Chlorogenic acid (CGA), also known as 3-caffeoylquinic acid, is a polyphenolic compound produced by plants through the shikimic acid pathway during aerobic respiration. This water-soluble phenylacrylate is widely found in higher dicotyledonous plants, ferns, and many traditional Chinese medicinal plants, earning it the nickname “plant gold” for its diverse biological activities. CGA is particularly abundant in coffee beans and is known for its potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties. It has been studied for its potential health benefits, including liver and kidney protection, regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism, and neuroprotective effects. Additionally, CGA has applications in the food industry as a functional food ingredient, food additive, and for enhancing food storage and packaging materials.
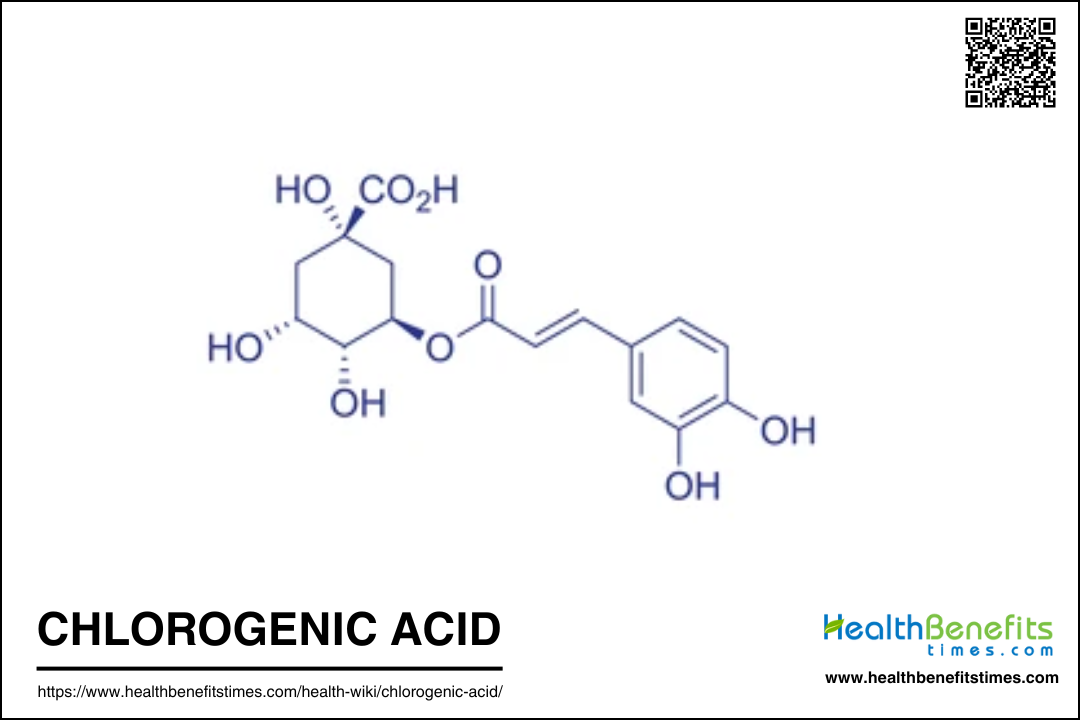
Chemical structure and composition of Chlorogenic acid
Chlorogenic acid (CGA) is a phenolic compound belonging to the hydroxycinnamic acid family, primarily formed by the esterification of caffeic acid and quinic acid. It is one of the most abundant polyphenols in the human diet, commonly found in coffee, tea, and various fruits such as apples and pears. The chemical structure of CGA includes several isomers, with 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid (5-CQA) being the most prevalent. The structure of CGA is characterized by the presence of a quinic acid moiety esterified with a caffeic acid moiety, which can be linked at different positions, resulting in various isomers such as 3-CQA, 4-CQA, and 5-CQA. The fragmentation behavior of these isomers can be studied using advanced techniques like LC-MS/MS, which helps in distinguishing between them based on their unique dissociation pathways. The presence of CGA in the diet is associated with numerous health benefits, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and metabolic regulatory effects.
