| Flesh Color | Orangery-yellow |
| Taste | Sharp, somewhat acid taste |
| Plant Parts Used | Bark, leaves, flowers, fruit, root |
| Season | July to September |
| Health Benefits |
|
| Precautions |
|
Plant Description
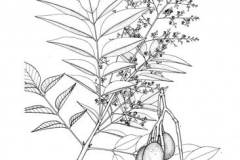
Hog plum is a small, elegant, deciduous tree with a dense and spreading crown and grows up to 20 m (66 ft.) tall and at least 1.5 m (4.9 ft.) in trunk diameter. Its bark is greyish-brown, thick, rough, often deeply grooved, with blunt, spine like projections. When slashed, it is pale pink, darkening rapidly. Branches are low and branchlets are glabrous. The plant is found growing along roadsides, fence rows, and pastures, forests in the coastal, moist limestone, lower mountain regions, evergreen lowland forest or semi-deciduous forest. The plant prefers a medium to heavy, well-drained, fertile soil.
Leaves
Leaves are alternate, compound, comprising five to nine pairs of leaflets, once pinnate with an odd terminal leaflet. Stipules are absent and rachis is about 30-70 cm long. Leaflets are elliptic, oblong or oblong lanceolate, broadly acuminate, glabrous about 5-11 cm long and 2-5 cm wide. Apex is long acuminate, asymmetric, truncate or cuneate. Margins are entire, glabrous or thinly puberulous.
Flower
Inflorescence is branched, terminal panicle with male, female and hermaphrodite flowers. About 5 sepals are present and are shortly deltoid, 0.5-1 cm long. About 5 petals are white or yellow, oblong, 3 mm long, valvate in bud, becoming reflexed; stamens 10, inserted beneath a fleshy disc; ovary superior, 1-2 mm long while styles are short and erect. Flowering normally takes place in between January to May.
Fruits
Fertile flowers are followed by an ovoid or ellipsoid drupe, 3-4 cm long and 2-2.5 cm in diameter. They are initially green turning to dull light orange to yellow or brown as they mature. The fruits are found in clusters of 1-20. Epicarp is thin, enclosing a juicy orange or yellow mesocarp about 3-6 mm thick; endocarp is large, with a soft, fibrous, grooved coat surrounding about 4-5 small seeds. The fruits have a sharp, somewhat acid taste and are edible. Fruits appear in between July to September. The seed has an oil content of 31.5%.
Ethno-medical Information on Hog plum (Spondias mombin)
| Plant Parts Used | Country | Ethno-medical Uses | Type Extract/Route | Used for | ||
| Bark | Africa | · Bark and/or leaves used for coughs, fever, constipation, yaws, gonorrhea, Tape worm, stomach problems, and as a childbirth aid. | Infusion/Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Bolivia | · Used for wounds and injuries. | Poultice/External | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Brazil | · Used for malaria | Infusion / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Brazil | · Used for malaria, fever, diarrhea, and vaginal infections. | Not Stated | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Brazil | · Used as an astringent, anti-inflammatory, stomachic, anthelmintic, vermifuge and antispasmodic; for diarrhea, dysentery, and hemorrhoids. | Decoction/Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Brazil | · Used for tonsillitis and sore throat. | Infusion/Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Brazil | · Used as an antispasmodic, astringent, tonic, emetic; for diarrhea, gonorrhea, and hemorrhoids
· Used to reduce swelling in the feet caused by erysipelas |
Decoction/Oral
Decoction/External |
Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Brazil | · Used as an astringent and emetic; for fever, diarrhea, dysentery, blenorrhagia, and hemorrhoids. | Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Brazil | · Used as an emetic, astringent, tonic, and stimulant; for colic, stomach problems, erysipelas, and blenorrhagia. | Decoction / Oral Decoction / External | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Brazil | · Used as an astringent, emetic; for diarrhea, dysentery, blenorrhagia, and hemorrhoids. | Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Caribbean | · Used as an antiviral, myorelaxant, and utero-tonic | Not Stated | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Colombia | · Tikuna Indians use it as a contraceptive, analgesic and hemostat; for diarrhea, metrorrhagia and stomachache. | Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Colombia | · Used as a contraceptive and for menstrual disorders. | Infusion / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Colombia | · Used for diarrhea and vaginal infections. | Not stated | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Colombia | · Used as a contraceptive. | Infusion / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Colombia | · Used as a wash for wounds. | Decoction / External | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Cuba | · Used for uterine cancer. | Decoction / Douche | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Guianas | · Used for coughs and colds.
