 Adenitis refers to the inflammation of a gland or lymph node. It is often caused by an infection, which can be bacterial, viral, or parasitic. Tuberculous adenitis, for example, is a form of adenitis where the lymph nodes are infected by tuberculosis bacteria, often presenting as a neck mass. This condition can lead to symptoms like swelling, pain, and tenderness, particularly in areas where lymph nodes are concentrated, such as the neck, underarms, groin, and abdomen. It can be triggered by various factors, including infections, autoimmune diseases, and in rarer cases, cancer. Recognizing the signs of adenitis is important for maintaining overall health and wellness, as it highlights the significance of a well-functioning immune system and the body’s complex interrelated systems. For those interested in holistic health, understanding and addressing adenitis is key to nurturing the body’s natural defenses and ensuring comprehensive well-being.
Adenitis refers to the inflammation of a gland or lymph node. It is often caused by an infection, which can be bacterial, viral, or parasitic. Tuberculous adenitis, for example, is a form of adenitis where the lymph nodes are infected by tuberculosis bacteria, often presenting as a neck mass. This condition can lead to symptoms like swelling, pain, and tenderness, particularly in areas where lymph nodes are concentrated, such as the neck, underarms, groin, and abdomen. It can be triggered by various factors, including infections, autoimmune diseases, and in rarer cases, cancer. Recognizing the signs of adenitis is important for maintaining overall health and wellness, as it highlights the significance of a well-functioning immune system and the body’s complex interrelated systems. For those interested in holistic health, understanding and addressing adenitis is key to nurturing the body’s natural defenses and ensuring comprehensive well-being.
Types of Adenitis
Adenitis, a condition characterized by the inflammation of the lymph nodes, is a health concern that can manifest in various forms, each with its unique set of symptoms and treatment approaches. Understanding the different types of adenitis is crucial for identifying the appropriate holistic health and wellness strategies to manage this condition effectively. Here are the primary types of adenitis you should be aware of:
1. Lymphadenitis
Lymphadenitis, or swollen lymph nodes, indicates that your immune system is combating an infection, whether it’s from common viruses or more severe bacterial pathogens. This condition can be caused by various infectious agents, including Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which leads to tuberculous lymphadenitis, a chronic granulomatous inflammation with caseated necrosis. These nodes, integral to the lymphatic system, capture harmful agents to prevent further infection. Holistic health practices suggest that recognizing lymphadenitis is essential, and supporting the body with rest, hydration, and proper nutrition, along with natural remedies like warm compresses, lymphatic massages, and herbal supplements such as echinacea, can aid in recovery. The condition can present as localized, affecting nodes near the infection, or generalized, involving multiple groups of nodes. It’s important to monitor symptoms and seek medical advice for persistent or severe lymphadenitis to ensure effective treatment and to exclude serious underlying issues.
2. Mesenteric adenitis
Mesenteric adenitis, also known as mesenteric lymphadenitis. Mesenteric adenitis specifically affects the lymph nodes in the mesentery and is often mistaken for appendicitis due to similar symptoms such as abdominal pain. It can be diagnosed via CT scans, which typically show enlarged lymph nodes with a normal appendix. Common among children and young adults, it shares symptoms with appendicitis, including abdominal pain—often in the lower right area—fever, and a feeling of being unwell. Although the condition can cause concern, it is typically self-limiting and resolves on its own without the need for specific medical treatment. The root of the inflammation is usually an infection, which could be viral or bacterial. A holistic health perspective encourages supporting the immune system through adequate rest, staying hydrated, and maintaining a nutritious diet, in addition to following medical guidance for symptom management and monitoring the condition to ensure relief and proper care.
