Mindblown: a blog about philosophy.
-
Calculus (calculi)
Hardened, mineral deposits that can form a blockage in the urinary system. Stone concretion in some part of the body A stone usually composed of mineral salts (e.g., kidney stones and gallstones) or calcified deposits on the teeth. A hard substance that may accumulate on the teeth. Kidney stones and gallstones. Synonym for gallstones or…
-
Calcium (Ca)
Is the most abundant mineral in the body found mainly in bones and teeth. It is required for muscle contraction, blood vessel expansion and contraction, secretion of hormones and enzymes, and transmitting impulses throughout the nervous system. Dietary sources include milk, yoghurt, cheese, Chinese cabbage, kale, broccoli, some green leafy vegetables, fortified cereals, beverages and…
-
Ca2+ ATPase (PMCA)
Is a transport protein in the plasma membrane of cells that serves to remove calcium (Ca2+) from the cell.
-
Cadaver
A dead body, corpse, as one preserved for anatomical study. A dead body, especially one used for dissection. Dead human body; corpse. Cadavers are used by physicians and other scientists to study anatomy and disease. Autopsies performed on cadavers allow doctors to identify disease sites, to help determine causes of death, and to provide tissue…
-
Caco-2 cell line
A continuous line of heterogeneous human epithelial colorectal adenocarcinoma cells.
-
Cachexia
Physical wasting with loss of weight, muscle atrophy, fatigue, weakness caused by disease. The condition of extreme emaciation and wasting seen in patients with advanced cancer and AIDS. Due partly to an inadequate intake of food and mainly the effects of the disease in increasing metabolic rate (hypermetabolism) and the breakdown of tissue protein. General…
-
C-Src
A cellular non-receptor tyrosine kinase.
-
C-jun NH(2)-terminal kinase
Enzymes that belong to the family of the MAPK superfamily of protein kinases. These kinases mediate a plethora of cellular responses to such stressful stimuli, including apoptosis and production of inflammatory and immunoregulatory cytokines in diverse cell systems. cf: MAPK.
-
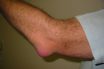
Bursitis
Condition characterized by inflammation of one or more bursae (small sacs) of synovial fluid in the body. An inflammation of the bursa, which is a synoviallined sac of fluid that helps reduce friction between tendon and bone or tendon and ligament. Inflammation of the bursa sac, can be an overuse syndrome. This condition involves inflammation…
-
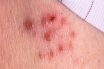
Bullae
Blisters; circumscribed, fluid-containing, elevated lesions of the skin, usually more than 5 mm in diameter.
Got any book recommendations?