· Used for hemorrhages and sores. |
Decoction / Oral Decoction / External | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Guinea | · Used for leprosy. | Decoction / External | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Guinea | · Used for coughs. | Not stated / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Guyana | · Creoles use it for diarrhea and stomachaches. | Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Haiti | · Used for urethritis. | Infusion / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Mexico | · Used by the Mayas for dysentery. | Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Mexico | · Used for bladder and kidney stones. | Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Nicaragua
|
· Used for fever, diarrhea and infections.
· Used for skin rashes and sores. |
Decoction / Oral
Decoction / External |
Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Nicaragua | · Garifuna Indians use it for fever, infections, and diarrhea and skin rashes. | Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Peru | · Shipibo-Conibo Indians use it as a cicatrizant, hemostat, astringent, vaginal wash, and antibacterial; for wounds, debility, dehydration, diarrhea and infections. | Decoction / Oral Decoction / External | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Peru | · Used for vaginal infections and following an abortion or miscarriage. | Infusion / Douche | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Peru | · Used for ovarian cancer. | Infusion / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Peru
|
· Used as an antispasmodic, astringent, analgesic, contraceptive and stomachic; for asthma, diarrhea, vaginal infections, erythema, cysts, laryngitis, menstrual pain and psoriasis. | Infusion / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Peru | · Resin extracted from the bark and used as a vulnerary and cicatrizant for wounds. | Resin / External | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Peru | · Used as a contraceptive. | Infusion / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Peru | · Used for tuberculosis, diarrhea, and intestinal ulcers. | Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Peru | · Combined with cedar, cashew, and guava leaves and used for vaginal infections and wounds. | Decoction / Douche | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Peru | · Used as an astringent; for fem ale reproductive tract and genital disorders.
· Used as a contraceptive |
Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Peru | · Used for yeast infections, fungal infections, and skin fungi. | Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Peru | · Powdered bark is used on the site of snakebite. | Powder / External | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Peru | · Powdered bark is used as a hemostat for cuts, wounds, and hemorrhages.
· Used as an antiseptic wash for wounds. · Taken for diarrhea and intestinal ulcers. |
Powder / External Decoction/External
Decoction / Oral |
Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Peru | · Used as a hemostat and vulnerary for wounds.
· Used for erysipelas, leishmaniasis, and vaginal infections. |
Powder / External Decoction / External | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Peru | · Used as an antispasmodic, contraceptive, and stomachic; for blenorrhagia, hemorrhoids, digestive problems, dermatitis, diarrhea, erythema, cysts, laryngitis, psoriasis, menstrual pain, intestinal ulcers, vaginal infections, and tuberculosis. | Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Peru | · Campa-Ashaninca Indians use it as an astringent; for cutaneous leishmaniasis | Powdered / External | Tapir | ||
| Bark | Peru | · Used for wounds.
· Used as an antiseptic vaginal wash. · Used for gastritis, dysentery, stomach pain, renal and kidney problems, hemorrhoids, blenorrhagia, herpes, diarrhea, menstrual pain, excessive menstrual bleeding, ulcers, uterine problems, and vaginal problems. · Used as a contraceptive, and for internal and external hemorrhages. |
Poultice / External Decoction / Douche Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Upper Volta | · Used for leprosy. | Not stated | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Venezuela | · Warao Indians use it for diarrhea, cough, pertussis, stomachache, skin lesions, and dysentery. | Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Bark | Various | · Used in the tropics as an astringent; for diarrhea, dysentery, hemorrhoids, gonorrhea and leucorrhea.
· Used to heal wounds. |
Decoction / Oral Powder / External | Human Adult | ||
| Stem bark | Guianas | · Used as a sudorific; for gonorrhea, diarrhea, stomachache, and fatigue. | Infusion / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Bark/Leaf | Belize | · Used for sores, rashes, and insect stings. | Decoction / External | Human Adult | ||
| Bark/Leaf | Jamaica | · Used for edema. | Infusion / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Bark/Leaf | Peru | · Used for anemia. | Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Bark/Leaf | Peru | · Used for diarrhea. | Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | Belize | · Used for diarrhea and dysentery.