3. Sebaceous adenitis
Sebaceous adenitis (SA) is a chronic skin condition characterized by inflammation and degeneration of sebaceous glands, leading to symptoms like scaling, alopecia, and sometimes intense itching. It is relatively rare and can affect various species, including cats, dogs, and humans. Symptoms include hair loss, scaling, and a moth-eaten skin appearance, with certain dog breeds being genetically predisposed to the condition. Although the exact cause is unknown, it is thought to involve an autoimmune response. A holistic management plan, crucial for improving life quality, may involve topical treatments to alleviate skin irritation, dietary changes to bolster skin health, and possibly supplements to correct nutritional deficiencies. Working with a healthcare provider to tailor a treatment strategy that combines traditional and holistic methods is vital for those affected by this challenging condition, as there is no known cure. This comprehensive approach is in line with health and wellness principles, focusing on the overall care need
4. Cervical adenitis
Cervical adenitis encompasses various types, including atypical mycobacterial cervical adenitis (AMCA), which typically presents as a unilateral mass in children, and cervical tuberculous adenitis, often seen in young adults from Southeast Asia. Signaling the immune system’s response to fight off infections like strep throat, mononucleosis, or dental issues. Symptoms include tender, swollen lymph nodes, fever, and sore throat. While antibiotics or anti-inflammatory medications are common treatments, a holistic health perspective encourages natural remedies and lifestyle changes, such as herbal supplements, proper hydration, rest, and stress management, to aid the bodies healing. Whether the inflammation is due to viral infections like rhinovirus or bacterial sources such as Staphylococcus aureus, understanding the cause is key to effective treatment. Early recognition and medical consultation can enhance recovery and prevent further complications.
5. Tuberculous adenitis (scrofula)
Tuberculous adenitis, also known as scrofula, is a type of adenitis where the lymph nodes, particularly in the neck, are infected by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, leading to gradual, painless swelling. While it can occur anywhere in the body, it’s most common in the cervical region and poses a greater risk to those with compromised immune systems or a history of tuberculosis exposure. Diagnosis combines clinical assessment, imaging, and microbiological tests, with culture as the definitive method. Treatment involves antituberculous drugs and possibly surgery for complications. A holistic health approach, incorporating strong immune support through nutrition, stress reduction, and exercise, alongside medical treatment, is essential for effective management and prevention of scrofula’s complications. Early detection and a blend of conventional and holistic therapies are key to tackling this health challenge, particularly in areas with high tuberculosis rates.
Causes and Risk Factors of Adenitis
Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with adenitis is crucial for early detection and effective management. Here are the key contributors to the development of this condition:
1. Bacterial infections
Bacterial infections are a significant cause of adenitis, with various risk factors contributing to susceptibility. Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis, and Haemophilus influenzae type b are common pathogens beyond the neonatal period, with socioeconomic factors, age, and genetic variations influencing risk. Adenovirus infections, often mistaken for bacterial infections, can lead to hospitalization in children, especially when presenting with respiratory distress, wheezing, or acute gastroenteritis. These bacteria can enter through small skin injuries, leading to symptoms that range from mild swelling to severe pain, depending on the body’s immune response. People with weakened immune systems or chronic skin conditions are more susceptible to adenitis. To prevent this condition, it’s vital to maintain a strong immune system with good nutrition, regular exercise, stress management, and sufficient sleep. Additionally, practicing good hygiene and quickly treating any infections are key steps in reducing the risk of adenitis and ensuring lymphatic health.
2. Viral infections
Adenitis, marked by swollen and tender lymph nodes, is commonly incited by viral infections such as the Epstein-Barr virus and the common cold. These viruses activate the body’s immune defenses, causing the lymph nodes to expand as they strive to combat the infection. Particularly vulnerable are those with compromised immune systems, including children and teenagers whose immune responses are still maturing. To lower the risk and alleviate the symptoms of adenitis, it is essential to adopt a holistic approach to health that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and effective stress management. By bolstering the immune system through these healthy lifestyle choices and good hygiene, individuals can better protect themselves against the onset of adenitis.
3. Fungal Infections
Fungal infections, particularly those caused by Candida albicans, are significant risk factors for adenitis, especially in neonates and immunocompromised individuals. Neonates with invasive fungal infections often have preceding fungal colonization and may suffer from intrauterine growth restriction. Risk factors heightening susceptibility to these infections include extended antibiotic use, which alters the body’s natural flora, and health conditions like diabetes or HIV/AIDS that impair immune function. Environments laden with fungi, such as moist areas or organically rich soil, also pose a risk. To mitigate these risks, holistic health strategies advocate for bolstering the immune system with balanced nutrition, effective stress management, and consistent exercise, underscoring the significance of a comprehensive approach to health for preventing and managing adenitis.
