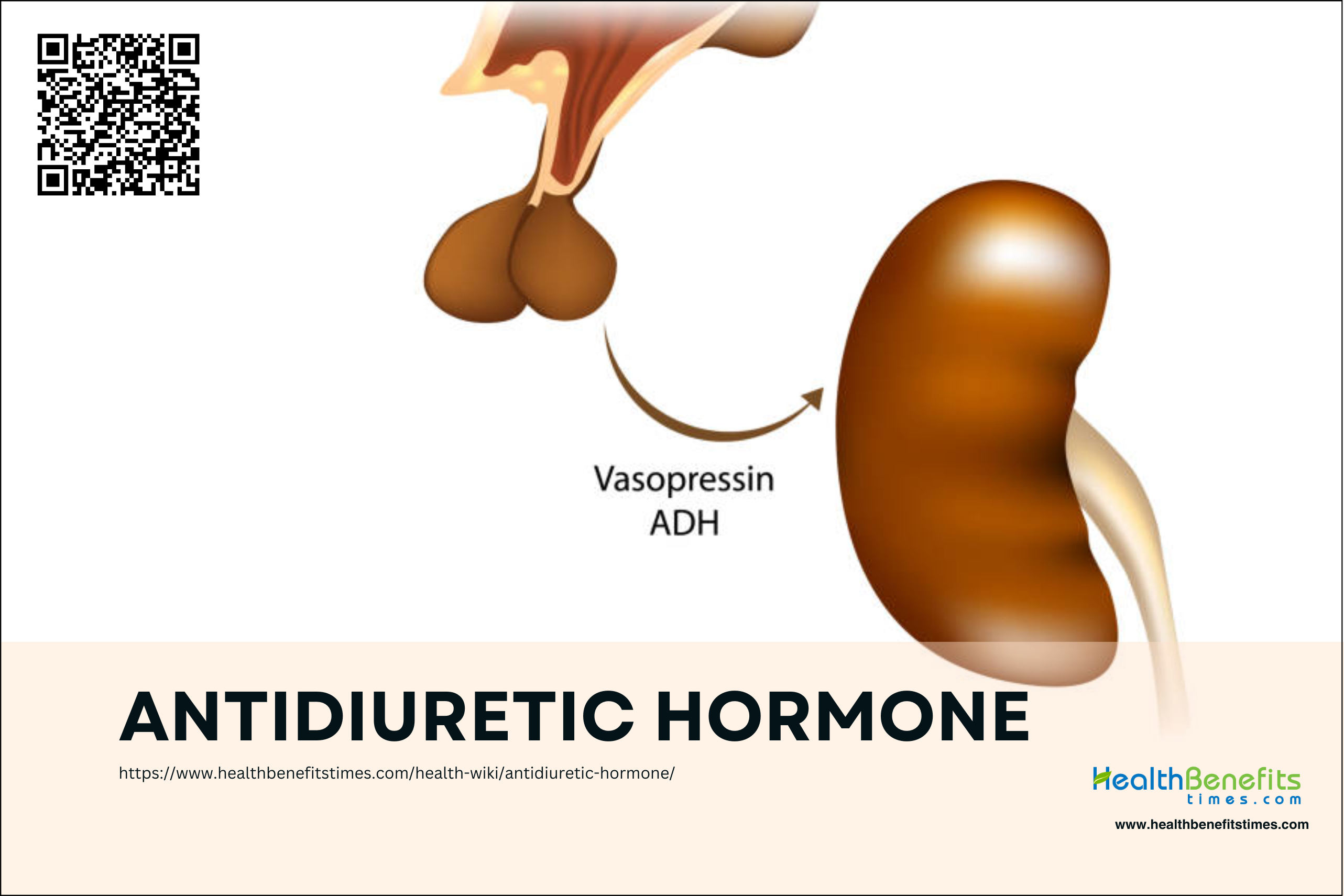
 Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), also known as vasopressin, is a crucial hormone involved in regulating the body’s water balance and blood pressure, demonstrating the interconnectedness of the endocrine system. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), primarily arginine vasopressin in humans, regulates water retention by acting on kidney cells, promoting water reabsorption. Produced by the hypothalamus and stored in the pituitary gland, ADH plays a precise role in controlling the reabsorption of water by the kidneys, which is essential for maintaining fluid balance and preventing dehydration or hyponatremia, a condition characterized by low sodium levels. A comprehensive understanding of ADH’s function is essential not only for healthcare professionals but also for individuals interested in health and wellness, as it underscores the significance of equilibrium and the interdependence of bodily systems in promoting optimal health.