· Used for wounds and inflammations. |
Decoction / Oral Poultice / External | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | Brazil | · Used for gastralgia, dyspepsia, and diarrhea. | Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | Brazil | · Used internally and externally as an antiviral for herpes. | Infusion / Oral Infusion / External | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | Brazil | · Used for constipation, gastralgia, and laryngitis.
· Used for eye infections. |
Infusion / Oral Infusion / Ocular | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | Brazil | · Used as an astringent, antibacterial, molluscicidal, and antiviral: for angina, laryngitis, mouth inflammation, tonsillitis, prostatitis, and herpes. | Infusion / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | Brazil | · Used for fever, constipation, stomach pain, childbirth complications, pain in the eye and ears, and as a stomachic and refrigerant. | Infusion / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | Brazil | · Used for stomach pain, constipation, fever, cystitis, urethritis, sore throat, laryngitis. | Not stated / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | Cameroon | · Used for chronic diarrhea. | Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | Dominca | · Used after childbirth to induce lactation. | Infusion / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | Ghana | · Used to stop postpartum hemorrhage. | Plant / Oral | Sheep and Goats | ||
| Leaf | Guadeloupe | · Used to facilitate childbirth and speed delivery. | Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | Guatemala | · Used for gonorrhea. | Infusion / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | Guianas | · Used for diarrhea, dysentery, and in an abortifacient preparation.
· Used for hemorrhages and sores. |
Decoction / Oral Decoction / External | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | Ivory Coast | · Used as a hemostatic. | Leaves / External | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | Jamaica | · Used as a cold remedy. | Decoction / Internal | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | Mali | · Decoction drunk or used as a lotion during the course of childbirth. | Decoction / Various | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | Nicaragua | · Used for diarrhea. | Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | Nigeria | · Used for tapeworms, malignant tumors and to aid childbirth. | Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | Nigeria
|
· Used as a laxative and as a child birth aid (to stop bleeding during late Pregnancy, to stop bleeding, labor pains and stomach pains after childbirth). | Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | Nigeria | · Used as an oxytocic (induces childbirth) and to expel placenta. | Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | Nigeria | · Used as an abortifacient and for diarrhea. | Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | Nigeria | · Used as a febrifuge, astringent, diuretic and laxative; for cholera, thrush, gonorrhea, dizziness, cough, fever, yaws, sore throat, cough, diarrhea, tapeworm , and fever. Use for eye ailments, cuts, sore, wounds, and burns. | Decoction / Oral Infusion / External | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | Nigeria | · Used for various nervous disorders. | Tincture / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | Peru
|
· Used for postpartum infections of the uterus, yeast infections, bacterial Infections, and as a childbirth aid. | Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | Peru | · Used for heat rash. | Infusion / External | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | Peru | · Used as an antiseptic wash for wounds. | Infusion / External | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | Peru | · Used for illnesses of the throat and tonsils. | Infusion / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | Peru | · Used for dysentery, diarrhea, vaginal infections, and stomach problems.
· Used for dermatitis, rashes and skin eruptions. |
Decoction / Oral Infusion / External | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf | West Indies | · Used for diarrhea. | Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf/Stem | Guianas | · Used as an eyewash. | Decoction / Ocular | Human Adult | ||
| Leaf/Flower | Various | · For stomachache, biliousness, urethritis, cystitis, eye inflammation, and throat inflammation. | Infusion / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Fruit | Brazil | · Used for angina, stomach ulcers, vaginal and uterine disorders. | Juice / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Fruit | Brazil | · Eaten as a food. Used on ice creams, liqueurs, jams, etc. | Fruit/Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Fruit | Brazil | · Fruit juice taken for fevers, cystitis, and urethritis. | . Juice / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Fruit | Brazil | · Fruit or juice taken as a heart tonic. | Fruit / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Fruit | Cameroon | · Used for chronic diarrhea. | Fruit / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Fruit | Ecuador | · Eaten as a food. | Fruit / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Fruit | Guianas | · Fresh fruit eaten as a mild laxative. Stewed and eaten for diarrhea. | Fruit / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Fruit | Nigeria | · Used as a febrifuge, anti-inflammatory and expectorant. | Fruit / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Fruit | Panama | · Eaten as a food. | Fruit / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Fruit | Peru | · Used as a vomitive and an astringent. | Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Fruit | Peru | · Used for healing wounds. | Decoction / External | Human Adult | ||
| Fruit | Peru | · Campa-Ashaninca Indians use it as tapir bait when hunting. | Fruit / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Fruit | Peru | · Eaten in large quantities it is vomitive.