Sources of Chlorogenic Acid
Chlorogenic acid is a powerful antioxidant found in various natural sources and supplements. It is known for its potential health benefits, including weight management and improved glucose metabolism. Below are the primary sources of chlorogenic acid:
1. Natural Sources
Coffee is one of the richest sources of CGA, with coffee drinkers consuming up to 1 gram of CGA per day. Tea, particularly green tea, also contains significant amounts of CGA. Fruits such as apples, artichokes, and carrots are notable sources, contributing to the dietary intake of CGA. Vegetables, including burdock and betel leaves, also provide substantial amounts of this beneficial compound. The presence of CGA in these natural sources contributes to its widespread availability in the human diet, offering various health benefits such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective effects.
2. Supplements
These supplements are designed to provide a concentrated dose of CGA, which can be beneficial for individuals looking to enhance their antioxidant intake or manage specific health conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and obesity. Despite its low oral bioavailability, CGA supplements have gained popularity due to their potential therapeutic effects, including modulation of glucose and lipid metabolism, and anti-inflammatory properties. However, it is important to note that the bioavailability and metabolism of CGA can vary significantly among individuals, influenced by factors such as gut microflora. Therefore, while CGA supplements can be a convenient way to increase intake, their efficacy may depend on individual metabolic responses.
Health Benefits of Chlorogenic Acid
Chlorogenic acid is a potent antioxidant that offers numerous health benefits. It is known for its ability to aid in weight management, improve glucose metabolism, and provide anti-inflammatory effects. Below are some of the key health benefits of chlorogenic acid:
1. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Chlorogenic acid (CGA) is renowned for its potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. It mitigates oxidative stress by scavenging free radicals and enhancing the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD). CGA also modulates inflammatory pathways, reducing the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines like tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and increasing anti-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-4 (IL-4). These properties contribute to its protective effects against various chronic diseases, including cardiovascular diseases and neurodegenerative disorders.
2. Blood Pressure Regulation
CGA has been shown to have a beneficial effect on blood pressure regulation. In a randomized trial, the acute intake of CGA significantly lowered both systolic and diastolic blood pressure in healthy volunteers. This hypotensive effect is attributed to the enhancement of nitric oxide status, which plays a crucial role in vascular health and endothelial function. The reduction in blood pressure observed with CGA consumption suggests its potential as a natural intervention for managing hypertension and improving cardiovascular health.
3. Blood Sugar and Insulin Regulation
CGA plays a significant role in regulating blood sugar and insulin levels. It has been found to modulate glucose metabolism, thereby reducing the risk of diabetes and related metabolic disorders. CGA inhibits glucose absorption in the intestine and enhances insulin sensitivity, which helps in maintaining optimal blood sugar levels. Studies have demonstrated that CGA supplementation can decrease diet-induced insulin resistance, making it a promising non-pharmacological approach for diabetes management.
4. Weight Management
CGA has been associated with weight management and anti-obesity effects. It influences lipid metabolism and reduces fat accumulation, which can help in preventing obesity. In animal studies, CGA supplementation prevented weight gain induced by a high-fat and high-fructose diet, highlighting its potential in managing diet-induced obesity. The modulation of gut microbiota and enhancement of energy metabolism are proposed mechanisms through which CGA exerts its weight management benefits.
5. Cardiovascular Health
CGA contributes to cardiovascular health by reducing the risk of myocardial infarction and other heart-related conditions. It exerts cardioprotective effects by minimizing inflammatory damage and oxidative stress in the heart. In experimental models, CGA administration before myocardial infarction significantly reduced infarct size and myocardial injury, demonstrating its protective role. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of CGA are key factors in its ability to improve cardiovascular outcomes.
6. Neuroprotective Effects
CGA has shown promising neuroprotective effects, potentially reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases. It protects against oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain, which are major contributors to neurological degeneration. Studies have indicated that CGA supplementation can prevent cognitive decline and neuronal damage following ischemic events, highlighting its potential in neuroprotection. The modulation of synaptic function and enhancement of antioxidant defenses are mechanisms through which CGA exerts its neuroprotective effects.