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), also known as vasopressin, is a crucial hormone involved in regulating the body’s water balance and blood pressure, demonstrating the interconnectedness of the endocrine system. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), primarily arginine vasopressin in humans, regulates water retention by acting on kidney cells, promoting water reabsorption. Produced by the hypothalamus and stored in the pituitary gland, ADH plays a precise role in controlling the reabsorption of water by the kidneys, which is essential for maintaining fluid balance and preventing dehydration or hyponatremia, a condition characterized by low sodium levels. A comprehensive understanding of ADH’s function is essential not only for healthcare professionals but also for individuals interested in health and wellness, as it underscores the significance of equilibrium and the interdependence of bodily systems in promoting optimal health.
Functions of Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
Understanding the functions of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) can empower individuals to better manage their hydration and overall well-being. The following is a list of key functions of ADH that contribute to homeostasis and health optimization.
1. Water Reabsorption
The antidiuretic hormone is essential for regulating the body’s water balance and plays a crucial role in overall health. By signaling the kidneys to increase water reabsorption, ADH helps conserve water, reduce urine output, and maintain stable blood pressure and volume. Understanding the function of ADH is important for those focusing on holistic health, as it supports kidney health and ensures effective operation of cells and organs in a well-hydrated state. The hormone’s ability to regulate water retention is vital for preventing dehydration and maintaining a stable internal environment, known as homeostasis, which is essential for optimal health and fitness. Recognizing the significance of ADH can assist individuals in managing their fluid intake and promoting wellness in their daily lives.
2. Blood Pressure Regulation
The hormone ADH plays a crucial role in maintaining blood pressure balance. It is released by the posterior pituitary gland in response to low blood pressure situations. ADH acts on the kidneys to reduce water loss and increase blood volume, while also causing blood vessels to constrict, thereby raising blood pressure. This dual action of ADH is essential for ensuring adequate blood flow to our organs. Understanding the function of ADH can help individuals make informed lifestyle choices that support their body’s natural processes and promote cardiovascular health. Recognizing the importance of ADH in blood pressure regulation highlights the broader concept of hormonal balance in maintaining overall health and well-being.
3. Circadian Rhythm Regulation
The hormone ADH plays a crucial role in regulating the circadian rhythm, ensuring synchronization of our internal biological clock with the natural day-night cycle. Its levels increase at night, promoting hydration to prevent sleep disturbances related to drinking or urination. ADH’s functions extend beyond water conservation to include regulation of blood pressure and kidney function, which are essential for maintaining alertness during the day and restfulness at night. By managing fluid and electrolyte balance, ADH contributes to the coordination of important physiological processes, supporting overall well-being and a stable internal environment. Understanding and aligning with these rhythms can significantly improve sleep quality and holistic health.
4. Role in Social Behavior and Stress Response
The hormone ADH, which is essential for managing stress and social behavior, plays a critical role in our ability to connect with others and respond to pressure. It helps regulate blood pressure and anxiety levels by constricting blood vessels during times of stress, which in turn impacts our social interactions and may influence bonding and aggression. Understanding the extensive effects of ADH on both physical and emotional health provides valuable insights for holistic health strategies. These strategies not only aid in stress management but also promote the development of healthy social relationships, highlighting the interconnectedness of well-being. Embracing this knowledge can lead to more balanced and fulfilling lifestyles, where mental, physical, and community wellness are in harmony.
5. Regulating blood volume
Regulating blood volume by promoting water reabsorption in the kidneys involves acting on the renal cortical collecting ducts. This process triggers the translocation of AQP2 water channels to the cell surface, which increases water permeability and reduces urine output. It stimulates the kidneys to retain water and concentrate urine, leading to a decrease in urine output and an increase in water reabsorption during times of dehydration. This mechanism not only helps maintain blood volume but also supports stable blood pressure and the circulatory system. Understanding the function of ADH is essential for managing fluid intake and promoting kidney health, which are vital for maintaining the delicate balance necessary for optimal bodily function and preventing dehydration. Recognizing the significance of ADH highlights the complex relationship between hydration and overall well-being in our health and fitness pursuits.
