Phenylpropanoids are a diverse class of organic compounds produced by plants through the phenylpropanoid metabolic pathway. These compounds are derived from the amino acid phenylalanine and play crucial roles in various aspects of plant life, including defense against pathogens and environmental stresses, structural support, and signaling. The phenylpropanoid pathway is responsible for synthesizing a wide range of important plant metabolites, such as lignin (a key component of cell walls), flavonoids, anthocyanins, and other phenolic compounds. These molecules contribute to plant growth, development, and survival by providing mechanical strength, pigmentation, UV protection, and antimicrobial properties. Additionally, phenylpropanoids have gained significant attention in human health research due to their potential therapeutic benefits, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties.
Chemical structure and natural occurrence in Phenylpropanoid plants
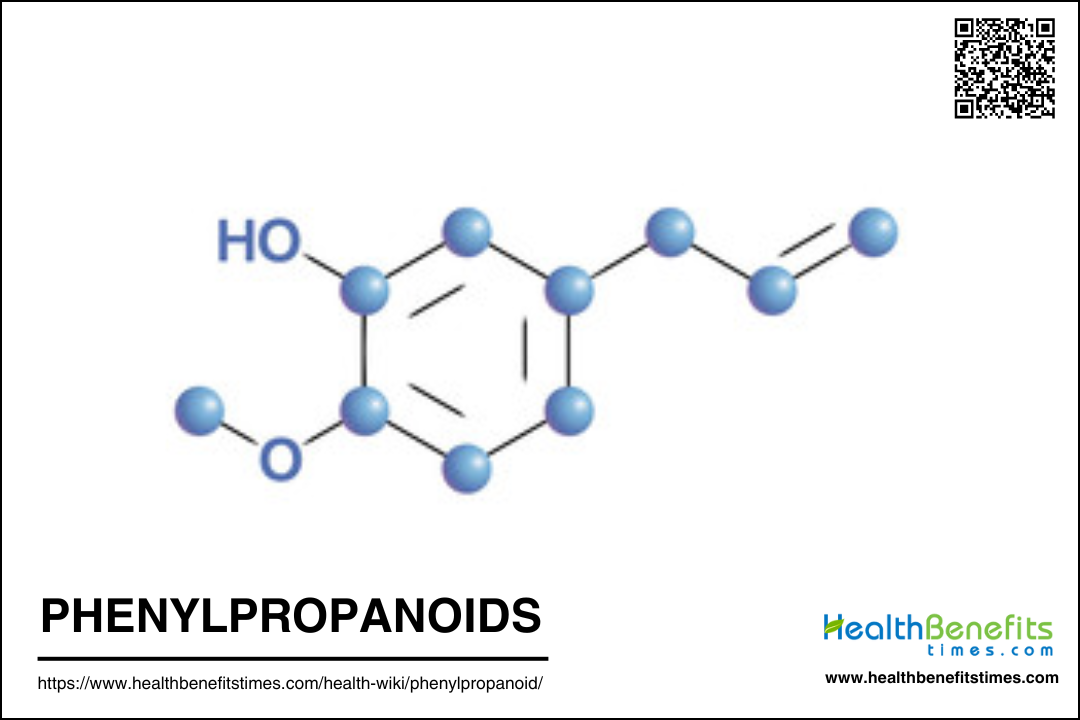
Phenylpropanoids are a diverse class of plant secondary metabolites derived primarily from the amino acid phenylalanine, and to a lesser extent from tyrosine in some monocots. These compounds include flavonoids, monolignols, phenolic acids, stilbenes, and coumarins, and are synthesized through the phenylpropanoid pathway, which is a crucial metabolic route in plants. Structurally, phenylpropanoids are characterized by a phenyl ring with a three-carbon side chain (C6-C3 structure), which can be further modified by various enzymatic reactions to produce a wide array of compounds. These metabolites play significant roles in plant development, including the formation of structural components like lignin, which is essential for cell wall integrity, and in plant defense mechanisms against biotic and abiotic stresses. Phenylpropanoids also contribute to the plant’s interaction with its environment by attracting pollinators, providing protection against pathogens, and mediating plant-pollinator interactions through floral pigments. Additionally, these compounds have been recognized for their beneficial effects on human health, exhibiting activities such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties. The biosynthesis and regulation of phenylpropanoids involve complex networks of genes and enzymes, with recent studies highlighting the roles of miR828, ta-siRNAs, and R2R3-MYBs in their regulatory mechanisms.