· Skin of fruit is astringent. · Fruit or juice taken for anemia. |
Fruit / Oral Fruit skin / External Fruit / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Fruit | Peru | · Eaten as a food. | Fruit / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Fruit | Peru | · In large quantities it is an emetic. Eaten for anemia. | Fruit / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Fruit | Peru | · Fruit juice taken for fevers, cystitis, and urethritis. | Juice / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Flowers | Jamaica | · Used for colds. | Infusion / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Flowers | Belize | · Used as an astringent for diarrhea, gonorrhea, and sore throat. | Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Flowers | Brazil | · Used as a cardiac tonic for debility, weakness, and heart palpitations. | Infusion / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Flowers | Brazil | · Used for eye infections. Used heart conditions, laryngitis, children’s diarrhea and as a stomachic. | Infusion / Ocular Infusion / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Flowers | Guianas | · Used for mouth sores. | Infusion / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Flowers | Peru | · Used for cataracts. | Infusion / Ocular | Human Adult | ||
| Root + Leaf | Guatemala | · Used for gonorrhea. | Infusion / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Root | Guianas | · Used for dysentery. | Infusion / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Root | Peru | · Used to treat tuberculosis, diarrhea, and as a childbirth aid.
· Used as an adjunctive with antibiotics. |
Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Root | Peru | · Used for vaginal infections and hemorrhoids. | Decoction / Not stated | Human Adult | ||
| Root | Peru | · Used as a gastric analgesic. | Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Seed | Brazil | · Used as a diuretic for urinary and bladder problems. | Infusion / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Seed | Brazil | · Used for leucorrhea. | Decoction / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Gum | Various | · Used as an expectorant and to expel tapeworms. | Not stated / Oral | Human Adult | ||
| Plant | Haiti | · Used as a laxative; for coughs, gonorrhea, ophthalmia, sore throat, and urethritis. | Not stated | Human Adult | ||
| Plant | Panama | · Cuna Indians use it for asthma, colds, and congestion. | Not stated | Human Adult | ||
| Plant | Trinidad | · Used as an astringent, and gargle; for colds, diarrhea, erysipelas, nephritis, sores, sore throat, and thrush. | Not stated | Human Adult | ||
| Plant | Various | · Used as an analgesic, astringent, diuretic, laxative, and vermifuge; for asthma, cancer, colds, congestion, cough, diarrhea, erysipelas, fever, gonorrhea, leprosy, malignancy, nephritis, ophthalmia, sore, swelling, thrush, tumors, urethritis, and wounds. | Not stated | Human Adult | ||
Health benefits of Hog Plum
Hog plums known as June plums, Yellow Mombin or Monkey Mombin are a juicy fruit of hog plum tree found in tropical countries and comes diverse ranges of colors. There are lots of essential vitamins and nutrients present in hog plums that help fight against some free radicals that might be harmful to human health. Some of the nutritional benefits of these fruits include the following:
1. Enhances Bone Health
Hog plum is a fat-free, sodium-free, cholesterol-free fruit and is considered as a good source of vitamin K that helps in proper bone health.
Vitamin K not only helps in blood clotting, but it also helps to improve the bones by making them strong, thus helping in the prevention of bones health conditions like bone fractures, etc., its effects on osteoporosis has not been proven medically, though most people take it for this cause.
Research also indicates that hog plums consist of copper that maintains the bone and other connective tissues in the body system and is also needed for proper assimilation of vitamin C.
2. Promotes Muscle Strength
Thiamine is one of the vitamins which could be found in hog plum, it has a lot of functions it performs in the body with one of them being its ability to help in muscle contraction and conduction of nerve signals. Its deficiency can lead to numerous symptoms such as muscle weakness which could even lead to confusion in most cases. Sufficient consumption of this fruit can help in eliminating the chances of this condition.
3. Good for Digestive Health
Hog plums consist of good amount of dietary fiber which plays a key role in maintaining a healthy digestive system. The fiber content helps in improving the general functions of the digestive health, and as well prevents any form of issues that could arise as a result of poor digestion and other digestive health conditions like bloating and gas.
