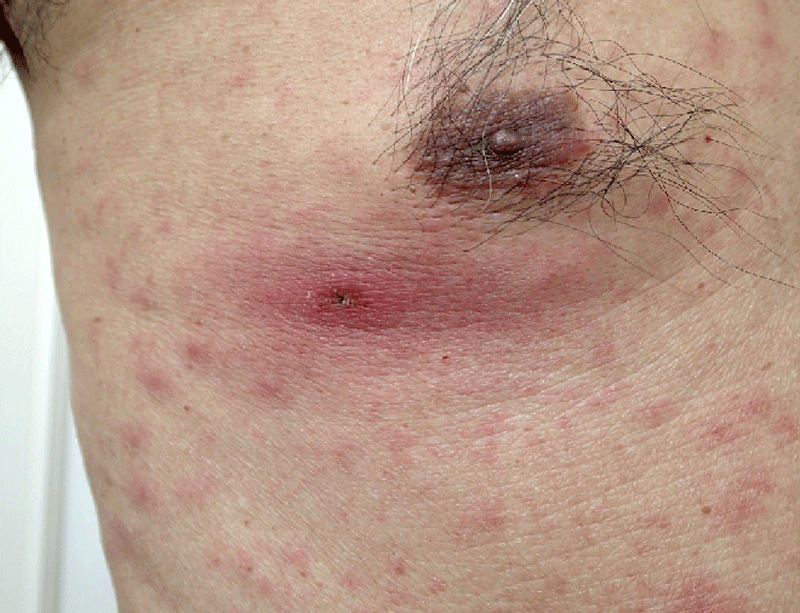
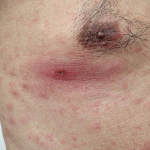
 Disease of eastern Asia, surrounding islands, and Australia, caused by Rickesttsia organisms transmitted to humans by mites. Symptoms include a dark lesion at the site of the bite, lymph node enlargement, fever, muscle ache, rash, and in severe cases cardiovascular and nervous system involvement.
Disease of eastern Asia, surrounding islands, and Australia, caused by Rickesttsia organisms transmitted to humans by mites. Symptoms include a dark lesion at the site of the bite, lymph node enlargement, fever, muscle ache, rash, and in severe cases cardiovascular and nervous system involvement.
A disease, widely distributed in SE Asia, caused by the parasitic microorganism Rickettsia tsutsugamushi and transmitted to man through the bite of mites. Only larval mites of the genus TrombicuIa are involved as vectors. Symptoms include headache, chills, high temperature (104°F), a red rash over most of the body, a cough, and delirium. A small ulcer forms at the site of the bite. Scrub typhus is treated with tetracycline antibiotics.
An acute febrile illness, occasionally complicated by pneumonia, meningoencephalitis, respiratory distress syndrome, or septic shock caused by Orientia tsutsugamushi. Generally limited to Asian and Pacific nations, the disease is transmitted to humans by the bites of infected mites and chiggers. It can be treated with tetracyclines or azithromycin. The mortality rate in untreated patients is about 1% to 4%.