Types of Phenylpropanoids
Phenylpropanoids encompass a wide variety of plant-derived compounds, each with unique structures and functions. These compounds are categorized based on their chemical characteristics and biological roles. Below are two types of phenylpropanoids:
1. Simple Phenylpropanoids
Simple phenylpropanoids, such as cinnamic acid and p-coumaric acid, are fundamental building blocks in the phenylpropanoid pathway. These compounds are derived from the amino acid phenylalanine through the action of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL), which converts phenylalanine to cinnamic acid, and cinnamate 4-hydroxylase (C4H), which further converts cinnamic acid to p-coumaric acid. These simple phenylpropanoids serve as precursors for a variety of secondary metabolites, including flavonoids, lignins, and coumarins, which play crucial roles in plant structure, pigmentation, and defense mechanisms. The biosynthesis of these compounds is tightly regulated and involves a complex network of enzymes and genes, ensuring that plants can adapt to various biotic and abiotic stresses.
2. Complex Phenylpropanoids
Complex phenylpropanoids, such as lignin, flavonoids, and coumarins, are derived from simple phenylpropanoids through a series of enzymatic reactions that add complexity and diversity to their structures. Lignin, for example, is a major structural component of plant cell walls and is synthesized from monolignols, which are derived from hydroxycinnamic acids. Flavonoids, another group of complex phenylpropanoids, are synthesized from p-coumaric acid and play essential roles in UV protection, pigmentation, and defense against pathogens. Coumarins, which are also derived from hydroxycinnamic acids, have various biological activities, including antimicrobial and antioxidant properties. The biosynthesis of these complex phenylpropanoids involves multiple enzymes and regulatory mechanisms, highlighting the intricate nature of the phenylpropanoid pathway.
Functions of Phenylpropanoids in Plants
Phenylpropanoids are essential compounds in plants, contributing to a wide range of physiological and biochemical processes. They are involved in plant defense, structural integrity, and pigmentation. Below is a list of the key functions of phenylpropanoids in plants:
1. Defense against Biotic Stresses
Phenylpropanoids play a crucial role in plant defense against biotic stresses, such as pathogens and herbivores. These compounds can act as preformed or inducible antimicrobial agents, creating physical and chemical barriers to prevent infection. They also function as signal molecules that activate defense gene expression locally and systemically. For instance, flavonoids and other phenylpropanoids can interfere with the cellular machinery of pathogens and pests, thereby inhibiting their growth and spread. The biosynthesis of these compounds is often upregulated in response to biotic stress, enhancing the plant’s defensive capabilities.
2. Defense against Abiotic Stresses
Phenylpropanoids are also vital in defending plants against abiotic stresses such as drought, salinity, and UV radiation. These compounds help in scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby protecting cellular components from oxidative damage. Under stress conditions, the phenylpropanoid biosynthetic pathway is activated, leading to the accumulation of phenolic acids and flavonoids, which enhance the plant’s tolerance to environmental constraints. This biochemical response is crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis and ensuring plant survival under adverse conditions.
3. Structural Support
Phenylpropanoids contribute significantly to the structural integrity of plants. Lignin, a complex phenylpropanoid polymer, is a major component of the plant cell wall, providing rigidity and resistance to mechanical stress. This structural support is essential for the plant’s ability to grow upright and withstand environmental pressures. Additionally, other phenylpropanoid derivatives, such as hydroxycinnamic acids and lignans, also contribute to cell wall fortification and overall plant architecture. The evolution of these pathways has been pivotal in enabling plants to colonize terrestrial environments.
4. Plant Development and Reproduction
Phenylpropanoids are integral to various aspects of plant development and reproduction. They regulate processes such as cell division, hormonal balance, and organ development. Flavonoids, a subclass of phenylpropanoids, are known to influence auxin transport, thereby affecting root and shoot development. These compounds also play roles in pollen tube growth, seed maturation, and dormancy, ensuring successful reproduction. The diverse metabolic routes of phenylpropanoids contribute to the dynamic regulation of plant growth and developmental transitions.
