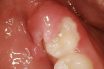
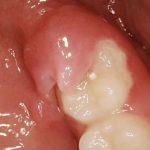
 Acute inflammation of the gingiva and/or mucosa surrounding a partially erupted tooth. Also known as operculitis.
Acute inflammation of the gingiva and/or mucosa surrounding a partially erupted tooth. Also known as operculitis.
Inflammation of the gum around the crown of a tooth. Pericoronitis usually affects a partially impacted tooth, typically the third molar (wisdom tooth). If there is an opposing tooth, it may be difficult and painful to close the jaw. The infection produces swelling of the gum and may result in fever and continual pain. When left untreated, pericoronitis can spread into surrounding gum and bone tissues, presenting serious complications. It is generally caused by the presence of food particles and the subsequent growth of bacteria in the spaces between the gum and the tooth. The infection can be treated with antibiotics. If pericoronitis recurs and becomes chronic, an oral surgeon may be needed to remove some of the gum tissue and allow the tooth to emerge. If there is not adequate room for the tooth to develop and emerge normally, it may need to be extracted. Wisdom teeth are normally extracted when the tissue around them is infected. This is due to the difficulty in keeping the gums clean in that hard-to-reach location.
Pericoronitis is a gum condition characterized by irritation and inflammation caused by the partially erupted crown of a tooth.