4. Autoimmune disorders
Autoimmune disorders are significant risk factors for adenitis, as they can trigger inflammation in various glands. Genetic and environmental factors, such as organic solvents, infections, and possibly vaccines, contribute to the development of autoimmune diseases (ADs). Autoimmune disorders like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, where the body’s immune system erroneously targets its own lymphatic tissue. This misdirected immune response leads to chronic inflammation, resulting in painful and swollen lymph glands. Additionally, certain medications, including phenytoin and hydralazine, may contribute to the development of adenitis as an adverse effect. Understanding these triggers is crucial for those seeking holistic health, fitness, and wellness, as managing autoimmune conditions and medication side effects can be integral to alleviating the symptoms of adenitis.
5. Inflammatory conditions
Inflammatory conditions such as ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, and chronic infections can lead to an increased risk of adenitis, which is the inflammation of a gland, often a lymph node. The persistent inflammatory state promotes carcinogenesis through mechanisms like DNA damage, inhibition of apoptosis, and stimulation of angiogenesis. Inflammatory conditions provoke an immune response that results in the enlargement and tenderness of lymph nodes, essential in the body’s defense system. Factors such as poor nutrition, stress, and exposure to toxins can increase the risk of such inflammation. A holistic health perspective emphasizes the importance of a balanced lifestyle and a comprehensive treatment approach that not only alleviates adenitis symptoms but also addresses the underlying causes, such as appendicitis, inflammatory bowel diseases, and connective tissue disorders. This integrative strategy is key to bolstering the body’s natural defenses and promoting long-term wellness.
6. Medications
Medications that relax the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) have been implicated as a risk factor for adenocarcinomas, including esophageal adenocarcinoma. Medications healing, can also lead to unintended side effects such as adenitis, an inflammation of the lymph nodes. Drugs like phenytoin for seizures and antibiotics like penicillin can trigger immune reactions, resulting in swollen lymph nodes, especially in those with medication sensitivities or autoimmune disorders. Chemotherapy drugs may also weaken the immune system, increasing the risk of lymph node infections and inflammation. It’s vital for patients on these medications to be monitored for signs of lymph node issues and to have open discussions with their healthcare providers to manage any potential risks, including adenitis. Always consult a healthcare professional before making changes to your medication regimen.
Symptoms of Adenitis
Adenitis, the inflammation of the lymph nodes, presents a range of symptoms that can often mimic other health conditions, making accurate diagnosis crucial for effective treatment. Symptoms typically include pain, tenderness, and swelling in the affected lymph nodes, often accompanied by fever and general malaise. This article delves into the common symptoms and diagnostic approaches for adenitis, providing essential insights for those seeking a holistic understanding of this condition.
1. Noticeable swollen and tender lymph nodes
Adenitis is characterized by swollen and tender lymph nodes, often presenting with fever, chills, and malaise. Diagnosis can be challenging, requiring a high index of clinical suspicion and may involve laboratory tests, imaging like ultrasound or CT scans, and sometimes biopsy. Swollen and tender lymph nodes are key indicators of adenitis, reflecting the body’s immune reaction to infection or inflammation. These small, bean-shaped glands, crucial to our immune system, often become inflamed and are most commonly found in the neck, armpits, and groin. The swelling and pain, which can be felt as soft bumps under the skin, may also be accompanied by fever, fatigue, or night sweats. It’s essential to seek medical advice if these symptoms arise. Identifying the root of the issue is vital for crafting a tailored holistic health plan that promotes healing and well-being.
2. Fever and general malaise
When the body’s lymphatic system responds to an infection or inflammation, fever and general malaise are often the initial symptoms. These signs, which may include a warm forehead, chills, sweating, and an elevated body temperature, indicate the body’s attempt to fight off harmful pathogens. Accompanied by a feeling of overall discomfort or weakness, they suggest that the body is directing its energy towards the immune response. Adenitis, the inflammation of the lymph nodes typically caused by bacterial, viral, or fungal infections, can result in additional symptoms such as a sore throat, abdominal pain, and noticeable swelling in areas with dense lymph node clusters, such as the neck, armpits, or groin. A healthcare professional will typically conduct a thorough medical history and physical examination, and may also recommend blood tests, imaging studies, or a lymph node biopsy to identify the cause of the inflammation and rule out more serious conditions. Recognizing and addressing these symptoms promptly is crucial for effectively managing adenitis, especially from a holistic health perspective that emphasizes the interconnectedness of physical and mental well-being.