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) and Disorders
It is a hormone that signals the kidneys to retain water, thereby reducing urine output. However, imbalances in antidiuretic hormone (ADH) can lead to disorders that disrupt this delicate equilibrium, affecting overall health and wellness. Below, we explore a number of conditions associated with ADH dysregulation, emphasizing the importance of hormonal balance for holistic health.
- Infertility
- Insomnia
- Head injuries
- Delayed puberty
- Genetic disorders
- Frequent urination
- Change in appetite
- Autoimmune disorders
- Fluctuations in blood pressure
- Fluctuations in body temperature
- Tumours in the hypothalamus or regions near the pituitary gland
Side Effects of Antidiuretic Hormone
Like any regulatory substance, it can have unintended side effects when levels are imbalanced. Below, we will explore a list of potential side effects that can arise from the abnormal activity of Antidiuretic Hormone.
1. Diarrhea
While antidiuretic hormone (ADH) therapy is crucial for managing conditions such as diabetes insipidus and hyponatremia, it can occasionally result in diarrhea, disrupting the body’s fluid and electrolyte equilibrium. This uncommon side effect may lead to dehydration and further electrolyte imbalances, counteracting the therapy’s objective of promoting water retention in the kidneys. Individuals undergoing ADH therapy should monitor their hydration levels closely and seek advice from their healthcare provider if they experience persistent or severe diarrhea. Timely management of these symptoms is essential to preserve the efficacy of the treatment and maintain overall health, in line with a holistic approach to wellness that emphasizes the body’s innate equilibrium.
2. Nausea
Nausea is a significant side effect of chemotherapy, often ranked as one of the most distressing by patients, despite the use of 5HT3 antagonists as standard antiemetic therapy. The onset of nausea indicates that ADH may be impacting the stomach lining or the body’s water and sodium balance, causing discomfort. If nausea persists, it is crucial to consider personalized health strategies, which may involve dietary adjustments or hydration practices, to alleviate this symptom and maintain the body’s balance. For individuals receiving ADH treatments, understanding and addressing these symptoms is crucial as they are integral to the overall treatment plan and the patient’s quality of life. Taking an integrative approach to managing these effects can lead to improved health outcomes and well-being.
3. Weakness
Understanding the impact of hormones such as antidiuretic hormone (ADH), also known as vasopressin, on the human body is crucial. ADH plays a role in regulating water retention and blood pressure. However, an excess of ADH can lead to symptoms such as physical weakness caused by syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH), where an excess of fluid causes swelling of the body’s cells, leading to impaired muscle and cellular functions. This weakness can manifest as fatigue or decreased strength, affecting daily activities and overall physical fitness. It is important for individuals focused on maintaining wellness to recognize these signs of ADH imbalance early and address them through proper hydration, nutrition, and treatment adjustments to preserve health and vitality.
4. Abdominal cramps
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) therapy, commonly used to treat diabetes insipidus and manage fluid balance, may cause abdominal cramps as a side effect due to its influence on the smooth muscle contractions of the gastrointestinal tract. These cramps, often accompanied by nausea and belching, indicate the body’s response to the hormone and should be addressed by healthcare providers to prevent more serious complications. To alleviate such discomfort, individuals undergoing ADH treatment should maintain proper hydration, consume a diet high in fiber, and utilize stress-reduction techniques. These holistic practices not only complement medical interventions but also promote overall digestive health. It is important to monitor and discuss persistent or severe symptoms with a healthcare professional to adjust therapy and ensure patient well-being.
5. Sweating
Excessive sweating, known as hyperhidrosis, can be a troublesome symptom when levels of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) become elevated, leading to an overactive response in the sweat glands and disrupting the body’s fluid and electrolyte balance. This condition not only causes physical discomfort but can also result in social and psychological difficulties. It is important to recognize that such symptoms may indicate underlying health issues, necessitating a consultation with a healthcare professional. To address hyperhidrosis holistically, it is advisable to maintain proper hydration, practice stress-reduction techniques, and utilize natural remedies that support hormonal balance and aid in detoxification. Understanding the relationship between ADH and sweating is essential in implementing a comprehensive health approach that promotes the body’s natural thermoregulation and detoxification processes, ultimately contributing to overall well-being.



