Mindblown: a blog about philosophy.
-
Anaplasia
A reversion of differentiation in cells and is characteristic of malignant neoplasms (tumours). Loss of structural differentiation, as seen in malignant neoplasms. Failure of the body cells to function normally, cancer. The loss of a cell’s typical characteristics, caused by cancer. Medical term for a cell that has become less differentiated and more “primitive” in…
-
Anaphylotoxins
Are fragments (C3a, C4a or C5a) that are produced during the pathways of the complement system. They can trigger release of substances of endothelial cells, mast cells or phagocytes, which produce a local inflammatory response.
-
Anaphoretic
An antiperspirant.
-
Analeptic
A central nervous system (CNS) stimulant medication. A substance that stimulates the central nervous system. A drug used to make someone regain consciousness or to stimulate a patient. Drug that stimulates (e.g., caffeine) the central nervous system or strengthens or invigorates the body. A drug that restores consciousness to a patient in a coma or…
-
Anaesthetic
A substance that decreases partially or totally nerve the sense of pain. A substance that causes localised or general loss of sensation. A substance given to someone to remove feeling, so that he or she can undergo an operation without pain. The term used to refer to the collective group of drugs that induce anesthesia,…
-
Anaesthesia
Condition of having sensation temporarily suppressed. Loss of feeling or sensation. Although the term is used for loss of tactile sensibility, or of any of the other senses, it is applied especially to loss of the sensation of pain, as it is induced to permit performance of surgery or other painful procedures. A state, deliberately…
-
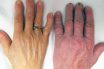
Anaemia
A blood disorder in which the blood is deficient in red blood cells and in haemoglobin. A reduction below normal in the number of erythrocytes per cu. mm., in the quantity of haemoglobin, or in the volume of packed red cells per 100 ml. of blood which occurs when the equilibrium between blood loss (through…
-
Amyotrophy
Progressive wasting of muscle tissues. adj. amyotrophic. Atrophy or wasting of the muscles. Amyotrophy is a common symptom of motor neuron diseases, such as ALS, but it is also seen in many other conditions, including diabetes, syphilis, and cancer. A progressive loss of muscle bulk associated with weakness of these muscles. It is caused by…
-
Amyloid beta (Ab or Abeta)
A peptide of 39–43 amino acids that appear to be the main constituent of amyloid plaques in the brains of Alzheimer’s disease patients.
-
Amoebicidal
Lethal to amoeba. Destructive to amoebas. An agent that kills amoebas. A substance that destroys amoebas.
Got any book recommendations?