3. Redness and Heat
Adenitis, particularly adenoviral conjunctivitis, often presents with redness of the eye and can be accompanied by heat sensation. This condition can also result in tenderness, pain, fever, and swelling in the affected area. Healthcare professionals rely on these symptoms, particularly redness and heat, as important indicators for diagnosis. A physical examination is typically conducted to evaluate these signs, and additional tests such as blood work or ultrasounds may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. It is essential for individuals experiencing persistent symptoms to promptly seek medical evaluation, as early detection can lead to more effective treatment by combining traditional and holistic health practices to achieve optimal wellness.
4. Pain or Discomfort
Adenitis, particularly adenomyosis, is characterized by a spectrum of pain symptoms that significantly impact patients’ quality of life. The majority of adenomyosis patients experience pain, with 71.8% reporting symptoms such as dysmenorrhea, which can range from mild to severe, and progressive pain. Pain or discomfort in the affected area is often one of the primary indicators of adenitis, a condition characterized by inflammation of the lymph nodes. This discomfort may present as tender or sharp pain, especially when the lymph nodes are palpated or during movements that strain the affected region. Individuals may also experience a general feeling of malaise or sensitivity around the swollen nodes. A prompt diagnosis usually requires a comprehensive physical examination by a healthcare professional, who may also suggest blood tests, imaging studies, or a biopsy to identify the root cause of the lymph node inflammation and to exclude other health issues.
5. Systemic Symptoms
When experiencing systemic symptoms such as fever, chills, night sweats, malaise, fatigue, weight loss, and a decrease in appetite, it may indicate that your body is responding to an infection or inflammation, commonly associated with adenitis. These symptoms, along with discomfort or tenderness in the lymph nodes, are part of a complex immune response. A holistic health perspective views these symptoms not in isolation but as interconnected reactions within the body. To address these symptoms, a comprehensive approach is recommended, including nutritional support, stress management, and immune modulation. Accurate diagnosis and treatment of adenitis require a thorough medical evaluation, which may include a history, physical examination, and possibly blood tests or imaging. Consulting with a healthcare provider is essential to develop an integrative treatment plan that supports your overall health and wellness goals.
How Is Adenitis Diagnosed?
In order to obtain an accurate diagnosis, healthcare professionals utilize a combination of medical history assessment, physical examinations, and specific diagnostic tests. The following is a list of key steps taken to precisely identify this immune system-related condition within a holistic health framework.
1. Thorough Medical History
A thorough medical history is crucial as it guides clinicians in suspecting the disease, especially in patients presenting with symptoms like heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, or infertility. This important step involves a thorough discussion with patients regarding their symptoms, how long they have been experiencing them, any recent illnesses, and their complete health history, including family health patterns. This detailed examination goes beyond just physical symptoms, taking into account the patient’s individual health history in the diagnostic process. It helps identify potential causes or genetic factors that may impact adenitis, distinguishing it from conditions like mesenteric lymphadenitis that have similar presentations. This comprehensive method not only results in a more accurate diagnosis but also enables the development of a personalized treatment plan that meets the individual’s unique health requirements.
2. Physical Examination
Physical examination plays a crucial role in the initial assessment of adenitis. For instance, in the case of adenomyosis, a benign uterine disorder, the physical examination may reveal an enlarged, tender uterus, which can guide the clinician towards a suspicion of the disease. The physical examination is also essential in the outpatient setting, where it can help establish a diagnosis when a patient presents with specific symptoms. This is followed by palpation to assess the tenderness, size, and texture of the lymph nodes. Soft, movable nodes typically suggest a benign condition, while hard, immovable nodes may indicate more serious health issues. The examination also involves identifying signs of infection and systemic symptoms that could impact the lymph nodes. By examining the location, size, and consistency of the nodes, as well as checking for related symptoms in areas such as the throat, ears, or skin, healthcare professionals obtain a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s health. This holistic approach, recognizing the interconnectedness of bodily systems, is crucial for determining the next steps in diagnosis, which may include blood tests or imaging, to accurately diagnose adenitis and develop an effective treatment plan.
