Mindblown: a blog about philosophy.
-
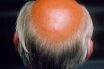
Alopecia
Is the loss of hair on the body. Absence of hair from areas where it is normally present. Hair loss; baldness; absence of hair from skin areas where it is normally present. A lack or loss of bodily hair that is most obvious on the scalp, which tends to develop patchy hair loss. Partial or…
-
Allostasis
The process of achieving stability, or homeostasis, through physiological or behavioral change.
-

Allergic
Pertaining to, caused, affected with, or the nature of the allergy. Having an allergy to something.
-
Allergenic
Having the properties of an antigen (allergen), immunogenic. A substance capable of inducing an allergic response. Producing an allergic reaction. Amidst the intricacies of allergic responses, there exists a remarkable substance endowed with the ability to incite such reactions within susceptible individuals. Functioning as an allergenic substance, leading to the development of allergies.
-
Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH)
An enzyme involved in the break-down of alcohol. A primary enzyme in the metabolism of alcohol, which oxidizes it to acetaldehyde. Eighty-five percent of the Japanese population and other Asian populations have an atypical ADH enzyme, which is about five times faster than normal. Consumption of alcohol by such persons leads to accumulation of acetaldehyde,…
-
Alexiteric
A preservative against contagious and infectious diseases, and the effects of poisons. Protecting against infection, venom and poison. Something that thwarts the action of venom.
-
Alexipharmic
An antidote, remedy for poison. Medicine that is intended to counter the effects of poison; an antidote to poison or infection. That which obviates the effects of a poison.
-
Aldose reductase, aldehyde reductase
An enzyme in carbohydrate metabolism that converts glucose to sorbitol. An enzyme that makes up part of the metabolic pathway that converts glucose to fructose and sorbitol, two chemicals that may damage nerves, the retina, and the lens of the eye when they accumulate excessively, e.g., in poorly controlled diabetes mellitus.
-
Albuminaria
Excessive amount of albumin in the urine, a symptom of severe kidney disease.
-
Alanine transaminase (ALT)
Also called Serum Glutamic Pyruvate Transaminase (SGPT) or Alanine aminotransferase (ALAT), an enzyme present in hepatocytes (liver cells). When a cell is damaged, it leaks this enzyme into the blood. An enzyme (formerly called serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase [SGPT]) that is elevated in patients with liver disease or may be increased by certain psychiatric medications. Because…
Got any book recommendations?