Mindblown: a blog about philosophy.
-
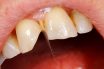
Tooth fracture
Breakage of natural tooth or polymer‐based or ceramic prosthetic tooth.
-
Tooth form
The characteristics of the curves, lines, angles, and contours of various teeth that permit their identification and differentiation.
-
Tooth extrusion
The tendency of a tooth to continue the state of eruption. It can be excessive when the forces that naturally limit eruption are not present. Also known as overeruption.
-
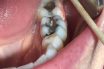
Tooth extraction
Removal of a tooth or teeth. The removal of a tooth. Tooth extraction is generally performed by a dentist or oral surgeon because of tooth decay, advanced gum disease, severe fracture, dental impaction, overcrowding, or malocclusion (irregular alignment).
-
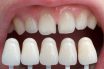
Tooth color selection
To choose an appropriate shade of a tooth or teeth so as to harmoniously match the needs of a patient.
-
Tooth arrangement
The art of placing teeth into determined ideal positions on a denture base so as to achieve the desired results related to esthetic and functional objectives. Trial placements are frequently done allowing for further movement to enhance the initial results.
-
Tonus, muscle
The slight continuous contraction of muscle that aids in the maintenance of posture and in the return of blood to the heart. A state of low-level muscle contraction at rest.
-
Tongue thrusting
The infantile pattern of suckle swallow in which the tongue is placed between the incisor teeth or alveolar ridges during the initial stages of deglutition, resulting sometimes in an anterior open occlusion, deformation of the jaws, and/or abnormal function.
-
Tomography
Imaging by sections or sectioning. Radiological imaging of serial planes (“cuts”) through an anatomical structure. A noninvasive technique designed to show detailed images of internal structures in a selected plane of the body. The scanning of a particular part of the body using X-rays or ultrasound. Procedure of making a radiographic image of a selected…
-
Tomograph
An apparatus that is used to create a tomogram. The machine allows for the movement of the film in one direction, while the source of radiation moves in an opposite direction to produce images at a targeted depth within the tissues. An x-ray tube attached to a Bucky diaphragm by a rigid rod allowing rotation…
Got any book recommendations?