7. Mood and Cognitive Function
It enhances cognitive performance by modulating neurotransmission and reducing inflammation in the brain. In animal studies, CGA supplementation prevented cognitive impairments induced by a high-fat and high-fructose diet, suggesting its potential in improving brain health. The alteration of gut microbiota and the resulting impact on the gut-brain axis are proposed mechanisms for the cognitive benefits of CGA.
8. Hepatoprotective Effects
CGA exhibits hepatoprotective effects, protecting the liver from various forms of injury. It reduces oxidative stress and inflammation in the liver, which are key factors in liver damage. In studies involving lipopolysaccharide-treated rats, CGA supplementation attenuated liver injury and improved liver function. The modulation of lipid metabolism and enhancement of antioxidant defenses are mechanisms through which CGA exerts its hepatoprotective effects. These findings suggest that CGA could be a valuable natural compound for liver health.
Applications and Uses of Chlorogenic acid
Chlorogenic acid is a versatile compound with a wide range of applications and uses. It is utilized in various industries, including food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics, due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Below are some of the primary applications and uses of chlorogenic acid:
1. Food Industry
Chlorogenic acid (CGA) has significant applications in the food industry due to its antioxidant, antimicrobial, and prebiotic properties. It is used as a food additive to enhance the shelf life and nutritional value of food products by preventing lipid oxidation and microbial growth. CGA also plays a role in food storage and packaging materials, helping to maintain the quality and safety of food items. Additionally, its ability to modulate glucose and lipid metabolism makes it a valuable component in functional foods aimed at managing metabolic disorders. Microencapsulation techniques have been developed to stabilize CGA, thereby expanding its use in various food products.
2. Cosmetic Industry
In the cosmetic industry, chlorogenic acid is valued for its antioxidant properties, which help in protecting the skin from oxidative stress and environmental damage. It is incorporated into skincare products to reduce signs of aging, such as wrinkles and fine lines, by neutralizing free radicals. CGA also exhibits anti-inflammatory properties, making it beneficial for soothing irritated skin and reducing redness. Furthermore, its ability to scavenge free radicals and chelate metal ions enhances its effectiveness in cosmetic formulations aimed at improving skin health and appearance. The development of liposoluble derivatives of CGA has further broadened its application in cosmetic products.
3. Pharmaceutical and Health Applications
Chlorogenic acid has a wide range of pharmaceutical and health applications due to its diverse biological activities. It has been shown to possess antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antidiabetic, and antihypertensive properties, making it a potential therapeutic agent for managing metabolic syndrome and related disorders. CGA also exhibits neuroprotective, hepatoprotective, and cardioprotective effects, which contribute to its use in preventing and treating chronic diseases. Additionally, its antimicrobial properties make it a candidate for developing natural alternatives to synthetic antibiotics. The ability of CGA to modulate lipid and glucose metabolism further underscores its potential in pharmaceutical applications aimed at treating obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
Potential Side Effects and Risks of Chlorogenic Acid
While chlorogenic acid offers numerous health benefits, it is important to be aware of its potential side effects and risks. Overconsumption or sensitivity to this compound can lead to adverse reactions. Below are some of the potential side effects and risks associated with chlorogenic acid:
1. Caffeine-Related Side Effects
These include increased heart rate, jitteriness, and potential exacerbation of anxiety symptoms. Studies have shown that caffeine can significantly raise plasma homocysteine levels, which is a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Additionally, caffeine’s stimulatory effects on the central nervous system can lead to sleep disturbances and heightened anxiety, particularly in sensitive individuals.
2. Gastrointestinal Issues
Chlorogenic acid can influence gastrointestinal function, potentially leading to issues such as stomach upset, nausea, and diarrhea. Research indicates that coffee, which contains chlorogenic acid, can modify gastrointestinal hormone secretion and glucose tolerance, suggesting that chlorogenic acid might affect gastrointestinal motility and absorption processes. These effects can contribute to gastrointestinal discomfort and disturbances in some individuals.
3. Increased Homocysteine Levels
Consumption of chlorogenic acid has been linked to increased plasma homocysteine levels, a known risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. A study demonstrated that chlorogenic acid intake resulted in a 12% increase in plasma homocysteine levels compared to placebo. This elevation in homocysteine levels could potentially contribute to an increased risk of cardiovascular events, although the long-term implications require further investigation.
