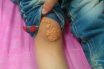
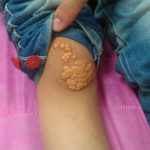
 A small yellow plaque in the skin due to a fat deposit.
A small yellow plaque in the skin due to a fat deposit.
A yellow fatty mass, often on the eyelids and hands, found in people with a high level of cholesterol in the blood.
Benign, fatty, yellowish plaque, nodule, or tumor in the subcutaneous layers of the skin, usually due to accumulation of cholesterol and related compounds.
A yellow-orange nodule (solid mass of tissue) with sharply defined borders beneath the surface of the skin. Xanthomas commonly appear on the elbows, hands, feet, knees, and but-tocks. Growths range in size from small to more than 3 inches in diameter. Although they may be unsightly, xanthomas are painless and non-cancerous. They most frequently affect people with elevated blood cholesterol levels or genetic cholesterol disorders. The goal of treatment is to manage any underlying disorders, such as diabetes, cirrhosis, or hypercholesterolemia. Reducing triglyceride and cholesterol levels can help reduce the occurrence of xanthomas. If the growths become bothersome, they can be removed surgically.
A yellowish swelling, nodule, or plaque in the skin resulting from deposits of fat. The presence of xanthomata is usually accompanied by a raised blood cholesterol level. There are several types; for example, xanthomata palpebrarum, in which the plaques appear on the eyelids in the elderly.
Soft, yellow skin plaques or nodules that contain deposits of lipoproteins inside histiocytes; they are esp. likely to be found on the skin of patients with hyperlipidemia.
The presence of lipid-rich yellowish formations or growths on the skin or internal tissues is commonly identified as xanthomas. These fatty deposits can manifest in various shapes and sizes, often appearing as nodules or patches. Xanthomas can develop in different areas of the body and are associated with underlying metabolic disorders or lipid abnormalities. Medical attention is typically required for evaluation and management of xanthomas to determine the underlying cause and ensure appropriate treatment.
Xanthomas are yellowish fatty deposits that can appear in the skin, frequently found on the elbows or buttocks. These deposits could be linked to hyperlipidemia, a condition characterized by elevated levels of fats in the bloodstream.