3. Imaging Techniques
Adenitis, commonly referred to as adenomyosis, is diagnosed using non-invasive imaging techniques. Transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and CT scans are the primary methods for detecting this condition. Ultrasound is commonly used as the initial test because of its ability to quickly display enlarged lymph nodes and their characteristics. For a more detailed analysis, CT scans can identify clusters of swollen lymph nodes and differentiate adenitis from similar conditions, such as appendicitis. MRI is especially effective in producing clear images of soft tissues, assisting in the differentiation of adenitis without exposing the patient to radiation. These methods, when interpreted by an experienced radiologist, are essential components of a comprehensive health strategy, providing accurate diagnosis and guiding treatment decisions to ensure a holistic approach to well-being and fitness.
4. Biopsy
A biopsy is an essential diagnostic tool that plays a significant role in the comprehensive approach to wellness. This procedure, which is minimally invasive, involves removing tissue from an affected lymph node and examining it under a microscope to identify any abnormal cells. It helps differentiate between benign conditions and more serious issues such as infections, autoimmune diseases, or cancers. By utilizing the information obtained from a biopsy, healthcare providers can develop personalized treatment plans that support the body’s natural healing processes. Various biopsy techniques, including fine needle aspiration, core needle biopsy, and excisional biopsy, are chosen based on the location of the lymph node, the suspected cause of the condition, and the need for a thorough tissue analysis. The diagnosis of sclerosing adenosis, core biopsy has shown to be accurate in the majority of cases, even when cancer is coexistent, as demonstrated in a study where core biopsy was accurate in six out of seven malignancies associated with sclerosing adenosis. Techniques like ultrasound-guided core biopsy are particularly effective in diagnosing specific conditions with minimal invasiveness, ensuring that the treatment is in line with the body’s natural healing processes and the principles of holistic health.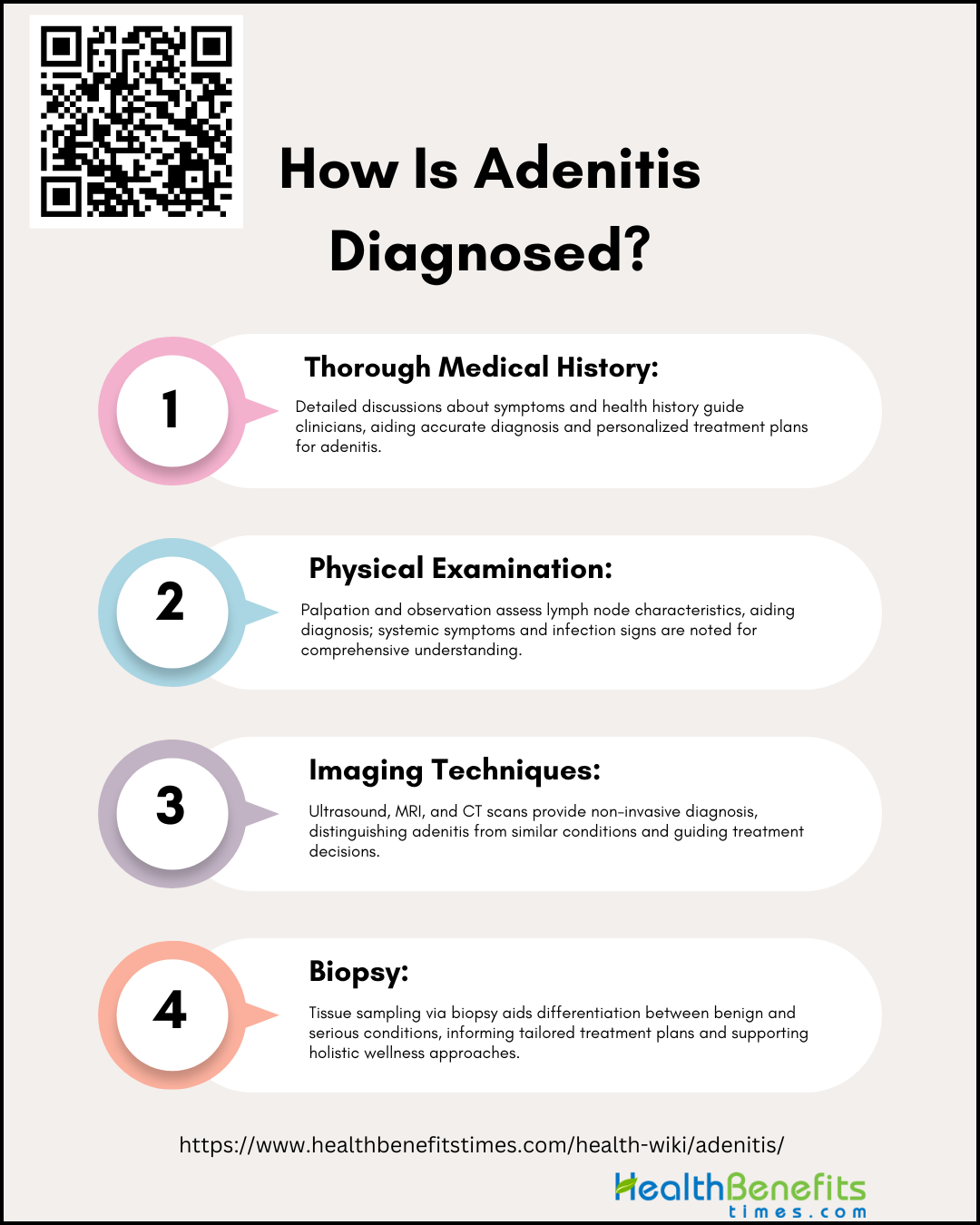
Treatment and Management for Adenitis
Effective management usually involves the administration of antibiotics for bacterial infections, as well as supportive therapies like hydration and pain relief. Holistic approaches may also include stress reduction techniques and dietary modifications to enhance overall immune function.
1. Antibiotics for bacterial infections
