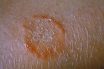
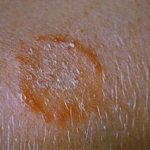
 Ringworm, fungal infection on the skin.
Ringworm, fungal infection on the skin.
Dermatomycosis; any number of skin fungus infections, such as ringworm, athlete’s foot, and so forth. It is generally slow to acquire and hard to get rid of.
Any of a group of fungus-caused skin diseases, usually characterized by skin lesions, scaling and itchiness; also called roundworm.
Lesions of dermatophytoses which may present in the feet (pedi), nails (unguium), groin area (cruris), or any superficial skin surface (versicolor).
A general term for a group of related skin infections caused by different species of fungi; or a fungal skin infection characterized by ring-shaped, red, scaly, or blistery patches. Fungi thrive in warm moist areas and cause tinea infections such as jock itch (tinea cruris) in the groin area and athlete’s foot (tinea pedis) between the toes. Other locations of tinea include the body (tinea corporis), the face (tinea faciei), and scalp (tinea capitis). Tinea versicolor is a fungal infection characterized by a rash consisting of white or brown patches on the trunk.
Any fungal skin disease occurring on various parts of the body.
Technical term for ringworm, a contagious condition caused by fungal infection and not a parasite; characterized by itching, scales, and, sometimes, painful lesions.
A surface-level infection affecting the skin, hair, or nails, caused by a fungal organism and commonly recognized as ringworm.
These are prevalent fungal infections affecting the skin, hair, or nails, primarily caused by a type of fungi known as dermatophytes. Commonly referred to as ringworm, these infections can be contracted from various sources including other people, animals, soil, shower surfaces, or inanimate objects like chairs or carpets.
The most prevalent form of tinea infection is tinea pedis, commonly known as athlete’s foot. Tinea corporis, or body ringworm, leads to itchy, typically circular patches with a distinct edge. Tinea cruris, often referred to as jock itch, results in a red, itchy region that extends from the genital area to the inner thighs and is more frequently observed in males. Tinea capitis, or scalp ringworm, manifests as round, itchy patches of hair loss primarily in children. Nail ringworm, or tinea unguium, often involves scaling of the soles or palms and causes the nails to thicken and discolor to white or yellow.
Many forms of tinea can be readily identified by their visual characteristics, but lab cultures can provide definitive confirmation of the diagnosis. Treatment commonly involves the use of topical antifungal medications, such as creams or ointments. For more extensive infections or those impacting the hair or nails, oral medications may be required.