4. Allergic Reactions
While not commonly reported, allergic reactions to chlorogenic acid can occur. Symptoms may include skin rashes, itching, and respiratory issues. The literature on chlorogenic acid does not extensively cover allergic reactions, but given its presence in various plant species, individuals with plant-based allergies should exercise caution. Further research is needed to fully understand the prevalence and mechanisms of such allergic responses.
5. Impact on Blood Sugar Levels
Chlorogenic acid has been shown to modulate glucose metabolism, which can impact blood sugar levels. Studies indicate that chlorogenic acid can delay glucose absorption in the intestines, potentially leading to lower postprandial blood glucose levels. However, this effect can vary, and in some cases, it might lead to hypoglycemia, especially in individuals with diabetes or those on glucose-lowering medications.
6. Blood Pressure Concerns
A randomized trial showed that chlorogenic acid intake resulted in a significant reduction in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure. While this effect can be beneficial for cardiovascular health, individuals with already low blood pressure or those on antihypertensive medications should monitor their blood pressure closely to avoid hypotension.
7. Anxiety and Sleep Disturbances
The presence of caffeine in chlorogenic acid-containing beverages like coffee can lead to anxiety and sleep disturbances. Caffeine is known to stimulate the central nervous system, which can exacerbate anxiety symptoms and interfere with sleep patterns. Individuals sensitive to caffeine or those with anxiety disorders should be cautious with their intake of chlorogenic acid-rich products to avoid these adverse effects.
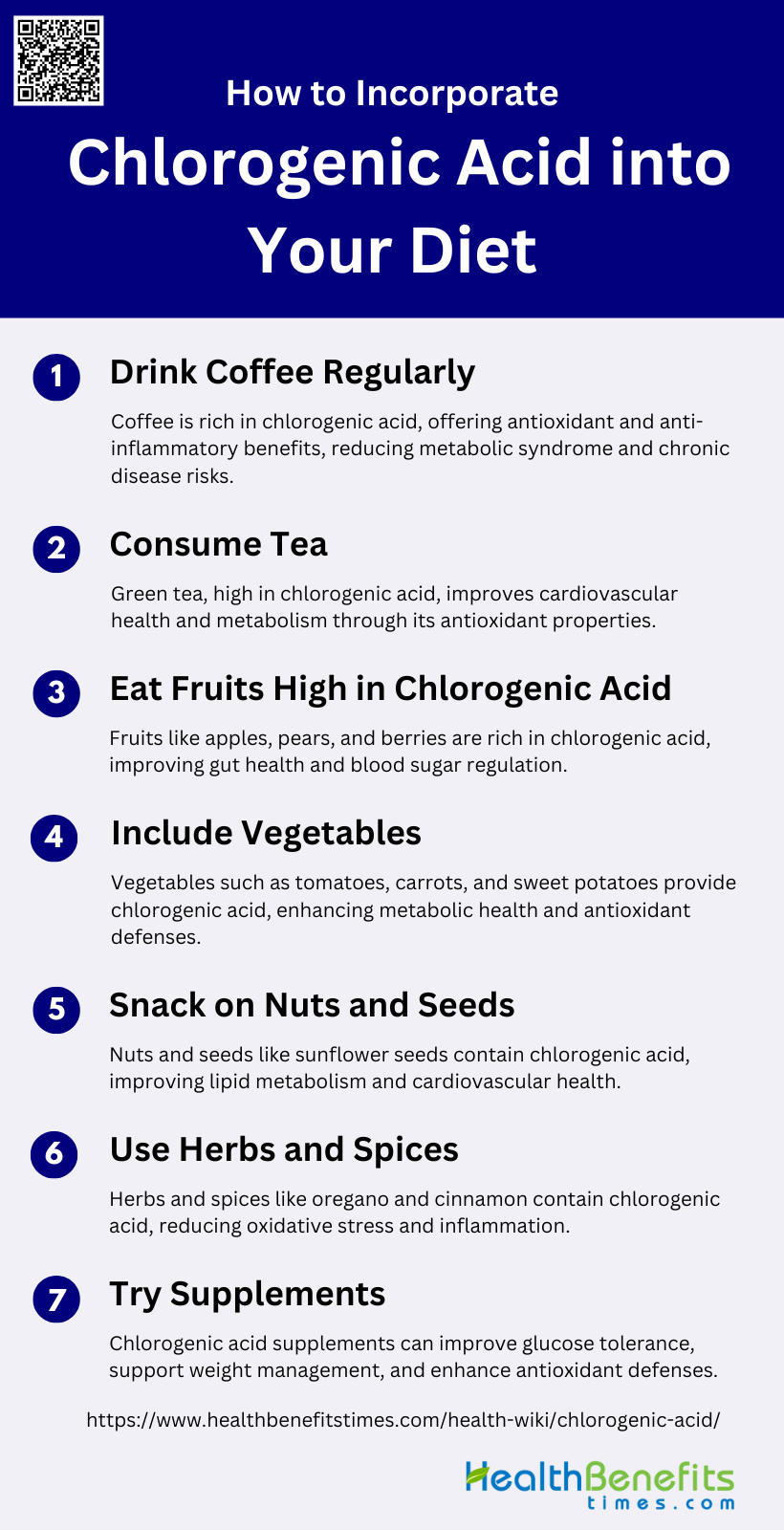
How to Incorporate Chlorogenic Acid into Your Diet
Incorporating chlorogenic acid into your diet can be simple and beneficial for your health. This powerful antioxidant can be found in various foods and supplements. Below are some effective ways to include chlorogenic acid in your daily diet:
1. Drink Coffee Regularly
Chlorogenic acid (CGA) is a major component of coffee, making it one of the most accessible sources of this beneficial compound. Regular coffee consumption has been linked to a variety of health benefits, including reduced risks of metabolic syndromes and chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of CGA contribute to these protective effects, making coffee a convenient and enjoyable way to incorporate CGA into your diet.
2. Consume Tea