The management of adenitis, an inflammation of the lymph glands, often necessitates the use of antibiotics, particularly when bacterial infections are involved. Oral antibiotics are commonly prescribed for bacterial etiologies, with a focus on targeting specific pathogens like Staphylococcus aureus and Haemophilus influenzae. A thorough medical evaluation is necessary to identify the responsible bacteria and choose the appropriate antibiotic, especially broad-spectrum ones for severe cases. It is important to use antibiotics judiciously to prevent resistance and to complete the prescribed treatment regimen to fully eliminate the infection. To support the body’s immune system and mitigate potential effects of antibiotics on gut health, a comprehensive approach including a balanced diet, adequate hydration, rest, and possibly probiotics is recommended. Seeking guidance from a healthcare provider is essential to develop a personalized treatment plan that promotes overall well-being and aligns with individual health goals.
2. Acetaminophen
Acetaminophen, also known as Tylenol, is a commonly used medication for reducing pain and fever associated with swollen lymph nodes, a condition known as adenitis. It is known for its gentle effects on the stomach and heart, in contrast to NSAIDs, and is considered safe when used as directed. Acetaminophen, a widely used antipyretic and analgesic, is considered safe within recommended doses but can cause severe liver and kidney damage when overdosed. While acetaminophen does not treat the underlying cause of lymph node inflammation, it can be part of a comprehensive health plan that includes rest, hydration, and natural remedies to support the immune system. It is advisable to consult a healthcare provider to ensure that acetaminophen aligns with your overall wellness approach and does not interfere with other treatments.
3. NSAIDs
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a cornerstone in the management of adenitis, providing effective pain relief and reducing inflammation. Studies have shown that NSAIDs like diclofenac and etoricoxib significantly improve pain symptoms compared to placebo, with diclofenac 150 mg/day being particularly effective. These medications work by inhibiting the body’s production of inflammatory substances, providing significant relief for individuals with swollen lymph nodes. It is important to use NSAIDs cautiously, following healthcare guidance to prevent interactions with other medications and potential side effects such as gastrointestinal issues or cardiovascular risks. Taking NSAIDs with food can help alleviate stomach discomfort. Furthermore, combining NSAIDs with natural anti-inflammatory agents like turmeric or ginger may enhance treatment efficacy, potentially reducing the reliance on NSAIDs and aligning with a holistic approach to health and wellness that includes adequate rest, hydration, and a balanced diet for optimal recovery and overall well-being.