5. Signaling and Regulation
Phenylpropanoids function as signaling molecules that regulate various physiological processes in plants. They are involved in local and systemic signaling pathways that activate defense responses and modulate gene expression. For example, MYB transcription factors are key regulators of phenylpropanoid biosynthesis, orchestrating the production of these compounds in response to environmental cues. This regulatory network ensures that phenylpropanoid levels are finely tuned to meet the plant’s needs, whether for growth, defense, or adaptation to changing conditions.
Phenylpropanoids in Everyday Life
Phenylpropanoids are organic compounds that significantly impact our daily lives through their presence in various foods, medicines, and cosmetics. They contribute to flavors, fragrances, and health benefits. Here are some common ways phenylpropanoids are encountered in everyday life:
1. Industrial Applications
Phenylpropanoids have a wide range of industrial applications due to their diverse biological activities. They are extensively used in the food industry for preservation, packaging films, and edible coatings owing to their antimicrobial and antioxidant properties. In the pharmaceutical industry, phenylpropanoids are utilized for their therapeutic benefits, including anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and neuroprotective activities. Additionally, these compounds find applications in the textile industry as colorants, in biofuels as antioxidant additives, and in sensors for detecting biologically relevant molecules. Their multifunctional properties make them valuable across various industrial sectors.
2. Dietary Sources
Phenylpropanoids are abundant in a variety of dietary sources, including fruits, vegetables, cereal grains, beverages, spices, and herbs. These compounds are major biologically active components in human diets and are also found in essential oils, propolis, and traditional medicines. Specific phenylpropanoids like p-methoxycinnamic acid (p-MCA) are derived from plants and have been extensively studied for their nutraceutical applications, playing a vital role in the prevention and treatment of chronic diseases. Their presence in everyday foods contributes significantly to their health benefits, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer activities.
3. Consumer Products
Phenylpropanoids are incorporated into various consumer products due to their beneficial properties. They are present in dietary supplements and skin care products, leveraging their antioxidant, antimicrobial, and photoprotective effects. These compounds are also used in perfumes and cosmetics as active natural ingredients, enhancing the product’s efficacy and appeal. The versatility of phenylpropanoids in consumer products underscores their importance in enhancing the quality and functionality of everyday items, making them indispensable in the consumer goods market.
4. Cosmetic Applications
In the cosmetic industry, phenylpropanoids are highly valued for their antioxidant, UV-screening, and anti-inflammatory properties. They are used in formulations to protect the skin from oxidative stress and UV radiation, thereby preventing premature aging and skin damage. Ethyl ferulate, a specific phenylpropanoid, has been highlighted for its neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory activities, making it a promising ingredient in cosmetic products aimed at skin health and rejuvenation. The incorporation of phenylpropanoids in cosmetics not only enhances product efficacy but also offers natural and safe alternatives to synthetic ingredients.
Health Benefits of Phenylpropanoids
Phenylpropanoids are natural compounds found in many plants, offering numerous health benefits. They possess antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties, contributing to overall well-being. Here are some of the key health benefits of phenylpropanoids:
1. Antioxidant Properties
Phenylpropanoids are renowned for their potent antioxidant properties, which play a crucial role in neutralizing free radicals and protecting cells from oxidative stress. These compounds, found abundantly in plants, fruits, and vegetables, exhibit significant radical scavenging activities. For instance, verbascoside and isoverbascoside from Lippia citriodora have been shown to enhance antioxidant enzyme activities in blood cells, thereby mitigating oxidative damage. Additionally, phenylpropanoid glycosides from broomrapes demonstrated strong antiradical action, further underscoring their antioxidant potential.
2. Anti-inflammatory Effects
Phenylpropanoids exhibit notable anti-inflammatory effects, which are beneficial in managing various inflammatory conditions. Compounds isolated from Chinese olive, for example, have been shown to significantly inhibit the production of nitric oxide and reduce the expression of pro-inflammatory mediators such as iNOS and COX-2 in microglia cells. Similarly, ethyl ferulate, a phenylpropanoid, has demonstrated anti-inflammatory activities, making it a promising candidate for nutraceutical and pharmaceutical applications.