Tea, particularly green tea, is another excellent source of chlorogenic acid. The consumption of tea has been associated with numerous health benefits, including improved cardiovascular health and enhanced metabolic function. The polyphenolic compounds in tea, including CGA, contribute to its antioxidant capacity, which helps in reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. Regular tea drinking can thus be a beneficial addition to your diet for increasing CGA intake.
3. Eat Fruits High in Chlorogenic Acid
Fruits such as apples, pears, and berries are rich in chlorogenic acid. These fruits not only provide a natural source of CGA but also offer additional nutrients and fiber that are beneficial for overall health. Consuming these fruits can help improve gut health, regulate blood sugar levels, and provide antioxidant protection. Including a variety of these fruits in your daily diet can be an effective way to boost your CGA intake.
4. Include Vegetables
Vegetables like tomatoes, carrots, and sweet potatoes are also good sources of chlorogenic acid. These vegetables can be easily incorporated into meals and provide a range of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. The consumption of CGA-rich vegetables has been shown to support metabolic health, improve gut microbiota, and enhance antioxidant defenses. Regularly including these vegetables in your diet can help you reap the benefits of CGA.
5. Snack on Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds, such as sunflower seeds and flaxseeds, contain chlorogenic acid and can be a healthy snack option. These foods are also rich in healthy fats, protein, and fiber, making them a nutritious addition to your diet. Snacking on nuts and seeds can help improve lipid metabolism, support cardiovascular health, and provide sustained energy. Incorporating these snacks into your daily routine can help increase your CGA intake.
6. Use Herbs and Spices
Herbs and spices like oregano, thyme, and cinnamon are not only flavorful but also contain chlorogenic acid. Adding these herbs and spices to your meals can enhance the taste while providing additional health benefits. The antioxidant properties of CGA in these herbs and spices can help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, contributing to overall health and well-being. Using a variety of these herbs and spices in cooking can be an easy way to incorporate more CGA into your diet.
7. Try Supplements
For those who may find it challenging to get enough chlorogenic acid from food sources alone, supplements can be a convenient option. CGA supplements are available in various forms, including capsules and powders. These supplements can help improve glucose tolerance, support weight management, and enhance antioxidant defenses. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen to ensure it is appropriate for your individual health needs.