4. Improves Hemoglobin Production
Hog plum is a good source mineral such as iron which helps in the production of hemoglobin and myoglobin which helps to transfer oxygen throughout the body systems.
Iron content in the fruits helps in improving the Hemoglobin which is the iron and oxygen-binding proteins located in the blood; it also helps in the improvement of the iron and oxygen-binding proteins also in the muscles which are known as Myoglobin. Iron is a vital micronutrient that is essential to the body and functions great in the preventing of anemia and other blood conditions.
5. Serves as Diuretic and Febrifuge
Consumption of hog plum fruits or its juice is medicinal and may treat several health conditions. It helps the body to successfully and adequately remove fluids (water) from the body through urine, which is to mention that it helps in reducing the quantity of salt (sodium) within the body thus decreasing the danger of high vital sign.
It also acts as a febrifuge, within the sense which will functions as a substitute for fever medications, because it can help within the reduction and treatment of fever/malaria which has been used locally in many tropical areas thanks to its properties like flavonoids, anthraquinones, sesquiterpenes, quinoline and more.
6. Role in weight control
Hog plum consists of a lot of fiber or dietary fiber. Each 100 grams of hog plum consists of 29 calories. So hog plum helps in weight loss. Hog plum helps prevent indigestion and constipation.
7. Treat anemia
To eliminate anemia, you need to eat hog plum. Pomegranates are rich in iron which helps in keeping the hemoglobin level at the right level. As a result, it plays an effective role in preventing anemia.
8. Keep skin healthy
Hog plum fruit helps in maintaining good health of skin, hair and nails. To reduce skin acne, hog plum is very useful to keep the skin bright. Hog plum consists of a lot of vitamin C which is very essential to keep the skin bright. So hog plum can be eaten regularly to keep the skin healthy and radiant.
9. Protects Against Heart Disease
Researchers found that hog plums were naturally high in antioxidants, which they compared to the heart medication. Research found that hog plums helps to reduce overall cholesterol levels and that their antioxidant effect on heart health. The conclusion was that hog plums may be beneficial for overall heart health, but longer term research is needed.
10. Treat Dysentery
Leaves and bark of this tree consists of several flavanoida, saponins and tannins. The content is very useful to cure dysentery and cough cure. To make herbal potions to cure dysentery we simply take kedondong bark about 5 gm., select the skin fresh and clean. After it was sliced in the form of small pieces and boiled with 2 cups water until the remaining half. Then set aside to be warmer, then strain and drink the water. It is considered one of the best cures for dysentery.
11. Common Diseases
Leaves of hog plums are used to making antiseptic soap, and it helps to treat a sore throat, cough, malaria, and other common diseases. The leaves of hog plums are traditional herbal product, and it’s used for alternative medicines.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y-F6jaarhaA
Traditional uses and benefits of Hog Plums
- It is used in traditional medicine against lower back pain, rheumatism, digestive track problems, angina, sore throat, malarial fever, diarrhea, urethritis, gonorrhea, stomach pain, colds, dysentery, laryngitis, ophthalmia, and many others.
- Bark is used in a remedy for gonorrhea, diarrhea, coughs and colds, hemorrhages, stomach-aches and to alleviate fatigue.
- Plant extracts exhibit antibacterial properties, and a decoction of the bark or root bark is considered antiseptic.
- An infusion is used to treat dysentery.
- Leaf decoctions are used to treat diarrhea, dysentery, colds, fevers and gonorrhea.
- Decoction of the leaves and young stems is used as eyewash in ophthalmia.
- Decoction is used in the treatment of laryngitis, ophthalmia and children’s diarrhea.
- It is stewed and eaten to cure diarrhea.
- In South American herbal medicine systems as well as in other parts of the world ubos leaves are widely used for female reproductive tracts issues.
- It is a common midwife’s remedy to help induce labor, reduce bleeding and pain during and after childbirth, to bring on the flow of breast milk, and as a vaginal wash to prevent or treat uterine or vaginal infections after childbirth.
- Leaves are also a common remedy for various digestive problems including stomachaches, diarrhea, dyspepsia, gastralgia, colic, and constipation.