3. Anticancer Activities
The anticancer activities of phenylpropanoids are well-documented, with these compounds showing potential in inhibiting cancer cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis. Phenylethanoid glycosides, a subclass of phenylpropanoids, possess significant anticancer properties, although their therapeutic application is limited by poor bioavailability. Moreover, phenylpropanoids have been studied for their ability to modulate molecular and cellular processes in tumor models, highlighting their potential as anticancer agents.
4. Cardioprotective Benefits
Phenylpropanoids offer cardioprotective benefits by exerting various protective effects on the cardiovascular system. These compounds have been shown to possess hypotensive, vasorelaxant, antiplatelet aggregation, and antidyslipidaemic properties. Essential oils rich in phenylpropanoids have demonstrated protective effects against ischemia/reperfusion injury and heart hypertrophy, making them promising agents for cardiovascular health. Additionally, phenylpropanoid glycosides have shown potential in treating cardiovascular diseases associated with oxidative stress.
5. Antimicrobial Properties
The antimicrobial properties of phenylpropanoids make them effective against a wide range of pathogens. These compounds have been found to possess antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal activities. For instance, phenylethanoid glycosides exhibit significant antibacterial properties, contributing to their potential use in treating infections. The antimicrobial effects of phenylpropanoids are also leveraged in the food industry for preservation and in the pharmaceutical industry for developing antimicrobial agents.
6. Neuroprotective Effects
Phenylpropanoids have shown promising neuroprotective effects, which are beneficial in managing neurodegenerative diseases. Compounds from Chinese olive, for example, have demonstrated significant neuroprotective activities by reducing neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in microglia cells. Ethyl ferulate has also been highlighted for its neuroprotective properties, making it a potential candidate for treating neuroinflammatory conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease.
7. UV Protection
Phenylpropanoids provide effective UV protection, which is beneficial for skin health. These compounds act as natural UV screens, protecting the skin from harmful UV radiation. The photoprotective properties of phenylpropanoids are utilized in cosmetic products to prevent skin damage and aging caused by UV exposure. Their ability to absorb UV light and neutralize free radicals makes them valuable ingredients in sunscreens and other skincare products.
8. Antidiabetic Effects
Phenylpropanoids exhibit significant antidiabetic effects, which are beneficial in managing diabetes and its complications. Compounds from Chinese olive have shown remarkable antidiabetic activities by modulating glucose metabolism and reducing oxidative stress. Additionally, phenylethanoid glycosides have demonstrated antidiabetic properties, although their clinical application is limited by bioavailability issues. These findings highlight the potential of phenylpropanoids in developing antidiabetic therapies.
Environmental and Ecological Importance of Phenylpropanoid
Role in Ecosystems
Phenylpropanoids play a crucial role in maintaining biodiversity and ecosystem stability. These compounds are involved in various plant-environment interactions, contributing to plant development and stress responses. For instance, phenylpropanoids such as lignin and flavonoids are essential for cell wall integrity, which supports plant structure and defense mechanisms against pathogens and herbivores. Additionally, phenylpropanoids help plants cope with abiotic stresses like drought, salinity, and UV radiation by scavenging reactive oxygen species and modulating stress-responsive pathways. This multifaceted role enhances plant resilience, thereby supporting ecosystem stability and biodiversity by enabling plants to thrive in diverse environmental conditions.
Sustainable Uses
Phenylpropanoids hold significant potential for sustainable agriculture and environmental protection. Their role in plant defense mechanisms can be harnessed to develop pest-resistant crops, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. Moreover, phenylpropanoids contribute to the production of biofuels and biomaterials, offering renewable alternatives to fossil fuels and synthetic materials6. The metabolic engineering of phenylpropanoid pathways in plants can enhance the production of valuable compounds like flavonoids and lignins, which have applications in pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, and the bioenergy sector. By leveraging the natural properties of phenylpropanoids, we can promote more sustainable agricultural practices and environmental conservation efforts.