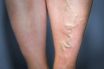
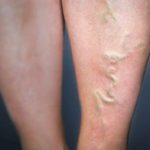
 Occurs when there is inflammation and clot in a surface vein.
Occurs when there is inflammation and clot in a surface vein.
Inflammation of a vein associated with thrombus formation.
The blocking of a vein by a blood clot, sometimes causing inflammation.
Inflammation of a vein, in conjunction with the formation of a blood clot (thrombus). It occurs as a result of trauma to the blood vessels; prolonged immobilization and consequent venous stasis; hypercoagulability of the blood; infection; or irritation. Treatment includes rest of the affected area (most often the legs), moist heat, and the use of anticoagulants and agents (e.g., streptokinase) to dissolve clots. Close monitoring to detect signs of pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, or other serious complication is essential.
Vein inflammation and thrombus (clot) formation.
Formation of a blood clot in a vein, most often in the leg, accompanied by inflammation; may also occur at site of intravenous line.
Inflammation of a vein because of the formation of a blood clot (thrombus); also known as phlebitis. Thrombophlebitis usually develops in the veins of the legs and less commonly in the arms. If it affects the superficial veins, it can be treated with medications, such as analgesics to stop pain and anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce swelling. Support stockings help in some cases, as do elevating the leg and applying warm compresses. Thrombophlebitis affecting a deep vein is a more serious condition known as deep vein thrombosis.
Inflammation of the veins combined with clot formation.
Inflammation of a vein in conjunction with the formation of a thrombus. It usually occurs in an extremity, most frequently a leg.
Vein inflammation, typically occurring in the legs, resulting in swelling and sensitivity in the affected region.
Phlebitis, an inflammation of a vein segment typically near the skin’s surface, can lead to clot formation in the affected area. This can arise from minor vein injury or as a complication of conditions like varicose veins or Buerger’s disease. The impacted blood vessel becomes swollen, red, and sensitive, exhibiting hardness. Fever and discomfort may also manifest, and a blood clot might develop.
The treatment typically involves using a bandage for support, taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications, and occasionally antibiotics. The condition generally resolves within 10 to 14 days.
Inflammation of a vein along with the formation of a blood clot.