- Leaves are considered to be antiviral, antibacterial, anti-candidal, and antiseptic and used in numerous microbial problems including colds and flu, cystitis, urethritis, sore throats, herpes, yeast infections, gonorrhea, eye and ear infections, and used externally for infected wounds, cuts, burns, and rashes.
- Leaves are also considered to be an excellent vermifuge and anthelmintic and often used for intestinal worms and parasites in humans as well as their livestock.
- Bark is widely used as a contraceptive and abortive, as well as for ovarian and uterine cancer.
- It is considered analgesic and antispasmodic and used for arthritis, rheumatism, muscle and joint pain, injuries and inflammation.
- Bark consists of a great deal of astringent tannins and is usually prepared in decoctions for diarrhea and dysentery, blenorrhagia, hemorrhoids, and for internal and external wounds and bleeding.
- Bark is also used for tonsillitis, laryngitis, malaria, fever, erysipelas, bladder and kidney stones, snakebite, and intestinal ulcers.
- Bark is also considered to be a good topical antiseptic and healing remedy for all types of wounds, rashes, psoriasis, dermatitis, leishmaniasis, leprosy, and other skin problems.
- Flowers are typically prepared in an infusion and used for eye infections and cataracts, as a soothing tea for sore throat, laryngitis and mouth sores, as well as a heart tonic.
- Root is used as an antimicrobial for tuberculosis, diarrhea and vaginal infections.
- Leaves serve as antiseptics as they are also used in making antiseptic soaps, treating sore throat, cough, malaria and another related sickness.
- Barks, the juice, and the fruit have therapeutic benefits that make them useful to traditional herbalists for alternative medicines.
- It has been used in many parts of Africa for alleviating many health conditions like pain, cough, indigestion, fever, inflammation, convulsions and lots more.
- Fruit decoction is used to bathe wounds and heal sores in the mouth.
- Syrup prepared from the fruit is taken to overcome chronic diarrhea.
- The astringent bark decoction is a remedy for mange, ulcers, dysentery and for bloating caused by intestinal gas in infants.
- Sap of the bark is used to treat stomatitis in infants in Philippines.
- The juice of the fresh leaves is a remedy for thrush.
- An infusion of shredded leaves is valued for washing cuts, sores and burns in Southwestern Nigeria.
- Gum-resin of the tree is mixed with pineapple or soursop juice for treating jaundice.
- Tea made from the flowers and leaves is taken to relieve stomach ache, biliousness, and urethritis, cystitis and eye and throat inflammations.
- Decoction of the young leaves is a remedy for diarrhea and dysentery in Belize.
- Juice of crushed leaves and the powder of dried leaves are used as poultices on wounds and inflammations.
- The gum is used as an expectorant and to expel tapeworms.
Culinary Uses
- The pulp can be eaten fresh or made into desserts or juice.
- Seeds are also edible.
- Fruit can be consumed raw or cooked.
- It is also used for making jams, ice cream etc.
- Unripe fruits are pickled and used like olives.
- Young leaves can be cooked and used as a vegetable.
- The shoot tastes like cassava and can be eaten raw or boiled.
- When fresh water is unavailable, water from the roots of this tree can be drunk.
- Sap from the roots has been drunk in place of water when the latter was not available.
- Fruit pulp is either eaten fresh or made into juice, concentrate, jellies, and sherbets.
- In Thailand this fruit is called makok and is used in som tam as a secondary ingredient.
Other Facts
- Wood is used for posts, boxes, matches, general carpentry, tool handles, etc.
- The tree is occasionally planted to provide shade for coffee plants.
- Ashes from the roots have been used in making soap.
- The heartwood is cream to buff in color; it is not demarcated from the sapwood.
- Trunks are occasionally used for dugouts and the stems for posts, boxes, matches, general carpentry, tool handles, millwork, utility plywood, and furniture components.
- Logs need to be promptly processed to minimize deterioration from insect attack.
- The wood is suitable for fuel.
- It is commonly used for living fence posts, in farmlands and shelter by artisans.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=28816#null
http://www.hear.org/pier/species/spondias_mombin.htm
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Spondias+mombin
https://rain-tree.com/ubos.htm
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=SPMO
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-2480696
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/SPXMO
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spondias_mombin
https://gringlobal.irri.org/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=35334
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/51047