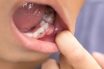
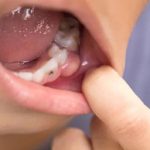
 A generally viscous, yellowish‐white fluid formed in infected and inflamed tissue consisting of white blood cells, cellular debris, necrotic tissue, and bacteria.
A generally viscous, yellowish‐white fluid formed in infected and inflamed tissue consisting of white blood cells, cellular debris, necrotic tissue, and bacteria.
A mixture of white blood cells and cellular debris resulting from an infection and inflammation.
A yellow liquid composed of blood serum, pieces of dead tissue, white blood cells and the remains of bacteria, formed by the body in reaction to infection.
Thick, yellowish or greenish fluid, containing dead white blood cells, bacteria, and dead tissue, formed at an infection site.
A thick, yellow-to-white fluid that consists of white blood cells, cell debris, and dead tissue cells. Pus forms in infected tissue of body structures and is produced by the inflammatory process.
Thick, white, yellow or greenish fluid, found in abscesses, ulcers, and on inflamed and discharging surfaces generally. Its colour and consistency are due to the presence of white blood corpuscles and cells debris. Bacteria that normally produce pus are streptococcus, pneumococcus and escherichia coli.
Protein-rich fluid (exudate) containing white blood cells, especially neutrophils, and cell debris produced during inflammation. It commonly is caused by infection with pyogenic (pus forming) bacteria such as streptococci, staphylococci, gonococci, and pneumococci. Normally, pus is yellow; red pus may contain blood from the rupture of small vessels, and bluish-green pus may contain Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Pus that has been walled off by a membrane is called an abscess.
The yellowish or greenish fluid product of an infection, composed of dead cells and cell debris.
The mixture of fluids, phagocytes, and dead cells that accumulates at the site of an infection.
A whitish-yellow material produced by the body in response to a bacterial infection. It consists of tissue fluid and dead white blood cells.
Pus, a pale yellow or greenish creamy fluid, emerges at the location of a bacterial infection. Comprising numerous deceased white blood cells, partially digested tissue, both living and deceased bacteria, and additional elements, this creamy fluid is formed. In cases where pus accumulates within a solid tissue region, it is termed an abscess.
The fluid result of an inflammatory response. It contains a high concentration of white blood cells that have engulfed bacteria and perished during this process.