4. Antiviral medications for viral infections
In the management of adenitis caused by viral infections, Antiviral medications such as oseltamivir, zanamivir, peramivir, and baloxavir marboxil play a crucial role in inhibiting viral replication, thereby alleviating symptoms and limiting the progression of the infection. Intravenous ribavirin has shown promise in treating severe adenovirus disease in immune-compromised children, with some patients achieving complete recovery. Initiating antiviral therapy promptly upon the onset of illness is essential for optimal efficacy. For individuals interested in a holistic approach to healthcare, it is important to complement medical interventions with restorative practices such as adequate rest, hydration, and a nutrient-rich diet. It is advisable to consult a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate antiviral medication for your specific health needs and overall well-being.
5. Pain Management
The management of adenitis-related pain can be approached through various strategies. Genetic approaches, such as the introduction of recombinant adeno-associated viral vectors containing the μ-opioid receptor gene into primary afferent neurons, have shown promise in potentiating the anti-nociceptive effects of morphine, suggesting a new avenue for pain management. Managing adenitis pain requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the entire individual, rather than just the symptoms. Gentle, non-invasive techniques such as warm compresses can help reduce swelling and discomfort in inflamed lymph nodes. A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods like turmeric, ginger, and omega-3 fatty acids can aid in the body’s healing process. Alternative therapies such as acupuncture and lymphatic massage have shown effectiveness in reducing pain and improving lymph circulation. Incorporating mindfulness and relaxation techniques can also help in managing pain perception. While traditional treatments may involve antibiotics and pain medications like acetaminophen or NSAIDs, it is important to consult a healthcare professional to ensure that any new treatment complements existing medical care and addresses individual health needs.
6. Rest and Hydration
When dealing with adenitis, which is characterized by swollen lymph nodes, it is crucial to prioritize rest and hydration to support the body’s healing processes. Sufficient rest helps conserve energy for the immune system to effectively combat the infection and reduces stress, which can impede recovery. Adequate hydration is also essential, as a consistent intake of fluids such as water and herbal teas aids in the elimination of toxins, promotes proper blood circulation, and delivers essential nutrients to cells. By emphasizing both rest and hydration, individuals can not only alleviate symptoms of adenitis but also prevent complications such as the spread of infection or the formation of abscesses. By incorporating these simple yet impactful health practices, individuals can improve their overall well-being and expedite their recovery.
Complications and Prognosis of Adenitis
Understanding the potential risks and factors that contribute to recovery is essential for effectively managing this condition. In the following section, we will examine the key complications and prognostic indicators linked to adenitis.
1. Abscess formation
Adenitis can lead to serious complications, such as abscess formation, which may mimic malignancy and complicate diagnosis and prognosis. Abscess formation resulting from adenitis, characterized by swollen lymph nodes containing pus, is a serious health concern that can lead to severe pain and swelling. It is crucial to promptly seek medical attention to prevent the spread of infection and preserve the health of the lymphatic system. Holistic health practices emphasize the importance of early detection and treatment, which may include the use of warm compresses, drainage, antibiotics, or natural remedies to support the body’s healing process. To prevent complications and ensure a speedy recovery, individuals should be vigilant of their symptoms and consult with healthcare professionals. Maintaining good hygiene and addressing the underlying causes of adenitis are also essential in preventing abscess formation and promoting overall well-being.
2. Spread of infection
The spread of infection, particularly in deep neck infections (DNI) can lead to a worsened prognosis with involvement of multiple neck spaces. If left untreated, the infection causing adenitis can spread through the lymphatic system or bloodstream, potentially resulting in systemic infection or sepsis, a life-threatening condition characterized by the body’s exaggerated response to infection. Early and effective treatment is essential, often requiring a combination of conventional medical care and holistic therapies to support the body’s natural healing mechanisms. While mesenteric adenitis is typically benign and tends to resolve on its own, the risk of sepsis highlights the importance of prompt medical intervention to prevent the infection from progressing and ensure a positive outcome.
3. Chronic Adenitis
Chronic adenitis, especially in the setting of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), is linked to a poorer prognosis. Chronic adenitis, the persistent inflammation of lymph nodes, is a health concern that can impact overall well-being, often indicating chronic infections, immune disorders, or, less commonly, cancer. To effectively manage chronic adenitis, individuals should prioritize a healthy lifestyle including good hygiene, regular physical activity, and a nutritious diet, and work closely with healthcare providers to customize their wellness plans.
Prevention and Self-Care for Adenitis
While medical intervention may be necessary at times, there are also effective prevention and self-care strategies that can support the body’s healing process and enhance overall well-being. Here are some holistic approaches to consider:
1. Good hygiene practices
Maintaining excellent personal hygiene is crucial in preventing adenitis, a condition characterized by inflammation of the lymph nodes often triggered by infections. A simple yet powerful defense against such infections is regular handwashing with soap and water, especially before eating and after using the restroom, or when in contact with sick individuals or pets. Personal items such as toothbrushes should be kept separate to prevent cross-contamination. In addition to cleanliness, adopting a lifestyle that prioritizes sufficient rest, effective stress management, and a nutrient-rich diet that supports the immune system is essential. These practices, when consistently followed, not only reduce the risk of adenitis but also improve overall health and well-being.
2. Boosting the immune system
To prevent adenitis and enhance self-care, it is essential to boost the immune system. This involves consuming a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and essential nutrients, engaging in regular exercise to enhance lymphatic circulation, getting adequate rest for cellular repair, and practicing stress-reducing activities such as meditation and yoga for equilibrium. Incorporating herbs like echinacea and astragalus, as well as essential vitamins C, D, and zinc, can further enhance immune function. Adopting these habits not only aids in preventing adenitis but also promotes overall health and well-being naturally. Consistent physical activity, proper hydration, and attention to micronutrients like vitamins C and E are also crucial for maintaining a robust immune system and protecting against infections.
3. Seeking prompt medical attention
Seeking prompt medical attention is crucial in the prevention and management of adenitis, as timely interventions can significantly reduce the frequency of acute adenolymphangitis (ADL) attacks and prevent the progression of conditions such as lymphatic filariasis. When it comes to protecting your health, prompt action at the first sign of trouble is crucial. If you experience symptoms such as tender, swollen lymph nodes, fever, or night sweats, it is important to seek medical attention promptly. Early detection and treatment of adenitis not only help prevent more severe complications such as abscesses or sepsis, but also allow for the incorporation of natural remedies and lifestyle changes to support your body’s recovery. A timely visit to a healthcare professional can result in an accurate diagnosis, preventing the confusion of mistaking it for other serious conditions and ensuring a comprehensive approach to your health and well-being.
4. Stay Up-to-Date with Vaccinations
It is essential to prioritize the body’s natural defenses, with a key aspect being the maintenance of up-to-date vaccinations. Vaccines play a crucial role in protecting against infections that can lead to swollen lymph nodes, a sign of adenitis. They function by priming the immune system to recognize and combat harmful pathogens, serving as a protective shield against a variety of bacterial and viral threats. Adhering to recommended immunization schedules, including booster shots, not only enhances personal health but also helps safeguard community health by reducing the spread of infectious diseases. This proactive approach to healthcare is especially important for children, whose immune systems are still developing and more vulnerable to infections. By ensuring that vaccination records are current, individuals take a significant step towards comprehensive self-care, aligning with natural health practices to promote the body’s equilibrium and resilience.
5. Exercise Infection Control
Regular exercise can play a crucial role in the prevention of acute respiratory infections (ARI), as evidenced by a study showing that moderate intensity sustained exercise reduced the global severity of ARI compared to a control group. Effective infection control requires a comprehensive approach, including practicing good hygiene such as frequent hand-washing, avoiding the sharing of personal items, maintaining up-to-date vaccinations, and following safe practices to prevent blood-borne infections. Additionally, strengthening the immune system through a diet rich in antioxidants, regular exercise, and adequate rest is essential for reducing the risk of infections. These collective efforts not only aid in the prevention of adenitis but also promote a strong immune system, leading to a safer and healthier lifestyle.

